
Many periodic tables along the right side of the table separate metals from nonmetals. The metals are to the left of the line (except for hydrogen, which is a nonmetal), the nonmetals are to the right of the line, and the elements immediately adjacent to the line are the metalloids.
Where are non metals and metals placed on the periodic table?
The nonmetals are a group of elements located on the right side of the periodic table (except for hydrogen, which is on the top left). There are also known as non metals and non-metals.
What are the 22 non metals?
What are the twenty two non-metals? The nonmetal element group consists of hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, sulfur and selenium. The elements at the top of the group are gases, but they become liquids and solids moving down the group. The halogens are fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine.
Where are semiconductors located on periodic table?
compare semiconductors with both metals and nonmetals in terms of their ability to conduct electricity, and state where the semiconductor are located on the periodic table. Semiconductors can conduct energy but not as well as metals. Non metals can't conduct energy at all but semiconductors can . semi conductor are located on the pink section.
Where are metals and nonmetals located?
Where are metals nonmetals and metalloids located on the periodic table? Metals are located on the left of the periodic table, and nonmetals are located on the upper right. Click to see full answer. Also question is, where are metals metalloids and nonmetals on periodic table?
What are some examples of metalloids?
What are the elements in the periodic table?
What are the characteristics of nonmetals?
Which element is considered a metal?
What are the properties of metals?
See 2 more
About this website
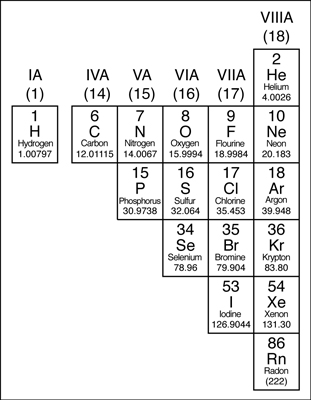
Where are the metalloids located on the periodic table?
Metalloids belong to p-block elements and it is placed on the right side of the periodic table. Metalloids exhibit the properties of both metals as well as non-metals.
Where are the metals and non-metals located?
Metals are located on the left of the periodic table, and nonmetals are located on the upper right. They are separated by a diagonal band of semimetals.
Where are the metals found?
Most of the metal on Earth, especially iron, is found within the Earth's core. Metal is scattered unevenly throughout the Earth's crust, mixed with rock, and combined with oxygen and other elements. Some rock types, such as granite, only hold trace amounts of metal.
Where are minerals and metals located?
Minerals can be found throughout the world in the earth's crust but usually in such small amounts that they not worth extracting. Only with the help of certain geological processes are minerals concentrated into economically viable deposits. Mineral deposits can only be extracted where they are found.
How many nonmetals are there in the periodic table?
There are 18 nonmetals on the Periodic table. All these nonmetals are located on the upper right corner of the Periodic table (Hydrogen is located on the left top corner) In the above image, the nonmetals are represented in yellow color. [ Note: Astatine (atomic number 85) shows characteristics of nonmetals (halogens) as well as metalloids.
What are nonmetals?
Or in other words nonmetals are those elements which do not possess the properties of metals.
How many electrons are in the outermost orbit of a nonmetal?
Nonmetals have 4 to 8 electrons in their outermost orbit. (Halogens have 7 electrons and noble gases have 8 electrons in outermost orbit)
Why are nonmetals oxidizing agents?
Nonmetals are oxidizing agents because they gain electron/s during a chemical reaction and get reduced.
What does it mean when a solid nonmetal breaks?
Solid nonmetals are brittle in nature. That means they break easily when force is applied on them.
Which nonmetals are the most reactive?
Actually the halogens are the most reactive nonmetals, but we know that as we move down the group, the electronegativity decreases. In other words, Fluorine is at the top of the halogen group and it has less atomic size plus it needs only one electron to complete the octet.
Which element has the highest electronegativity?
Also the atomic size of fluorine is very small. (Check this Periodic table guide, for atomic size trend) And because of its smaller size and need of only one electron, it has the highest electronegativity. Electronegativity is nothing but a tendency to attract the electron pair towards it.
Where are metalloids found in the periodic table?
Also we can say that metalloids are present in the diagonal region of the p block on Periodic table.
What is the color of the metalloids in the periodic table?
June 10, 2021 August 25, 2020 by Admin. Metalloids are located between the metals and nonmetals. The orange color on the Periodic table represents metalloids . They form a separating boundary between the metals and nonmetals. In other words, metalloids (semimetals) are located on the right side of the post transition metals and on the left side ...
What are the properties of metalloids?
Let us discuss the physical properties as well as chemical properties of metalloids/semimetals.
What is the chemical reaction between halogens and metalloids?
Metalloids + Halogens = Compounds (metalloid s elements reacts with halogens and finally compounds are formed by this chemical reaction) Metalloids have different metallic allotropes as well as nonmetallic allotropes. Metalloids have the property to form glasses on oxidation and so that are used in glass manufacturing.
What are elements that show some properties of metals as well as solid nonmetals called?
The elements that show some properties of metals as well as solid nonmetals are called metalloids . Metalloids look like metals, but they are not. Metalloids are brittle like solid nonmetals. Metalloids are neither conductor nor insulated. Source ( James L Marshall, Silicon, Germanium / CC BY-SA, CC BY ) The examples of metalloids are:
Why are metalloids called semiconductors?
Metalloids are called semiconductors because they are not good conductors like metals and also they are not bad conductors like nonmetals. They have the conductivity which is higher than nonmetals, but lower than metals. Hence metalloids are known as semiconductors.
How many metalloids are there?
Hence, there are total 6 known metalloids/semimetals on the Periodic table.
What are some examples of metalloids?
Examples of metalloids include boron, silicon, and arsenic. Metalloids have some of the properties of metals and some nonmetallic characteristics. Dull or shiny. Usually conduct heat and electricity, though not as well as metals. Often make good semiconductors.
What are the elements in the periodic table?
Elements of the periodic table are grouped as metals, metalloids or semimetals, and nonmetals. The metalloids separate the metals and nonmetals on a periodic table. Also, many periodic tables have a stair-step line on the table identifying the element groups.
What are the characteristics of nonmetals?
Nonmetals exhibit very different properties from metals. Examples of nonmetals include oxygen, chlorine, and argon. Nonmetals display some or all of the following characteristics: 1 Dull appearance 2 Usually brittle 3 Poor conductors of heat and electricity 4 Usually less dense, compared to metals 5 Usually low melting point of solids, compared with metals 6 Tend to gain electrons in chemical reactions
Which element is considered a metal?
Elements to the left of the line are considered metals. Elements just to the right of the line exhibit properties of both metals and nonmetals and are termed metalloids or semimetals. Elements to the far right of the periodic table are nonmetals. The exception is hydrogen (H), the first element on the periodic table.
What are the properties of metals?
Metals exhibit the following properties: Usually solid at room temperature (mercury is an exception) High luster (shiny) Metallic appearance. Good conductors of heat and electricity. Malleable (can be bent and pounded into thin sheets) Ductile (can be drawn into wire) Corrode or oxidize in air and seawater.
