
What are melanocytes in hair?
Melanocyte. All melanocytes, whether resident in the basal epidermis or in the matrix of the hair, have migrated there during embryonic life from a region known as the neural crest. Each epidermal melanocyte is associated with a group of neighbouring keratinocytes ( keratin -synthesizing epidermal cells) into which its dendrites transfer pigment.
Where are melanocytes found?
See all videos for this article melanocyte, specialized skin cell that produces the protective skin-darkening pigment melanin. Birds and mammals possess these pigment cells, which are found mainly in the epidermis, though they occur elsewhere—e.g., in the matrix of the hair.
What type of melanin is produced by melanocytes?
Melanocyte. The melanin produced by melanocytes is of two kinds: dark brown eumelanin and pale red or yellowish phaeomelanin. Both are formed within the melanocytes by the initial oxidation of the amino acid tyrosine with the aid of the enzyme tyrosinase; subsequently their synthetic pathways diverge.
How do keratinocytes obtain melanosomes from melanocytes?
Melanocytes produce melanosomes in the golgi zone of the cell. The melanosomes are then moved to the tips of their cellular processes. Keratinocytes then ingest the tips of the melanocytic dendrites by phagocytosis, allowing them to take in the melanosomes. This process is called apocopation [13].
Where are melanocytes in hair found and what are the two types?
Abstract. Melanocytes in human skin reside both in the epidermis and in the matrix and outer root sheath of anagen hair follicles.
What part of the hair contains melanin?
hair cortexThe hair cortex also contains melanin. Made by specialised cells named melanocytes, melanin is the pigment responsible for the hair color. Situated near the hair bulb the melanocytes inject pigments into keratinocytes of the new hair shaft.
Are melanocytes in the hair follicle?
Melanocytes in each hair follicle produce melanin pigments for the hair during each hair cycle. The key to understanding the mechanism of cyclic melanin production is the melanocyte stem cell (MelSC) population, previously known as 'amelanotic melanocytes'.
Which part of hairs have pigment granules of melanin?
Cortex, the middle layer of the hair is the primary source of mechanical strength and water uptake. It provides color and texture to the hair. The cortex contains melanin, which colors the fiber based on the number, distribution and types of melanin granules.
Where are pigmentation and melanocytes located?
Melanocytes and Pigmentation. Melanocytes are specialized cells that are distributed in the skin, other epithelial surfaces and the eye (1 ). In the skin, melanocytes are typically distributed at infrequent but regular intervals along the basal layer of the epidermis ( Figure 36-1) and in hair follicles ( 2 ).
What is the function of melanocytes?
A primary function of melanocytes is the distribution of packages of the pigment melanin to neighboring keratinocytes. Distribution of pigment is accomplished through the transfer of melanosomes, a unique organelle where the chemical steps in melanin biosynthesis occur ( 3 ).
What are the roles of melanocytes in skin?
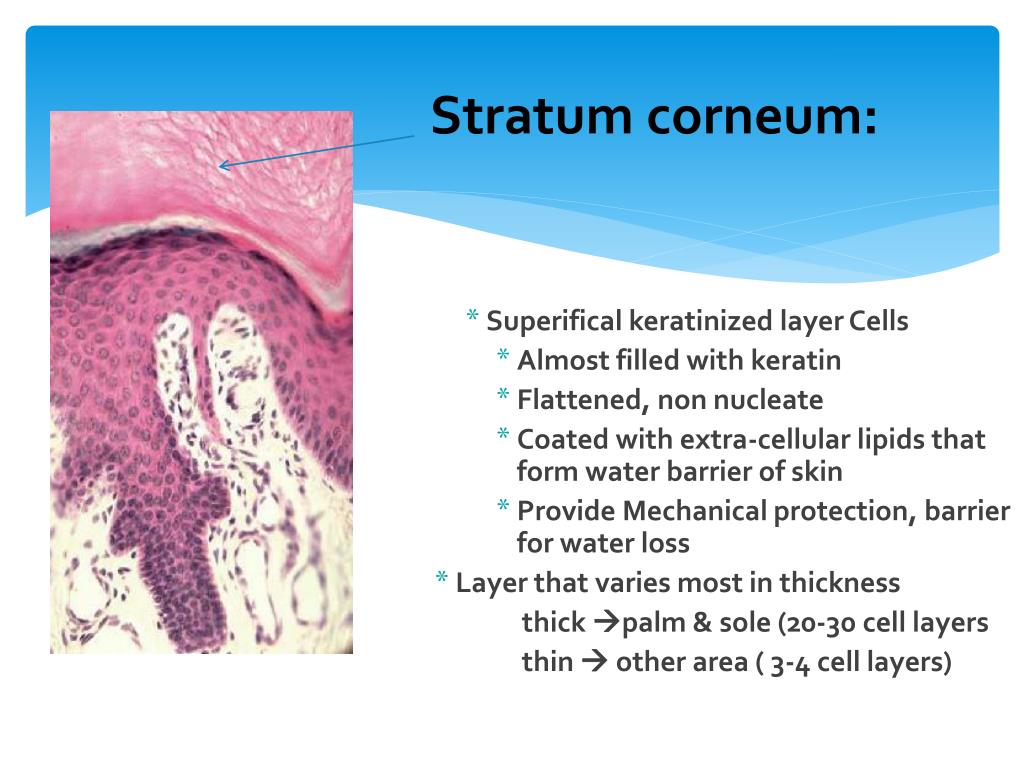
Melanocytes play a major role in protecting the skin from ultraviolet radiation through the production of melanosomes that are transferred to keratinocytes to protect their nuclei. Melanocytes are derived from neural crest and can be found within basal layer of the epidermis, the hair bulb, and the outer root sheath of hair follicles. Melanocytes have dark-staining nuclei that are typically smaller than those of the surrounding basal keratinocytes and may have a clear halo of cytoplasm that is an artifact of tissue processing (Figure 3). Melanocytes have hemidesmosomes but lack tonofilaments and desmosomes. Although melanocytes have dendritic processes, these are usually difficult to visualize on hematoxylin–eosin-stained preparations. Melanocytes usually represent approximately one out of ten cells in the basal layer but may be more prevalent in skin that has been repeatedly exposed to ultraviolet light.
What is hair graying?
Hair Graying as a Model for Aging Research. Melanocytes are melanin-producing cells derived from immature melanocytes or the so-called melanoblasts, which migrate from the neural crest during embryogenesis. Follicular melanocytes show cyclical activation, and “melanogenesis” (to produce melanin) is coupled with anagen in so-called anagen-coupled ...
What is the cell type that expresses BCL2?
Melanocytes in the skin are generally long-lived, nonproliferative cells that constitutively express the anti-apoptotic molecule BCL2, but are able to proliferate in response to inflammation during tissue damage or following excessive solar radiation. View chapter Purchase book. Read full chapter. ...
Why do rats not produce melanin?
The ordinary laboratory rat is, of course, an albino mutant, and does not produce melanin due to defect in the gene for tyrosinase.
When do matrix melanocytes proliferate?
Matrix melanocytes start to proliferate from anagen IIIa onward; this becomes prominent in anagen IIIb, and melanin is then produced and transferred to hairs. At the end of anagen phase, mature melanocytes die by apoptosis during regression of the cycling portion of the hair follicle in catagen phase [26].
Where are melanocytes located?
Melanocytes are melanin -producing neural crest -derived cells located in the bottom layer (the stratum basale) of the skin's epidermis, the middle layer of the eye (the uvea ), the inner ear, vaginal epithelium, meninges, bones, and heart. Melanin is a dark pigment primarily responsible for skin color. Once synthesized, melanin is contained in ...
How many melanocytes are in the epidermis?
Typically, between 1000 and 2000 melanocytes are found per square millimeter of skin or approximately 5% to 10% of the cells in the basal layer of epidermis.
What are the stimuli that affect melanogenesis?
Numerous stimuli are able to alter melanogenesis, or the production of melanin by cultured melanocytes, although the method by which it works is not fully understood. Certain melanocortins have been shown in laboratory testing to have effect on appetite and sexual activity in mice. Eicosanoids, retinoids, oestrogens, melanocyte-stimulating hormone, endothelins, psoralens, hydantoin, forskolin, cholera toxin, isobutylmethylxanthine, diacylglycerol analogues, and UV irradiation all trigger melanogenesis and, in turn, pigmentation. Increased melanin production is seen in conditions where adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) is elevated, such as Addison's and Cushing's disease. This is mainly a consequence of alpha-MSH being secreted along with the hormone associated with reproductive tendencies in primates. Alpha-MSH is a cleavage product of ACTH that has an equal affinity for the MC1 receptor on melanocytes as ACTH.
What happens when ultraviolet rays penetrate skin?
When ultraviolet rays penetrate the skin and damage DNA, thymidine dinucleotide (pTpT) fragments from damaged DNA will trigger melanogenesis and cause the melanocyte to produce melanosomes, which are then transferred by dendrites to the top layer of keratinocytes.
How to treat vitiligo?
Vitiligo is a skin disease where people suffer from melanin lack in certain areas in the skin. The way to treat vitiligo is by exposure to UV light called, Phototherapy. It can UVB or UVA. UVA is needed when the Melanocyte are deep in the skin where UVB does not reach. UVA + Psoralen is a common treatment for Vitiligo. It is more effective than narrowband UVB 313 nanometer when the spots are in the hands and legs.
What are the precursors of melanocytes?
The precursor of the melanocyte is the melanoblast. In adults, stem cells are contained in the bulge area of the outer root sheath of hair follicles. When a hair is lost and the hair follicle regenerates, the stem cells are activated. These stem cells develop into both keratinocyte precursors and melanoblasts - and these melanoblasts supply both hair and skin (moving into the basal layer of the epidermis ). There is additionally evidence that melanocyte stem cells are present in cutaneous nerves, with nerve signals causing these cells to differentiate into melanocytes for the skin.
What is the pigment that is responsible for skin color?
Melanin is a dark pigment primarily responsible for skin color. Once synthesized, melanin is contained in special organelles called melanosomes which can be transported to nearby keratinocytes to induce pigmentation. Thus darker skin tones have more melanosomes present than lighter skin tones.
Where are melanoma stem cells found?
A better understanding of how melanoma arises may lead to ways to detect and treat the disease earlier. Melanocyte stem cells are found within hair follicles, shown here. Ivan Mattioli / iStock via Getty Images. Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer. Its most deadly form is melanoma.
Where does melanoma come from?
Melanoma develops from melanocytes. These cells are found in the skin, eyes, and hair. They produce a natural pigment called melanin. Melanoma often first appears in the skin’s outermost layer, the epidermis. Then it invades the layer below the epidermis, called the dermis.
What cells move hair into the epidermis?
The researchers found that with the start of the hair’s growth phase, mutated melanocyte stem cells migrated up the hair follicle and into the epidermis. Such movement doesn’t take place under normal conditions.
Can melanoma be caused by melanocytes?
The findings will require confirmation in human studies, but they suggest that melanoma can arise from melanocyte stem cells in hair follicles as well as from melanocytes in skin layers.
What are the two types of melanins that determine hair color?
Pheomelanins: give hair light colors. Different amounts of these two types of melanin also determine hair color, as shown below: Hair color. Types of melanin. black. large amounts of eumelanin. brown. moderate amounts of eumelanin. blond.
What is the role of melanin in hair?
Melanin protects hair from the sun. According to Nikki Goddard, a certified hairstylist with an associate degree in cosmetology, melanin plays another crucial biological role in hair: It protects hair against sun rays (photoprotection) and ultraviolet (UV) radiance. “The latter is conditioned by the type of melanin and its concentration.
What vitamins are good for gray hair?
Your best bet is to eat healthy foods that are high in antioxidants, protein, and copper. Studies have also found that taking vitamins B12 and B6 may prevent premature graying hair.
Why does my hair turn gray?
When the production of this pigment slows down, hair turns gray or white. Since these colors largely symbolize growing older, many are keen to boost melanin production and restore their color as soon as possible. Read on to find out how to increase melanin production in the hair. This includes which foods to add to your diet ...
What foods help with melanin production?
Since copper plays a role in melanin production, you’ll also want to include the following foods into your diet: 1 crabmeat 2 almonds 3 lentils 4 peanuts 5 beef liver 6 white mushrooms
What determines the color of hair?
Melanin determines the color of hair. Your hair color is determined by the type and amount of melanin in your hair. Genetics play a huge role in which type of melanin you’re born with. The two types of melanin you may have are: Eumelanins: give hair dark colors. Pheomelanins: give hair light colors.
What vitamins help with hair and nails?
Lastly, vitamins A, C, and E have shown promising results on improving hair, skin, and nails. For example, research has found that these vitamins help protect the skin again UV damage from the sun.
What is the function of melanocytes?
Melanocytes are branched, or dendritic, and their dendrites are used to transfer pigment granules to adjacentepidermal cells. All melanocytes, whether resident in the basal epidermis or in the matrix of the hair, have migrated there during embryonic life from a region known as the neural crest.
Which cell produces skin-darkening pigment?
Study how melanocytes produce skin-darkening melanin and the dangers of long exposure to sunlight. Melanocytes produce the protective skin-darkening pigment melanin. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. See all videos for this article. Melanocyte , specialized skincellthat produces the protective skin-darkening pigmentmelanin.
What is the color of melanin?
The melanin produced by melanocytes is of two kinds: dark brown eumelanin and pale red or yellowish phaeomelanin. Both are formed within the melanocytes by the initial oxidation of the amino acidtyrosinewith the aid of the enzymetyrosinase; subsequently their syntheticpathways diverge.
What causes a loss of pigmentation in vitiligo?
Both suntans and postinflammatory pigmentation result from the overproduction of melanin. The absence of melanocytes, which occurs in vitiligo, results in a loss of melanin pigmentation. Conditions such as albinismand phenylketonuriaare caused by reduced or absent synthesis of melanin by melanocytes.
Types of melanin
Melanin is produced in a specific cell-type called melanocytes found in skin, eyes and hair follicles. Melanin is also found in the brain. The type and amount of melanin and how it is distributed in cells is what creates differences in hair, skin and eye colour.
Untangling genetic complexity
In our study, we used genome-wide association studies (GWAS, pronounced ghee-was) to identify genetic regions associated with hair colour across our autosomal chromosomes. GWAS identifies overlapping associations in a gene of interest or other functional genomic elements.
Pigmentation pathways
By studying the genetic factors determining hair colour, we can increase our understanding of how pigmentation occurs. This helps us further understand pigmentation diseases and their genetic risk factors, such as the role of pigmentation in cutaneous melanoma and in vitiligo.

Overview
Role in the immune system
In addition to their role as UV radical scavengers, melanocytes are also part of the immune system, and are considered to be immune cells. Although the full role of melanocytes in immune response is not fully understood, melanocytes share many characteristics with dendritic cells: branched morphology; phagocytic capabilities; presentation of antigens to T-cells; and production and release of cytokines. Although melanocytes are dendritic in form and share many characteri…
Function
Through a process called melanogenesis, melanocytes produce melanin, which is a pigment found in the skin, eyes, hair, nasal cavity, and inner ear. This melanogenesis leads to a long-lasting pigmentation, which is in contrast to the pigmentation that originates from oxidation of already-existing melanin.
There are both basal and activated levels of melanogenesis; in general, lighter-skinned people h…
Clinical significance
• Melanoma - Cancer affecting melanocytes
• Melanocytic tumors
• Melanocytic tumors of uncertain malignant potential
• Vitiligo - Decreased number of melanocytes due to autoimmune destruction causing decreased melanin
See also
• Chromatophore (the pigment cell type found in poikilotherm animals)
• Eye color
• Mole (skin marking)
• Tanning activator
Further reading
• Ito S (June 2003). "The IFPCS presidential lecture: a chemist's view of melanogenesis". Pigment Cell Research. 16 (3): 230–6. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0749.2003.00037.x. PMID 12753395.
• Millington GW (May 2006). "Proopiomelanocortin (POMC): the cutaneous roles of its melanocortin products and receptors". Clinical and Experimental Dermatology. 31 (3): 407–12. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2230.2006.02128.x. PMID 16681590. S2CID 25213876.
External links
• Histology image: 07903loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University - "Eye: fovea, RPE"
• Histology image: 08103loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University - "Integument: pigmented skin"