
Where did plasmids come from?
Where did plasmids come from? At their most basic level, plasmids are small circular pieces of DNA that replicate independently from the host’s chromosomal DNA. They are mainly found in bacteria, but also exist naturally in archaea and eukaryotes such as yeast and plants. Do plasmids exist in eukaryotes?
What are plasmids capable of?
Plasmids are today known for their ability to transfer from one species of bacteria to another through a process known as conjugation (contact between cells that is followed by transfer of DNA content). In the process, they are capable of conferring antibiotic resistance properties to other species of bacteria.
Do humans cells contain plasmids?
The nuclei of human cells do not contain any foreign DNA, therefore human cells do not contain plasmid DNA. Nonetheless, the field of gene therapy uses plasmids for the insertion of therapeutic genes in the human body. These plasmids can positively affect diseased or infected cells by triggering therapeutic genes in them.
What do cells have plasmids?
Yes, Plasmids naturally exist in all bacterial cells. Plasmids are a small, circular, double-stranded DNA molecule, which is naturally found in all Bacterial cells. These plasmids are separated from chromosomal DNA and have the capability to replicate independently.

Are plasmids found in the nucleus or cytoplasm?
They are present in the cytoplasm of bacteria and are capable of undergoing self-replication independent of genomic DNA. It also helps in the conjugation process, which helps in the transfer of genetic material from one bacteria to another one.
What are plasmids found in?
bacteriaAt their most basic level, plasmids are small circular pieces of DNA that replicate independently from the host's chromosomal DNA. They are mainly found in bacteria, but also exist naturally in archaea and eukaryotes such as yeast and plants.
Where do plasmids reside?
Most plasmids inhabit bacteria, and indeed around 50% of bacteria found in the wild contain one or more plasmids. Plasmids are also found in higher organisms such as yeast and fungi.
Where can plasmids be found in eukaryotic cells?
Plasmid DNA in eukaryotes occurs inside the nucleus, though it is extrachromosomal in nature. Plasmids are DNA fragments themselves are a separate entity from the chromosomal DNA even if they both occur inside the nucleus.
What cells have plasmids?
Plasmids naturally exist in bacterial cells, and they also occur in some eukaryotes. Often, the genes carried in plasmids provide bacteria with genetic advantages, such as antibiotic resistance. Plasmids have a wide range of lengths, from roughly one thousand DNA base pairs to hundreds of thousands of base pairs.
Where are plasmids found in prokaryotic cells?
In addition to the chromosome, many prokaryotes have plasmids, which are small rings of double-stranded extra-chromosomal ("outside the chromosome") DNA. Plasmids carry a small number of non-essential genes and are copied independently of the chromosome inside the cell.
Are plasmids found in all bacteria?
Yes, Plasmids naturally exist in all bacterial cells. Plasmids are a small, circular, double-stranded DNA molecule, which is naturally found in all Bacterial cells. These plasmids are separated from chromosomal DNA and have the capability to replicate independently.
Are plasmids found in animal cells?
Based on the presence of the nucleus and other membrane-bound cellular organelles, the cell is further classified into prokaryotic, eukaryotic, plant and animal cells....Plant, Animal and Bacterial Cells: Comparisons.Plant CellAnimals CellBacterial CellPresentPresentAbsentPlasmidsAbsentAbsentPresentPlastids32 more rows•Feb 4, 2021
Where do plasmids come from quizlet?
Plasmids are most commonly found in the cytoplasm of bacterium or protozoan, but they can also occurs in certain eukaryotic cells. DNA genes into the plasmid vectors, which results in a recombinant plasmid.
Is plasmid present in mitochondria?
Abstract. Plant mitochondria contain small extrachromosomal DNAs in addition to a large and complex main mitochondrial genome. These molecules can be regarded as extrachromosomal replicons or plasmids, of which there are two forms, circular and linear.
Do eukaryotes have plasmid DNA in cytoplasm?
DNA in a nucleus, plasmids are found in a few simple eukaryotic organisms. DNA is a single molecule, found free in the cytoplasm; additional DNA is found on one or more rings called plasmids.
Is plasmid an organelle?
Unlike eukaryotic cells, prokaryotic cells do not contain membrane-bound organelles. However, they do contain some non-membranous organelles such as ribosomes, flagella, and plasmids (circular DNA structures that are not involved in reproduction). Examples of prokaryotic cells include bacteria and archaeans.
Are plasmids found in all bacteria?
Yes, Plasmids naturally exist in all bacterial cells. Plasmids are a small, circular, double-stranded DNA molecule, which is naturally found in all Bacterial cells. These plasmids are separated from chromosomal DNA and have the capability to replicate independently.
Is plasmid present in animal cell?
Animal cells are eukaryotic cells that contain a membrane-bound nucleus. They are different from plant cells in several fundamental factors....Plant, Animal and Bacterial Cells: Comparisons.Plant CellAnimals CellBacterial CellPresentPresentAbsentPlasmidsAbsentAbsentPresentPlastids32 more rows•Feb 4, 2021
Are plasmids present in humans?
In general, human pathogen-related small circular deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) molecules are bacterial plasmids and a group of viral genomes.
What are plasmids give any two examples?
Col plasmids, which contain genes that code for bacteriocins, proteins that can kill other bacteria. Degradative plasmids, which enable the digestion of unusual substances, e.g. toluene and salicylic acid. Virulence plasmids, which turn the bacterium into a pathogen. e.g. Ti plasmid in Agrobacterium tumefaciens.
What is a plasmid?
A plasmid is a small, circular piece of DNA that is different than the chromosomal DNA, which is all the genetic material found in an organism ’s chromosomes. It replicates independently of chromosomal DNA. Plasmids are mainly found in bacteria, but they can also be found in archaea and multicellular organisms. Plasmids usually carry at least one gene, and many of the genes that plasmids carry are beneficial to their host organisms. Although they have separate genes from their hosts, they are not considered to be independent life.
What is a plasmid in eukaryotes?
In eukaryotes, plasmid refers to non-chromosomal DNA that can be replicated in the nucleus, such as a virus. Conjugative – A category of plasmids that start the process of sexual conjugation in bacteria. Bacteriocin – a protein produced by a plasmid in a bacterium that kills other bacteria of a closely related strain.
How do plasmids transfer genetic material?
Bacteria reproduce by sexual conjugation, which is the transfer of genetic material from one bacterial cell to another, either through direct contact or a bridge between the two cells. Some plasmids contain genes called transfer genes that facilitate the beginning of conjugation. Non-conjugative plasmids cannot start the conjugation process, and they can only be transferred through sexual conjugation with the help of conjugative plasmids.
What color are plasmids in a bacterium?
This simplified figure depicts a bacterium’s chromosomal DNA in red and plasmids in blue.
What are the genes that make bacteriocins?
Col Plasmids. Col plasmids contain genes that make bacteriocins (also known as colicins), which are proteins that kill other bacteria and thus defend the host bacterium. Bacteriocins are found in many types of bacteria including E. coli, which gets them from the plasmid ColE1.
What happens when a virulence plasmid is inside a bacterium?
When a virulence plasmid is inside a bacterium, it turns that bacterium into a pathogen, which is an agent of disease. Bacteria that cause disease can be easily spread and replicated among affected individuals. The bacterium Escherichia coli (E. coli) has several virulence plasmids. E. coli is found naturally in the human gut and in other animals, ...
What is the function of a F plasmid?
Fertility plasmids, also known as F-plasmids, contain transfer genes that allow genes to be transferred from one bacteria to another through conjugation. These make up the broad category of conjugative plasmids. F-plasmids are episomes, which are plasmids that can be inserted into chromosomal DNA. Bacteria that have the F-plasmid are known as F positive (F + ), and bacteria without it are F negative (F – ). When an F + bacterium conjugates with an F – bacterium, two F + bacterium result. There can only be one F-plasmid in each bacterium.
What is a plasmid?
a small, circular, double stranded DNA molecule, which can replicate independently from its chromosomal DNA. If plasmids are used for experiments, they are called vectors. Click again to see term 👆. Tap again to see term 👆. because genes in plasmids often provide the bacteria with genetic advantages, including for example antibiotic resistance. ...
Why are plasmids important?
because genes in plasmids often provide the bacteria with genetic advantages, including for example antibiotic resistance. Scientists use plasmids as tools for cloning, transferring and manipulating genes. Click card to see definition 👆. Tap card to see definition 👆. Why are they important.
Why are plasmids important?
Plasmids have been key to the development of molecular biotechnology. They act as delivery vehicles, or vectors, to introduce foreign DNA into bacteria. Using plasmids for DNA delivery began in the 1970s when DNA from other organisms was first ‘cut and pasted’ into specific sites within the plasmid DNA.
Why is it important to keep a plasmid around?
However, by protecting its bacterial host from stress-related death, a plasmid maximises its chances of being kept around.
What is the DNA of a bacterial cell?
The DNA of most bacteria is contained in a single circular molecule, called the bacterial chromosome. The chromosome, along with several proteins and RNA molecules, forms an irregularly shaped structure called the nucleoid. This sits in the cytoplasm of the bacterial cell. In addition to the chromosome, bacteria often contain plasmids – small ...
What are the features of a plasmid vector?
Key features of a typical plasmid vector are an origin of replication (to ensure the vector is copied within bacteria), a gene for antibiotic resistance (to ensure the vector is not lost by bacteria) and a set of recognition sites for restriction enzymes (to make it straightforward to insert foreign DNA into the vector).
How many copies of a plasmid can be made in one cell?
For this reason, plasmids can copy themselves independently of the bacterial chromosome, so there can be many copies of a plasmid – even hundreds – within one bacterial cell.
What happens if you lose a plasmid from a cell?
These plasmids are effectively holding their host bacterial cell hostage – if they are ever lost from the cell, they won’t be able to provide the antidote and the cell will die. Explore topics.
Which side of the plate does kanamycin resistance occur?
On the left-hand side of the plate, the bacteria lack the kanamycin resistance plasmid and have been unable to grow.
Plasmid Definition
Functions of Plasmids
- Plasmids have many different functions. They may contain genes that enhance the survival of an organism, either by killing other organisms or by defending the host cellby producing toxins. Some plasmids facilitate the process of replication in bacteria. Since plasmids are so small, they usually only contain a few genes with a specific function (as opposed to a large amount of noncoding D…
General Types of Plasmids
- Conjugative and Non-Conjugative
There are many ways to classify plasmids from general to specific. One way is by grouping them as either conjugative or non-conjugative. Bacteria reproduce by sexual conjugation, which is the transfer of genetic material from one bacterial cell to another, either through direct contact or a b… - Incompatibility
Another plasmid classification is by incompatibility group. In a bacterium, different plasmids can only co-occur if they are compatible with each other. An incompatible plasmid will be expelled from the bacterial cell. Plasmids are incompatible if they have the same reproduction strategy in …
Specific Types of Plasmids
- There are five main types of plasmids: fertility F-plasmids, resistance plasmids, virulence plasmids, degradative plasmids, and Col plasmids.
Applications of Plasmids
- Humans have developed many uses for plasmids and have created software to record the DNA sequences of plasmids for use in many different techniques. Plasmids are used in genetic engineering to amplify, or produce many copies of, certain genes. In molecular cloning, a plasmid is a type of vector. A vector is a DNA sequence that can transport foreign genetic material from …
Related Biology Terms
- Bacteria– Single-celled microbes that were one of the first types of lifeforms to evolve on Earth; they can exist independently or inside other organisms.
- Episome – In bacteria, a plasmid that can be inserted into the chromosome. In eukaryotes, plasmid refers to non-chromosomal DNA that can be replicated in the nucleus, such as a virus.
- Conjugative– A category of plasmids that start the process of sexual conjugation in bacteria.
- Bacteria– Single-celled microbes that were one of the first types of lifeforms to evolve on Earth; they can exist independently or inside other organisms.
- Episome – In bacteria, a plasmid that can be inserted into the chromosome. In eukaryotes, plasmid refers to non-chromosomal DNA that can be replicated in the nucleus, such as a virus.
- Conjugative– A category of plasmids that start the process of sexual conjugation in bacteria.
- Bacteriocin– a protein produced by a plasmid in a bacterium that kills other bacteria of a closely related strain.
Quiz
- 1. Which is NOT one of the five main types of plasmids? A. Fertility F-plasmids B. DNA Plasmids C. Col Plasmids D.Virulence Plasmids 2. What is a non-conjugative plasmid? A. A plasmid that cannot be replicated B. A plasmid that cannot trigger the sexual conjugation process C. A plasmid that codes for toxins that kill conjugative plasmids D.A plasmid that prevents the sexual conjugat…
What Are plasmids?
- Plasmids are small circular DNA fragments, double-stranded, self-replicating extra chromosomal structures found in many microorganisms. The term Plasmid was coined by Joshua Lederberg in 1952. Plasmids are important as genetic tools, which are used to introduce, manipulate or delete certain genes from the host cell.
Properties of Plasmids
- They are extra chromosomal DNA fragments present in the cell.
- They are double stranded structures. Exceptions are the linear plasmids in bacteria Streptomyces spp and Borrelia spp.
- They can replicate independently.
- The absence of a plasmid in the cell does not affect cell functioning, but the presence of a pla…
- They are extra chromosomal DNA fragments present in the cell.
- They are double stranded structures. Exceptions are the linear plasmids in bacteria Streptomyces spp and Borrelia spp.
- They can replicate independently.
- The absence of a plasmid in the cell does not affect cell functioning, but the presence of a plasmid in the cell is usually beneficial.
Structure of Plasmids
- 1. Every plasmid has certain essential elements. These are as follows – 1. Origin of replication (OR) –This refers to a specific location in the strand where the replication process begins. In plasmids, this region is A=T rich region as it is easier to separate the strands during replication. 2. Selectable marker site –This region consists of Antibiotic resistance genes which are useful in th…
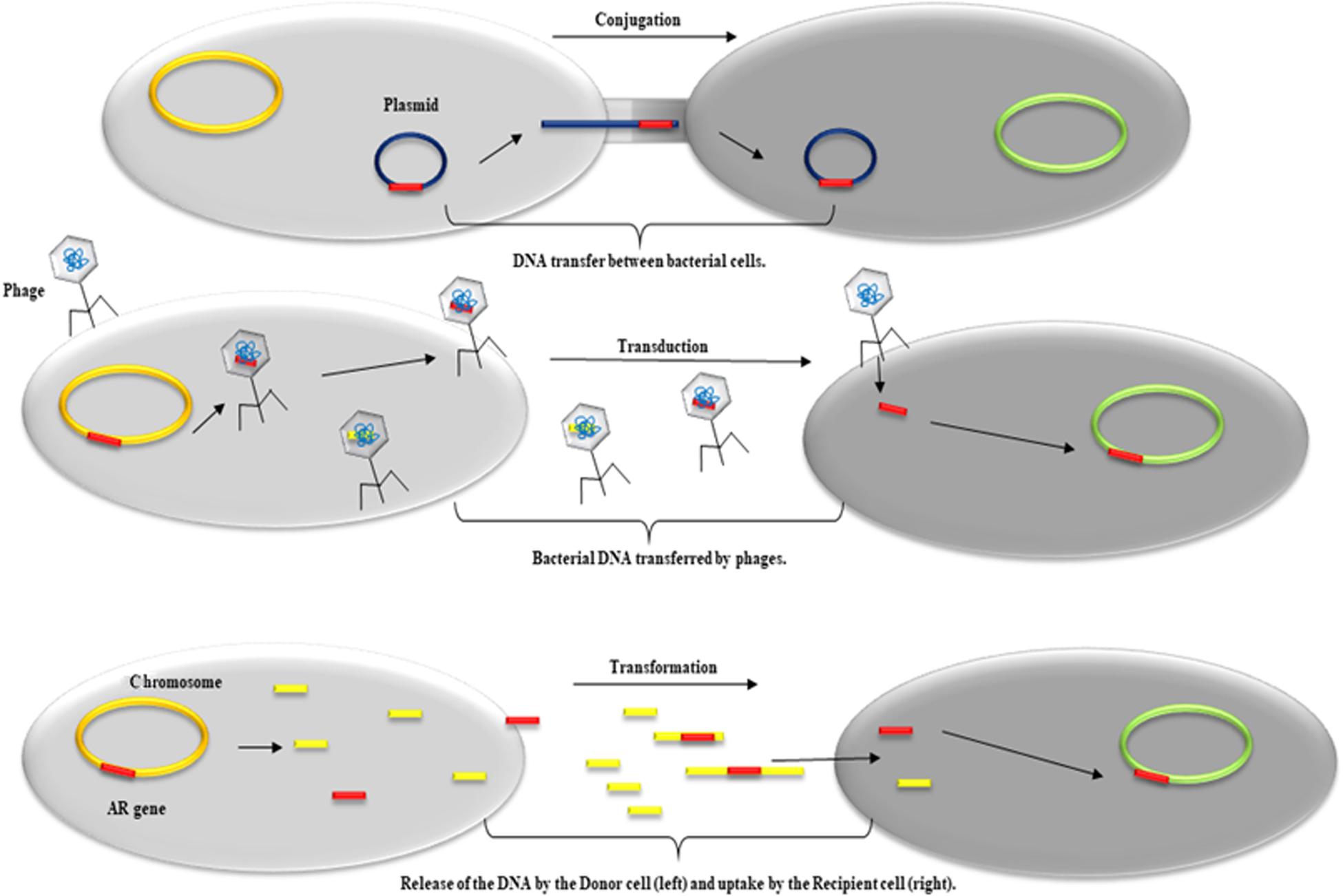
Transfer of Plasmid
- Plasmids are transferred by the process of Conjugation: 1. The process of conjugation involves two cells: a donor cell and a recipient cell. 2. The donor cells form a conjugation bridge now as pilus and attaches to the recipient cell. 3. One copy of the plasmid is transferred from donor to recipient cell. The other methods by which the plasmids can be transferred are transduction and …
Types of Plasmids
- Based on the presence of the TRA gene plasmids can be classified into two types: 1. Conjugative plasmids –these plasmids contain TRA (transfer) gene and are commonly seen in bacteria. 2. Non-conjugative plasmids – these types of plasmids lack the TRA genes. Based on functions the plasmids can be classified into the following types:
Functions and Applications of Plasmids
- The important use of plasmids is that they can be used as vectors to insert a specific gene into other organisms due to their capacity to incorporate a gene and replicate inside the cell.
- They are an important factor in bacteria as they carry antibiotic resistance genes.
- Degradative plasmids can be used to degrade industrial chemicals which are a threat to the environment.
- The important use of plasmids is that they can be used as vectors to insert a specific gene into other organisms due to their capacity to incorporate a gene and replicate inside the cell.
- They are an important factor in bacteria as they carry antibiotic resistance genes.
- Degradative plasmids can be used to degrade industrial chemicals which are a threat to the environment.
- As plasmids are easy to manipulate, they are being used in gene therapy as well.
References
- Rozwandowicz, M., Brouwer, M., Fischer, J., Wagenaar, J. A., Gonzalez-Zorn, B., Guerra, B., Mevius, D. J., & Hordijk, J. (2018). Plasmids carrying antimicrobial resistance genes in Enterobacteriace...
- https://blog.addgene.org/plasmids-101-what-is-a-plasmid
- https://www.news-medical.net/life-sciences/What-are-Plasmids.aspx
- Rozwandowicz, M., Brouwer, M., Fischer, J., Wagenaar, J. A., Gonzalez-Zorn, B., Guerra, B., Mevius, D. J., & Hordijk, J. (2018). Plasmids carrying antimicrobial resistance genes in Enterobacteriace...
- https://blog.addgene.org/plasmids-101-what-is-a-plasmid
- https://www.news-medical.net/life-sciences/What-are-Plasmids.aspx
- https://www.microscopemaster.com/plasmids.html