Where Do We Find Obstacle Departure Procedures? If you are using Jeppesen charts then look at the back of the “dash 9” page and you will find a description under the title “OBSTACLE DP” For government charts ODP procedures are listed in the front of the approach chart booklets under the heading “Takeoff Minimums and Obstacle Departure Procedures”.
Are obstacle departure procedures mandatory?
Obstacle departure procedures are not mandatory unless of course, it was included with the ATC clearance. Typically the ATC clearance will not include the ODP unless the controller assigns it for separation. It is the pilot’s responsibility to avoid obstacles until at or above the minimum vectoring altitude.
How are departure procedures listed in the IFR?
Textual departure procedures and diverse vector areas are listed by airport in the IFR Takeoff Minimums and (Obstacle) Departure Procedures, Section L, of the Terminal Procedures Publications (TPP) while SIDs and complex obstacle departure procedures will be published graphically in the Instrument Approach Procedure Charts
What are the different types of departure procedures?
There are two types of DPs, Obstacle Departure Procedures (ODP), printed either textually or graphically, and Standard Instrument Departures (SID), always printed graphically. All DPs, either textual or graphic may be designed using either conventional or RNAV criteria.
How do you identify take off obstacles?
These obstacles are identified on the SID chart or in the Take-off Minimums and (Obstacle) Departure Procedures section of the U. S. Terminal Procedure booklet. These obstacles are especially critical to aircraft that do not lift off until close to the departure end of the runway or which climb at the minimum rate.
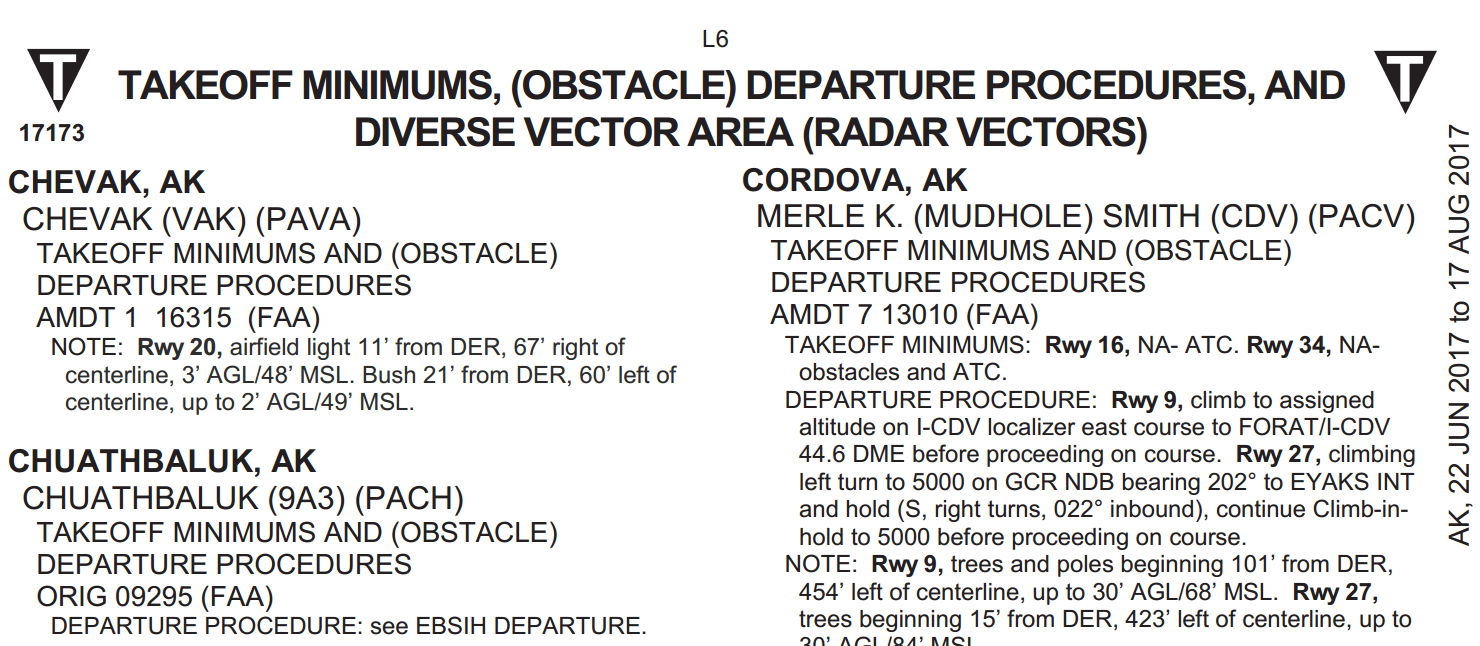
Where are departure procedures published?
These textual procedures are published in the Take-Off Minimums and (Obstacle) Departure Procedures section of the Terminal Procedures Publications and/or appear as an option on a Graphic ODP.
How do I find the SID or ODP?
4:4211:57ODP and SID Departure Procedures // IFR Flying - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe other type of dp is the standard instrument departure or sid sids are always published inMoreThe other type of dp is the standard instrument departure or sid sids are always published in graphical. Form along with a textual description like this sid for grand junction.
Does every airport have an ODP?
Obstacle departure procedures are not mandatory unless of course, it was included with the ATC clearance. Typically the ATC clearance will not include the ODP unless the controller assigns it for separation. It is the pilot's responsibility to avoid obstacles until at or above the minimum vectoring altitude.
Where can I find ODP in ForeFlight?
Fortunately, Foreflight and most of the other electronic flight planning tools list the ODPs under the Procedures tab of the airport. Click on Departures and then Takeoff Minimums. You still have to scroll through several pages of text to find the procedure if it is not a named graphic procedure.
Does a SID provide obstacle clearance?
While the primary purpose of a SID is to ease pilot and controller workload while getting the aircraft into the system, they also provide obstacle clearance.
What are instrument departure procedures?
1:4117:17Standard Instrument Departures (SID) Obstacle Departure Procedure ...YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipFor this reason specific departure procedures are designed at airports to minimize confusion. AndMoreFor this reason specific departure procedures are designed at airports to minimize confusion. And increase capacity. Let's have a look at the westchester 7 departure. Again. This is what's known as a
Where are takeoff minimums published?
If you use ForeFlight, look under the "Procedures - Departure" tab on the airport description page and click on "Takeoff Minimums." Non-standard minimums are published when there are obstacle departure procedures to ensure you maintain safe clearance.
What is RNAV departure?
Specifically, RNAV departures require the flight crew to program the FMS correctly before departure and to modify the FMS to align with air traffic control (ATC) clearance changes before and during flight. Errors in programming can lead to unexpected and possibly large deviations from the nominal flight path.
What are SIDs in aviation?
A Standard Instrument Departure Route (SID) is a standard ATS route identified in an instrument departure procedure by which aircraft should proceed from take-off phase to the en-route phase.
What are terminal procedures?
Filed Under: The National Airspace System. While the en route charts provide the information necessary to safely transit broad regions of airspace, the United States Terminal Procedures Publication (TPP) enables pilots to guide their aircraft in the airport area.
What is ATC's departure restriction?
ATC may assign departure restrictions, clearance void times, hold for release, and release times, when necessary, to separate departures from other traffic or to restrict or regulate the departure flow.
What to do if a pilot cannot establish contact on clearance delivery frequency?
If a pilot cannot establish contact on clearance delivery frequency or has not received an IFR clearance before ready to taxi, the pilot should contact ground control and inform the controller accordingly.
What to do if takeoff clearance is not received?
If a takeoff clearance is not received within a reasonable amount of time after clearance to line up and wait, ATC should be contacted.
What is ATC in line up and wait?
If landing traffic is a factor during line up and wait operations, ATC will inform the aircraft in position of the closest traffic within 6 flying miles requesting a full-stop, touch-and-go, stop-and-go, or an unrestricted low approach to the same runway. Pilots should take care to note the position of landing traffic.
What runway is Cessna 210 holding in position?
Tower: “Delta 1011, continue, traffic a Cessna 210 holding in position Runway 24L.”. ATC will normally withhold landing clearance to arrival aircraft when another aircraft is in position and holding on the runway. Never land on a runway that is occupied by another aircraft, even if a landing clearance was issued.
How long before taxi time do pilots call?
Participating pilots call clearance delivery or ground control not more than 10 minutes before proposed taxi time.
When do pilots call ground control?
When the IFR clearance is received on clearance delivery frequency, pilots call ground control when ready to taxi. Normally, pilots need not inform ground control that they have received IFR clearance on clearance delivery frequency. Certain locations may, however, require that the pilot inform ground control of a portion ...
Why is visibility required on runways?
Sometimes, certain runways are not authorized, or a higher ceiling and visibility is required in order for a pilot to avoid obstacles visually. Other times, a steeper climb gradient will be required or a specific departure course will be defined.
Is it important to plan the vertical?
However, there is an even more important aspect of "planning the vertical," and that occurs during an instrument departure. While failure to plan properly during the approach can result in a missed approach or a last-minute diving attempt to reach the runway, failure to follow the proper climb procedure during departure can (and has) resulted in deadly accidents.
Do you have to follow takeoff minimums?
If, however, we find nonstandard takeoff minimums or a published ODP, we need to carefully study the information. Although we are not required to follow takeoff minimums or departure procedures while operating under FAR Part 91, it is important to realize that those procedures exist to protect us during departures. Sometimes, certain runways are not authorized, or a higher ceiling and visibility is required in order for a pilot to avoid obstacles visually. Other times, a steeper climb gradient will be required or a specific departure course will be defined. Whatever the departure procedure requires, we should have a solid plan to remain clear of all the obstacles and terrain.
Is it legal to fly IFR without ATC?
Those of us who are instructors are the best hope for preventing these accidents. We simply must explain that a "cleared as filed" or "cleared direct" IFR clearance does not assure terrain or obstacle clearance when departing from airports without ATC radar coverage. It is perfectly legal, but really dumb for FAR Part 91 flights to launch into instrument meteorological conditions (IMC) without a clear plan to reach the minimum en route altitude while avoiding mountains or other obstructions.
What is a VCOA?
VISUAL CLIMB OVER AIRPORT (VCOA)− A departure option for an IFR aircraft, operating in visual meteorological conditions equal to or greater than the specified visibility and ceiling, to visually conduct climbing turns over the airport to the published “climb−to” altitude from which to proceed with the instrument portion of the departure. VCOA procedures are developed to avoid obstacles greater than 3 statute miles from the departure end of the runway as an alternative to complying with climb gradients greater than 200 feet per nautical mile. Pilots are responsible to advise ATC as early as possible of the intent to fly the VCOA option prior to departure. These textual procedures are published in the ‘Take−Off Minimums and (Obstacle) Departure Procedures’ section of the Terminal Procedures Publications and/or appear as an option on a Graphic ODP.
What is the role of pilots in the VCOA?
Pilots are responsible to advise ATC as early as possible of the intent to fly the VCOA option prior to departure. These textual procedures are published in the ‘Take−Off Minimums and (Obstacle) Departure Procedures’ section of the Terminal Procedures Publications and/or appear as an option on a Graphic ODP. see more.
How to tell ATC you're flying an ODP?
It's always best to tell ATC you're flying the ODP by putting it in the remarks of your flight plan from a non-towered airport. If there's a tower, you could could still notify Tower you wish to fly the ODP and you could get a clearance to do so. But that would be more for practice or where you couldn't meet a non-standard climb requirement published for the diverse vector area. That's a pretty rare situation.
What should pilots notify ATC of?
(I guess this assumes you have more than one engine.) Pilots should notify ATC as soon as possible of reduced climb capability in that circumstance.
How far do you have to be to fly ODP?
If you're getting specific departure instructions as part of your clearance or from a Tower controller before departure, you simply fly those instructions. Like the ODP, those instructions commence after you're 400 feet AGL unless specified otherwise, and assume 200 feet per NM, unless specified otherwise (non-standard diverse vector area or on a published procedure included in your clearance).
What is it called when an aircraft turns in any direction?
If a departing aircraft may turn in any direction from a runway within the limits of the assessment area and remain clear of obstacles, that runway passes what is called a diverse departure assessment and no obstacle departure procedure is established. The fact that an obstacle departure procedure is established means there is something in ...
Is missed approach a balked landing?
One issue that was not addressed here is that if one is flying an IAP on an IFR clearance and continues below the MDA for that procedure and then goes missed approach, it is not really a missed approach. It is a balked landing and your route of flight should not include the missed approach routing if you can't rejoin the altitude and route by the departure end of the runway. A missed approach route and altitude is predicated on executing the missed approach at the missed approach point and altitude and being able to climb at 200'/NM to avoid TERPed obsticles. If you can't get back to the MDA by the DER (departure end of the runway), then you should fly the ODP if one is published. The ODP is designed to keep you clear of obsticles from the runway elevation +35' at the DER. Note that the ODP may have a climb gradient that exceeds 200'/NM and if it does, it will so state on the ODP plate.
What are the two types of departure procedures?
There are two types of Departure Procedures – Obstacle Departure Procedures or ODPs and Standard Instrument Departures – the more common SID. Obstacle Departure Procedures are pre-planned IFR procedures which provide obstruction clearance from the terminal area to the appropriate enroute structure. ODPs are recommended for obstruction clearance ...
When departing a Class G airport, should you assume that your clearance accounts for obstacles?
When departing a Class G (non-towered) airport, you shouldn’t assume that your clearance accounts for obstacles. ODPs are rarely assigned by ATC. A clearance direct to the first fix on the flight plan doesn’t imply that the path is clear. It’s up to you to use the ODP if necessary to keep from hitting anything.
What is a SID in aviation?
SIDs are primarily designed for system enhancement and to reduce pilot/controller workload. ATC clearance must be received prior to flying a SID. Although not required by regulation, (Part 91) pilots should fly the ODP at night, during marginal VFR or IMC conditions, whenever one is available.”.
Where are ODPs in Foreflight?
If using ForeFlight, ODPs from the Terminal Procedures Publication are found in the "Procedures" tab under "Departures."
Where is ODP in airport?
The ODP will be in the procedures area of the software if they are graphical. The textual version will be in the Airport/Facilities guide only, so it too must be checked.
Is ODP safe on a runway?
The minimums apply to the ODP, so the ODP for a runway is predicated upon compliance with the T/O minima for that runway, and is not guaranteed to be safe unless the minima (especially climb gradient) are met.
Do VFR pilots know what ODP is?
Great words of wisdom for IFR rated pilots, but most VFR pilots may not even know what the ODP is and how to get a copy for airports. I show my student pilots an IFR low book at least once during the time we do their required 3 hours of instrument familiarization, but that is the last time they probably will ever see them until they do IFR training later in their flying career.
When does the segment of the procedure that requires the pilot to see and avoid obstacles end?
That segment of the procedure that requires the pilot to see and avoid obstacles ends when the aircraft crosses the specified point at the required altitude
Who is responsible for obstacle clearance?
Beyond this distance, the pilot is responsible for obstacle clearance if not operating on a published route, if below (having not reached) the MEA or MOCA of a published route, or an ATC assigned altitude
How far can an ODP be?
ODPs are normally designed to terminate within these distance limitations, however, some ODPs will contain routes that may exceed 25/46 NM; these routes will ensure obstacle protection until reaching the end of the ODP
What is standard instrument departure?
Standard Instrument Departures are air traffic control (ATC) procedures printed for pilot/controller use in graphic form to provide obstruction clearance and a transition from the terminal area to the appropriate en route structure
When is a climb gradient required?
Compliance with a climb gradient for these purposes is mandatory when the procedure is part of the ATC clearance, unless increased takeoff minimums are provided and weather conditions allow compliance with these minimums
How far above the DER is the climb gradient?
The standard required obstacle clearance (ROC) of 48 feet per NM to clear these obstacles would require a climb gradient greater than 200 feet per NM for a very short distance, only until the aircraft was 200 feet above the DER
How high above the departure end of runway elevation is the turn?
If an initial turn higher than 400 feet above the departure end of runway elevation is specified in the DP, the turn should be commenced at the higher altitude
What is ODP in aviation?
OBSTACLE DEPARTURE PROCEDURE (ODP)- A preplanned instrument flight rule (IFR) departure procedure printed for pilot use in textual or graphic form to provide obstruction clearance via the least onerous route from the terminal area to the appropriate en route structure. ODPs are recommended for obstruction clearance and may be flown without ATC clearance unless an alternate departure procedure (SID or radar vector) has been specifically assigned by ATC. (Source: FAA Pilot/Controller Glossary)
Can I fly in VMC?
According to all this information ATC would expect you to follow this procedure, at least in IMC. If you like to fly it in VMC and it does not disagree with your ATC clearance you are also welcome to do so. If there is any confusion I tend to ask and clarify the situation.
Do I need to fly the ODP if I am an IFR?
I'd recommend reading this link: Obstacle Departure Procedures . Seems to have the answer you're looking for: in short if you are IFR you must fly the ODP unless you meet one of the alternative requirements or ATC advises you otherwise.
