See more

What was Yugoslavia called before?
The Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes was created in 1918 and in 1929 it was renamed the Kingdom of Yugoslavia. The Serbian royal House of Karađorđević became Yugoslavia's royal dynasty.
What does the word Yugoslavia mean?
Borrowed from Serbo-Croatian Jugoslavija, in turn from jug (“south”) and slavija (“Slavia, the land of the Slavs”). Literally, the land of the South Slavs.
Who named Yugoslavia?
After a decade of acrimonious party struggle, King Alexander I in 1929 prorogued the assembly, declared a royal dictatorship, and changed the name of the state to Yugoslavia. The historical regions were replaced by nine prefectures (banovine), all drafted deliberately to cut across the lines of traditional regions.
When did it stop being called Yugoslavia?
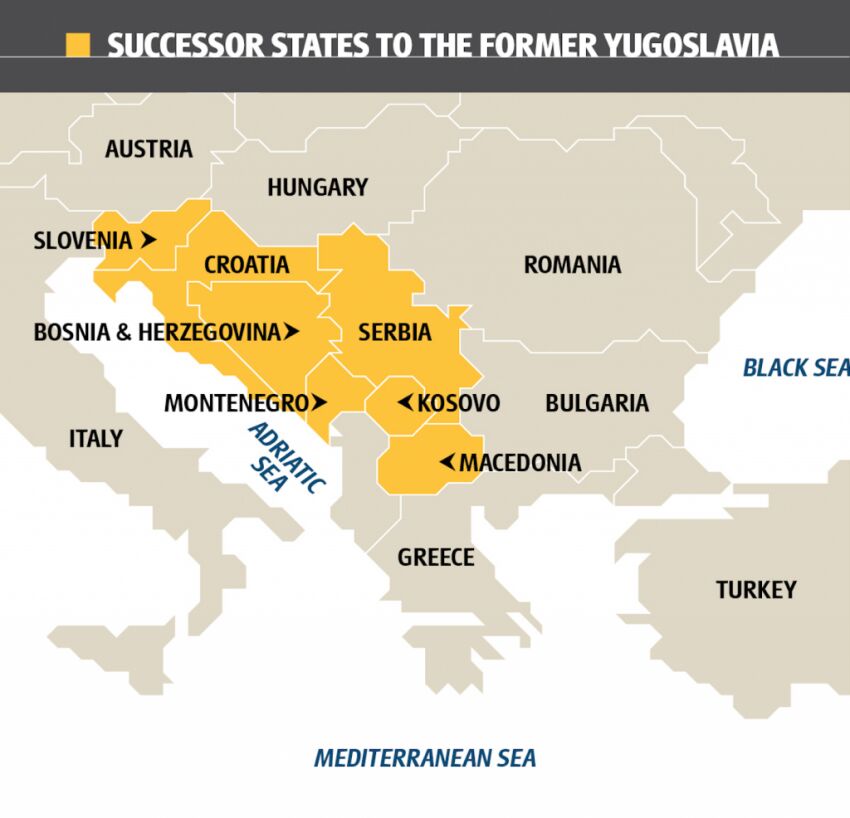
Specifically, the six republics that made up the federation - Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia (including the regions of Kosovo and Vojvodina) and Slovenia. On 25 June 1991, the declarations of independence of Slovenia and Croatia effectively ended SFRY's existence.
What was Croatia called before?
the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and SlovenesHistorical Backgound It was known as the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes. In 1929, the name of this new nation was changed to Yugoslavia. After World War II, the former prewar kingdom was replaced by a federation of six equal republics.
Why is Yugoslavia no longer a country?
The varied reasons for the country's breakup ranged from the cultural and religious divisions between the ethnic groups making up the nation, to the memories of WWII atrocities committed by all sides, to centrifugal nationalist forces.
What country did Yugoslavia used to be?
In 1963, the country was renamed again, as the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SFRY). The six constituent republics that made up the SFRY were the SR Bosnia and Herzegovina, SR Croatia, SR Macedonia, SR Montenegro, SR Serbia, and SR Slovenia....Yugoslavia.Yugoslavia Jugoslavija ЈугославијаDemonym(s)Yugoslav28 more rows
When did Croatia split from Yugoslavia?
June 25, 1991 – April 28, 1992Breakup of Yugoslavia / Period
Why was Albania not part of Yugoslavia?
Answer and Explanation: Although it is part of the Balkan Peninsula, Albania was never part of Yugoslavia. This is likely because Albania is, in fact, not a Slavic country.
Why is Croatia split in two?
When Yugoslavia broke up in 1991, the newly independent Croatia was now split in two. Twelve miles of Bosnia-Herzegovinian coastline separate the Dubrovnik region from the rest of Croatia to the north. The Neum corridor gives Bosnia and Herzegovina a shorter coastline than any other nation on earth aside from Monaco.
Is Yugoslavia part of NATO?
The North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO) carried out an aerial bombing campaign against the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia during the Kosovo War....NATO bombing of Yugoslavia.Date24 March – 10 June 1999 (78 days)Territorial changesUN Resolution 1244; de facto separation of Kosovo from Yugoslavia under UN temporary administration2 more rows
What language is spoken in Yugoslavia?
Official languages Serbo-Croatian, pluricentric language and dialect continuum of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Montenegro and Serbia, split into four national standard varieties used in respective countries after the breakup of Yugoslavia: Bosnian, Croatian, Montenegrin and Serbian.
What does Yugo mean in English?
yugo m (plural yugos) yoke (bar or frame of wood by which two animals are joined)
What does Yugo mean in Yugoslavia?
And so, rather than be absorbed by a non-Slavic power, the South Slavs decided that there was safety in numbers, and banded together to form the Kingdom of the Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes (1918), later known as the Kingdom of Yugoslavia (Land of the South Slavs — yugo means "south").
Is Yugoslavia a Slavic country?
The country of Yugoslavia, first known as the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes, was founded in 1918 as a South Slavic state. Its very name means Land of the South Slavs.
What language is spoken in former Yugoslavia?
Serbo-CroatianOfficial languages Serbo-Croatian, pluricentric language and dialect continuum of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Montenegro and Serbia, split into four national standard varieties used in respective countries after the breakup of Yugoslavia: Bosnian, Croatian, Montenegrin and Serbian.
What was the first Yugoslavia?
The first Yugoslavia. After the Balkan Wars of 1912–13 ended Ottoman rule in the Balkan Peninsula and Austria-Hungary was defeated in World War I, the Paris Peace Conference underwrote a new pattern of state boundaries in the Balkans.
What was the name of the country that was changed to Yugoslavia?
After a decade of acrimonious party struggle, King Alexander I in 1929 prorogued the assembly, declared a royal dictatorship, and changed the name of the state to Yugoslavia. The historical regions were replaced by nine prefectures ( banovine ), all drafted deliberately to cut across the lines of traditional regions.
How big was Yugoslavia in square miles?
The postwar Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (Socijalistička Federativna Republika Jugoslavija) covered 98,766 square miles (255,804 square km) and had a population of about 24 million by 1991.
What was the Balkans' new state?
The major beneficiary there was a newly created Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes, which comprisedthe former kingdoms of Serbia and Montenegro (including Serbian-held Macedonia), as well as Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Austrian territory in Dalmatiaand Slovenia, and Hungarian land north of the Danube River. Great difficulty was experienced in crafting this multinational state. Croats favoured a federal structure that would respect the diversityof traditions, while Serbs favoured a unitary statethat would unite their scattered population in one country. The unitarist solution prevailed. The 1921 constitution established a highly centralized state, under the Serbian Karadjordjević dynasty, in which legislative power was exercised jointly by the monarchy and the Skupština (assembly). The king appointed a Council of Ministers and retained significant foreign policyprerogatives. The assembly only considered legislation that had already been drafted, and local government acted in effect as the transmission belt for decisions made in Belgrade.
What countries are part of Yugoslavia?
It included the current countries of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, North Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia, Slovenia, and the partially recognized country of Kosovo. Learn more about Yugoslavia in this article.
What countries were part of the former Serbian-held Macedonia?
The major beneficiary there was a newly created Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes, which comprised the former kingdoms of Serbia and Montenegro (including Serbian-held Macedonia), as well as Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Austrian territory in Dalmatia and Slovenia, and Hungarian land north of the Danube River.
Where is Yugoslavia located?
Full Article. Yugoslavia, former federated country that was situated in the west-central part of the Balkan Peninsula. This article briefly examines the history of Yugoslavia from 1929 until 2003, when it became the federated union of Serbia and Montenegro (which further separated into its component parts in 2006).
What was the name of the Yugoslavia?
However, the kingdom was better known colloquially as Yugoslavia (or similar variants); in 1929 it was formally renamed the " Kingdom of Yugoslavia ".
When was Yugoslavia a part of Serbia?
When the Kingdom of Yugoslavia was proclaimed in 1929, most of the region eventually became a part of the Danubian Banate, with a small part going to the City of Belgrade. Banat Republic (1918) Region of Banat, Bačka and Baranja that proclaimed unification with Serbia.
What was the name of the country that was formed after the collapse of Austria-Hungary?
Yugoslavia was a state concept among the South Slavic intelligentsia and later popular masses from the 17th to early 20th centuries that culminated in its realization after the 1918 collapse of Austria-Hungary at the end of World War I and the formation of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes.
Which countries did Serbia invade?
Serbian military forces quickly overran the territory of the Kingdom of Serbia (including the present-day North Macedonia) as well as that of the Kingdom of Montenegro, Banat, Bačka and Baranja and Syrmia, but stopped on the borders of the other Habsburg territories that would form the short-lived State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs, anticipating an official union between them and Serbia.
What was the original purpose of Montenegro?
See also: Kingdom of Montenegro. Montenegro was originally created by the national-romantic desire of liberation the lands which belonged to the State of Zeta, later of unification of South Slavic lands, and remained conservative in its ideology as compared with the other parts of the future Yugoslavia.
What did the Slovenian people request in the May Declaration?
In Vienna on 31 May 1917, Anton Korošec read the May Declaration in which the Slovenian people requested that the Austro-Hungarian Empire change from a dual to a triple monarchy: Austria-Hungary should not be divided to only Austria and Hungary anymore, but to three parts: Austria, Hungary and Yugoslavia.
When was the South Slavic Federation created?
In 1848 , a plan was created for the creation of a South Slavic Federation. The plan initiated by the Serbian government was made up of the members of the Secret Belgrade Circle, among whom there were people close to the ruling circles.
What was the name of the new Yugoslavia after WWII?
When WWII ended, the Partisans, led by Tito, took control of Yugoslavia and proclaimed the establishment of a new Yugoslavia, called the Federal People’s Republic of Yugoslavia. The new communist federation was comprised of 6 republics: Serbia, Montenegro, Macedonia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Slovenia.
How many republics were there in the Yugoslavia?
There were six republics in the federation: Serbia, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, and Slovenia. At first, Yugoslavia was a constitutional monarchy, but it then became a communist state under the leadership of Josip Broz Tito. After Tito died, the unity of the federation began to falter.
What was the name of the federation of states in which Southern Slavic languages were dominant?
Yugoslavia was a federation of states in which Southern Slavic languages were dominant.
Why did participatory democracy not take shape in Yugoslavia?
Although workers controlled industries in Yugoslavia in theory, the reality was that full participatory democracy in the workplace was not able to take shape because of the monopoly of the Yugoslav Communist Party.
Who was the leader of Yugoslavia during the Cold War?
As the ruler of Yugoslavia, Josip Tito steered the country on a course that was independent of the Soviet Union and the other communist states of the Cold War-era Eastern Bloc. In fact, at times, his relations with the USSR were quite frosty.
When did Serbia and Montenegro become a country?
In 1992, Serbia and Montenegro proclaimed the establishment of a new Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, composed only of their two countries. Shortly thereafter, Yugoslavia was expelled from the United Nations and suspended from the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE).
When did the idea of a Southern Slavic federation begin?
The Formation Of Yugoslavia. Map of the former republic of Yugoslavia. The idea of a Southern Slavic federation began to take shape in the early 20th century, as the two empires that had dominated the region of the Southern Slavs, the Austro-Hungarian Empire and the Ottoman Empire, were on the decline. The last hurrah of these two empires was World ...
What Yugoslavia family records will you find?
There are 3,000 census records available for the last name Yugoslavia. Like a window into their day-to-day life, Yugoslavia census records can tell you where and how your ancestors worked, their level of education, veteran status, and more.
How many immigration records are there for the last name Yugoslavia?
There are 642 immigration records available for the last name Yugoslavia. Passenger lists are your ticket to knowing when your ancestors arrived in the USA, and how they made the journey - from the ship name to ports of arrival and departure.
What did your Yugoslavia ancestors do for a living?
Census records can tell you a lot of little known facts about your Yugoslavia ancestors, such as occupation. Occupation can tell you about your ancestor's social and economic status.
How to find out where a family lived in Yugoslavia?
Use census records and voter lists to see where families with the Yugoslavia surname lived. Within census records, you can often find information like name of household members, ages, birthplaces, residences, and occupations.
Where does the word "Yugoslavia" come from?
Yugoslavia is the english transcription of “Jugoslavija”, and comes from Serbo-Croatian “jug” (south), and “Slavija” (the Land of the Slavs), with in-between what I suppose is the interfix “ -o- ” (a particle without any semantic meaning : “ -o- ”), to link the 2 main words into a compound-word (like the former name of the local language itself : srpsk o hrvatski : serbo-croatian).
Who created the second Yugoslavia?
First thing to understand is that second Yugoslavia (SFRY) was created by Britain and with the US help to serve as a Trojan horse inside communist block, as a buffer zone to block Russia’s access to the Adriatic sea and to pull away as many countries as possible from Russia (aka Non-Aligned Movement).
What does Jugoslavija mean?
Grossly, Jugoslavija means “The Land of the Slavs of the south”. Or better : “the Land of South Slavs” as Quora User commented.
Why did the Serbs orchestrate war?
They orchestrated war to distract people while they were getting fatter and fatter from all the money they stole from people.
What were the relations between the USSR and Yugoslavia?
Soviet-Yugoslav relations - bilateral relations between the USSR and Yugoslavia, established June 25, 1940 . Relations between the two countries developed very ambiguously - until 1940 they were openly hostile, in 1948 they again became aggravated and in 1949 they were torn apart. In 1953-1955, bilateral relations were restored, but until the collapse of Yugoslavia remained very restrained. SFRY was recognized by the USSR as a socialist state and participated in the CMEA (although it did not become a member of this organization). However, Yugoslavia did not join the internal affairs department and in some cases did not support Soviet foreign policy (for example, Soviet intervention in the affairs of other socialist countries). In the 1960s and 1980s, trade between the two countries was significant and grew until 1985. The USSR also became a major consumer of Yugoslav cultural products: in the 1960s and 1980s, translations of books by Yugoslav writers were published in large numbers in the Soviet Union, and Yugoslav films were shown.
When did the Kingdom of Serbs change its name?
Before that, like Dragi Raos mentionned in comment, “Kraljevina Jugoslavija” (Kingdom of Yugoslavia”) was also the name of the former Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes; name change happened in 1929.”.
When did Yugoslavia split?
It was the short name of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia which dismantled itself between 1991 and 1992 in 5 independant countries : Slovenia, Croatia, Macedonia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (later : Serbia and Montenegro), the last splitting in 2006 after a referendum for independence held in Montenegro, Serbia being the continuing State of the previous entity (FRY of 1992–2003 and S&M of 2003–2006).
Who was the first president of Yugoslavia?
The birth of Yugoslavia is in some ways attributable to US President Woodrow Wilson who, at the Versailles Peace Conference in 1919, actively supported the formation of the Kingdom of the Slovenes, Croats, and Serbs—the predecessor of Yugoslavia. During the Bosnian War of 1992-1995, the United States, under President Clinton, gave decisive leadership to ending that conflict in 1995 with the Dayton Peace Accords. The United States continues to have a special attachment to the seven states that were formerly part of Yugoslavia and enjoys close relations with these seven states. Today, like the United States, the area of Yugoslavia is multiculturally diverse and widely engaged with the international and regional communities in order to improve the lives of its citizens.
When did Croatia occupy Slovenia?
These four years of struggle ended in 1995. In 1998, Croatia was able to occupy all of eastern Slovenia.
What is the history of Kosovo?
The area is rich with Serbian history. The World Factbook states that “during the medieval period, Kosovo became the center of a Serbian Empire and saw the construction of many important Serb religious sites.” 5 It was also here that the Serbs suffered a major defeat by the Ottoman Turks in the Battle of Kosovo in 1389. The Albanian presence continued to grow and, by the end of the 19th century, Albanians had become the dominant ethnic group in Kosovo. 6
When did Slovenia become independent?
In 1991, driven by the goal of full freedom from the Serb majority, Slovenia declared its independence after a ten-day struggle. Slovenia is the most flourishing of the former member states of Yugoslavia, enjoying strong economic benefits from a stable political system.
Who was the leader of Serbia in 1989?
He led Yugoslavia until his death in 1980. After almost a decade of weak internal leadership, Slobodan Milosevic became President of Serbia in 1989. An ultra-nationalist, Milosevic advocated Serb domination which led to the violent breakup of Yugoslavia in 1991.
When did Montenegro become a member of the United Nations?
It began transitioning to full independence despite a loose state union in 2003 known as “Serbia and Montenegro.” The 14 years of transition passed peacefully and in June 2006, following a decade of negotiations, Montenegro became the 192nd member state of the United Nations. The United States played a significant role in the negotiations that led to Montenegrin independence in 2006, and the bilateral relationship remains favorable today.
Is Bosnia a sovereign state?
Bosnia and Herzegovina was confirmed as a sovereign state. Today, the country is slightly smaller than West Virginia and has a population of over four and a half million. 1. However, the political solution that ended the war is complex. There are two tiers of government.
When did Yugoslavia become a country?
In 1963, it was renamed the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia and lasted until 1991, when Croatia and Slovenia proclaimed their independence. When did Yugoslavia end
When did Yugoslavia change its name?
In 1963 it changed its name to the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia.
When did Serbia and Montenegro break up?
Serbia and Montenegro tried to preserve the union, so in 1992 they formed the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, which finally disintegrated in 2003 .
When did the Yugoslavia monarchy end?
At the end of the war with the victory of the Allies , in 1945, the monarchy was abolished and the Federal People’s Republic of Yugoslavia was created . The longest and most stable period in the history of Yugoslavia then began.
When did Croatia and Slovenia separate?
These tensions led to the separation of Croatia and Slovenia, which, in June 1991, proclaimed their independence. As this secession was rejected by the federal government, dominated by the Serbs, the so-called Yugoslav Wars began.
Who inhabited the Balkan Peninsula?
At the beginning of the 20th century the Balkan Peninsula was inhabited for the most part by the South Slavs. Among them, Croats and Slovenes were integrated into the Austro-Hungarian Empire , while Serbs and Montenegrins had gained independence from the Ottoman Empire in 1878.
What was the significance of the Balkan Wars in 1913?
In 1913, the triumph of Serbia and Montenegro over the Turks in the Balkan Wars contributed to exacerbating the Pan-Slavic sentiment of the peoples of the region.

Overview
Yugoslavia was a state concept among the South Slavic intelligentsia and later popular masses from the 19th to early 20th centuries that culminated in its realization after the 1918 collapse of Austria-Hungary at the end of World War I and the formation of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes. However, the kingdom was better known colloquially as Yugoslavia (or similar variants); in 1…
Origins of the idea
The first idea of a state for all South Slavs emerged in the late 17th century, a product of visionary thinking of Croatian writers and philosophers who believed that the only way for southern Slavs to regain lost freedom after centuries of occupation under the various empires would be to unite and free themselves from tyrannies and dictatorships.
In 1848, a plan was created for the creation of a South Slavic Federation. The plan initiated by the Serbian …
Yugoslav Committee
During the early period of World War I (which started in 1914), a number of prominent political figures, including Ante Trumbić, Ivan Meštrović, Nikola Stojadinović and others from South Slavic lands under the Habsburg Empire fled to London, where they began work on forming a committee to represent the South Slavs of Austria-Hungary, choosing London as their headquarters.
The Yugoslav Committee was formed on 30 April 1915 in London, and began to raise funds, esp…
State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs
As the Habsburg Empire dissolved, a pro-Entente National Council of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs took power in Zagreb on 6 October 1918. On 29 October, a Yugoslavist Croatian Sabor (parliament) declared independence and vested its sovereignty in the new State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs, and two days later it declared its wish to enter state of union with Serbia and Montenegro. Soon afterward on 5 November the National Council in Zagreb asked the Serbian military for help in c…
Kingdom of Serbia
In the 1915 Serbian campaign the Serbian Army suffered a complete defeat by the Central Powers and Serbia was overrun. Nevertheless, after recuperating on Corfu, the Serbians returned to combat in 1917 on the Macedonian front together with other Entente forces. Serbian and French forces began to defeat Austro-Hungarian and Bulgarian forces in the Vardar valley in September 1918 and, on …
Aftermath
A plebiscite was also held in the Province of Carinthia, which opted to remain in Austria. The Dalmatian port city of Zara (Zadar) and a few of the Dalmatian islands were given to Italy. The city of Fiume (Rijeka) was declared to be the Free State of Fiume, but it was soon occupied by the Italian poet and revolutionary Gabriele D'Annunzio for several months. Turned into a "free state", Fiume was a…
See also
• Adriatic Question
• Kingdom of Yugoslavia
• Yugoslavia
• Congress of Oppressed Nationalities of the Austro-Hungarian Empire
Notes
1. ^ Durković-Jakšić, Ljubomir (1957). Srbijansko-crnogorska saradnja 1830–1851. Belgrade: Naučno delo.
2. ^ History of the municipal theatre Archived June 23, 2007, at the Wayback Machine from Corfu cityhall Quote: "The Municipal Theatre was not only an Art-monument but also a historical one. On its premises the exiled Serbian parliament, the Skoupsina, held up meetings in 1916, which decided the creation of the new Unified Kingdom of Yugoslavia."
The Formation of Yugoslavia
Tito’s Yugoslavia
- As the ruler of Yugoslavia, Josip Tito steered the country on a course that was independent of the Soviet Union and the other communist states of the Cold War-era Eastern Bloc. In fact, at times, his relations with the USSR were quite frosty. At the same time, Tito maintained some ties to the West, whose aid helped his regime survive. Tito’s regime was initially highly centralized, but und…
The Disintegration of Yugoslavia
- During his rule, Tito was able to keep nationalistsentiment under control, often using force to do so. He continuously promoted the ideology of Pan-Slavism, which the Yugoslav federation was supposed to exemplify. When Tito died in 1980, however, the nationalism that he tried so hard to suppress began rising to the surface. In 1989, a Serb nationalist named Slobodan Milošević bec…