When was the Bohr model created?
When was the Bohr model created? 1913 In July of 1913, Danish physicist Niels Bohr published the first of a series of three papers introducing this model of the atom, which became known simply as the Bohr atom.
When was the Rutherford model created?
Rutherford's model shows that an atom is mostly empty space, with electrons orbiting a fixed, positively charged nucleus in set, predictable paths. This model of an atom was developed by Ernest Rutherford, a New Zealand native working at the University of Manchester in England in the early 1900s.
Who developed the electron cloud model?
Erwin Schrodinger, an Austrian physicist came up with the electron cloud model in 1926. The electron cloud refers to a region outside the nucleus where an electron is most likely to be found. Before understanding what an electron cloud model is, it is important to know about the forces that bind the electrons together.
When was the difference engine created?
Updated: 02/27/2019 by Computer Hope The difference engine is a mechanical calculator first developed by Charles Babbage in 1822. It is capable of computing several sets of numbers and making a hard copies of the results. Due to a lack of funding, he was never able to complete a full-scale functional version of this machine.
Who proposed the electron cloud model in 1920s?
Erwin SchrödingerIn the 1920s, Erwin Schrödinger proposed that electrons travel in waves, which means their exact positions cannot be determined. He developed an equation to calculate the chances of an electron being in any given place.
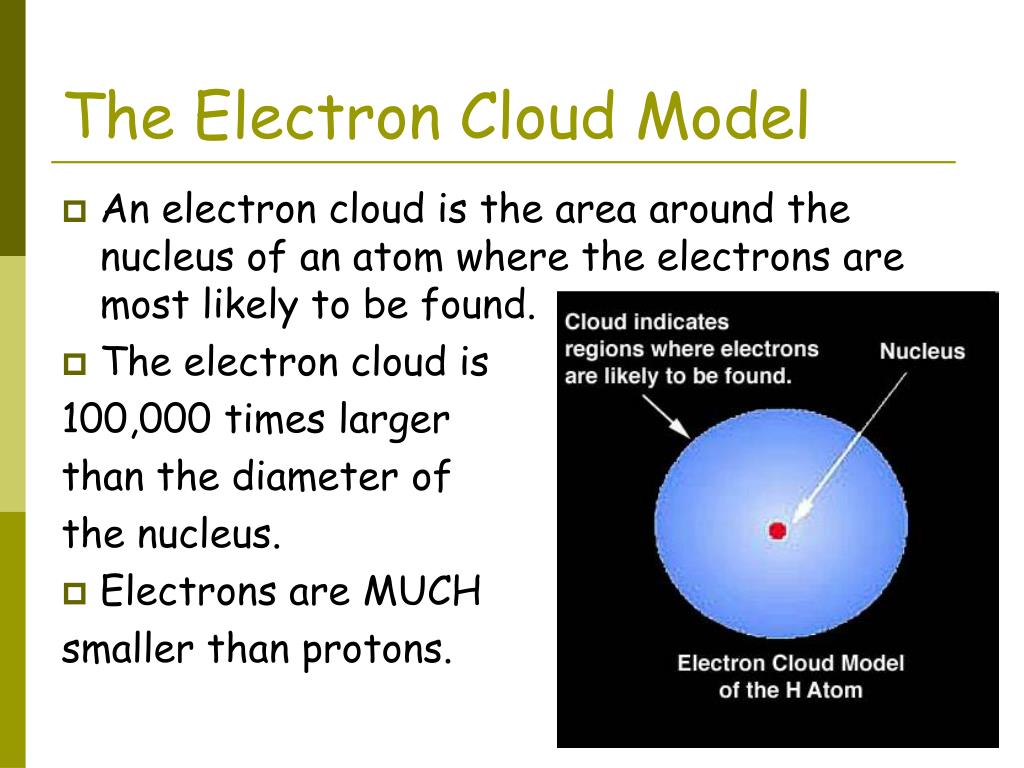
What was the electron cloud model?
The electron cloud model is a model of an atom in which the atom consists of a small but massive nucleus surrounded by a cloud of rapidly moving electrons. The electron cloud model says that we cannot know exactly where an electron is at any given time, but the electrons are more likely to be in specific areas.
Did Bohr discover the electron cloud?
In 1913, the Danish physicist Niels Bohr proposed a model of the electron cloud of an atom in which electrons orbit the nucleus and were able to produce atomic spectra.
Is the Bohr model the same as the electron cloud model?
The cloud model is different from the Bohr model as the latter predicts a definite path for the electrons around the nucleus while the former only predicts an area around the nucleus where electrons may be found.
Why is the electron cloud model significant?
An electron cloud is a visual model of the most likely locations for electrons in an atom. Scientists use the electron cloud model to describe the possible locations of electrons around the nucleus.
Who predicted the electron cloud?
Erwin SchrodingerOne such example is the Electron Cloud Model proposed by Erwin Schrodinger. Thanks to this model, electrons were no longer depicted as particles moving around a central nucleus in a fixed orbit. Instead, Schrodinger proposed a model whereby scientists could only make educated guesses as to the positions of electrons.
What model did Bohr create?
In 1913 Bohr proposed his quantized shell model of the atom (see Bohr atomic model) to explain how electrons can have stable orbits around the nucleus.
What replaced Bohr model?
The Schrödinger wave equation replaced Bohr's ideas about electron location with an uncertainty factor. The location of the electron can only be given as a probability that the electron is somewhere in a certain area.
What is an electron cloud in simple terms?
noun. : the system of electrons surrounding the nucleus of an atom.
What does the electron cloud model describe quizlet?
It tells us that electrons are found in defined energy states in outside of the nucleus of the atom.
Who discovered the electron cloud model Why was it significant?
Austrian physicist Erwin Schrödinger (1887-1961) developed an “Electron Cloud Model” in 1926. It consisted of a dense nucleus surrounded by a cloud of electrons at various levels in orbitals. Schrödinger and Werner Heisenburg (1901-1976) mathematically determined regions in which electrons would be most likely found.
Which best describes an electron cloud?
The electron cloud model describes the atom as containing a dense nucleus of protons and neutrons surrounded by regions of space (clouds) where electrons are most likely to be found.
Why is it called an electron cloud?
An electron cloud kind of looks like a cloud. It is thicker in the center and fades out at the edges. The term cloud also describes the many possib...
Who came up with the electron cloud model?
Erwin Schrodinger came up with the electron cloud model, building on the work of several other physicists. Louis de Broglie's particle-wave duality...
What best describes an electron cloud?
The electron cloud is a particular area in which an electron is likely to be. We can't say exactly where an electron is, but we can use its wave fu...
What is another name for an electron cloud?
An electron cloud can be thought of as a probability field, the area in space where an electron is likely to be. In an atom, these fields, specific...
Why is it called the electron cloud model?
The electron cloud model shows a particular area in which an electron is likely to be. In a simple atom like Helium for instance, the probability f...
What is the electron cloud model used for?
The electron cloud is used to describe the behavior of electrons, and it is useful in building a model of the atom. The electron cloud shows the ar...
What is an electron cloud model?
The model is used to describe the probable locations of electrons around the atomic nucleus. The electron cloud is also defined as the region where an electron forms a three-dimensional standing wave, the one that does not move relative to the atomic nucleus. The model does not depict electrons as particles moving around the nucleus in a fixed orbit. Based on quantum mechanics, it gives the probable location of electrons represented by an ‘electron cloud’.
What does the cloud of electrons mean?
It consisted of a nucleus surrounded by clouds of electrons. The clouds indicate the probable positions of electrons in an atom. Greater density of electrons in a certain area is indicative of a higher probability of finding electrons in that atomic region. ► Werner Heisenberg, best known for his uncertainty principle, ...
What did Rutherford discover about atoms?
Till that time, atoms were believed to be the indivisible units of matter. His revolutionary discovery proved the conventional theory wrong. ► In 1909, Rutherford brought out the fact that the positive charge and the mass of an atom is concentrated towards its center, and that electrons orbit around the atomic center.
What is an orbital in an atom?
An orbital is a mathematical function that describes the wave-like behavior of electrons in an atom.
What is the force of attraction between the electrons and the nuclear protons?
It’s an electromagnetic force; a force of attraction that exists between the electrons and the nuclear protons, and binds them to the atom. The attractive force of an electron is directly proportional to its distance from the atomic nucleus. Hence the energy required to separate an electron from the atom varies inversely with its distance from ...
What is the electron cloud model?
The electron cloud model shows a particular area in which an electron is likely to be. In a simple atom like Helium for instance, the probability field is a sphere surrounding the nucleus, and the electron is more likely to be closer to the nucleus than far away from it. The probability field is denser in the middle and fizzles outward, and so it actually resembles the cloud of possible and probable locations for the electron.
Who came up with the electron cloud?
Erwin Schrodinger came up with the electron cloud model, building on the work of several other physicists. Louis de Broglie's particle-wave duality particles with mass, Max Planck's and Albert Einstein's work with quantum physics, Neil Bohr's earlier model of the atom, Werner Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle, and Schrodinger's wave function formula all contributed towards the concept of the electron cloud.
What was Heisenberg's idea of quantum physics?
In 1927, Heisenberg realized that there was an inherent uncertainty when measuring quantum particles. His thought experiment described an attempt to measure the position of a very small particle with a microscope. For an observer to do that, light would have bounce off of the quantum particle, but that photon of light would be enough to change the direction of a particle that small. This would mean that its direction or momentum would now be off, and the observer wouldn't know by precisely how much. More precise measurements of a quantum particle's position would require a stronger microscope, meaning higher-energy photons, meaning more uncertainty about the particle's momentum after the observation. Heisenberg realized that this was an essential component of quantum physics, not a limitation.
What was Schrodinger's wavefunction?
In 1926, Schrodinger developed his wavefunction model, giving a probability for an electron to be in a particular location. He wrote to Albert Einstein in April of 1926, "This whole conception falls entirely within the framework of wave mechanics ." Schrodinger's wavefunction was especially exciting to the physics community at large because it complemented Heisenberg's then-new mathematics for determining the position and energy of quantum particles, rather than correcting or refuting it.
Why did Schrodinger create the electron cloud model?
Schrodinger created the electron cloud model to explain certain unknowns in quantum physics, but he knew that it didn't explain everything. He did not like this his equation did not directly describe the properties of a particle, and that it didn't really even define what a wave function was. The electron cloud model was built as a compromise, leaving some unknowns but erasing some others. In time, perhaps a better model will emerge.
What is the quantum physics of electrons?
Electrons are very small particles, having a mass of {eq}9.1094 cdot 10^ {-31}: kg {/eq}, so their behavior is explained mostly by quantum physics. So for an electron, the uncertainty principle holds, and we can confidently treat it as a wave function. With the proper math, we can describe an electron's position as a probability field, normally distributed around the nucleus of an atom. The wave function of an electron also explains why the electron doesn't hang out in the nucleus. The energy needed to keep it there is too high.
How many electrons does a hydrogen atom have?
Let's look at a simple atom to see what the electron cloud model describes. A Hydrogen atom has one proton and one electron. A classic and probably more familiar model for the Hydrogen atom looks like this
When was the electron cloud invented?
It is defined mathematically, describing a region with a high probability of containing electrons . The phrase "electron cloud" first came into use around 1925, when Erwin Schrödinger and Werner Heisenberg were seeking for a way to describe the uncertainty of the position of electrons in an atom.
What is an electron cloud?
An electron cloud is the region of negative charge surrounding an atomic nucleus that is associated with an atomic orbital. It is defined mathematically, describing a region with a high probability of containing electrons .
Why do chemists use electron cloud models?
Chemists use the electron cloud model to map out the atomic orbitals for electrons; these probability maps are not all spherical. Their shapes help predict the trends seen in the periodic table. Cite this Article. Format.
What is the cloud of electrons?
The electron cloud is the location around the nucleus that contains negatively-charged electrons.
Where are electrons found in the cloud?
In the cloud model, there are regions where an electron may likely be found, but it's theoretically possible for it to be located anywhere, including inside the nucleus .
Why is it called an electron cloud?
This model identified as electron cloud model as each orbital surround the nucleus of the atom be similar to a fuzzy cloud around the nucleus. The deepest area of the cloud is which e- having its highest chances to be present in that time. As it’s very similar to normal cloud and it’s of -vely charged electron, so acknowledged as electron cloud.
How do electrons move in the electron cloud?
The e- try to move from negative charged parts to positive one as these are having excess electron, where as +ve one need more electron to full fill it’ s orbital. So, e- will jump one zone to other ones, hence current also flows through in reverse direction.
Who discovered the neutrons?
James Chadwick invented neutron, used scattering data to calculate the mass of this neutral particle.
What is Bohr's model of electron energy?
Bohr’s model treats electron energy level as evidently well-defined as an orbital path surround the nucleus (similar to a model, just like the way planet is encircling the Sun).
How do electrons move in a circuit?
The move of the electron happens from negatively charged parts to ones that were positively charged. Any circuit’s negatively charged pieces have additional electrons, whereas the pieces want more, additional electrons. The electrons then jump to another level. The current can flow through the system when the electrons move.
Why do electrons have the same charge?
The electrons maintain particle-like properties; for example, every wave state has the same electric charge because of its electron particle. Each wave state has one distinct, discrete spin (spin up or spin down) determined by its superposition.
What is the mass of an electron?
The rest mass of the electron is 9.1093837015 × 10-31 kg. This is 1/ 1836th times of proton.