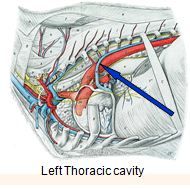
Intercostal vein. The posterior veins drain the spaces from the back. The anterior veins drain out the anterior regions. The superior veins drain blood from the second, third, and fourth intercostal spaces. The supreme veins drain from the first costae. Lastly, the subcostal veins are situated directly under the lowermost rib and are similar to the posterior veins.
Where do the posterior intercostal veins drain?
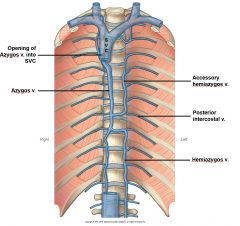
The intercostal veins run above the intercostal arteries, which run above the intercostal nerves. The posterior intercostal veins drain into the azygos vein (right side), and hemiazygos and accessory hemiazygos veins (left side).
What vein drains into the superior vena cava?
The intercostal veins run above the intercostal arteries, which run above the intercostal nerves. The posterior intercostal veins drain into the azygos vein (right side), and hemiazygos and accessory hemiazygos veins (left side). The latter two veins ultimately drain into the azygos vein. The azygos vein then drains into the superior vena cava.
What are the different types of intercostal veins?
The intercostal veins are a group of veins which drain the area between the ribs ("costae"), called the intercostal space. They can be divided as follows: Anterior intercostal veins. Posterior intercostal veins Posterior intercost vein that drain into the Supreme intercostal vein - 1st intercostal space.
What veins anastomose to form the posterior intercostal veins?
Each posterior intercostal vein forms an anastomosis with the ipsilateral anterior intercostal veins. The first posterior intercostal vein drains directly into the brachiocephalic vein. The second and third posterior intercostal veins anastomose to form the left and righ superior intercostal veins .
Where do the intercostal arteries drain?
The left superior intercostal vein drains into the left brachiocephalic vein, while the right counterpart drains to the superior vena cava via the azygous vein. The remaining fourth to eleventh posterior intercostal veins drain to either the azygous or hemizygous veins.
Which vein drains the anterior intercostal veins?
internal thoracic veinAnterior intercostal veinsDrains tointernal thoracic veinArteryanterior intercostal arteriesIdentifiersLatinvenae intercostales anteriores6 more rows
What does the left superior intercostal vein drain into?
The left superior intercostal vein forms by the union of the 2nd to 4th left posterior intercostal veins. It courses superiorly to the left of the midline, arches posteriorly lateral to the aortic arch to drain into the left brachiocephalic vein.
Which vein drains directly into the superior vena cava?
The azygos vein is another vein that drains into the superior vena cava. This vein is unpaired. It runs along the right aspect of the thoracic vertebral column and enters into the thorax at the aortic hiatus of the diaphragm. The azygos vein forms from the joining of the right subcostal and ascending lumbar veins.
Where do the anterior intercostal veins come from?
The anterior intercostal veins originate from the intercostal space just inferior to anterior aspects of their respective ribs and drain into the internal thoracic and musculophrenic veins.
What drains the first intercostal space?
supreme intercostal veinThe supreme intercostal vein drains the 1st intercostal space posteriorly opening into the vertebral or brachiocephalic veins.
What does the accessory hemiazygos vein drain?
The accessory hemiazygos vein, also called the superior hemiazygos vein, drains the superior left hemithorax. In a majority of cases there is a small connection to the left superior intercostal vein, and rarely, 1–2% of the time, the accessory hemiazygos vein drains into the brachiocephalic vein [3].
Where do the anterior intercostal arteries come from?
The 1st to 6th anterior intercostal arteries arise directly from the lateral aspect of the internal thoracic artery. The 7th to 9th arise from the musculophrenic artery, a branch of the internal thoracic artery.
Which vein drains blood from the second, third, and fourth intercostal spaces?
The posterior veins drain the spaces from the back. The anterior veins drain out the anterior regions. The superior veins drain blood from the second, third, and fourth intercostal spaces. The supreme veins drain from the first costae.
What is the term for the veins that drain the rib cage?
Intercostal vein. Medically reviewed by the Healthline Medical Network — Written by the Healthline Editorial Team on January 21, 2018. Intercostal vein is a term that is used to describe the numerous veins that function to drain the rib cage’s intercostal spaces.
What are the divisions of the intercostal space?
A handful of different divisions of these veins exist. These divisions are posterior veins, anterior veins, superior veins, supreme veins, and subcostal veins. The posterior veins drain the spaces from the back.
Which vein drains into the superior intercostal vein?
The superior intercostal vein then drains into the Azygous vein.
What is the intercostal space?
Intercostal spaces, viewed from the left. The intercostal veins are a group of veins which drain the area between the ribs ("costae"), called the intercostal space . They can be divided as follows: Posterior intercost vein that drain into the Supreme intercostal vein - 1st intercostal space.
What veins drain into the musculophrenic vein?
One posterior and two anterior intercostal veins occupy each intercostal space. Anteriorly, they drain into the musculophrenic and internal thoracic veins . Posterior venous drainage is more anatomically variable. The first posterior intercostal veins drain into the vertebral vein or the brachiocephalic vein.
Which artery enters the intercostal space?
The intercostal arteries (ICA) enter the intercostal space both anteriorly and posteriorly. The superior intercostal artery, a branch of the subclavian artery, supplies the first two spaces posteriorly. Separate branches of the descending thoracic aorta then supply the remaining nine intercostal spaces posteriorly. The right-sided branches traverse from their origin at the aorta across their corresponding vertebrae and anterior longitudinal ligament, behind the hemiazygos vein and thoracic duct ( Sinnatamby and Last, 2011 ).
What drains the axillary vein?
The large epithelial and mesenchymal surface area of the superior, central, and lateral aspects of the breast is drained by tributaries that enter the axillary vein. Venous supply from the pectoralis major and minor muscles also drains into tributaries that enter the axillary vein. Perforating veins of the internal mammary venous system drain the medial aspect of the breast and the pectoralis major muscle. This large venous plexus can be observed to traverse the intercostal musculature and terminate in the innominate vein, providing a direct embolic route to the venous capillary network of the lungs. Each plexus of veins in the lateral and medial aspects of the breast is observed to have multiple, racemose anastomotic connections.
What veins are tributaries of the Azygos vein?
Other tributaries of the azygos vein include esophageal, bronchial, mediastinal, and pericardial veins. The azygos vein courses superiorly and arches (from posterior to anterior) around the superior aspect of the right primary bronchus. It then terminates by entering the superior vena cava.
What causes a bleed in the pleural cavity?
One of the most serious complications is intercostal bleeding, caused either by damage to the intercostal artery or vein. It is very common to obtain bloodstained fluid from the pleural space but there are a number of different indications of acute bleeding. A change in the degree of blood staining during the procedure should raise suspicions, especially if the fluid was previously straw colored. Using ultrasound to check that the echogenicity of the fluid has not increased can be helpful. Haemodynamic instability is a late sign, and speed of onset depends on the type of bleed and the degree of damage. Likewise, if the pleural cavity has been fully drained but a new effusion is shown on a post procedure x-ray then this should raise the possibility of a haemothorax. An intercostal artery laceration will usually present within hours of the procedure, but a slow venous bleed can be more insidious. Unfortunately, bleeding may not always become evident at the time of the procedure, even with patients who have straw colored fluid. The tubing which is being used to drain the fluid could tamponade a bleed and so the damage only becomes evident once the procedure has been completed, although this is less likely.
Which vein is the accessory hemiazygos vein?
However, the left superior intercostal vein normally is a tributary of the left brachiocephalic vein. The accessory hemiazygos vein ends either by draining into the hemiazygos vein or by crossing the vertebral column from left to right, just above the hemiazygos vein, to drain into the azygos vein. View chapter Purchase book.
Where does the hemiazygos vein enter the thorax?
The hemiazygos vein enters the thorax through the aortic hiatus. It then continues superiorly along the left anterior aspect of the vertebral bodies. Along its path the hemiazygos vein receives the lower four or five left intercostal veins. It also frequently receives the accessory hemiazygos vein.
How many pairs of intercostal veins are there?
Intercostal veins. There are eleven pairs of posterior intercostal veins, ni ne pairs of anterior intercostal and one pair of subcostal veins supplying the thoracic wall. Each posterior intercostal vein forms an anastomosis with the ipsilateral anterior intercostal veins.
Where do the first and second posterior intercostal arteries originate?
The first and second posterior intercostal arteries originate from the superior (supreme) intercostal artery, a branch of the costocervical trunk. Third to eleventh posterior intercostal arteries arise directly from the posterior surface of the thoracic aorta.
What is the internal thoracic vein?
The internal thoracic veins accompany the internal thoracic arteries. They unite at about the third costal cartilage to form a single internal intercostal vein that is medial to the accompanying artery.Like most veins in the body, the internal thoracic vein has several valves along its length to promote the unidirectional flow of blood. It receives segmental tributaries at each intercostal level (similar to the points at which the corresponding arteries emerge). The pericardiophrenic vein also drains deoxygenated blood by way of the internal thoracic veins. The internal thoracic vein eventually drains directly into the ipsilateral brachiocephalic vein .
What are the subcostal arteries?
The subcostal arteries are direct branches of the thoracic aorta. They are analogous to the posterior intercostal artery, so if there was a 12th intercostal space, they would be the 12th intercostal arteries. Like its preceding counterparts, each subcostal artery gives the anterior and posterior branches that travel along with the subcostal space below the twelfth rib. On the left side, the artery passes behind the accessory hemiazygous vein, while on the right side it passes in front of the twelfth thoracic vertebra and behind the thoracic duct and azygous vein. On either side, the arteries are posteriorly related to the sympathetic trunk, diaphragm, and adjacent pleura.
Why is it important to know the arteries and veins of the chest wall?
Knowledge of the arteries and veins that supply the chest wall is not only important for passing exams, but also for certain emergency situations that pop up during clinical practice. This article will discuss the arteries and veins of the thoracic wall. However, a brief review of the intercostal space and the chest wall anatomy will also be included.
How many branches does the internal thoracic artery have?
The internal thoracic artery gives off five sets of branches :
What is the thoracic wall?
The thoracic wall or chest wall is a musculoskeletal structure that has a vast vascular supply. Most of the arteries of the thoracic cavity arise directly from the thoracic aorta; while others arise from its branches.
What veins drain into the musculophrenic vein?
One posterior and two anterior intercostal veins occupy each intercostal space. Anteriorly, they drain into the musculophrenic and internal thoracic veins . Posterior venous drainage is more anatomically variable. The first posterior intercostal veins drain into the vertebral vein or the brachiocephalic vein. The second to fourth posterior veins usually amalgamate to form the superior intercostal vein, which on the right then drains into the azygos vein and on the left into the left brachiocephalic vein (Sinnatamby and Last, 2011 ).
Which artery enters the intercostal space?
The intercostal arteries (ICA) enter the intercostal space both anteriorly and posteriorly. The superior intercostal artery, a branch of the subclavian artery, supplies the first two spaces posteriorly. Separate branches of the descending thoracic aorta then supply the remaining nine intercostal spaces posteriorly. The right-sided branches traverse from their origin at the aorta across their corresponding vertebrae and anterior longitudinal ligament, behind the hemiazygos vein and thoracic duct (Sinnatamby and Last, 2011 ).
What is bleed into the pleural space?
Bleeding into the pleural space often involves disruption or laceration of intercostal arteries and veins. Anatomical variations are common. The intercostal spaces comprise of three muscle layers (external, internal and innermost intercostals) with the neurovascular bundle situated in the plane between the internal and innermost muscle layers (Fig. 2) ( Sinnatamby and Last, 2011; Standring, 2016 ).
How many intercostal spaces are used for block surgery?
Blocks are performed two to three intercostal spaces cranial and caudal to the affected area (e.g., planned incision, fractured rib).
What is the angle of the collateral intercostal artery?
Cadaveric studies show that the collateral intercostal artery (CIA) originates from the posterior ICA at an average distance of 4–5.5 cm from the midline, forming an acute angle of 40–60 degrees with it. The CIA then traverses the intercostal space to reach the superior border of its inferior rib ( Da Rocha et al., 2002; Shurtleff and Olinger, 2012) ( Fig. 2 ). Contrary to classic anatomy teaching, the size of the posterior ICA and its collateral branch vary depending on the location of the interspace. At the 2nd intercostal space the average diameter of the posterior ICA and its CIA are about the same (1.4–1.5 mm) ( Da Rocha et al., 2002 ). Going inferiorly with each intercostal space the size of the posterior ICA increases while the size of its accompanying CIA tends to plateau at 1 mm ( Da Rocha et al., 2002, Shurtleff and Olinger, 2012 ).
Where is the Azygos-Hemiazygos system located?
The azygos-hemiazygos system forms an H-shaped network in the posterior mediastinum, anterior to the body of the thoracic vertebrae (see Figure 2.4). The azygos vein gives the entire right arm of the H, the hemiazygos gives the left lower and the accesory hemiazygos vein the left upper segment. The azygos vein starts at T12 to L2 with the confluence of the right ascending lumbar and subcostal veins. The azygos vein ascends on the right side up to the level of T4, then passes anterior to form an arch joining the SVC. Major tributaries of the azygos vein are the right posterior fifth to eleventh intercostal veins and the right superior intercostal vein draining the second to fourth intercostal veins. The hemiazygos vein starts similar to the azygos vein but on the left side of the vertebral column at T12-L2. It courses cranial and at the level of T8 it crosses over to join the azygos vein. Major tributaries of the hemiazygos vein are the left posterior eighth to eleventh intercostal veins. The accessory hemiazygos vein has more variation than the azygos and hemiazygos veins. Usually it drains the left superior intercostal vein (which in turn drains the left second to fourth intercostal veins) and the left posterior fifth to seventh intercostal veins. At the level of T7 it either crosses over to the right and joins the azygos or stays on the left and joins the hemiazygos vein. If the connection between the accessory hemiazygos and the rest of the azygos-hemiazygos system is not developed, the accessory hemiazygos vein will drain through the left superior intercostal vein into the left brachiocephalic vein. The azygos-hemiazygos system receives several small veins from the viscera of the chest and freely anastomoses with the vertebral venous plexuses as well. The azygos-hemiazygos system provides an important collateral pathway in case of IVC or SVC obstruction.7
Where is the superior vena cava?
The superior vena cava (SVC) starts at the confluence of the brachiocephalic veins behind the first right costal cartilage, and ends at the level of the third right costal cartilage where it drains into the right atrium. The SVC is about 7 cm long and 2 cm wide. Halfway along its course, before it enters the pericardium, the SVC receives the azygos arch. The brachiocephalic veins are formed at the confluence of the subclavian and internal jugular veins behind the sternoclavicular joints (see Figure 2.4). The right brachiocephalic vein is short, about 2–3 cm, and lies anterior to the innominate artery.7 The left one is about 6 cm long and courses obliquely behind the manubrium from left to right, anterior to the left subclavian, common carotid arteries, and superior to the aortic arch. Major tributaries of the brachiocephalic veins are the vertebral, internal thoracic, and inferior thyroid veins. The first intercostal vein drains into the brachiocephalic veins on both sides. The left superior intercostal vein is connected to the left brachiocephalic vein, whereas on the right it joins the azygos vein. There are no valves in either the SVC or the brachiocephalic veins.