What are the countries did Buddhism spread from?
The Story and Spread of Buddhism
- Birth of a Buddha: A Buddhist Legend. Before the Buddha was born, his mother, Maya, dreamed a white elephant, thought to foretell her child’s future greatness, descended from heaven and ...
- Going Forth: The Four Sights. ...
- Enlightenment: The Cessation of All Things. ...
- Buddha’s Teachings: A Crash Course. ...
- Buddha’s Death and the Spread of Buddhism. ...
Where did Buddhism originally start?
Buddhism. Buddhism is one of the world’s major religions. It originated in India in 563–483 B.C.E. with Siddhartha Gautama, and over the next millennia it spread across Asia and the rest of the world. Buddhists believe that human life is a cycle of suffering and rebirth, but that if one achieves a state of enlightenment ( nirvana ), it is ...
What did Buddhism stress everywhere it spread?
Everywhere it spread, Buddhism stressed. meditation and ethical behavior. Greek politics resembled Indian politics in. the tendency of regional fragmentation.
What caused Buddhism to spread?
- Hinduism isn't a proselytizing religion, while Buddhism is more keen on proselytizing.
- Hinduism teaches Brahminism which is not a popular idea to non-Indians
- Hinduism is a superstitious belief, it is not compatible with Chinese cultures.

Where did Buddhism spread first?
northern IndiaDuring its first century of existence, Buddhism spread from its place of origin in Magadha and Kosala throughout much of northern India, including the areas of Mathura and Ujjayani in the west.
Where did Buddhism mainly spread?
Buddhism spread across Asia through networks of overland and maritime routes between India, Southeast Asia, Central Asia, and China. The transmission of Buddhism to Central Asia and China corresponded with the development of the silk routes as channels for intercultural exchanges.
When did Buddhism start spreading?
A famous king, named Ashoka, and his son helped to spread Buddhism throughout South India and into Sri Lanka (Ceylon) (3rd century B.C.E.).
How did Buddhism spread from its place of origin?
Though Buddhist beliefs originated in India, they spread quickly. Buddhism moved through trade networks, traveling on Silk Road caravans through Central Asia to China and aboard merchant ships to Southeast Asia. Buddhism also got some help from powerful leaders.
Where did Buddhism come from and spread in Asia?
Buddhism is thought to have entered Southeast Asia from trade with India, China and Sri Lanka during the 1st, 2nd and 3rd centuries. One of the earliest accounts of Buddhism in Southeast Asia was of a Theravada Buddhist mission sent by the Indian emperor Ashoka to modern-day Burma in 250 BCE.
How did Buddhism spread to the West?
Buddhism first came to North America through Chinese immigrants who settled in the western parts of the United States beginning in the 1840s, as well as by North Americans and Europeans who visited Asia and brought back with them Buddhist texts.
Where did Buddhism spread from into Afghanistan?
The Mauryans brought Buddhism from India and controlled the area south of the Hindu Kush until about 185 BC when they were overthrown.
How did Buddhism spread to Japan?
Buddhism was officially transmitted to Japan in 525, when the monarch of the Korean kingdom of Baekje sent a mission to Japan with gifts, including an image of the Buddha, several ritual objects, and sacred texts. Buddhism's journey from India to China, Korea, and Japan had taken about a thousand years.
How did Buddhism spread in Sri Lanka?
According to Sinhalese tradition, Buddhism was first brought to Sri Lanka by a mission sent out from eastern India during the reign of the Mauryan emperor Ashoka (c. 273–232 bce). The leader of the mission to Sri Lanka, Mahendra (Mahinda), is described as Ashoka's son.
When did Buddhism spread to Southeast Asia?
Malaysia and Indonesia With the help of the monk Gunavarman and other Indian missionaries, Buddhism gained a firm foothold on Java well before the 5th century ce. Buddhism was also introduced at about this time in Sumatra, and by the 7th century the king of Srivijaya on the island of Sumatra was a Buddhist.
What factors led to the spread of Buddhism?
Top 11 Causes for the Rise of Buddhism in IndiaInfluence of Time: 6th Century B.C. was an ideal time for the spread of Buddhism. ... Simple Doctrines: As compared with Jainism, Buddhism was essentially simple. ... Simple Language: ... Personality of Buddha: ... Inexpensive: ... No Caste Harried: ... Royal Patronage: ... Role of the Universities:More items...
How did Buddhism spread in China?
It is widely believed that Buddhism entered China via the Silk Road under the Han Dynasty. After trade and travel was established with the Yuezhi, who by that time were forced southward toward India, Yuezhi monks began to travel with the merchant caravans; preaching their religion along the Silk Road.
When did Buddhism start?
The history of Buddhism spans from the 6th century BCE to the present. Buddhism arose in the eastern part of Ancient India, in and around the ancient Kingdom of Magadha (now in Bihar, India ), and is based on the teachings of Siddhārtha Gautama.
What is the history of Buddhism?
The history of Buddhism is also characterized by the development of numerous movements, schisms, and schools, among them the Theravāda, Mahāyāna and Vajrayāna traditions, with contrasting periods of expansion and retreat.
What was the dominant religion in Burma?
During the Mon Hanthawaddy Kingdom (1287–1552), Theravada Buddhism was the dominant religion in Burma, with strong ties to Sri Lankan Buddhism. One of their kings, Dhammazedi, is particularly known for his reformation of Burmese Buddhism from the Sri Lankan Mahavihara tradition between 1476 and 1479.
What are the three arrows in Buddhism?
Mahāyāna (red arrow), Theravāda (green arrow), and Tantric - Vajrayāna (blue arrow). The overland and maritime "Silk Roads" were interlinked and complementary, forming what scholars have called the "great circle of Buddhism". Part of a series on.
Where were the stupas built?
During his reign, stupas and monasteries were built in the Gandhāran city of Peshawar (Skt. Purusapura ), which he used as a capital. Kushan royal support and the opening of trade routes allowed Gandharan Buddhism to spread along the Silk Road to Central Asia, the Tarim Basin and thus to China.
How did India influence Southeast Asia?
Since around 500 BCE, the culture of India has exerted influence on Southeast Asian countries. Land and maritime trade routes linked India with the region and both Hindu and Buddhist beliefs became influential there during the period of the Indianization of Southeast Asia. For more than a thousand years, Indian influence was, therefore, the major factor that brought a certain level of cultural unity to the various countries of the region. The Pāli and Sanskrit languages and Indian scripts, together with Theravāda and Mahāyāna Buddhism, Brahmanism, and Hinduism, were transmitted from direct contact and through sacred texts and Indian literature such as the Rāmāyaṇa and the Mahābhārata.
Where did Buddhism decline after the Hephthalite Empire?
However it continued to thrive in adjacent areas like the Swat Valley of Pakistan, Gilgit, Kashmir and in Afghanistan (in sites such as Bamiyan ).
When did Buddhism start?
When Gautama passed away around 483 B.C., his followers began to organize a religious movement. Buddha’s teachings became the foundation for what would develop into Buddhism. In the 3rd century B.C., Ashoka the Great, the Mauryan Indian emperor, made Buddhism the state religion of India.
Who is the founder of Buddhism?
Founder of Buddhism. Siddhartha Gautama, the founder of Buddhism who later became known as “the Buddha,” lived during the 5th century B.C. Gautama was born into a wealthy family as a prince in present-day Nepal. Although he had an easy life, Gautama was moved by suffering in the world.
How many followers does Buddhism have?
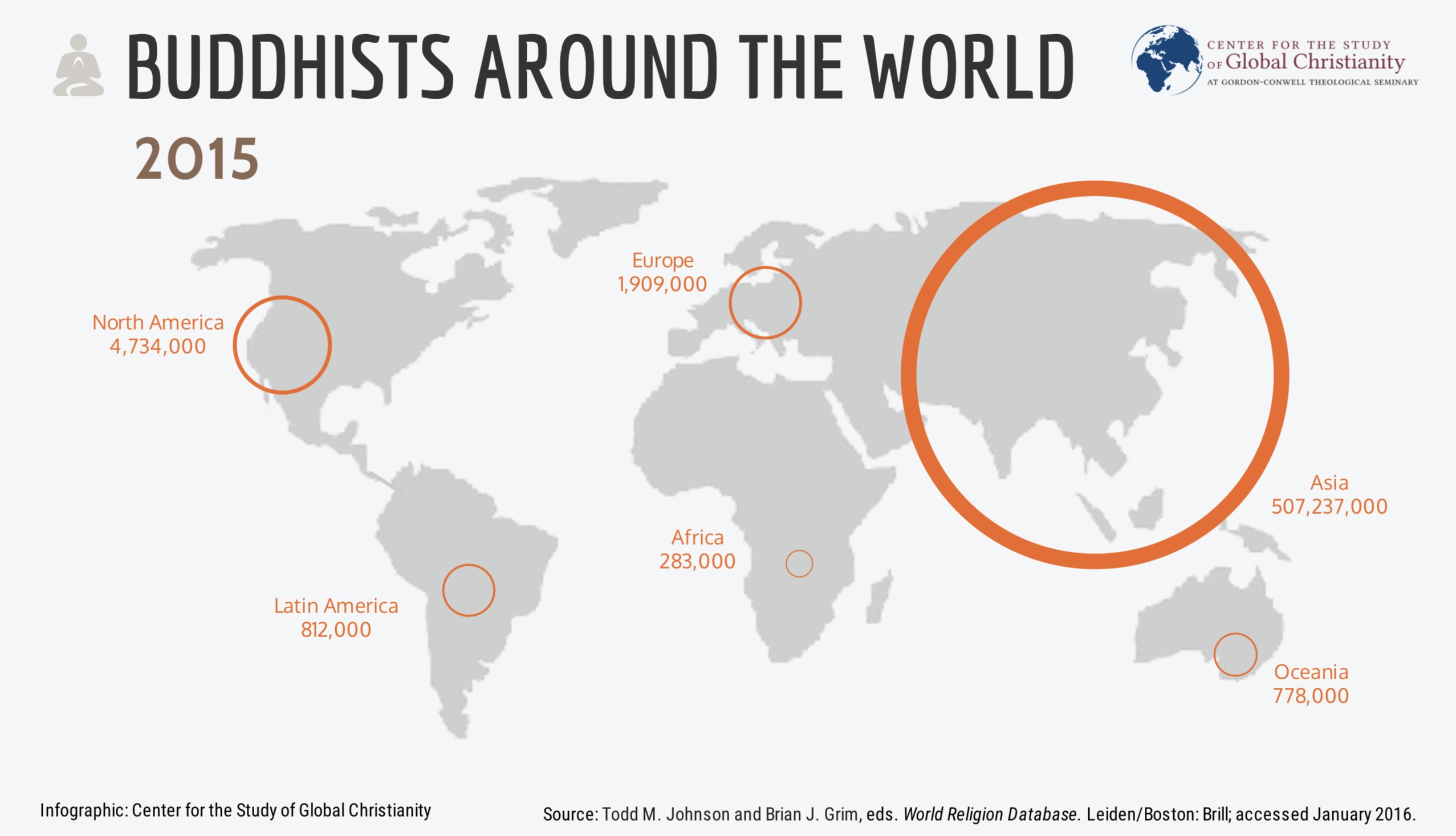
Contents. Buddhism is a faith that was founded by Siddhartha Gautama (“the Buddha”) more than 2,500 years ago in India. With about 470 million followers, scholars consider Buddhism one of the major world religions.
Why do Buddhists meditate?
Buddhists often meditate because they believe it helps awaken truth. There are many philosophies and interpretations within Buddhism, making it a tolerant and evolving religion. Some scholars don’t recognize Buddhism as an organized religion, but rather, a “way of life” or a “spiritual tradition.”.
What is the Buddhist holiday?
Buddhist Holidays. Every year, Buddhists celebrate Vesak, a festival that commemorates Buddha’s birth, enlightenment and death. During each quarter of the moon, followers of Buddhism participate in a ceremony called Uposatha. This observance allows Buddhists to renew their commitment to their teachings.
What is the most important teaching of Buddhism?
Buddha’s most important teachings, known as The Four Noble Truths, are essential to understanding the religion . Buddhists embrace the concepts of karma (the law of cause and effect) and reincarnation (the continuous cycle of rebirth).
What does Buddha mean in the Bible?
The religion’s founder, Buddha, is considered an extraordinary man, but not a god. The word Buddha means “enlightened.”.
Where did Buddhism originate?
Buddhism is one of the world’s major religions. It originated in India in 563–483 B.C.E. with Siddhartha Gautama, and over the next millennia it spread across Asia and the rest of the world. Buddhists believe that human life is a cycle of suffering and rebirth, but that if one achieves a state of enlightenment ( nirvana ), ...
Where is Mahayana Buddhism found?
Mahayana Buddhism is common in Tibet, China, Taiwan, Japan, Korea, and Mongolia. It emphasizes the role models of bodhisattvas (beings that have achieved enlightenment but return to teach humans). Theravada Buddhism is common in Sri Lanka, Cambodia, Thailand, Laos, and Burma (Myanmar).
What is the meaning of karma in Buddhism?
This is connected to “ karma ,” which refers to how a person’s good or bad actions in the past or in their past lives can impact them in the future. There are two main groups of Buddhism: Mahayana Buddhism and Theravada Buddhism. Mahayana Buddhism is common in Tibet, China, Taiwan, Japan, Korea, and Mongolia.
What is the Buddha's teaching?
The Mahabodhi Temple in Bihar, India—the site of his enlightenment—is now a major Buddhist pilgrimage site. The Buddha taught about Four Noble Truths. The first truth is called “Suffering ( dukkha ),” which teaches that everyone in life is suffering in some way. The second truth is “Origin of suffering ( samudāya ).”.
Where is the Dalai Lama lit?
Incense are lit inside of Kun Yam Temple in Macao. Incense and meditation play an important role in Buddhism.
Who was the leader of the Tibetan school of Buddhism?
The head of the Tibetan school of Buddhism and traditional leader of Tibet, the Dalai Lama, fled from China-controlled Tibet in 1959 to India in fear of his life. Many Tibetan Buddhists actively resist Chinese control of the region.
What is the role of incense in Buddhism?
spiritual principle mostly associated with Hinduism and Buddhism, in which the intentions and actions of an individual influence the future of that individual. to engage in deep thought, contemplation, or introspection.
Where did Buddhism spread?
A wave of conversion began, and Buddhism spread not only through India, but also internationally. Ceylon, Burma, Nepal, Tibet, central Asia, China, and Japan are just some of the regions where the Middle Path was widely accepted.
How long did Buddha travel?
Even Brahmins and members of the nobility were converted. The Buddha died in 483 B.C.E., after 45 years of traveling and teaching.
How did Siddharta achieve his goal?
Siddharta sought enlightenment through concentration. He sat under a pipal tree, practiced intense meditation, and fought off all worldly temptations. After 40 days, he reached the ultimate goal — nirvana. He came to understand his previous lives and finally gained release from the cycle of suffering.
What did Siddharta call Buddha?
Upon his enlightenment, his followers began to call him Buddha, which means, "Enlightened One". Siddharta discovered that he needed to find another way — something in between his rich and impoverished lifestyles. He resolved to follow the Middle Path. Siddharta sought enlightenment through concentration.
What was the Buddha's last breath?
Upon his death, the Buddha passed into a state of nirvana, the ultimate release from suffering in which the self no longer exists and salvation is achieved. Included in his last breaths were four words of inspiration: "Strive on with awareness.". And his followers did.
What were the monks and nuns called?
Small communities of monks and nuns, known as bhikkus, sprung up along the roads that Buddha traveled. Devoted to his teachings, they dressed in yellow robes and wandered the countryside to meditate quietly. For almost 200 years, these humble disciples were overshadowed by the dominant Hindu believers.
Where was Siddharta Gautama?
These methods of self-denial eventually led him to a revelation. Siddharta Gautama was a prince in a kingdom near the present day border of India and Nepal.

Overview
The history of Buddhism spans from the 6th century BCE to the present. Buddhism arose in Ancient India, in and around the ancient Kingdom of Magadha, and is based on the teachings of the ascetic Siddhārtha Gautama. The religion evolved as it spread from the northeastern region of the Indian subcontinent throughout Central, East, and Southeast Asia. At one time or another, it influenced most of Asia.
Life of the Buddha
Siddhārtha Gautama was the historical founder of Buddhism. The early sources state he was born in the small Shakya (Pali: Sakka) Republic, which was part of the Kosala realm of ancient India, now in modern-day Nepal. He is thus also known as the Shakyamuni (literally: "The sage of the Shakya clan"). The republic was ruled by a council of household heads, and Gautama was born to one of t…
Mauryan empire (322–180 BCE)
• The Maurya Empire under Emperor Aśoka was the world's first major Buddhist state. It established free hospitals and free education and promoted human rights.
• The words "Bu-dhe" (𑀩𑀼𑀥𑁂, the Buddha) and "Sa-kya-mu-nī" ( 𑀲𑀓𑁆𑀬𑀫𑀼𑀦𑀻, "Sage of the Shakyas") in Brahmi script, on Ashoka's Lumbini pillar inscription (circa 250 BCE).
Mahāyāna Buddhism
The Buddhist movement that became known as Mahayana (Great Vehicle) and also the Bodhisattvayana, began sometime between 150 BCE and 100 CE, drawing on both Mahasamghika and Sarvastivada trends. The earliest inscription which is recognizably Mahayana dates from 180 CE and is found in Mathura.
The Mahayana emphasized the Bodhisattva path to full Buddhahood (in contras…
Shunga dynasty (2nd–1st century BCE)
The Shunga dynasty (185–73 BCE) was established about 50 years after Ashoka's death. After assassinating King Brhadrata (last of the Mauryan rulers), military commander-in-chief Pushyamitra Shunga took the throne. Buddhist religious scriptures such as the Aśokāvadāna allege that Pushyamitra (an orthodox Brahmin) was hostile towards Buddhists and persecuted the Buddhis…
Greco-Buddhism
The Greco-Bactrian king Demetrius I (reigned c. 200–180 BCE) invaded the Indian Subcontinent, establishing an Indo-Greek kingdom that was to last in parts of Northwest South Asia until the end of the 1st century CE.
Buddhism flourished under the Indo-Greek and Greco-Bactrian kings. One of the most famous Indo-Greek kings is Menander (reigned c. 160–135 BCE). He may …
Kushan empire and Gandharan Buddhism
The Kushan empire (30–375 CE) was formed by the invading Yuezhi nomads in the 1st century BCE. It eventually encompassed much of northern India, Pakistan and Afghanistan. The Kushans adopted elements of the Hellenistic culture of Bactria and the Indo-Greeks. During Kushan rule, Gandharan Buddhism was at the height of its influence and a significant number of Buddhist center…
Spread to Central Asia
Central Asia was home to the international trade route known as the Silk Road, which carried goods between China, India, the Middle East and the Mediterranean world. Buddhism was present in this region from about the second-century BCE. Initially, the Dharmaguptaka school was the most successful in their efforts to spread Buddhism in Central Asia. The Kingdom of Khotan was one of the earlie…