Where do motor neurons carry signals from?
Motor neurons (motoneurons) carry signals from the central nervous system to the outer parts (muscles, skin, glands) of your body. Interneurons connect various neurons within the brain and spinal cord. The simplest type of neural pathway is a monosynaptic (single connection) reflex pathway, like the knee-jerk reflex.
Where do motor neurons transmit messages to?
Motor neurons have a long axon and short dendrites and transmit messages from the central nervous system to the muscles (or to glands). Interneurons are found only in the central nervous system where they connect neuron to neuron.
Where do the Sympathetic motor neurons originate from?
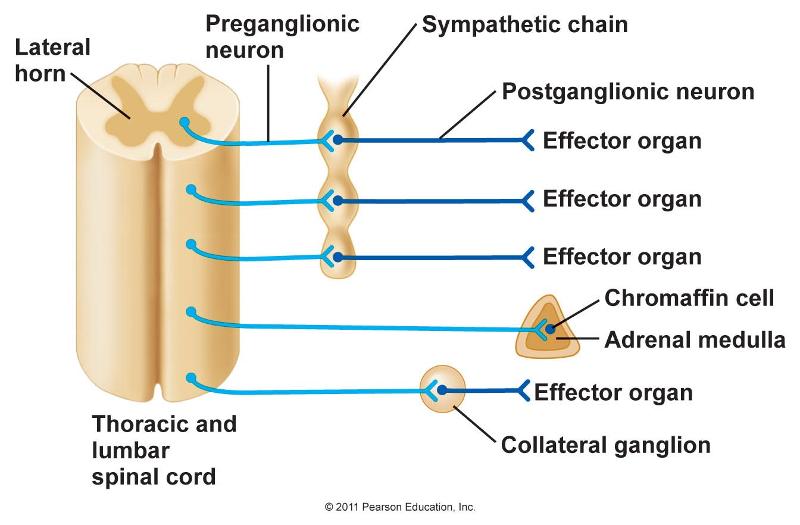
Where do sympathetic motor neurons originate? Most preganglionic neurons in the sympathetic nervous system originate in the spinal cord, as illustrated in Figure 16.27. The axons of these neurons release acetylcholine on postganglionic neurons within sympathetic ganglia (the sympathetic ganglia form a chain that extends alongside the spinal cord).
Where do sensory neurons and motor neurons found in?
They are mainly located in the dorsal root ganglion. This ganglion along with the neurons is collectively situated at the dorsal roots of the spinal cord in the Central Nervous System. Unlike the motor neurons, sensory neurons do not carry distinct axons and dendrites.

Where are most motor neurons located?
Motor neurons are a specialized type of brain cell called neurons located within the spinal cord and the brain. They come in two main subtypes, namely the upper motor neurons and the lower motor neurons. The upper motor neurons originate in the brain and travel downward to connect with the lower motor neurons.
Where are motor neurons located and what do they control?
The upper and lower motor neurons form a two-neuron circuit. The upper motor neurons originate in the cerebral cortex and travel down to the brain stem or spinal cord, while the lower motor neurons begin in the spinal cord and go on to innervate muscles and glands throughout the body.
Where are sensory and motor neurons located?
The central nervous system (CNS) consists of the brain and the spinal cord. It is in the CNS that all of the analysis of information takes place. The peripheral nervous system (PNS), which consists of the neurons and parts of neurons found outside of the CNS, includes sensory neurons and motor neurons.
Where are motor neurons located quizlet?
The cell bodies of motor neurons are located in the ventral horn gray matter of the spinal cord. The axons of these motor neurons leave the spinal cord through the ventral root and travel to the periphery to innervate skeletal muscles.
How many motor neurons are in the body?
500,000Motor neurons There are about 500,000 of them, carrying information from the CNS to peripheral effectors in the peripheral tissues and organ systems. Efferent fibers are the axons of motor neurons, and carry data away from the CNS.
What is the role of motor neurons?
Motor neurons of the spinal cord are part of the central nervous system (CNS) and connect to muscles, glands and organs throughout the body. These neurons transmit impulses from the spinal cord to skeletal and smooth muscles (such as those in your stomach), and so directly control all of our muscle movements.
What's the difference between sensory neurons and motor neurons?
Sensory Vs Motor Neurons When we compare motor neuron vs sensory neuron, the main function of Sensory Neurons is to send sensory signals from sensory organs to the central nervous system. Motor Nerves are responsible for sending motor commands from the central nervous system to the sensory organs to initiate actions.
Where are efferent neurons located?
the spinal cordOn the other hand, efferent neurons have their cell bodies located in the ventral horn of the spinal cord. From there, efferent axons leave the spinal cord through the ventral root, travel through the spinal nerves, and ultimately synapse with the skeletal muscle cells found in the neuromuscular junction.
Are neurons only in the brain?
In vertebrates, the majority of neurons belong to the central nervous system, but some reside in peripheral ganglia, and many sensory neurons are situated in sensory organs such as the retina and cochlea.
Which part of the spinal cord contains motor neurons?
ventral hornsThe ventral horns contains the cell bodies of motor neurons that send axons via the ventral roots of the spinal nerves to terminate on striated muscles.
Where are lower motor neurons located quizlet?
Cell bodies for lower motor neurons are located in the anterior grey matter of the spinal cord.
Are lower motor neurons part of the CNS?
The lower motor neuron (LMN) is the efferent neuron of the peripheral nervous system (PNS) that connects the central nervous system (CNS) with the muscle to be innervated. The entire function of the CNS is manifested through the lower motor neuron.
What do motor neurons do quizlet?
-Motor neurons are responsible for carrying a signal from the central nervous system (CNS) to an effector cell, which then carries out the desired response. -They are also involved in reflex arcs in which the signal comes from a sensory neuron instead of the brain.
What are the functional zones of a motor neuron?
To help students understand these concepts, we emphasize that neurons have three distinct functional zones: 1) the “input,” 2) the “integrative,” and 3) the “conductive” zones (Fig. 1).
Where are motor pathway located?
The connections between the motor cortex in the forebrain and motor neurons within the spinal cord are made up of two pyramidal tracts; the pyramidal system and the extrapyramidal system. These motor pathways are transmitted via the ventral horns within the spine.
Where are efferent neurons located?
the spinal cordOn the other hand, efferent neurons have their cell bodies located in the ventral horn of the spinal cord. From there, efferent axons leave the spinal cord through the ventral root, travel through the spinal nerves, and ultimately synapse with the skeletal muscle cells found in the neuromuscular junction.
Where are motor neurons located?
A motor neuron (or motoneuron or efferent neuron) is a neuron whose cell body is located in the motor cortex, brainstem or the spinal cord , and whose axon (fiber) projects to the spinal cord or outside of the spinal cord to directly or indirectly control effector organs, mainly muscles and glands. There are two types of motor neuron – upper motor ...
Where do lower motor neurons originate?
Lower motor neurons are those that originate in the spinal cord and directly or indirectly innervate effector targets. The target of these neurons varies, but in the somatic nervous system the target will be some sort of muscle fiber. There are three primary categories of lower motor neurons, which can be further divided in sub-categories.
How do motor neuron twitch?
A single motor neuron may innervate many muscle fibres and a muscle fibre can undergo many action potentials in the time taken for a single muscle twitch. As a result, if an action potential arrives before a twitch has completed, the twitches can superimpose on one another, either through summation or a tetanic contraction. In summation, the muscle is stimulated repetitively such that additional action potentials coming from the somatic nervous system arrive before the end of the twitch. The twitches thus superimpose on one another, leading to a force greater than that of a single twitch. A tetanic contraction is caused by constant, very high frequency stimulation - the action potentials come at such a rapid rate that individual twitches are indistinguishable, and tension rises smoothly eventually reaching a plateau.
What are the two types of motor neurons?
There are two types of motor neuron – upper motor neurons and lower motor neurons . Axons from upper motor neurons synapse onto interneurons in the spinal cord and occasionally directly onto lower motor neurons. The axons from the lower motor neurons are efferent nerve fibers that carry signals from the spinal cord to the effectors.
Which neuron in the spinal cord is responsible for the contraction of extrafusal muscle fibers?
The CNS activates alpha motor neurons in the spinal cord, which cause extrafusal muscle fibers to contract and thereby resist further stretching. This process is also called the stretch reflex . Beta motor neurons innervate intrafusal muscle fibers of muscle spindles, with collaterals to extrafusal fibres.
Which neuron innervates the viscera?
These motor neurons indirectly innervate cardiac muscle and smooth muscles of the viscera ( the muscles of the arteries ): they synapse onto neurons located in ganglia of the autonomic nervous system ( sympathetic and parasympathetic ), located in the peripheral nervous system (PNS), which themselves directly innervate visceral muscles (and also some gland cells).
What are the cells that make up the primary motor cortex?
The cells that make up the primary motor cortex are Betz cells, which are a type of pyramidal cell. The axons of these cells descend from the cortex to form the corticospinal tract. Corticomotorneurons project from the primary cortex directly onto motor neurons in the ventral horn of the spinal cord.
What are the components of motor neuron?
The structure of a motor neuron can be categorized into three components: the soma, the axon, and the dendrites. The soma is the cell body where the nucleus lies, and which controls the cells and is also where proteins are produced to maintain the functioning of the neuron. The dendrites are the branch-like structures found at the ends ...
What are the two types of motor neurons?
There are two types of motor neurons: 1 Lower motor neurons – these are neurons which travel from the spinal cord to the muscles of the body. 2 Upper motor neurons – these are neurons which travel between the brain and the spinal cord.
What neuron is responsible for muscle contraction?
Gamma motor neurons respond to stretch receptors of the skeletal muscle, also known as muscle spindles. Although known as a motor neuron, gamma motor neurons do not cause any motor function directly. Instead, they are thought to be activated alongside the alphas to fine-tune the muscle contraction. Special visceral efferent neurons (also known as ...
Which neuron innervates the head and neck?
Special visceral efferent neurons (also known as branchial motor neurons) are responsible for innervate the muscles of the head and neck.
Which type of neuron innervates extrafusal muscle fibers?
Beta motor neuron s are not as well categorized as alpha motor neurons, but are understood to also innervate extrafusal muscle fibers, as well as intrafusal fibers, which serve as specialized sensory organs and are innervated by both motor and sensory fibers.
What causes a lower motor neuron to be damaged?
If the lower motor neurons are damaged, this could be as a result of infections such as Lyme disease, trauma to the peripheral nerves or viruses that can attack the cells . Some of the symptoms of damage to lower motor neurons include muscle paralysis and muscle weakness.
Why do motor neuron diseases occur?
Motor neuron diseases come because of damage to the motor neurons. These diseases tend to affect muscle control and can also affect speaking, eating, breathing, and walking as a result.
Where are the large alpha motor neuron cells located?
The large alpha motor neuron cell body can be either in the brainstem or spinal cord. In the spinal cord, the cell bodies are found in the anterior horn and thus are called anterior horn cells. From the anterior horn cell, a single axon goes on to innervate many muscle fibers within a single muscle.
Why are upper motor neurons often consulted?
Upper motor neurons are often consulted in case of voluntary motor responses. This is because, voluntary actions are backed by thoughts.
What is the function of alpha motor neurons?
Alpha motor neurons innervate extrafusal muscle fibers and are the primary means of skeletal muscle contraction. The large alpha motor neuron cell body can be either in the brainstem or spinal cord. In the spinal cord, the cell bodies are found in the anterior horn and thus are called anterior horn cells. From the anterior horn cell, a single axon goes on to innervate many muscle fibers within a single muscle. The properties of these muscle fibers are nearly identical, allowing for controlled, synchronous movement of the motor unit upon depolarization of the lower motor neuron.
What neuron innervates muscle spindles?
Gamma motor neurons innervate muscle spindles and dictate their sensitivity. These neurons primarily respond to stretch of the muscle spindle. Despite being named a “motor neuron,” these neurons do not directly cause any motor function. It is thought that they get activated along with alpha motor neurons and fine-tune the muscle contraction (alpha-gamma coactivation). A disruption in either alpha or gamma motor neurons will result in a disruption of muscle tone
What happens when alpha motor neurons are disrupted?
A disruption in either alpha or gamma motor neurons will result in a disruption of muscle tone.
Which neuron controls both voluntary and involuntary movements?
Motor neurons divided into either upper or lower motor neuron es, forming various tightly controlled, complex circuits throughout the body. This controls both voluntary and involuntary movements through the innervation of effector muscles and glands. The upper and lower motor neurons form a two-neuron circuit.
Which neuron is involved in involuntary movements?
eg The rubrospinal tract is heavily involved in involuntary movements to improve and maintain the body's balance. Most of the movements relating to this tract occur in the arms; The tectospinal tract is related to the movements of the muscles in the neck; The reticulospinal tract has an important role in the control of autonomous actions in the body.
What is a motor neuron?
Definition. A motor neuron is a cell of the central nervous system. Motor neurons transmit signals to muscle cells or glands to control their functional output. When these cells are damaged in some way, motor neuron disease can arise. This is characterized by muscle wasting ( atrophy) and loss of motor function. Motor Neuron.
What is motor neuron disease?
Motor neuron disease describes a collection of neurodegenerative diseases that specifically affect the motor neurons, causing the death of the cells. There are various different types of motor neuron diseases, including amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), primary lateral sclerosis (PLS), bulbar onset MND or progressive bulbar palsy (PBP), and progressive muscular atrophy (PMA).
How many dendrites are there in a neuron?
Dendrites are the branch-like extensions found at one end of a neuron. These are the structures that receive information from the other neurons, and pass it along to the cell body to transmit the signal and activate the cell. There are usually around five to seven dendrites per neuron, but some, such as the Purkinje neurons in the brain, have over a thousand!
Why do motor neurons cause muscle weakness?
Because the motor neurons are no longer effectively signaling the muscles, motor neuron disease causes muscle weakening, stiffening, and wasting. This causes a diverse range of symptoms that are dependent upon the specific disease and the individual.
What causes lower motor neuron lesions?
The symptoms include muscle paralysis and weakness, and the lesions are usually caused by a systemic infection, such as Lyme disease, HIV, or the Herpes virus (which can cause Bell palsy).
What is the term for damage to the motor neurons of the brain?
An upper motor neuron lesion, also called pyramidal insufficiency, refers to damage to the motor neurons of the brain or brain stem that travel to the spinal cord. Such damage can occur as a result of a variety of disorders, including multiple sclerosis (MS), stroke, brain injury, or cerebral palsy.
How does motor neuron disease affect people?
The disease can impact a sufferers’ ability to eat and drink, talk, walk, and breathe. Eventually, most affected individuals will lose the ability to carry out these tasks entirely.
Where are motor neurons located?
About Motor Neurons. Motor neurons are a specialized type of brain cell called neurons located within the spinal cord and the brain. They come in two main subtypes, namely the upper motor neurons and the lower motor neurons. The upper motor neurons originate in the brain and travel downward to connect with the lower motor neurons.
Which type of splicing underlies motor neuron death in spinal muscular atrophy?
Dysregulation of Mdm2 and Mdm4 alternative splicing underlies motor neuron death in spinal muscular atrophy

Overview
A motor neuron (or motoneuron or efferent neuron ) is a neuron whose cell body is located in the motor cortex, brainstem or the spinal cord, and whose axon (fiber) projects to the spinal cord or outside of the spinal cord to directly or indirectly control effector organs, mainly muscles and glands. There are two types of motor neuron – upper motor neurons and lower motor neurons. Axons from upper mo…
Development
Motor neurons begin to develop early in embryonic development, and motor function continues to develop well into childhood. In the neural tube cells are specified to either the rostral-caudal axis or ventral-dorsal axis. The axons of motor neurons begin to appear in the fourth week of development from the ventral region of the ventral-dorsal axis (the basal plate). This homeodomain is known as the motor neural progenitor domain (pMN). Transcription factors here include Pax6, OLIG2, Nkx-6.1, …
Anatomy and physiology
Upper motor neurons originate in the motor cortex located in the precentral gyrus. The cells that make up the primary motor cortex are Betz cells, which are a type of pyramidal cell. The axons of these cells descend from the cortex to form the corticospinal tract. Corticomotorneurons project from the primary cortex directly onto motor neurons in the ventral horn of the spinal cord. Their axons synaps…
See also
• Betz cell
• Central chromatolysis
• Motor dysfunction
• Motor neuron disease
• Nerve
Sources
• Sherwood, L. (2001). Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (4th ed.). Pacific Grove, CA: Brooks-Cole. ISBN 0-534-37254-6.
• Marieb, E. N.; Mallatt, J. (1997). Human Anatomy (2nd ed.). Menlo Park, CA: Benjamin/Cummings. ISBN 0-8053-4068-8.