Full Answer
What safety precautions should I take when using resin?
When dealing with epoxy resin, what safety measures should I take?
- Work in a well-ventilated and clean environment.
- Consider donning a respirator, rubber gloves, and eye protection depending on the materials you’ll be working with.
- Clean up according to the manufacturer’s instructions. All waste products must be disposed of in line with local rules.
What precautions need to be taken when using throat culture?
- Use universal precautions for collecting and handling all specimens.
- Whenever possible, collect all culture specimens prior to administration of any antimicrobial agents.
- Avoid contamination with indigenous flora.
- Swabs are convenient but inferior to tissue and fluid. ...
- All specimens must be appropriately labeled with two patient identifiers. ...
What PPE is needed for contact precautions?
[1] PPE defined by the CDC required before entering a contact precaution designated room is always gloves and a gown. [2] Mask and eye protection are additionally required if contact with bodily secretions is possible. 2. Bloodborne precautions:
What does droplet precautions include?
the room of a patient under droplet precautions will be asked to wear a mask to prevent the spread of germs to themselves. Hand washing is another important part of droplet precautions to keep everyone’s hands clean and to avoid spreading germs through touching other people or objects in the patient’s room,

How to prevent germs in children?
To prevent your child or you from getting unwanted germs, wash hands with soap and water or use a waterless alcohol-based hand rub every time you enter and leave the room. Wash your hands with soap and water at these times: Before eating. When hands have dirt on them. After changing diapers. After using the restroom.
How to stop germs from spreading?
To prevent your child or you from getting unwanted germs, wash hands with soap and water or use a waterless alcohol-based hand rub every time you enter and leave the room.
Why do you put your child on droplet precautions?
Your child may be placed on droplet precautions as a safety measure if he or she has symptoms of these germs or if laboratory results show that your child has these germs. Your child may need to be on droplet precautions even if he or she seems to be well.
What is the green sign for the hospital?
A green sign will be posted at the entrance to the room when these precautions are needed so that everyone entering knows what to wear (Picture 1). Everyone (parents, family, guests, and healthcare workers) must wash their hands with soap and water or use waterless alcohol-based hand rub when entering and leaving the room.
How can germs be spread?
Droplet Precautions. Certain germs can be spread by droplets that come out of the mouth during talking or coughing or from drainage from the nose. These droplets may be big enough to see or too small to be seen.
What precautions do doctors use?
This means that the health care workers may use gloves, gown, mask, eye protection or face shields when taking care of your child. These precautions are required at all hospitals by Federal law to protect patients as well as health ...
Why are transmission-based precautions required?
These precautions are required at all hospitals by Federal law to protect patients as well as health care workers. Transmission-Based Precautions (Isolation) are used along with Standard Precautions when the spread of infection might not be completely stopped when using only Standard Precautions. The purpose of these precautions is ...
What to do if exam room is not available?
If an exam room is not available, provide the patient a facemask and place them in a separate area as far from other patients as possible while awaiting care
What diseases require droplet precautions?
Diseases requiring droplet precautions include, but are not limited to: Pertussis, Influenza, Diphtheria and invasive Neisseria meningitidis
How far can a droplet travel?
Droplets may contain microorganisms and generally travel no more than 3 feet from the patient.
Droplet Precautions
Droplet precautions are used in addition to routine practices for clients who are known or suspected to be infected with microorganisms that are spread through the air by large droplets.
Test your Knowledge
Clinical Procedures for Safer Patient Care — Thompson Rivers University Edition by Renée Anderson, Glynda Rees Doyle, and Jodie Anita McCutcheon is used under a CC BY 4.0 Licence. This book is an adaptation of Clinical Procedures of Safer Patient Care by Glynda Rees Doyle and Jodie Anita McCutcheon, which is under a CC BY 4.0 Licence.
How long are transmission precautions in effect?
Transmission-Based Precautions remain in effect for limited periods of time (i.e., while the risk for transmission of the infectious agent persists or for the duration of the illness (Appendix A). For most infectious diseases, this duration reflects known patterns of persistence and shedding of infectious agents associated with the natural history of the infectious process and its treatment. For some diseases (e.g., pharyngeal or cutaneous diphtheria, RSV), Transmission-Based Precautions remain in effect until culture or antigen-detection test results document eradication of the pathogen and, for RSV, symptomatic disease is resolved. For other diseases, (e.g., M. tuberculosis) state laws and regulations, and healthcare facility policies, may dictate the duration of precautions 12 ). In immunocompromised patients, viral shedding can persist for prolonged periods of time (many weeks to months) and transmission to others may occur during that time; therefore, the duration of contact and/or droplet precautions may be prolonged for many weeks. 500, 928-933
What are droplet precautions?
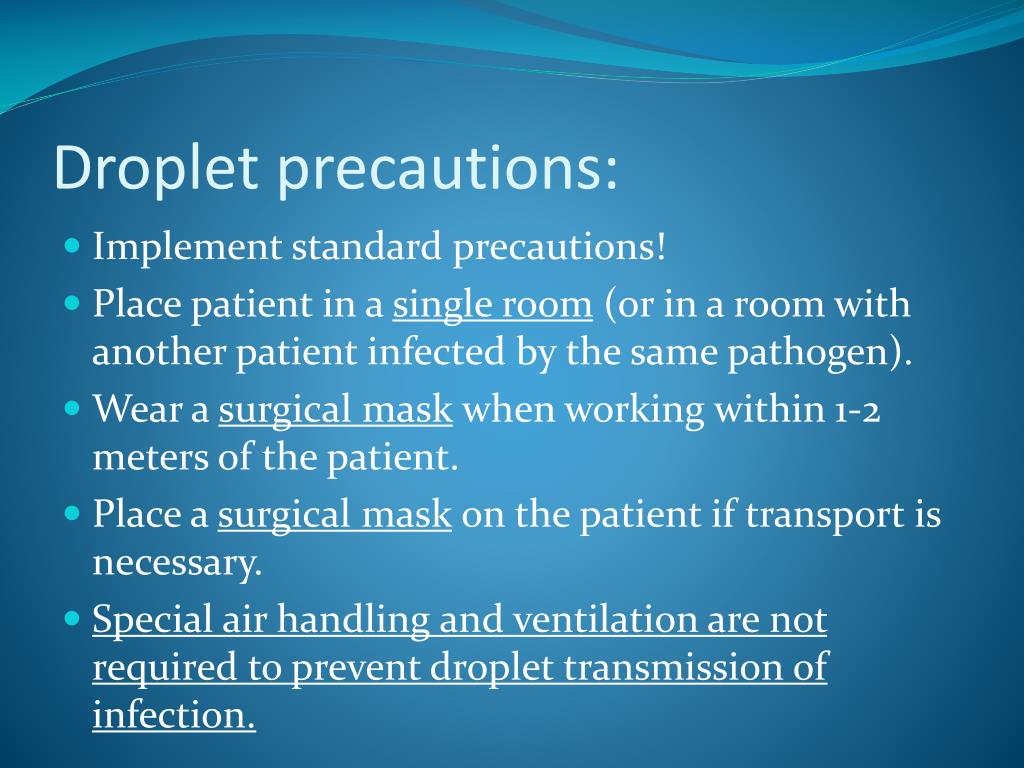
Droplet Precautions are intended to prevent transmission of pathogens spread through close respiratory or mucous membrane contact with respiratory secretions as described in I.B.3.b. Because these pathogens do not remain infectious over long distances in a healthcare facility, special air handling and ventilation are not required to prevent droplet transmission. Infectious agents for which Droplet Precautions are indicated are found in Appendix A and include B. pertussis, influenza virus, adenovirus, rhinovirus, N. meningitides, and group A streptococcus (for the first 24 hours of antimicrobial therapy). A single patient room is preferred for patients who require Droplet Precautions. When a single-patient room is not available, consultation with infection control personnel is recommended to assess the various risks associated with other patient placement options (e.g., cohorting, keeping the patient with an existing roommate). Spatial separation of ≥3 feet and drawing the curtain between patient beds is especially important for patients in multi-bed rooms with infections transmitted by the droplet route. Healthcare personnel wear a mask (a respirator is not necessary) for close contact with infectious patient; the mask is generally donned upon room entry. Patients on Droplet Precautions who must be transported outside of the room should wear a mask if tolerated and follow Respiratory Hygiene/Cough Etiquette.
What are the standard precautions?
Standard Precautions combine the major features of Universal Precautions (UP) 780, 896 and Body Substance Isolation (BSI) 640 and are based on the principle that all blood, body fluids, secretions, excretions except sweat, nonintact skin, and mucous membranes may contain transmissible infectious agents. Standard Precautions include a group of infection prevention practices that apply to all patients, regardless of suspected or confirmed infection status, in any setting in which healthcare is delivered ( Table 4 ). These include: hand hygiene; use of gloves, gown, mask, eye protection, or face shield, depending on the anticipated exposure; and safe injection practices. Also, equipment or items in the patient environment likely to have been contaminated with infectious body fluids must be handled in a manner to prevent transmission of infectious agents (e.g., wear gloves for direct contact, contain heavily soiled equipment, properly clean and disinfect or sterilize reusable equipment before use on another patient).
What are the two tiers of HICPAC/CDC precautions?
There are two tiers of HICPAC/CDC precautions to prevent transmission of infectious agents, Standard Precautions and Transmission-Based Precautions. Standard Precautions are intended to be applied to the care of all patients in all healthcare settings, regardless of the suspected or confirmed presence of an infectious agent. ...
How long does viral shedding last?
In immunocompromised patients, viral shedding can persist for prolonged periods of time (many weeks to months) and transmission to others may occur during that time; therefore, the duration of contact and/or droplet precautions may be prolonged for many weeks. 500, 928-933.
What is a protective environment?
A Protective Environment is designed for allogeneic HSCT patients to minimize fungal spore counts in the air and reduce the risk of invasive environmental fungal infections (see Table 5 for specifications). 11, 13-15 The need for such controls has been demonstrated in studies of aspergillus outbreaks associated with construction. 11, 14, 15, 157, 158 As defined by the American Insitute of Architecture 13 and presented in detail in the Guideline for Environmental Infection Control 2003, 11, 861 air quality for HSCT patients is improved through a combination of environmental controls that include
When are transmission-based precautions used?
Transmission-Based Precautions are used when the route (s) of transmission is (are) not completely interrupted using Standard Precautions alone. For some diseases that have multiple routes of transmission (e.g., SARS), more than one Transmission-Based Precautions category may be used.
What is PPE in healthcare?
Use personal protective equipment (PPE) appropriately, including gloves and gown. Wear a gown and gloves for all interactions that may involve contact with the patient or the patient’s environment. Donning PPE upon room entry and properly discarding before exiting the patient room is done to contain pathogens.
What is PPE in ambulatory care?
In ambulatory settings, place patients requiring contact precautions in an exam room or cubicle as soon as possible. Use personal protective equipment (PPE) appropriately, including gloves and gown.
What is transmission based precaution?
Transmission-Based Precautions are the second tier of basic infection control and are to be used in addition to Standard Precautions for patients who may be infected or colonized with certain infectious agents for which additional precautions are needed to prevent infection transmission. Source: Guideline for Isolation Precautions.
What is the best way to limit transport and movement of patients outside of the room?
If transport or movement outside of the room is necessary, instruct patient to wear a mask and follow Respiratory Hygiene/Cough Etiquette.
When to use droplet precautions?
Use Droplet Precautions for patients known or suspected to be infected with pathogens transmitted by respiratory droplets that are generated by a patient who is coughing, sneezing, or talking.
What equipment should be used for multiple patients?
Use disposable or dedicated patient-care equipment (e.g., blood pressure cuffs). If common use of equipment for multiple patients is unavoidable, clean and disinfect such equipment before use on another patient.
Do you need to wear a mask when transporting a patient?
Healthcare personnel transporting patients who are on Airborne Precautions do not need to wear a mask or respirator during transport if the patient is wearing a mask and infectious skin lesions are covered.
How far away from a patient is a droplet precaution?
3. Droplet precautions: . Droplet precautions are necessary when a patient infected with a pathogen, such as influenza, is within three to six feet of the patient. Infections are transmittable through air droplets by coughing, sneezing, talking, and close contact with an infected patient's breathing.
Why should health care workers be aware of bloodborne pathogens?
Health-care workers should be aware of bloodborne pathogens and consider safer practices and procedures when handling objects potentially contaminated with blood or bodily fluids to prevent injuries and possible spread of infections.
How much does isolation precautions increase hospital stays?
In the retrospective cohort study by Tran K. and Bell C. et al., patients on isolation precautions on average had a 17% increase in hospital stays and a 23% increase in healthcare cost due to lack of attention by healthcare staff.[10] Health-care members must provide consistently high-quality care and attention to any patient, regardless of social or health status. [Level 3] Team members in any healthcare organization should be aware of the length of stay increase as well as the lack of quality care in isolation precaution patient populations.
What is OSHA 2021?
Last Update: May 9, 2021. Definition/Introduction. The Centers for Disease Control (CDC) and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) are the regulating bodies of infection control, prevention, and awareness. Precautions are preventative steps needed to be taken by healthcare team members and staff at healthcare facilities ...
What is the purpose of precautions?
Precautions are preventative steps needed to be taken by healthcare team members and staff at healthcare facilities to prevent the spread of infections. There are universal standard precautions are the minimum infection prevention steps defined by the CDC as[1]:
Why is infection control important in healthcare?
Infection control through the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) and alert signs designed by the CDC, OSHA, and individual internal policies in healthcare facilities is critical for proper patient care and prevention of prolonged hospitalizations and decreasing healthcare costs. While awareness of precautions is appreciated, adherence to following the precautions appears to be lacking.[11] All healthcare team members and visitors to healthcare facilities must abide by those policies to encourage safe practices and reduce the spread of infections.
What is PPE in medical terms?
In addition to universal standard precautions, the Center for Disease Control (CDC) defines additional types of proper personal protective equipment (PPE) required for each kind of precaution.

III.A. Standard Precautions
III.B. Transmission-Based Precautions
- There are three categories of Transmission-Based Precautions: Contact Precautions, Droplet Precautions, and Airborne Precautions. Transmission-Based Precautions are used when the route(s) of transmission is (are) not completely interrupted using Standard Precautions alone. For some diseases that have multiple routes of transmission (e.g., SARS), mo...
III.C. Syndromic and Empiric Applications of Transmission-Based Precautions
- Diagnosis of many infections requires laboratory confirmation. Since laboratory tests, especially those that depend on culture techniques, often require two or more days for completion, Transmission-Based Precautions must be implemented while test results are pending based on the clinical presentation and likely pathogens. Use of appropriate Transmission-Based Precautio…
III.D. Discontinuation of Transmission-Based Precautions
- Transmission-Based Precautions remain in effect for limited periods of time (i.e., while the risk for transmission of the infectious agent persists or for the duration of the illness (Appendix A). For most infectious diseases, this duration reflects known patterns of persistence and shedding of infectious agents associated with the natural history of the infectious process and its treatment…
III.F. Protective Environment
- A Protective Environment is designed for allogeneic HSCT patients to minimize fungal spore counts in the air and reduce the risk of invasive environmental fungal infections (see Table 5 for specifications).11, 13-15 The need for such controls has been demonstrated in studies of aspergillus outbreaks associated with construction.11, 14, 15, 157, 158 As defined by the Ameri…