
What is a erythrocyte?
Erythrocytes (red blood cells or RBCs) are anucleate, biconcave cells, filled with hemoglobin, that transport oxygen and carbon dioxide between the lungs and tissues. They are produced in the red bone marrow by a process called erythropoiesis.
Where do red blood cells grow in the body?
Red blood cells grow in your bone marrow. Bone marrow creates almost all of the cells in your body. Red blood cells contain a protein called hemoglobin, which is responsible for carrying oxygen. What are the common conditions that affect red blood cells?
Do all erythrocytes have a nucleus?
Mature erythrocytes are the only cells in the body without a nucleus; however, a nucleus is present in the beginning stages of red blood cell formation. As maturation continues, the nucleus is lost after the cell divides asymmetrically with one portion containing the entire nucleus.
How many erythrocytes are in a drop of blood?
The erythrocyte, commonly known as a red blood cell (or RBC), is by far the most common formed element: A single drop of blood contains millions of erythrocytes and just thousands of leukocytes. Specifically, males have about 5.4 million erythrocytes per microliter ( µ L) of blood, and females have approximately 4.8 million per µ L.
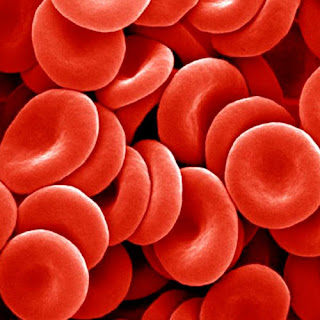
What does it mean when erythrocytes are low?
This means that the number of healthy red blood cells in the body is lower than needed. This could be a symptom of general anemia, sickle cell anem...
What are the two main functions of erythrocytes?
The two main functions of red blood cells are gas exchange and transportation. They bring oxygen from the lungs to target cells and tissues. They a...
What is another name for erythrocyte?
Erythrocyte is a medical and biological term for red blood cells. Erythrocytes are the mature and final version of red blood cells produced in the...
What does it mean when erythrocytes are high?
This means that the number of red blood cells in the body is higher than usual. It is a symptom of the genetic disorder polycythemia vera.
What are erythrocytes in blood?
Erythrocytes are mature red blood cells. They have a biconcave shape and no nucleus. Their pliable nature helps them move throughout the cardiovasc...
Where are erythrocytes produced?
Erythrocytes are produced in the bone marrow. The process of red blood cell creation is called erythropoiesis. Erythrocytes are formed from progenitor (ancestor or parent) cells in red marrow. The kidney produces a hormone called erythropoietin, which travels to the bone marrow and controls the maturation process of these progenitor cells. A mature erythrocyte is formed after several cellular generations.
What is the function of erythrocytes?
The major function of erythrocytes is gas exchange and transportation. They shuttle oxygen from the lungs to various cells and tissues in the body. They also remove carbon dioxide from cells as a waste product and deliver them back to the lungs for exhalation.
How many oxygen molecules can a red blood cell carry?
Red blood cells have the ability to transport oxygen and carbon dioxide because they contain hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is a protein made up of four subunits. Each subunit has an iron-containing heme group that binds and carries one oxygen molecule made of two oxygen atoms. Because hemoglobin has four subunits, it has the ability to carry up to four oxygen molecules. One red blood cell contains approximately 250 million hemoglobin. This means that just one erythrocyte has the potential to deliver approximately one billion oxygen molecules in just one pass.
Why do red blood cells have different colors?
Red blood cells have unique characteristics due to their shape and color. Erythrocytes get their red hue from an iron-containing molecule called heme. When heme's iron is bound to oxygen, it has the ability to absorb blue-green light while reflecting red-orange light. This is why oxygenated blood appears bright red to the human eye. When the iron in heme is bound to carbon dioxide, the same phenomenon occurs except the color is a much darker red. The bluish color that appears in human veins is more of an optical illusion rather than a result of deoxygenated blood. Since blue light's shorter wavelength cannot penetrate human tissue as deeply as red light's longer wavelength, blue light is more likely to be reflected from veins closest to the skin.
What is the term for red blood cells?
The term erythrocytes is another word for red blood cells. This medical and biological term is derived from ancient Greek and breaks down into erythro, meaning "red," and cyte, meaning "cell". Erythrocytes are defined as mature human red blood cells that maintain a biconcave (concave on both sides) discoid shape and do not contain a nucleus.
What is the term for the final version of red blood cells?
Erythrocyte is a medical and biological term for red blood cells. Erythrocytes are the mature and final version of red blood cells produced in the bone marrow.
Do erythrocytes have a nucleus?
Mature erythrocytes are the only cells in the body without a nucleus ; however, a nucleus is present in the beginning stages of red blood cell formation. As maturation continues, the nucleus is lost after the cell divides asymmetrically with one portion containing the entire nucleus. This portion is then swallowed by macrophages (a type of white blood cell). When a red blood cell loses its nucleus, it has been anucleated. The absence of a nucleus frees up space to carry and deliver more oxygen.
What are erythrocytes in the circulation?
During the first day or two that it is in the circulation, an immature erythrocyte, known as a reticulocyte , will still typically contain remnants of organelles. Reticulocytes should comprise approximately 1–2 percent of the erythrocyte count and provide a rough estimate of the rate of RBC production, with abnormally low or high rates indicating deviations in the production of these cells. These remnants, primarily of networks (reticulum) of ribosomes, are quickly shed, however, and mature, circulating erythrocytes have few internal cellular structural components. Lacking mitochondria, for example, they rely on anaerobic respiration. This means that they do not utilize any of the oxygen they are transporting, so they can deliver it all to the tissues. They also lack endoplasmic reticula and do not synthesize proteins. Erythrocytes do, however, contain some structural proteins that help the blood cells maintain their unique structure and enable them to change their shape to squeeze through capillaries. This includes the protein spectrin, a cytoskeletal protein element.
What is the most common form of erythrocytes?
Discuss the various steps in the lifecycle of an erythrocyte. Explain the composition and function of hemoglobin. The erythrocyte, commonly known as a red blood cell (or RBC), is by far the most common formed element: A single drop of blood contains millions of erythrocytes and just thousands of leukocytes.
How many erythrocytes are produced in a second?
Production of erythrocytes in the marrow occurs at the staggering rate of more than 2 million cells per second. For this production to occur, a number of raw materials must be present in adequate amounts. These include the same nutrients that are essential to the production and maintenance of any cell, such as glucose, lipids, and amino acids. However, erythrocyte production also requires several trace elements:
What is the molecule of hemoglobin?
Hemoglobin is a large molecule made up of proteins and iron. It consists of four folded chains of a protein called globin, designated alpha 1 and 2, and beta 1 and 2 ( [link] a ). Each of these globin molecules is bound to a red pigment molecule called heme, which contains an ion of iron (Fe 2+) ( [link] b ). Hemoglobin.
How long do erythrocytes live?
Thus, both are critical for the synthesis of new cells, including erythrocytes. Erythrocytes live up to 120 days in the circulation, after which the worn-out cells are removed by a type of myeloid phagocytic cell called a macrophage, located primarily within the bone marrow, liver, and spleen.
What is the shape of erythrocytes?
In wider vessels, erythrocytes may stack up much like a roll of coins, forming a rouleaux, from the French word for “roll.”. Shape of Red Blood Cells. Erythrocytes are biconcave discs with very shallow centers. This shape optimizes the ratio of surface area to volume, facilitating gas exchange.
Where does hemoglobin go?
In the lungs, hemoglobin picks up oxygen, which binds to the iron ions, forming oxyhemoglobin. The bright red, oxygenated hemoglobin travels to the body tissues, where it releases some of the oxygen molecules, becoming darker red deoxyhemoglobin, sometimes referred to as reduced hemoglobin.
How long do red blood cells live?
When a red blood cell travels through your blood vessels, it uses up its energy supply and only survives an average of 120 days.
What does red blood cells do to the body?
Red blood cells bring oxygen to the tissues in your body and release carbon dioxide to your lungs for you to exhale. Oxygen turns into energy, which is an essential function to keep your body healthy.
What is the function of red blood cells?
Red blood cells are responsible for transporting oxygen from your lungs to your body’s tissues. Your tissues produce energy with the oxygen and release a waste, identified as carbon dioxide. Your red blood cells take the carbon dioxide waste to your lungs for you to exhale.
What are the nutrients that help red blood cells grow?
You can maintain healthy red blood cells by eating a nutritious diet that is full of vitamins and minerals like iron, B9 (folic acid) and B12 , which includes:
Why does blood appear red?
Your blood appears red because red blood cells make up 40% of your blood.
How long does it take for red blood cells to release into the bloodstream?
Red blood cells develop in your body’s soft bone tissue (bone marrow) and release into your bloodstream after they fully mature, which takes about seven days.
Does cancer affect the number of red blood cells?
Cancer: Certain cancers and chemotherapy treatment for cancer can affect the number of red blood cells your body produces.
Where are erythrocytes formed?
Postnatal, erythrocytes are formed in the red bone marrow found this these 4 locations.
Where is spectrin found?
Spectrin is found in this part of erythrocytes.
Does the amount of erythrocytes in circulation fluctuate?
The amount of erythrocytes found in circulation is supposed to fluctuate.
What is the norm for red blood cells in urine?
As we have said, an indicator of the norm is considered when there are no red blood cells in the urine, or their number is 1-2 or three in the field of view. In any case, such a string as a result of analysis, such as “red blood cells in the urine of 1, 2, 3, 5, 10 and more,” should alert. It is possible that the doctor will advise to be re-examined.
What is the morphology of red blood cells?
In terms of morphology, red blood cells may differ, depending on which part of the urinary tract they came from. For example, in renal pathologies, these cells are dysmorphic (against the background of a large number of erythrocytes, they can be both dysmorphic and unchanged).
What does a red blood cell look like?
Red blood cells in the urinary fluid with an isotonic reaction look like yellowish or red discs concave from two planes. If the environment is hypotonic or alkaline, then the red blood cells can grow in size and be almost colorless - in medicine such structures are called “red blood cell shadows”. Under the conditions of an acidic environment or a concentrated uric fluid, they acquire uneven boundaries and become wrinkled. Normal and altered erythrocytes in the urine are well visualized when using the phase-contrast microscopic method.
Why is hemoglobin not detected in urine?
Hemoglobin without red blood cells in the urine is detected as a result of the destruction of the latter inside the vessels. This is typical for hemolytic anemia and possibly for intoxication, diseases of the spleen, allergies, infectious processes, injuries.
Can red blood cells be detected in urine?
In any case, the presence of red blood cells in the urine requires further examination to identify causal pathologies. And only on the basis of the established final diagnosis can predictions about possible complications be made.
Can erythrocyturia cause a change in color?
The patient may voice complaints about the change in color of the urinary fluid - this is possible in the case of severe erythrocyturia. Color may vary:
