Location:
- Upper motor neurons are either located in the cerebral cortex of the brain or the brain stem
- Lower motor neurons are located in the spinal cord, and their terminals extend all the way to the muscle fibers and tendons.
Where are motor neurons located?
Motor neurons are a specialized type of brain cell called neurons located within the spinal cord and the brain. They come in two main subtypes, namely the upper motor neurons and the lower motor neurons. The upper motor neurons originate in the brain and travel downward to connect with the lower motor neurons.
What is a typical motor neuron?
Motor neurons are the most common structure for neurons. Motor neurons are located in the central nervous system (CNS), specifically in the motor cortex, brainstem and spinal cord. Motor neurons are also known as efferent neurons, meaning they carry information from the CNS to muscles, and other peripheral systems such as organs and glands.
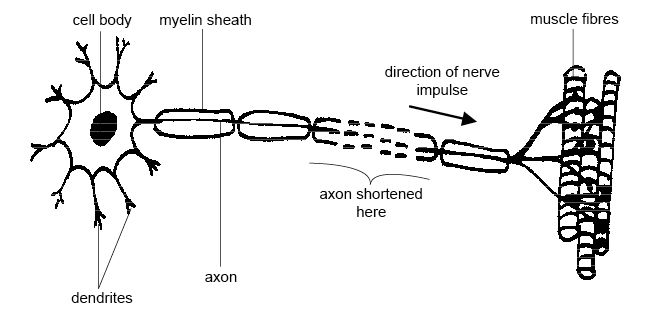
Where is the axon located on a neuron?
Where is an axon located? Structure of a neuron. At one end of the cell body (and indeed, around most of its periphery) are many small, branching protrusions called dendrites. Extending from the other end of the cell body at a location called the axon hillock is the axon, a long, thin, tube-like protrusion.
What is the structure of a motor neuron?
The structure of motor neurons is multipolar, meaning each cell contains a single axon and multiple dendrites. This is the most common type of neuron. Interneurons are neither sensory nor motor; rather, they act as the “middle men” that form connections between the other two types.
See more

Where are motor neurons found in the body and what is their function?
Motor neurons of the spinal cord are part of the central nervous system (CNS) and connect to muscles, glands and organs throughout the body. These neurons transmit impulses from the spinal cord to skeletal and smooth muscles (such as those in your stomach), and so directly control all of our muscle movements.
Where are motor neuron cell bodies housed quizlet?
Where are the cell bodies of lower motor neurons? located within the ventral (anterior) horns of the spinal cord and within the brain stem motor nuclei. Where are the cell bodies of Lower motor neurons? In the ventral/anterior portion of the central spinal cord grey matter, called the ventral horn.
Where are most efferent motor neuron cell bodies located?
On the other hand, efferent neurons have their cell bodies located in the ventral horn of the spinal cord. From there, efferent axons leave the spinal cord through the ventral root, travel through the spinal nerves, and ultimately synapse with the skeletal muscle cells found in the neuromuscular junction.
Which are locations of neuron cell bodies quizlet?
first (preganglionic) neurons have cell bodies in the CNS (brain and spinal cord) and synapse on second (postganglionic) neurons in autonomic ganglia.
Where are the cell bodies of lower motor neurons located quizlet?
Cell bodies for lower motor neurons are located in the anterior grey matter of the spinal cord. cell bodies for tertiary sensory neurons are located in the thalmus.
Which region of the spinal cord houses the cell bodies of motor neurons?
the anterior hornThe area of the grey matter closest to the front of the spinal cord is called the anterior horn. It contains the cell bodies of lower motor neurons. These neurons leave the spinal cord in the ventral roots and project to skeletal muscle. They are responsible for all voluntary and involuntary movements.
What are branchiomeric muscles?
Branchiomeric muscles are basically muscles of the face and neck. The general visceral neurons stimulate cardiac muscles, smooth visceral muscles, and also certain gland cells. Now, take a look at the diagrams given below.
How do motor neurons and sensory neurons communicate?
They transmit the impulse to the motor neurons in order to trigger a response. Sensory and motor neurons are connected by several interneurons; once the impulse reaches the lower motor neurons via the interneurons, the lower motor neurons as per the type of stimulation would either transmit the impulse further to upper motor neurons ...
How does the sensory system carry pain?
For instance, when one places his/her hand over a flame, the sensory neurons carry the stimulus of pain to the motor neurons via the neural network (interneurons). If this stimulus was to go to the brain and then return with an analyzed response, the person’s hand would keep burning till the motor neuron functioned.
What is the role of motor neurons in the nervous system?
Being the most basic units of the human nervous system, neurons play a vital role in sensing and responding to different external as well as internal stimuli. A motor neuron is one of the three types of neurons involved in this process.
What is the term for the degeneration of motor neurons?
Motor Neuron Disease (MND) A motor neuron disease affects the normal functioning of motor neurons, resulting in their degeneration and death. This leads to muscle weakness and atrophy to such an extent that basic voluntary muscle activity like speaking, swallowing, and breathing is largely affected. Let’s begin with the definition of a motor neuron.
What is the function of motor neurons?
Being the most basic units of the human nervous system, neurons play a vital role in sensing and responding to different external as well as internal stimuli. A motor neuron is one of the three types of neurons involved in this process.
Which neuron is specifically designed to stimulate organ-related muscles?
➔ Visceral neurons are specifically designed to stimulate organ-related muscles. The special visceral neurons control the branchiomeric muscles.
What neuron is responsible for muscle contraction?
Gamma motor neurons respond to stretch receptors of the skeletal muscle, also known as muscle spindles. Although known as a motor neuron, gamma motor neurons do not cause any motor function directly. Instead, they are thought to be activated alongside the alphas to fine-tune the muscle contraction. Special visceral efferent neurons (also known as ...
How does the axon work?
The axon works to transmit information it receives down its body to the dendrites at the end of the neuron. Motor neurons are known as multipolar neurons in terms of their structure. This means that they have a single axon and multiple dendrites. Motor neurons are the most common structure for neurons.
Which neuron innervates the head and neck?
Special visceral efferent neurons (also known as branchial motor neurons) are responsible for innervate the muscles of the head and neck.
Which type of neuron innervates extrafusal muscle fibers?
Beta motor neuron s are not as well categorized as alpha motor neurons, but are understood to also innervate extrafusal muscle fibers, as well as intrafusal fibers, which serve as specialized sensory organs and are innervated by both motor and sensory fibers.
What are the two types of motor neurons?
There are two types of motor neurons: 1 Lower motor neurons – these are neurons which travel from the spinal cord to the muscles of the body. 2 Upper motor neurons – these are neurons which travel between the brain and the spinal cord.
What causes a lower motor neuron to be damaged?
If the lower motor neurons are damaged, this could be as a result of infections such as Lyme disease, trauma to the peripheral nerves or viruses that can attack the cells . Some of the symptoms of damage to lower motor neurons include muscle paralysis and muscle weakness.
Why do motor neuron diseases occur?
Motor neuron diseases come because of damage to the motor neurons. These diseases tend to affect muscle control and can also affect speaking, eating, breathing, and walking as a result.
What is the difference between upper and lower motor neuron lesions?
An upper motor neuron lesion is a lesion anywhere from the cortex to the corticospinal tract . This lesion causes hyperreflexia, spasticity, and a positive Babinski reflex, presenting as an upward response of the big toe when the plantar surface of the foot is stroked, with other toes fanning out. On the other hand, lower motor neuron lesions are lesions anywhere from the anterior horn of the spinal cord, peripheral nerve, neuromuscular junction, or muscle. This type of lesion causes hyporeflexia, flaccid paralysis, and atrophy.
What is the most common motor neuron disease?
There are many forms of motor neuron disease, the most common of which is amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). This disease is unique in that it presents with both upper and motor neuron signs. The patient will typically present with weakness, along with spastic paralysis and hyperreflexia in the lower limbs and flaccid paralysis and hyporeflexia in the upper limbs. The patient may also present with fasciculations in both the tongue and extremities. Of note, there is no sensory loss. ALS is a progressive neurogenerative disease, and eventually, the patient will have serious dysarthria, dysphagia, extreme weakness, and dyspnea. The estimated median survival is 2 to 4 years, with the most common cause of death being respiratory failure. [12]
What are the two types of motor neurons?
In fact, within the classification of a “motor neuron,” there lies both upper and lower motor neurons, which are entirely different in terms of their origins, synapse points, pathways, neurotransmitters, and lesion characteristics. Overall, motor neurons (or motoneurons) comprise various tightly controlled, complex circuits throughout the body that allows for both voluntary and involuntary movements through the innervation of effector muscles and glands. The upper and lower motor neurons form a two-neuron circuit. The upper motor neurons originate in the cerebral cortex and travel down to the brain stem or spinal cord, while the lower motor neurons begin in the spinal cord and go on to innervate muscles and glands throughout the body. Understanding the difference between upper and lower motor neurons, as well as the pathway that they take, is crucial to being able to not only diagnose these neuronal injuries but also localize the lesions efficiently.
Where do motor neuron lesions occur?
Focusing mainly on the lateral corticospinal tract , it is essential to keep in mind that this neuronal pathway decussates at the level of the pyramids in the medulla. This crossing means that an upper motor neuron lesion above the medulla will cause symptoms on the contralateral side of the body. However, a lesion to the lateral corticospinal tract after it decussates will present on the ipsilateral side of the body.
Where are the branchial motor neurons located?
Branchial motor neurons innervate the muscles of the head and neck that derive from the branchial arches. They are in the brainstem. The branchial motor neurons and sensory neurons together form the nuclei of cranial nerves V, VII, IX, X, and XI. [1]
What causes paralysis in the lower limbs?
Poliomyelitis is another lower motor neuron disease. This disease results from poliovirus and results in the destruction of the anterior horn cells. Subsequently, the affected patient will experience weakness and lower motor neuron symptoms, including flaccid paralysis in the lower limbs. Usually, this presents asymmetrically. The patient may also provide a history of muscle aches or muscle spasm that occurred in the recent past. Unfortunately, this weakness and paralysis may extend up to involve the respiratory muscles. Many patients will recover some strength, but may later decompensate into “postpolio syndrome,” which is characterized by the onset of additional weakness, pain, and/or atrophy. Among other viral causes of anterior horn cell destruction are coxsackievirus, West Nile virus, and echovirus. [13]
What causes a lower motor neuron to be degenerated?
One group of genetic disorders that causes lower motor neuron disease is spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). There are many different forms of SMA, but all of them are characterized by degeneration of the motor nuclei in the brainstem, in addition to the anterior horn cells found in the spinal cord. One specific type of SMA is spinobulbar muscular atrophy (Kennedy disease). This x-linked disease usually presents in adulthood (age 30 to 50). First presenting signs typically include tremor, lower extremity weakness, and orolingual fasciculations. This pathology is a progressive disease that is later characterized by the above symptoms in addition to atrophy of limb, bulbar, and facial muscles. [13]