
Climate Zones
- A - Tropical Climates. Tropical moist climates extend north and south from the equator to about 15° to 25° latitude. ...
- C - Moist Subtropical Mid-Latitude Climates. This climate generally has warm and humid summers with mild winters. ...
- D - Moist Continental Mid-Latitude Climates. Moist continental mid-latitude climates have warm to cool summers and cold winters. The location of these climates is poleward of the "C" climates.
- E - Polar Climates. Polar climates have year-round cold temperatures with the warmest month less than 50°F (10°C). ...
What are the 5 major climate regions?
What Are The 5 Major Climate Zones What Makes Them Different? Tropics, dry, temperate, cold, and polar regions are the five types of climates in the world. Climate divisions take into account a variety of factors, including altitude, pressure, wind patterns, latitude, and geographical characteristics, such as mountains and oceans.
What are climate zones have a hot to cold range?
While the polar climate is extremely cold and the tropical climate is very hot, the temperate climate has some hot weather and some cold weather. While there is a lot of rain and snow in other zones, the temperate zone has just a moderate amount of rain and snow. The temperate climate zone circles the Earth in both the north and the south.
What climate zone do people most live in?
In Which Climate Zone Do Most People Live? Due to its larger size, the world’s human population is most concentrated in temperate zones, especially in the northern hemisphere. Tropics and polar climates are considered to be temperate climates.
How many climate zones are on Earth?
What Are The 3 Climate Zones On Earth? The Earth is neatly divided into three distinct climate zones, the polar, temperate, and tropical, according to the three cell convection model of each hemisphere.
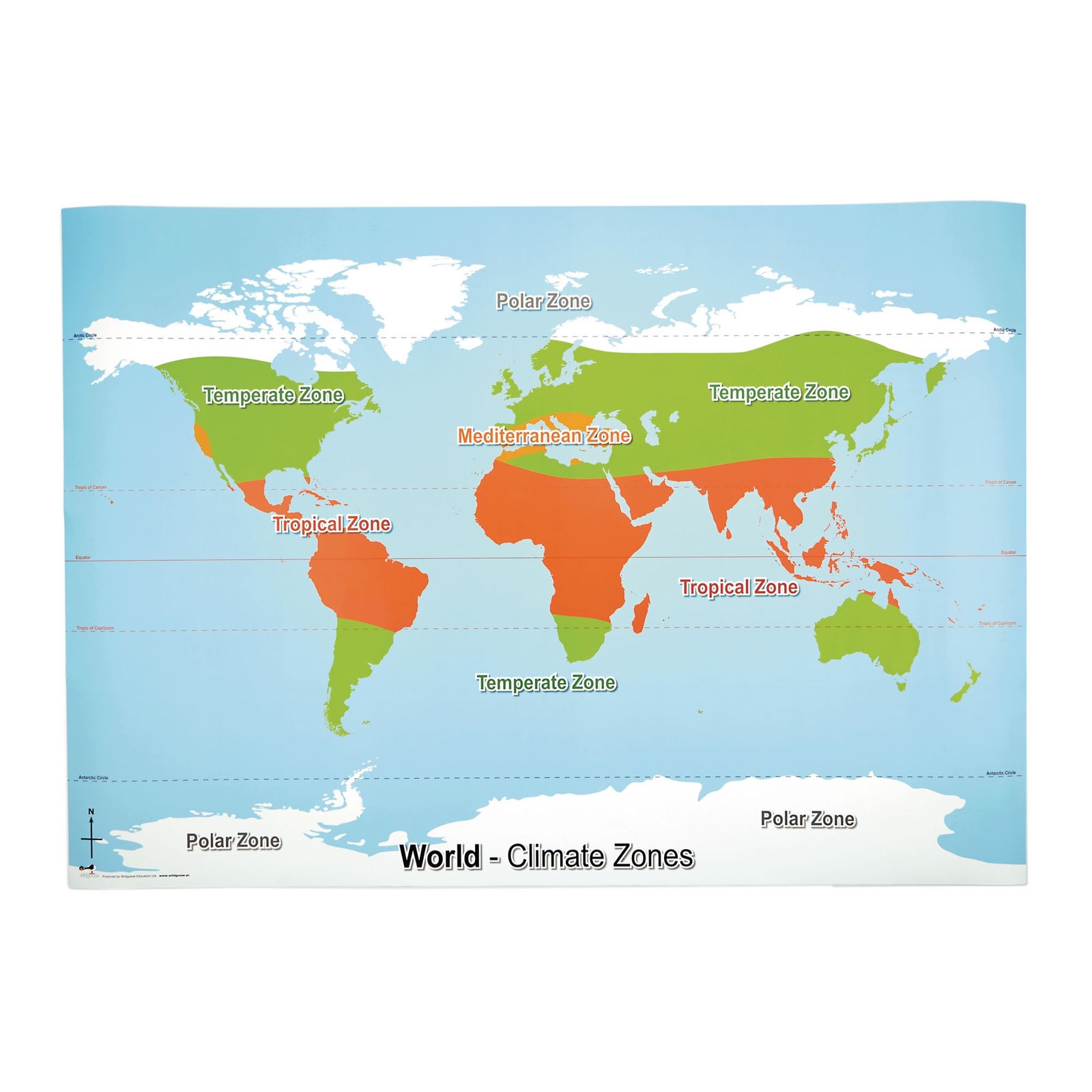
Where are the climate zones located?
World climate zones Tropical climates are close to the equator and have high temperatures and rainfall. Dry climates are immediately north and south of the tropical zone. Temperate climates are north and south of the dry zone, although they often overlap in latitude with continental climates in North America and Asia.
What are the 5 main climatic zones?
There are approximately five main climate types on Earth:Tropical.Dry.Temperate.Continental.Polar.
Why are climate zones located where they are?
The earth's tilt, rotation and land/sea distribution affect the global weather patterns we observe. While the weather varies from day-to-day at any particular location, over the years, the same type of weather will reoccur. The reoccurring "average weather" found in any particular place is called climate.
What are the 6 climate zones?
There are six main climate regions: tropical rainy, dry, temperate marine, temperate continental, polar, and highlands.
How many climate zones are there in the world?
The Earth has three main climate zones: tropical, temperate, and polar.
How many major climate zones are there in the world?
There are five general climate regions: tropical (low latitude), dry, mid-latitude, high latitude, and highland. Dry and highland cli- mates occur at several different latitudes. Within the five regions, there are variations that geographers divide into smaller zones.
Which country has the most climate zones?
As the proportionally longest and narrowest country in the world – stretching over 33 degrees in latitude – or 4,200km – from north to south, Chile has its fair share of different climate zones.
What do climate zones mean?
A climate zone is a world area or region distinguished from a neighbor by a major physical climatic characteristic that is of global scale.
What are the 7 main climate types?
How many climate zones are there and how do they differ?Tropical. Around the Equator we have tropical climates which are hot and humid, this is where you'll find the world's rainforests.Arid. Then there are arid or dry climates – like you'd find in deserts.Mediterranean. ... Temperate. ... Continental. ... Polar.
What are the 10 types of climate?
CLIMATE ZONE CLASSIFICATIONPOLAR AND TUNDRA. Polar climates are cold and dry, with long, dark winters. ... BOREAL FOREST. ... MOUNTAIN. ... TEMPERATE FOREST. ... MEDITERRANEAN. ... DESERT. ... DRY GRASSLAND. ... TROPICAL GRASSLAND.More items...
What are the 4 main climate zones?
There are 4 major climate zones:Tropical zone from 0°–23.5°(between the tropics) ... Subtropics from 23.5°–40° ... Temperate zone from 40°–60° ... Cold zone from 60°–90°
What are the 3 main climate zones?
According to the three cell convection model of each hemisphere the Earth neatly separates itself into three distinct climate zones; the polar, temperate, and the tropical zones.
What is a hot humid climate?
A hot-humid climate is generally defined as a region that receives more than 20 in. (50 cm ) of annual precipitation and where one or both of the following occur: A 67°F (19.5°C) or higher wet bulb temperature for 3,000 or more hours during the warmest 6 consecutive months of the year; or.
How cold is a cold climate?
A very cold climate is generally defined as a region with approximately 9,000 heating degree days (65°F basis) or more and fewer than approximately 12,600 heating degree days (65°F basis).
What is mixed dry climate?
A mixed-dry climate is generally defined as a region that receives less than 20 in. (50 cm) of annual precipitation, has approximately 5,400 heating degree days (65°F basis) or less, and where the average monthly outdoor temperature drops below 45°F (7°C) during the winter months.
When is the cold season?
The cold season is October through March in the Northern Hemisphere and April through September in the Southern Hemisphere.
How many degrees of temperature is subarctic?
A subarctic climate is generally defined as a region with approximately 12,600 heating degree days (65° basis) or more.
What is the extra climate zone?
The extra climate zone, labeled "H" on this map, is a special zone called the highlands. The highlands climate zone is characterized by weather that differs from the surrounding area because of mountains. Credit: NOAA (modified)
What are the different types of climates?
Today, climate scientists split the Earth into approximately five main types of climates. They are: A: Tropical. In this hot and humid zone, the average temperatures are greater than 64°F (18°C) year-round and there is more than 59 inches of precipitation each year. B: Dry.
How do weather satellites play a role?
Weather satellites mostly help with tracking conditions that are happening right now and forecasting weather in the near future. However, they also collect information that helps us monitor a region’s climate over time.
Why are climate zones so dry?
These climate zones are so dry because moisture is rapidly evaporated from the air and there is very little precipitation. C: Temperate. In this zone, there are typically warm and humid summers with thunderstorms and mild winters. D. Continental. These regions have warm to cool summers and very cold winters.
Why is the climate hotter at the equator?
For example, hot regions are normally closest to the equator. The climate is hotter there because the Sun’s light is most directly overhead at the equator.
What is the temperature in the polar zone?
E: Polar. In the polar climate zones, it’s extremely cold. Even in summer, the temperatures here never go higher than 50°F (10°C)!
What is a plant hardiness zone map?
This is called a Plant Hardiness Zone map. It’s a specific type of climate zone map that can help you figure out what kinds of plants will survive in your back yard. Image credit: USDA/Agricultural Research Service/Oregon State University
What are the two parameters that determine climate zones?
The first thing to know about climate zones is that we divide them up based on two parameters: temperature and moisture. The map at the top of this article, from Building Science Corporation, is one that seems to be in a lot of the curricula for home energy rater and other energy auditor classes. The fancy word for this type of division is hygrothermal, and Building Science Corp. has a nice interactive map of hygrothermal regions.
What does the number of zones tell you?
The number of each zone tells you how warm or cold it is. I wrote above that temperature is the parameter, but that’s not a full description, of course. It’s not just how cold or how hot the place gets. It’s based on accumulated temperature calculations called degree days. Basically, degree days combine the amount of time and the temperature difference below some base temperature.
What are the two parameters of hygrothermal regions?
All of North America is divided into climate zones based on the two parameters of temperature and moisture.
What is the 4th moisture division?
Notice the red line going horizontally across the Southeast. It divides the eastern, moist side of the US into moist and moister, basically. This division isn’t based on precipitation, though. It’s based on humidity. A climate zone is called warm-humid if the wet bulb temperature is:
What is a dry climate?
Dry (B). This is based on the amount of precipitation and the annual mean temperature. The calculation is 0.44 x (T F – 19.5), where T F is the annual mean temperature in degrees Fahrenheit. If the annual precipitation is less than the number you get, it’s a dry climate and the zone number has a B after it. El Paso, Texas, for example, is in climate zone 3B.
What is the climate zone of Atlanta?
Moist (A). This is designated by the letter A after the climate zone number. Here in Atlanta, we’re in climate zone 3A. The primary factor is precipitation. If it doesn’t meet the dry climate definition below, it may be moist. The other necessary condition is that it’s got to fall outside the marine climate conditions.
Is Illinois still on the 2009 climate zone?
Most states are still on the 2009 version. Maryland and Illinois have moved up to the tougher 2012 already. The climate zone definitions are the same in both versions. In addition to the basic definitions above, the IECC also tells you county-by-county what the local climate zone is.
How many climate zones are there?
Climate zones are divided into 13 major categories, with Zone 1a being the coldest and Zone 13b being the warmest. Each category is separated by 10°, starting at -60° Fahrenheit annual minimum for Zone 1, and increasing to 65° Fahrenheit annual minimum for Zone 13. Each category is divided into subcategories a and b.
Why do we use climate zones?
The primary reason a seasoned gardener will use climate zones is to see what new plants they can plant in their landscape, orchard, or veggie garden.
What temperature do plants need to go dormant?
So, when a plant is rated for zones 5-9, this means it could die at -25 °, but it needs to get colder than 30 ° over the winter to enter dormancy.
What is the average temperature of a plant in Zone 1A?
So, Zone 1a has an average annual minimum temperature of -60°, while Zone 1b has an average annual minimum temperature of -55°. Plants are categorized according to cold hardiness. However, most plants (perennials/biennials) also need a dormant period, which can only happen when temperatures decline to a certain point.
Do climate zones tell you when to plant?
This is why many seed packet and nursery stock labels use climate zones as a rough guide for planting dates. Climate zones definitely tell you what plants grow in your region. Climate zones generally tell you when plants should be planted in your region. Climate zones do not tell you the first/last frost dates in your region.
Do climate zones give you frost dates?
This is the information that drives planting calendars, and this is what many gardeners think they will get from climate zone maps. Although climate zones don’t technically give you annual high temperatures, frost dates, or other crucial information like average precipitation, climate zones are relatively uniform.
How many climate zones are there in California?
California has a diversity of climates not seen in other states, and the statewide provisions adopted into the California Energy Code accounts for these variations using a set of sixteen climate zones.
Can a ZIP code have more than one climate zone?
Where a ZIP code contains more than one climate region, local jurisdictions may , at their discretion, designate a single climate zone within the ZIP code as applying to the entire ZIP code.
How many climate zones are there?
In this system there are five major climate zones that are divided into 13 sub-zones, which themselves can again be split into finer groups.
What is the average temperature of a continental climate?
The average temperature of the warmest month is greater than 50° F (10° C), while the coldest month is less than 27 ° F (-3° C). The main subdivisions are the same as those for the temperate climate: Winter dry.
How much rain should be in the driest month of winter?
At least three times as much rain in the wettest month of winter as in driest month of summer. The driest month should have less than 30mm precipitation. On our map it is divided in a warm and cool climate. Color on the map for the cool climate. Color on the map for the warm climate.
How much precipitation is in the driest month?
Continuously wet. At least 30 mm precipitation in the driest month. The difference between the wettest and driest month is less than for the above two climates. Color on the map
What are some examples of climate zones on the Big Island?
Example of this climate zone on the Big Island: The lush and tropical Hamakua coast.
Do we have tundra climate?
Surprise! We do have a polar tundra climate on the Big Island on the summits of both Mauna Kea and Mauna Loa.
Does Big Island have a continental climate zone?
We don’t like cold winters that much and are not sorry to say that the Big Island does not host any continental climate zone :D
What is the average temperature in Zone 1?
Zone 1 can expect minimum average temperatures of -60 to -50 degrees F#N#Zone 1a has a minimum average temperature of -60 to -55 degrees F#N#Zone 1b has a minimum average temperature of -55 to -50 degrees F#N#Each of the two subzones can experience harsher temperatures depending on weather conditions.
What is a planting zone?
Planting zones are areas you can find on a growing zone map that show exactly which plants are best suited to thrive in your given area, or zone. When shopping for new plants for your garden landscape, the terms “plant hardiness zones,” “growing zones” and “planting zones” may at first seem a bit confusing.
What is Plant Hardiness?
Plant hardiness is the ability of a plant to survive adverse growing climates such as drought , flooding, heat and cold. The science behind plant hardiness can be complicated. Plant genetics determine the ability of a plant to withstand cold temperatures without damage. Each cultivar of a plant may have different hardiness levels based on their adaptations and genetics. Even different parts of a plant may be hardy in different ways. For example, the cold may cause your beloved perennial to die; however, the roots might be hardy enough to bring new growth in the spring.
What is a hardiness zone?
In essence, plant hardiness zones have been used by growers for years to simply identify the plants that are most likely to survive the winter in their area. Being able to understand a hardiness zone map means you’ll have a starting point for making wise planting decisions.
What is Zone 4?
Planting Zone 4 covers the southern coastal areas of Alaska, northern areas of the United States and high elevations found in the western mountains. These unique climates share minimum average temperatures of between -30 to -20 degrees F. Planting in this zone is less challenging than in colder zones, but the short growing season impacts both vegetables and flower bloom times.
What is the coldest zone for planting?
Planting Zone 1. USDA Plant Hardiness Zone 1 is the coldest zone designation for the United States. With minimum average temperatures between -60 to -50 degrees F, it can be a difficult zone for gardening. The majority of Zone 1 is located in Alaska.
Why is it so hard to grow herbs in Zone 11?
Growing herbs in Zone 11 can be difficult because of the extreme heat of summer. Many will not produce seeds due to the heat, so they must be planted as annuals during the cooler months. Some herbs you can begin planting in early spring include:

The Discovery of Earth’s Climate Zones
- The concept of climate zones dates back to ancient Greece. In the 6th century B.C., a pupil of Pythagoras was the first to suggest the idea.1 A few centuries later, the famous Greek scholar Aristotle hypothesized that the earth’s five circles of latitude (the Arctic Circle, Tropic of Capricorn, Tropic of Cancer, Equator, and Antarctic Circle) divid...
The Main Climate Zones
- Using his botanical hypothesis, Köppen determined that five major climates exist worldwide: tropical, dry, temperate, continental, and polar.
Regional Climate Zones
- Köppen’s five climate groups do a good job of telling us where the world’s hottest, coldest, and in-between climates are, but they don’t capture how local geographical features, such as mountains or lakes, influence seasonal precipitation and temperatures. Realizing this, Köppen split his main categories into subcategories called regional climates. Some of the above climate subzones ca…
Do Earth's Climate Zones Shift?
- As temperature and precipitation patterns across a region change, the region’s climate zone, which is based on those parameters, will also change. Between 1950 and 2010, human-caused climate change shifted nearly six percent of the global land area toward warmer and drier climate types, according to a 2015 study in Scientific Reports.4