What are Ruffini endings made of?
Ruffini endings are small, spindle-shaped, slowly adapting receptors found throughout the dermis, subcutaneous tissue, and some connective tissues. The structure of a Ruffini ending is made up of a single, branching sensory fiber in a thin capsule surrounded by collagen fibers.
What is the end of Ruffini nerve?
Nerve ending of Ruffini. E5.17.1.0.2.0.15 The Bulbous corpuscle or Ruffini ending or Ruffini corpuscle is a slowly adapting mechanoreceptor located in the cutaneous tissue between the dermal papillae and the hypodermis. It is named after Angelo Ruffini .
How long does it take for Ruffini endings to regenerate?
Furthermore, in experimental studies on nerve injury to the inferior alveolar nerve, the degeneration of Ruffini endings takes place immediately after nerve injury, with regeneration beginning from 3 to 5 days later, and the distribution and terminal morphology returning to almost normal at around 14 days.
Where are Ruffini endings found?
Which nerve endings are not involved in fine touch?
What is the capsule of a Meissner's corpuscle?
Where are the Pacinian corpuscles located?
Do free nerve endings have Schwann cells?
See 2 more
About this website
Where are Ruffini corpuscles located in the skin?
dermisIn glabrous skin (nasal skin, glans penis, prepuce) Ruffini corpuscles are located in the reticular layer of the dermis.
What Ruffini endings detect?
Ruffini endings detect stretch, deformation within joints, and warmth. Pacinian corpuscles detect transient pressure and high-frequency vibration.
Are Ruffini endings Thermoreceptors?
The Ruffini endings, enlarged dendritic endings with elongated capsules, can act as thermoreceptors. This spindle-shaped receptor is sensitive to skin stretch, contributing to the kinesthetic sense of and control of finger position and movement.
What sensory receptors are found in the skin?
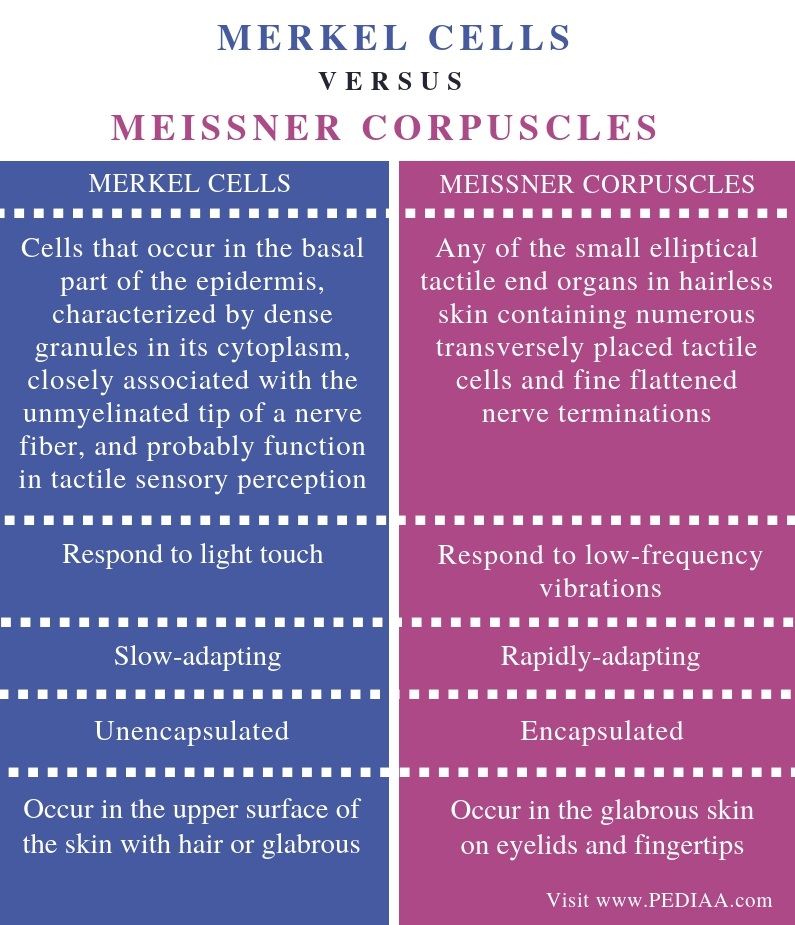
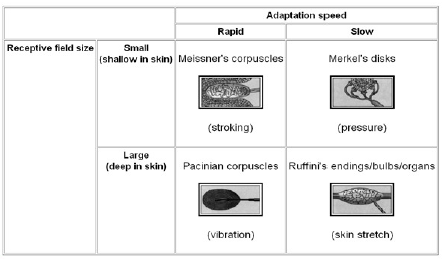
Sensory receptors exist in all layers of the skin. There are six different types of mechanoreceptors detecting innocuous stimuli in the skin: those around hair follicles, Pacinian corpuscles, Meissner corpuscles, Merkel complexes, Ruffini corpuscles, and C-fiber LTM (low threshold mechanoreceptors).
What touch receptors are found in the skin?
Mechanoreceptors: These receptors perceive sensations such as pressure, vibrations, and texture. There are four known types of mechanoreceptors whose only function is to perceive indentions and vibrations of the skin: Merkel's disks, Meissner's corpuscles, Ruffini's corpuscles, and Pacinian corpuscles.
What is the function of Ruffini corpuscles?
Ruffini Endings (or Corpuscles) are found in the superficial dermis of both hairy and glaborous skin where they record low-frequency vibration or pressure. These receptors adapt slowly to pressure that results in stretching of the skin. They record the sustained presence of pressure on the skin.
Where do you find temperature sensitive receptors?
Thermoreceptors are free nerve endings that reside in the skin, liver, and skeletal muscles, and in the hypothalamus, with cold thermoreceptors 3.5 times more common than heat receptors.
Where are warm receptors found?
Warm receptors are found primarily in deep tissues (e.g., muscle and viscera). Skin thermoreceptors are concentrated in orofacial regions around the mouth, tongue, nose, lips, eyes, and ears, as well as in regions on the hands and feet (paws in quadrupeds).
How many types of thermoreceptors are there?
two typesThermoreceptors are of two types, warmth and cold.
What is a Ruffini nerve ending?
Ruffini endings are small, spindle-shaped, slowly adapting receptors found throughout the dermis, subcutaneous tissue, and some connective tissues. The structure of a Ruffini ending is made up of a single, branching sensory fiber in a thin capsule surrounded by collagen fibers.
How do thermoreceptors in the skin detect temperature?
A classical model of the sensory system states that thermoreceptors (e.g., thermoTRPs) in skin nerve endings are sensors that transform temperature into the firing rate codes that are sent to the brain, where the codes are decoded as “cold” by a labeled line theory.
What do you mean by thermoreceptors?
A thermoreceptor is a non-specialised sense receptor, or more accurately the receptive portion of a sensory neuron, that codes absolute and relative changes in temperature, primarily within the innocuous range.
Ruffini ending | definition of Ruffini ending by Medical dictionary
The irritability that some people experience when the scab is present could be attributed to the increased tension developed in the dermal region, resulting in heightened sensory stimulation of the variety of sensory receptors which reside in the region, including Meisner's corpuscles (fine and discriminative touch), Paccinian corpuscles (coarse touch and pressure), Ruffini endings ...
The Ruffini ending as the primary mechanoreceptor in the ... - PubMed
The periodontal ligament receives a rich sensory nerve supply and contains many nociceptors and mechanoreceptors. Although its various kinds of mechanoreceptors have been reported in the past, only recently have studies revealed that the Ruffini endings--categorized as low-threshold, slowly adapting, type II mechanoreceptors--are the primary mechanoreceptors in the periodontal ligament.
Ruffini Endings (Ruffini Corpuscle) Mnemonic for USMLE - Pixorize
Ruffini Endings, also called Ruffini Corpuscles or Bulbous Corpuscles, are one of the four mechanoreceptors or sensory receptors found in the skin. They are primarily located in the reticular dermis of fingertips and joints. The structure of Ruffini endings consists of dendritic fiber endings branching into an capsule. Due to their location, these receptors are primarily responsible for ...
Ruffini ending | anatomy | Britannica
Other articles where Ruffini ending is discussed: senses: Mechanical senses: …next two, Merkel endings and Ruffini endings, to touch pressure; and the last one, Pacinian corpuscles, to vibration. Pacinian corpuscles are built in a way that gives them a fast response and quick recovery. They contain a central nerve fibre surrounded by onionlike layers of connective tissue that behave like…
[Difference in Responses of Free Nerve Endings and Ruffini-type Endings ...
1. There were two types of fast-adapting free nerve endings, discharging on effects and off-effects in response to square wave pressure stimuli and ramp mechanical stimuli and on-effects only. 2. Unencapsulated endings were distributed near the mentale foramen and again there were two types of fast …
Ruffini end-organ - Academic Dictionaries and Encyclopedias
Look at other dictionaries: Ruffini ending (brush corpuscle cylinder end-organ) — Ruf·fi·ni ending (brush, corpuscle, cylinder, end organ) (roo feґne) [Angelo Ruffini, Italian anatomist, 1864–1929] see under ending … Medical dictionary. Ruffini's corpuscle — Ruf·fi·ni s corpuscle ru̇ fē nēz or Ruf·fi·ni corpuscle nē n any of numerous oval sensory end organs occurring in ...
Structure
Ruffini corpuscles are enlarged dendritic endings with elongated capsules.
Function
This spindle-shaped receptor is sensitive to skin stretch, and contributes to the kinesthetic sense of and control of finger position and movement. They are at the highest density around the fingernails where they act in monitoring slippage of objects along the surface of the skin, allowing modulation of grip on an object .
Where are Ruffini endings found?
Ruffini endings are small, spindle-shaped, slowly adapting receptors found throughout the dermis, subcutaneous tissue, and some connective tissues. The structure of a Ruffini ending is made up of a single, branching sensory fiber in a thin capsule surrounded by collagen fibers.
Which nerve endings are not involved in fine touch?
Ruffini endings, Pacinian corpuscles, and Merkel nerve endings are not as involved with fine touch and are also found throughout the body in both skin types. Meissner's corpuscles however respond to light touches and are only found in the glabrous skin in areas of the body that require highly acute sensation such as the eyelids and fingertips. Hair follicle receptors are associated with hair follicles and therefore can only be found in hairy skin. Including the concept that some receptors are only located in glabrous skin vs hairy skin (or both) would also help in terms of knowing their functions.
What is the capsule of a Meissner's corpuscle?
However, unlike the Pacinian corpuscle that has concentric lamellae, the capsule of a Meissner’s corpuscle consists of a thin layer of epithelial cells surrounding a stack of Schwann cells. One or more nerve fibers reaches the base of the corpuscle and then winds its way between the stacks.
Where are the Pacinian corpuscles located?
They exist in the dermis (skin) all over the body and within joints, periosteum, connective tissue, and internal organs.
Do free nerve endings have Schwann cells?
They typically have minimal or no Schwann cells around their fibers. Free nerve endings are unspecialized and can function as nocireceptors (respond to pain), mechanoreceptors (respond to displacement), or thermoreceptors (respond to temperature).