
The 13 Original Colonies List
- Pennsylvania.
- New Jersey.
- Georgia. Connecticut.
- Massachusetts Bay.
- Maryland.
- South Carolina.
- New Hampshire.
- Virginia.
- New York.
- North Carolina.
...
The 13 Colonies.
| 13 Colonies Chart | ||
|---|---|---|
| New England Colonies | Middle Colonies | Southern Colonies |
| Connecticut | Delaware | Maryland |
| Rhode Island | Pennsylvania | Virginia |
What were the 13 original colonies in chronological order?
What were the 13 original colonies in chronological order? 13 Colonies Virginia/Jamestown: 1607 Massachusetts: 1620 New Hampshire: 1623 Maryland: 1632-1634 Connecticut: 1636 Rhode Island: 1636 Delaware: 1638 North Carolina: 1663 South Carolina: 1663 New York: 1664 . Were there only 12 colonies?
Who founded each of the 13 colonies and why?
The 13 colonies were in America but were controlled by Britain. Colonies are typically settled by people from the home country. In order to expand the British Empire against the Spanish rival, Queen Elizabeth of England established colonies in North America. Each colony was founded under different circumstances.
What are facts about the 13 colonies?
What were the 3 sections of the 13 colonies?
- The New England Colonies.
- The Environment of the New England Colonies.
- The natural resources of the New England Colonies.
- The Southern Colonies.
- The Environment of the Southern Colonies.
What are some interesting facts about the 13 colonies?
What are some interesting facts about the 13 colonies? 13 Colonies Fun Facts. The original 13 colonies were settlements created by the British. On large ships they brought over families and supplies to build new homes in an unfamiliar land. Many people left England and headed to America because they hoped to start a new life.

When were the 13 colonies established?
The Thirteen Colonies were complete with the establishment of the Province of Georgia in 1732, although the term "Thirteen Colonies" became current only in the context of the American Revolution.
What are the thirteen colonies?
v. t. e. The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies or the Thirteen American Colonies, were a group of British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America.
What was the population of the 13 colonies in 1760?
In 1760, the cities of Philadelphia, New York, and Boston had a population in excess of 16,000, which was small by European standards. By 1770, the economic output of the Thirteen Colonies made up forty percent of the gross domestic product of the British Empire.
How many colonies were there in the New World?
All thirteen colonies were part of Britain's possessions in the New World, which also included territory in Canada, Florida, and the Caribbean . The colonial population grew from about 2,000 to 2.4 million between 1625 and 1775, displacing Native Americans.
What is the name of the group of colonies that formed the United States?
Thirteen Colonies. The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies or the Thirteen American Colonies, were a group of British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America. Founded in the 17th and 18th centuries, they declared independence in 1776 and together formed the United States of America .
What did the British trade with the colonies?
The colonists traded foodstuffs, wood, tobacco, and various other resources for Asian tea, West Indian coffee, and West Indian sugar, among other items. American Indians far from the Atlantic coast supplied the Atlantic market with beaver fur and deerskins. British North America had an advantage in natural resources and established its own thriving shipbuilding industry, and many North American merchants engaged in the transatlantic trade.
How many slaves were there in the 13 colonies?
It was of economic importance in the export-oriented tobacco plantations of Virginia and Maryland and on the rice and indigo plantations of South Carolina. About 287,000 slaves were imported into the Thirteen Colonies over a period of 160 years, or 2% of the estimated 12 million taken from Africa to the Americas via the Atlantic slave trade. The great majority went to sugar colonies in the Caribbean and to Brazil, where life expectancy was short and the numbers had to be continually replenished. By the mid-18th century, life expectancy was much higher in the American colonies.
What color are the 13 colonies?
The states that were part of the 13 original colonies are colored red on this 13 colonies map. Source: Wikimedia commons.
When did the 13 colonies declare themselves independent?
During the war, each of the 13 colonies formed a Provincial Congress to lead them, now that they no longer accepted the laws of Great Britain. On July 4, 1776, the thirteen colonies declared themselves free and independent states at the Second Continental Congress by signing the Declaration of Independence.
How many colonies were there in the world?
Below are the original thirteen colonies, separated into three groups based on location: New England Colonies, Middle Colonies, and Southern Colonies. For each colony, we include its official name, the year it first became a colony of England, and the year it became a crown colony (which meant it was officially controlled by the British government, unlike regular colonies which sometimes had more ability to self-rule). There’s also additional information on how each colony was founded and the role it played during the Revolutionary War.
What were the Southern colonies based on?
Located in what is now considered the Southern United States, the Southern Colonies had economies based heavily on the cash crops of cotton, rice, and tobacco. They also had significantly higher numbers of slaves than most of the other colonies.
Why did Britain want colonies in North America?
Britain had an extensive history of colonization, and it wanted colonies in North America for multiple reasons, including to increase their trading opportunities, create new jobs, and bring in revenue from colonial workers and goods.
Why did the 13 colonies reject the Stamp Act?
At this meeting, colonial leaders rejected the tax because they had no representatives in British Parliament ( creating the phrase “no taxation without representation).
What were the main trade centers of the British colonies?
The fertile soil of these colonies allowed them to grow crops, particularly grains. Strong timber, iron, and shipbuilding industries helped make these colonies major trade centers. They were also the most diverse, both ethnically and religiously, of all the British colonies.
What are the 13 colonies?
All the 13 colonies were part of British America, which included the Caribbean, Florida, and Canada, hence the name British American Colonies.
What are the four colonies in the Mid Atlantic?
The region, alongside the Chesapeake Colonies, forms the Mid-Atlantic States. The four colonies were Delaware Colony, Province of New Jersey, Province of New York, and the Province of Pennsylvania. These colonies are the basis of the current states of Delaware, New Jersey, New York, and Pennsylvania. Initially, the Dutch occupied much of the region ...
What are the colonies in New England?
The colonies are currently five of the six New England states, including New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, Connecticut, Maine , and Vermont. Plymouth, Massachusetts. Plymouth Colony was established by Puritan English families, today known as the Pilgrims, who landed on the Atlantic coast using the Mayflower Ship.
What were the colonies in the South?
The colonies included the Colony of Virginia, the Province of Maryland, the Province of Georgia, and the Province of Carolina, split into South and North Carolina in 1712. East and West Florida colonies became part of the Southern Colonies in 1763, but the Spanish later took back Florida. The Southern Colonies became the states of Virginia, ...
Which colony was the first to be established?
In 1607, the London Company founded the Colony of Virginia as the first permanent English colony on the continent. In the same year, the Plymouth Company also established the Popham Colony near the Kennebec River, but the settlement lasted few years. The British colonies grew geographically and numerically along the Atlantic coast ...
What was the first European invasion of North America?
The invasion of North America by European powers began with the Spanish in 1565, followed by the British two decades later. The British invasion of the continent, motivated by religious, political, and economic factors, began with the Plymouth Company establishing a Roanoke settlement in modern-day Virginia. This first settlement failed terribly, partly because of the resistance from the Indigenous peoples living there. In the early 17th century, James VI granted charters to London Company and Plymouth Company to establish British colonies in North America.
Why did the first English colony fail?
This first settlement failed terribly, partly because of the resistance from the Indigenous peoples living there. In the early 17th century, James VI granted charters to London Company and Plymouth Company to establish British colonies in North America. In 1607, the London Company founded the Colony of Virginia as the first permanent English colony ...
Who were the 13 colonies?
The 13 original colonies had their beginnings under Queen Elizabeth I and saw its first permanent settlements under King James I of England. They would begin in Jamestown and eventually spread across the entire Atlantic coast, with exception of Florida. Each colony had its own founder and own set of ideas and each tended to be formed ...
Who discovered the 13 colonies?
13 Original Colonies: Beginnings. In 1492 Christopher Columbus accidentally discovered a New World. Although he died thinking he had reached India his discovery laid the foundations for expansion in Europe. Soon the Spanish Conquistadors and the Portuguese Explorers founded global empires for their respective countries.
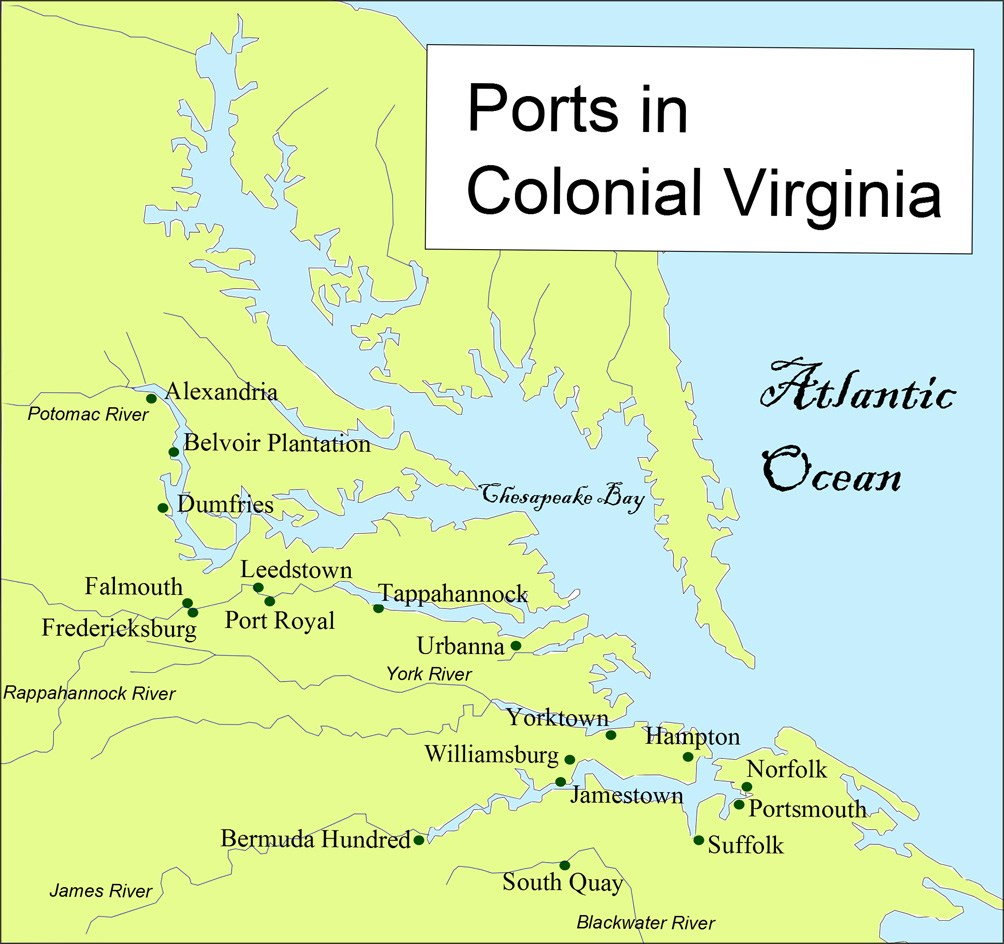
How did the Virginia colony get its name?
Virginia Colony gets its name from the Virgin Queen of England, Elizabeth I . Its first colony was a mysterious failure when all of the people from Sir Walter Raleigh ‘s Roanoke colony disappeared. Later, Jamestown became the first permanent English settlement in the New World.
What was the most ethnically diverse colony in North America?
The Middle Colonies were the most ethnically diverse British colonies in North America, with settlers coming from all parts of Europe. Civil unrest in Europe and other colonies saw an influx of immigrants to the Middle Colonies in the 18th century.
What was the Pennsylvania colony known for?
Pennsylvania Colony was founded by the Quaker William Penn in 1681. It became known for economic growth, fair treatment of the natives and religious freedom. Pennsylvania’s largest city Philadelphia was the largest city in the 13 original colonies by the time of the American Revolution.
What were the Middle Colonies known for?
Middle Colonies. The Middle Colonies had rich soil, allowing the area to become a major exporter of wheat and other grains. The lumber and shipbuilding industries enjoyed success in the Middle Colonies, and Pennsylvania saw moderate success in the textile and iron industry.
When was New Jersey consolidated into one?
New Jersey was consolidated into one Royal Colony in 1702.
How many colonies were there in the US?
Thirteen colonies were originally part of it, and they are also known as the original states of America. The very first Colony was Virginia (originally Jamestown), was founded in 1607 and the last of the 13 colonies to form was Georgia. Virginia, Delaware, Pennsylvania, Georgia, New Jersey, Connecticut, Massachusetts Bay, South Carolina, ...
Which colonies were united in order to be free from foreign rule?
Virginia, Delaware, Pennsylvania, Georgia, New Jersey, Connecticut, Massachusetts Bay, South Carolina, New Hampshire, Maryland, New York, Rhode Island and Providence, and North Carolina are the thirteen colonies which united in order to be free from foreign rule.
What was the first foreign colony in America?
Virginia. was home to one of the first ever foreign settlers of America. Founded in 1607, it was originally named Jamestown, after King James I. It was home to the first representative government in all of America, when the House of Burgesses met for the first time in 1619.
Why did France and England impose the Stamp Act on all written documents in America?
France lost the war, and England imposed the Stamp Act on all written documents in America to be able to pay debts incurred during the war. They put taxes on virtually everything, including paper, tea, glass and paint. These tax issues then led to the American Revolution ten years later.
When was Boston founded?
Massachusetts. was founded in 1630. Settlers from Shawmuth and Trimoutaine changed its name to Boston, which is still named after a city in England. In 1635, the first public school in America was founded and was named Boston Latin School. It is still standing and is now the oldest school in the whole of America.
Who were the first settlers of Connecticut?
The first settlers of Connecticut were originally Dutchmen who lived near modern-day Hartford. Puritans from the Massachusetts Bay were the first English settlers in the colony, and they founded several colonies within it, making Connecticut one of the most important centers of business and government.
When was the first English colony founded?
was founded in 1653 but it was the first places to be inhabited in the New World in 1587. It is home to the first English child born into the New World, but after three years, the first colonists mysteriously disappeared with no known trace up to this day.
1. Connecticut enacted the first constitution in America
In the late 1630s, the settlements of Windsor, Hartford and Wethersfield began unifying under a rudimentary form of government that was composed of magistrates and representatives from each town.
2. Maryland was founded as a haven for Catholics
George Calvert, the first Lord Baltimore, was a government official in England who became interested in colonizing North America.
3. Massachusetts was the birthplace of the American iron industry
In 1644, John Winthrop established the Saugus Works, which had a dam to provide water, a smelting furnace, a forge, and a rolling and slitting mill. The facility produced two types of iron—cast iron that could be poured into molds to make a product, and pig iron, large lumps that could be remelted and used in manufacturing.
4. Pennsylvania was created to pay a debt
After the British monarchy was restored in 1660 and Charles II took the throne, British admiral Sir William Penn, used some of his own personal wealth to rebuild and feed the Royal Navy.
5. New Jersey had the alternate name of New Caesarea
In 1664, King Charles II gave a charter for New Netherland, the land between the Connecticut and Delaware Rivers, to his brother James, the Duke of York.
7. New Hampshire offered parcels of land in exchange for one ear of corn each year
After the end of the French and Indian War in 1762, Governor Benning Wentworth, an appointee of King George III, felt it was time to increase the colony’s population.
8. Georgia was founded as a new home for impoverished people and debtors
In the 1730s, James Oglethorpe, a retired British army officer, decided to make it his mission to help the impoverished and debt-ridden inhabitants of London get a fresh start in life. He thought the best solution was for them to resettle in America.
What were the New England colonies?
The New England Colonies were Massachusetts, Rhode Island, Connecticut, and New Hampshire. Life in this region was more heavily structured and watched closely by the British because many of the points of trade were located in the seaports of New England. Religion was more strict, as the British only viewed Protestantism and later Christianity as legitimate religions. As traders, education was more emphasized in New England than in the other colonial regions, and the makeup of demographics was mostly white settlers. People of color were found in the south most commonly and did not make a large push to escape working on the plantations during Colonial America. Government was highly regulated in cities such as Boston because of the amount of sea trade being conducted, which lead to rapid development of the area.
Why were the colonies run individually?
The colonies were individually run because of small differences between them. While each settlement favored Great Britain initially, changes within the colonies caused new ones to form. For example, in 1636, Roger Williams was exiled from the Massachusetts Bay colony for having different political beliefs. He soon created the colony of Rhode Island as a place for other settlers with similar beliefs. For reasons similar to this, other colonies grew distinct from one another and life in each was similar, but not identical to that of other settlements.
Overview
The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies, the Thirteen American Colonies, or later as the United Colonies, were a group of British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America. Founded in the 17th and 18th centuries, they began fighting the American Revolutionary War in April 1775 and formed the United States of America by declaring full independence in July 1776. Just prior to declaring independence, the Thirteen Colonies in their tr…
British colonies
In 1606, King James I of England granted charters to both the Plymouth Company and the London Company for the purpose of establishing permanent settlements in America. The London Company established the Colony of Virginia in 1607, the first permanently settled English colony on the continent. The Plymouth Company founded the Popham Colony on the Kennebec River, but it was short-lived. The Plymouth Council for New England sponsored several colonization projects, …
17th century
The first successful English colony was Jamestown, established May 14, 1607, near Chesapeake Bay. The business venture was financed and coordinated by the London Virginia Company, a joint-stock company looking for gold. Its first years were extremely difficult, with very high death rates from disease and starvation, wars with local Native Americans, and little gold. The colony survived and flourished by turning to tobacco as a cash crop.
18th century
In 1702, East and West Jersey were combined to form the Province of New Jersey.
The northern and southern sections of the Carolina colony operated more or less independently until 1691 when Philip Ludwell was appointed governor of the entire province. From that time until 1708, the northern and southern settlements remained under one government. However, during this period, the two halves of the province began increasingly to be known as North Carolina an…
American Revolution
In response, the colonies formed bodies of elected representatives known as Provincial Congresses, and Colonists began to boycott imported British merchandise. Later in 1774, 12 colonies sent representatives to the First Continental Congress in Philadelphia. During the Second Continental Congress, the remaining colony of Georgia sent delegates as well.
Massachusetts Governor Thomas Gage feared a confrontation with the colonists; he requested r…
Thirteen British colonies population
The colonial population rose to a quarter of a million during the 17th century, and to nearly 2.5 million on the eve of the American revolution. The estimates do not include the Indian tribes outside the jurisdiction of the colonies. Good health was important for the growth of the colonies: "Fewer deaths among the young meant that a higher proportion of the population reached reproductive age, and that fact alone helps to explain why the colonies grew so rapidly." There w…
Religion
Protestantism was the predominant religious affiliation in the Thirteen Colonies, although there were also Catholics, Jews, and deists, and a large fraction had no religious connection. The Church of England was officially established in most of the South. The Puritan movement became the Congregational church, and it was the established religious affiliation in Massachusetts and Connecticut into the 18th century. In practice, this meant that tax revenues were allocated to ch…
Education
Higher education was available for young men in the north, and most students were aspiring Protestant ministers. Nine institutions of higher education were chartered during the colonial era. These colleges, known collectively as the colonial colleges were New College (Harvard), the College of William & Mary, Yale College (Yale), the College of New Jersey (Princeton), King's College (Columbia), the College of Philadelphia (University of Pennsylvania), the College of Rhode Island (…