
Each nucleotide in RNA contains a ribose sugar, with carbons numbered 1' through 5'. A base is attached to the 1' position, in general, adenine (A), cytosine
Cytosine
Cytosine is one of the four main bases found in DNA and RNA, along with adenine, guanine, and thymine. It is a pyrimidine derivative, with a heterocyclic aromatic ring and two substituents attached. The nucleoside of cytosine is cytidine. In Watson-Crick base pairing, it forms three hydrog…
Adenine
Adenine is a nucleobase. It is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid of DNA that are represented by the letters G–C–A–T. The three others are guanine, cytosine and thymine. Its derivatives have a variety of roles in biochemistry including cellular respiration, in the form of both t…
What base is found exclusively in RNA?
Uracil is the nitrogen base only found on RNA. The RNA is a single-stranded molecule which has a shorter chain of nucleotides. RNA is a polymer with a ribose and phosphate backbone and four different bases. Search for Other Answers. Uracil is absent from DNA.
Which bases pair up for RNA?
RNA contains uracil (U) instead of thymine (T). Keeping this in view, what are the base pairs for RNA? The four bases that make up this code are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C). Bases pair off together in a double helix structure, these pairs being A and T, and C and G. RNA doesn't contain thymine bases, replacing them ...
How many bases can be found in RNA?
RNA is transcribed with only four bases (adenine, cytosine, guanine and uracil), but these bases and attached sugars can be modified in numerous ways as the RNAs mature. Pseudouridine (Ψ), in which the linkage between uracil and ribose is changed from a C–N bond to a C–C bond, and ribothymidine (T) are found in various places (the most ...
What are the four nitrogenous bases found in RNA?
There are four nitrogenous bases found in RNA: adenine, guanine, cytosine, or uracil. Adenine and guanine are known as purine (def) bases while cytosine and uracil are known as pyrimidine bases (def) (see Fig. 3). Furthermore, what nitrogen base is found on RNA but not DNA?
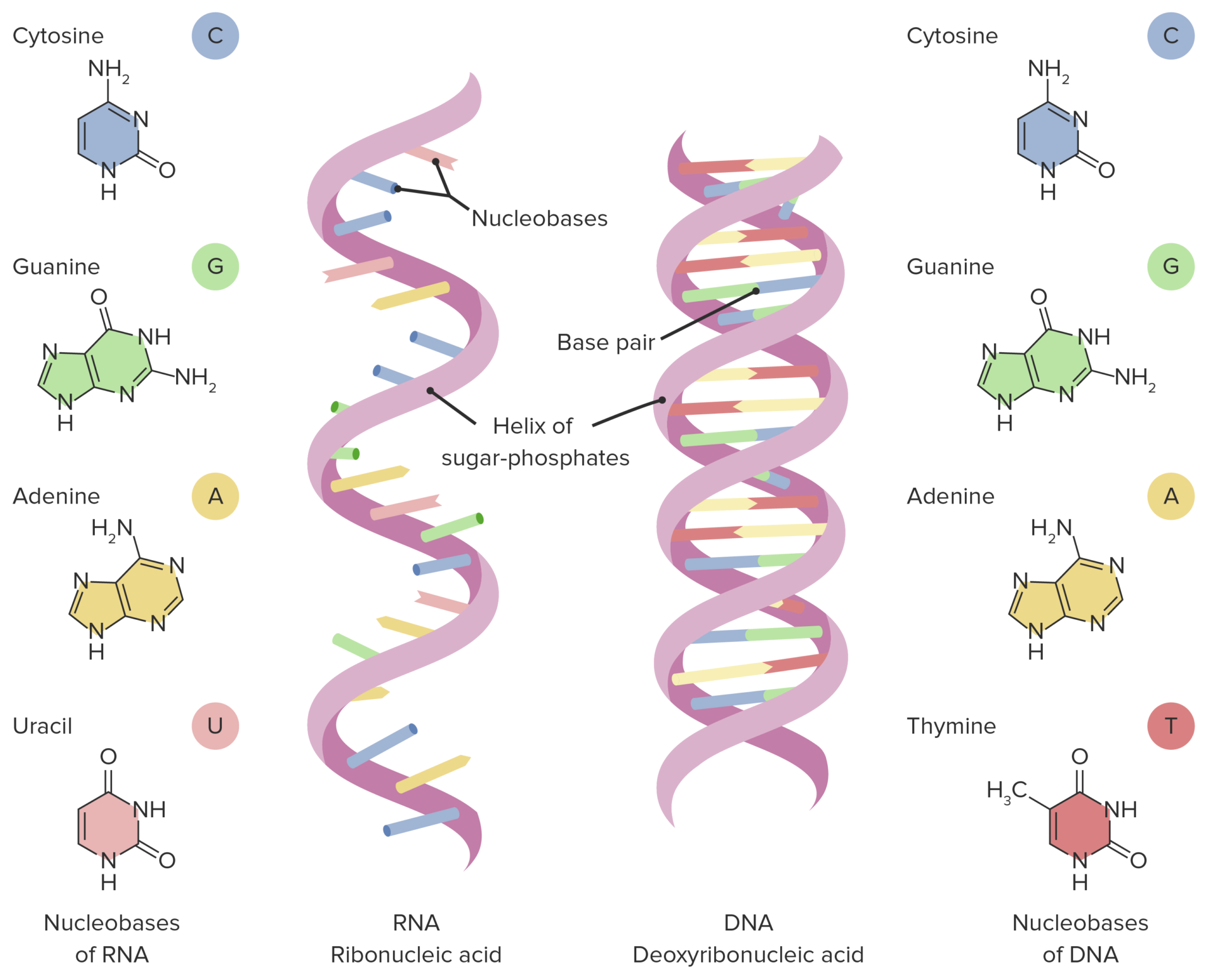
Where are the bases in RNA?
An RNA molecule has a backbone made of alternating phosphate groups and the sugar ribose, rather than the deoxyribose found in DNA. Attached to each sugar is one of four bases: adenine (A), uracil (U), cytosine (C) or guanine (G).
What is the base in RNA?
The bases used in DNA are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T). In RNA, the base uracil (U) takes the place of thymine.
Which bases are present in RNA molecule?
RNA consists of four nitrogenous bases: adenine, cytosine, uracil, and guanine. Uracil is a pyrimidine that is structurally similar to the thymine, another pyrimidine that is found in DNA.
How are the bases in DNA and RNA different?
DNA and RNA base pairing is slightly different since DNA uses the bases adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine; RNA uses adenine, uracil, cytosine, and guanine. Uracil differs from thymine in that it lacks a methyl group on its ring.
What are the base pairs for DNA and RNA?
DNA and RNA bases are also held together by chemical bonds and have specific base pairing rules. In DNA/RNA base pairing, adenine (A) pairs with uracil (U), and cytosine (C) pairs with guanine (G).
Which pyramid base is present in RNA in place of thymine?
UracilPyrimidine base present in RNA in place of thymine of DNA is Uracil.
Is present in the place of thymine in RNA?
In RNA, however, a base called uracil (U) replaces thymine (T) as the complementary nucleotide to adenine (Figure 3).
What are the 4 bases of RNA and how do they pair?
Attached to each sugar is one of four bases: adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) [GWA-NeeN] or thymine (T). The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between pairs of bases: adenine pairs with thymine, and cytosine pairs with guanine.
What does the U base stand for?
uracilRibonucleic acid (RNA) is very much like DNA. It has a phosphodiester linked sugar backbone and uses primarily 4 different nitrogenous bases. The bases are A, G, C and U. U stands for uracil. It is like a different dialect of the same language.
What do 3 RNA bases make?
In translation, three of these bases, known as codons on messenger RNA, code for a specific amino acid. Which amino acid, or residue, that they code for can be found by looking at the codon wheel (shown below). Sequences of these amino acids are what make up proteins.
What is the base of DNA?
The four bases in DNA are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T). These bases form specific pairs (A with T, and G with C). Base pair may also refer to the actual number of base pairs, such as 8 base pairs, in a sequence of nucleotides.
What do three RNA bases make?
The mRNA bases are grouped into sets of three, called codons. Each codon has a complementary set of bases, called an anticodon. Anticodons are a part of transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules.
What are the bases of purines?
purines and pyrimidines are nitrogeneous bases where Adenine and Guanine are Purine and Uracil and Cytosine are Pyrimidines .
What are the bases of DNA and RNA?
Adenine,Guanine and Cytosine are the three bases common in DNA and RNA but fourth base in RNA is Uracil instead of Thymine in DNA…hope it helps u
What are the 4 bases in RNA?
The 4 bases in RNA: Adenine, Guanine (both are purines) and Cytosine and Uracil (both are pyrimidines) In contrast. The 4 basses in DNA: Adenine, Guanine (Purines) and Cytosine and Thymine (pyrimidines) RNA and DNA differ by Uracil in RNA in the place of Thymine in the DNA.
What is the same as DNA?
Adenine, Guanine, Uracil and Cytosine. Its base composition is same as that of DNA except that there is Uracil in RNA while there is Thymine in DNA .
How many bases does RNA have?
RNA has four bases, Adenine and Guanine (both purines), and Uracil and Cytosine (both pyrimidines). Both the purines have two rings in their molecular structure, while the pyrimidines have a single ring only.
Why is uracil more efficient than thymine?
1) the molecule is more stable, and. 2) more energy was needed to form thymine. Since RNA is generally shorter-lived as mentioned above and more mass-produced than DNA, it would be more energetically efficient to use uracil rather than thymine as a base-pair with adenine in RNA.
What pairs with uracil?
Adenine pairs with Uracil and Guanine pairs with Cytosine.
How does RNA make proteins?
RNA makes proteins using amino acids . There are 20 different types of amino acids that make up a protein’s primary structure. Once a ribosome binds to an mRNA transcript, it starts decoding the mRNA codons and recruits tRNAs with the encoded amino acid. Codons are deciphered using the genetic code. In the genetic code, each codon represents a specific amino acid—for example, CUU codes for leucine and GGU codes for glycine. The genetic code is redundant in the fact that different codons can code for the same amino acid. For example, both UAU and UAC code for tryptophan. Once a ribosome finishes reading the mRNA, the amino acid sequence will fold and form a protein.
What is the function of RNA?
The primary function of RNA is to create proteins via translation. RNA carries genetic information that is translated by ribosomes into various proteins necessary for cellular processes. mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA are the three main types of RNA involved in protein synthesis.
What is the RNA polymerase used for?
During transcription, an RNA polymerase uses the 3’-5’ DNA template strand to synthesize a 5’-3’ RNA strand with complementary nucleotides. The newly synthesized RNA strand is nearly identical to the non-coding strand of DNA except for uracil substituting thymine.
How does RNA differ from DNA?
RNA differs from DNA in that it contains a uracil nucleotide instead of thymine and carries a 2’ hydroxyl group rather than a 2’ hydrogen. Due to its interaction with the solvent environment, the 2’ hydroxyl group contributes to RNA conformation. [9]
What is RNA 2021?
Last Update: May 9, 2021. Introduction. Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a molecule that is present in the majority of living organisms and viruses. It is made up of nucleotides, which are ribose sugars attached to nitrogenous bases and phosphate groups. The nitrogenous bases include adenine, guanine, uracil, and cytosine.
Why is RNA sequencing important?
RNA sequencing has the potential to be an efficient clinical diagnostic tool because of its ability to measure gene expression outside the physiological range, allele-specific expression, and defects in alternative splicing. [18] Sequencing RNA involves isolating the RNA, preparation of an RNA library, and utilization of next-generation sequencing technology. The transcriptome can then undergo analysis for any aberrant genes.
What is transcription in biology?
Transcription is the process of RNA formation from DNA, and translation is the process of protein synthesis from RNA. The means of RNA synthesis and the way that it functions differs between eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Specific RNA molecules also regulate gene expression and have the potential to serve as therapeutic agents in human diseases. ...
What is ribosomal RNA?
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is a component of cell organelles called ribosomes. A ribosome consists of ribosomal proteins and rRNA. Ribosomes are typically composed of two subunits: a large subunit and a small subunit. Ribosomal subunits are synthesized in the nucleus by the nucleolus. Ribosomes contain a binding site for mRNA and two binding sites for tRNA located in the large ribosomal subunit. During translation, a small ribosomal subunit attaches to an mRNA molecule. At the same time, an initiator tRNA molecule recognizes and binds to a specific codon sequence on the same mRNA molecule. A large ribosomal subunit then joins the newly formed complex. Both ribosomal subunits travel along the mRNA molecule translating the codons on mRNA into a polypeptide chain as they go. Ribosomal RNA is responsible for creating the peptide bonds between the amino acids in the polypeptide chain. When a termination codon is reached on the mRNA molecule, the translation process ends. The polypeptide chain is released from the tRNA molecule and the ribosome splits back into large and small subunits.
What are the three types of RNA?
Continue Reading. Well, there are three types of RNA: mRNA - which pre-form is sinterized by a replication of a section of the DNA in the nucleous. Posteriorly, it suffers a maturation still within the nucleous and, then, leaves it, moving into the cytoplasm (all of this if the cell is Eucariotic, if it is porcariotic it is formed on ...
What is RNA processing?
Thus, RNA processing refers to any modification made to RNA between its transcription and its final function in the cell. These processing steps include the removal of extra sections of RNA, specific modifications of RNA bases, and modifications of the ends of the RNA. Related Answer. Antonio Carusillo.
Where does mRNA migrate?
mRNA - which pre-form is sinterized by a replication of a section of the DNA in the nucleous. Posteriorly, it suffers a maturation still within the nucleous and, then, leaves it, moving into the cytoplasm (all of this if the cell is Eucariotic, if it is porcariotic it is formed on the cytoplasm where the DNA is and it does not suffer maturation). In the cytoplasm, it will attach itself to a rybossome where the instructions it carries to build a protein will be read.
Where does mRNA go after maturation?
Posteriorly, it suffers a maturation still within the nucleous and, then, leaves it, moving into the cytoplasm (all of this if the cell is Eucariotic, if it is porcariotic it is formed on the cytoplasm where the DNA is and it does not suffer maturation). In the cytoplasm, it will attach itself to a rybossome where the instructions it carries to build a protein will be read.
Where does RNA go in the cell?
Then it leaves the DNA and a portal opens on the nuclear wall, allowing the mRNA to pass. The RNA then goes to the ribosomes where the encoded data is used to create needed proteins, which then carry out tasks. The RNA could be found anywhere in the cell and it is also involved in other RNA-mediated tasks.
What are cells called?
Cells like those in our own bodies are called "eukaryotic" by biologists. Each cell (with very few exceptions) has a nucleus divided off from the rest by a nuclear envelope. They also have various other smaller strutures, e.g. mitochondria, chloroplasts in plant cells, etc. etc.. In "simple" cells, i.e. bacteria (including cyanobacteria, which used to be called blue-green algae) and archaeans, the cel
