What happens when your lymphatic system drains?
The lymphatic system, shown in green, is important for immunity. Lymphatic drainage is the natural function of the lymphatic system, which is an essential part of immunity. If this function isn't working properly, it can cause a build-up of fluid in tissues as well as more serious medical problems like lymphagitis and lymphoma.
What stimulates the lymphatic system?
“The lymphatic system is stimulated by moving your muscles and getting your heart rate up,” says MD Anderson Senior Physical Therapist Sarah Cleveland. “All these things stimulate the lymphatic flow.” The contraction of your muscles becomes the pump that helps the fluid get around your body. Know more about it here.
How to drain your lymphatic system?
While the research supporting the connection between dry brushing and lymphatic health is scant, many people (both professional and otherwise) swear by it for reducing cellulite and boosting circulation. Dry brushing is thought to boost lymphatic detoxification by opening up the pores, allowing toxins to be released freely via sweat.
How do you detox lymph nodes?
This Lymphatic Cleanse Can Balance Your Whole Body In 5 Simple Steps
- Detox your environment. The lymph must deal with the body's "waste products" that are produced internally like dead cells as well as toxins that are introduced from the external ...
- Stay hydrated. Lymph fluid is about 95 percent water and becomes thicker and less fluid when you are dehydrated. ...
- Incorporate red and raw foods. ...
- Move your lymph naturally. ...

How does lymph travel through the body?
The fluid and proteinswithin the tissues begin their journey back to the bloodstream by passing into tiny lymphatic capillaries that infuse almost every tissue of the body. Only a few regions, including the epidermisof the skin, the mucous membranes, the bone marrow, and the central nervous system, are free of lymphatic capillaries, whereas regions such as the lungs, gut, genitourinary system, and dermisof the skin are densely packed with these vessels. Once within the lymphatic system, the extracellular fluid, which is now called lymph, drains into larger vessels called the lymphatics. These vessels converge to form one of two large vessels called lymphatic trunks, which are connected to veinsat the base of the neck. One of these trunks, the right lymphatic duct, drains the upper right portion of the body, returning lymph to the bloodstream via the right subclavian vein. The other trunk, the thoracic duct, drains the rest of the body into the left subclavian vein. Lymph is transported along the system of vessels by musclecontractions, and valves prevent lymph from flowing backward. The lymphatic vessels are punctuated at intervals by small masses of lymph tissue, called lymph nodes, that remove foreign materials such as infectious microorganisms from the lymph filtering through them.
What is the lymphatic system?
See Article History. Lymphatic system, a subsystem of the circulatory system in the vertebrate body that consists of a complex network of vessels, tissues, and organs. The lymphatic system helps maintain fluid balance in the body by collecting excess fluid and particulate matter from tissues and depositing them in the bloodstream.
What is the role of the lymphatic system in the immune system?
In addition to serving as a drainage network, the lymphatic system helps protect the body against infection by producing white blood cells called lymphocytes, which help rid the body of disease-causing microorganisms.
Why is the lymphoid organ important?
The importance of the primary lymphoid organs is demonstrated by its involvement in autoimmune disease. Two autoimmune diseases, DiGeorge syndrome and Nezelof disease, result in the failure of the thymus to develop and in the subsequent reduction in T cell numbers, and removal of the bursa from chickens results in a decrease in B cell counts.
What system removes fluid from tissues?
The lymphatic system removes this fluid and these materials from tissues, returning them via the lymphatic vessels to the bloodstream. The lymphatic system also helps defend the body against infection. Read more about the circulatory system.
Which organs are the major sites of differentiation and proliferation?
The organs and tissues of the lymphatic system are the major sites of production, differentiation, and proliferation of two types of lymphocytes—the T lymphocytes and B lymphocytes, also called T cells and B cells, respectively. Although lymphocytes are distributed throughout the body, it is within the lymphatic system that they are most likely ...
Which system of the body is responsible for the flow of fluid and proteins back to the bloodstream?
The lymphatic system of the head and neck. The fluid and proteins within the tissues begin their journey back to the bloodstream by passing into tiny lymphatic capillaries that infuse almost every tissue of the body.
Where does the lymph drain from?
The superficial vessels drain lymph from the scalp, face and neck into the superficial ring of lymph nodes at the junction of the neck and head.
Where do the superficial lymph nodes drain?
Superficial Lymph Nodes. The superficial lymph nodes of the head and neck receive lymph from the scalp, face and neck. They are arranged in a ring shape; extending from underneath the chin, to the posterior aspect of the head. They ultimately drain into the deep lymph nodes.
What are the lymph nodes in the cervical system?
The nodes can be divided into superior and inferior deep cervical lymph node s. They are numerous in number, but include the prelaryngeal, pretracheal, paratracheal, retropharyngeal, infrahyoid, jugulodigastric (tonsilar), jugulo-omohyoid and supraclavicular nodes.
What is the collection of substances that enters the lymphatic vessels called?
Once this collection of substances enters the lymphatic vessels, it is known as lymph. Lymph is subsequently filtered by lymph nodes and directed into the venous system. This article will explore the anatomy of lymphatic drainage throughout the head and neck, and how this is relevant clinically.
What are the two major groups of lymphatic vessels?
The lymphatic vessels of the head and neck can be divided into two major groups; superficial vessels and deep vessels. Superficial Vessels. The superficial vessels drain lymph from the scalp, face and neck into the superficial ring of lymph nodes at the junction of the neck and head. Deep Vessels.
Why are my tonsils red?
The palatine tonsils can become inflamed due to a viral or bacterial infection. In such a case, they appear red and enlarged, and are accompanied by enlarged jugulo-digastric lymph nodes.
Which lymphatic system empties into the venous system via the left subclavian vein?
Left jugular lymphatic trunk - combines with the thoracic duct at the root of the neck. This empties into the venous system via the left subclavian vein. Right jugular lymphatic trunk - forms the right lymphatic duct at the root of the neck.
Which ducts are used to collect lymph?
Collecting ducts: Lymphatic vessels empty the lymph into the right lymphatic duct and left lymphatic duct (also called the thoracic duct). These ducts connect to the subclavian vein, which returns lymph to your bloodstream. The subclavian vein runs below your collarbone.
What is the lymphatic system?
Overview. The lymphatic system is a network of tissues, vessels and organs that work together to move lymph back into your your bloodstream. The lymphatic system is part of your immune system.
When should I call my doctor about an issue with my lymphatic system?
Call your doctor if you experience fatigue (extreme tiredness) or have unexplained swelling that lasts more than a few weeks or interferes with your daily activities .
What system collects excess fluid from cells and tissue throughout the body?
Maintains fluid levels in your body: As just described, the lymphatic system collects excess fluid that drains from cells and tissue throughout your body and returns it to your bloodstream, which is then recirculated through your body.
How to check if lymphatic system is working?
To see if your lymphatic system is working as it should, your doctor may use imaging tests such as a CT scan or MRI. These tests allow your doctor to see blockages in your lymphatic system.
How much plasma does the body use?
Some 20 liters of plasma flow through your body’s arteries and smaller arteriole blood vessels and capillaries every day. After delivering nutrients to the body’s cells and tissues and receiving their waste products, about 17 liters are returned to the circulation by way of veins. The remaining three liters seep through the capillaries and into your body’s tissues. The lymphatic system collects this excess fluid, now called lymph, from tissues in your body and moves it along until it's ultimately returned to your bloodstream.
Where are lymph nodes located?
A few of the more familiar locations of lymph nodes are in your armpit, groin and neck. Lymph nodes are connected to others by the lymphatic vessels.·.
Where does lymphatic drainage go in the body?
This major lymphatic vessel empties into the venous circulatory system at the junction between the left subclavian and internal jugular veins. Lymphatic drainage of the pelvis closely resembles the abdomen. Lymph from the pelvic viscera reaches the common iliac lymph nodes bypassing via relay nodes ( external iliac, internal iliac, sacral) located in the vicinity of the great pelvic blood vessels. The lumbar lymphatic trunks subsequently collect the lymph from the common iliac lymph nodes.
Which lymphatic drainage system is located in the posterior abdominal wall?
The lymphatic drainage of the posterior abdominal wall follows a similar pattern, with both superficial and deep lymphatic networks draining this region. Superficial drainage is achieved in both the lumbar and iliac regions via lymphatic vessels which follow the superficial circumflex blood vessels. The deeper lymphatic vessels follow two primary drainage pathways:
How big is a lymph node?
Normal and healthy lymph nodes have a diameter less than 1 cm. Although they may be larger in adolescents and children, a lymph node greater than 1 cm in diameter is considered lymphadenopathy. This condition can be localized, involving only a few lymph nodes in a respective area, or generalized, which is a frequent sign of a systemic disease.
How is lymph filtered?
Lymph is filtered through lymph nodes which house immune cells that continuously sample it, ready to mount an immune response. It is a similar situation to airport security checks - unavoidable by everyone due to their strategic positioning, uncomfortable for delinquents, and constantly checking every single person.
Where does lymph go from the pelvic viscera?
Lymph from the pelvic viscera reaches the common iliac lymph nodes bypassing via relay nodes ( external iliac, internal iliac, sacral) located in the vicinity of the great pelvic blood vessels. The lumbar lymphatic trunks subsequently collect the lymph from the common iliac lymph nodes.
Which vessels drain into the superficial inguinal lymph nodes?
In turn, lymphatic vessels found in the infraumbilical territory follow the superficial epigastric vessels and drain into the superficial inguinal lymph nodes. In contrast, the lymphatic vessels of the deep system follow the course of some slightly deeper vessels, and follow three primary pathways:
What is the role of the lymphatic system?
One important role of the lymphatic system includes the removal of various substances (cellular waste, water, proteins) from the interstitial fluid. It is also involved in fat absorption from the gut and protection against pathogens.
What to expect during lymphatic drainage?
What to Expect During a Lymphatic Drainage. If someone is giving you a lymphatic drainage massage, prepare to definitely feel them working on you —it’s not a Swedish massage, it’s definitely deeper. But also, expect to feel lighter when it’s over and to look more contoured.
How much does a De la Heart lymphatic drainage tool cost?
It's De la Heart's Lymphatic Drainage Body Tool ($29) —which the company graciously gifted to me for this story, full disclosure—with some jojoba oil to help the tool glide over your skin.
Is it important to raise a glass of water after lymphatic drainage?
Sure, they may not be as visible to someone else, but I’m not doing it for anyone else—just me. So, with that said, I’m raising a tall glass of water (as I mentioned, it’s important to stay hydrated after you do any form of lymphatic drainage) and cheers to new, at-home routines that can make you feel good about yourself as we all stay home and stay safe.
Is lymphatic drainage dangerous?
Since you’re promoting proper lymph movement—something your body is meant to do naturally—there is little risk with lymphatic drainage. However, you want to make sure you’re doing it properly. Always moving the lymph toward your heart with upward motions, and then downward motions on your belly toward your groin.
What is the collection of substances that enters the lymphatic system?
Once this collection of substances enters the lymphatic vessels it is known as lymph. It is subsequently filtered by lymph nodes, from which it returns to the circulation via the venous system.
Where do superficial lymphatic vessels originate?
The superficial lymphatic vessels of the upper limb initially arise from lymphatic plexuses in the skin of the hand (networks of lymphatic capillaries beginning in the extracellular spaces).
What is the term for inflammation of the lymphatic vessels?
Infection of the upper limb, resulting in lymphangitis (inflammation of lymphatic vessels, with tender, enlarged lymph nodes). The humeral group of lymph nodes is usually affected first, and red, warm and tender streaks are visible in the skin of the upper limb.
What is removal of lymph nodes?
Removal and analysis of the axillary lymph nodes is often a vital tool for the staging of breast cancers. Interruption of lymphatic drainage from the upper limb can however result in lymphoedema, a condition whereby accumulated lymph in the subcutaneous tissue leads to painful swelling of the upper limb.
What causes lymphadenopathy in the apical nodes?
caption] Axillary lymphadenopathy refers to enlargement of the axillary lymph nodes. Common causes include: Infection of the upper limb, resulting in lymphangitis (inflammation of lymphatic vessels, with tender, enlarged lymph nodes).
Where is the apical located?
Apical - Located in the apex of the axilla, close to the axillary vein and 1st part of the axillary artery. They receive lymph from efferent vessels of the central axillary lymph nodes, therefore from all axillary lymph node groups. The apical axillary nodes also receive lymph from those lymphatic vessels accompanying the cephalic vein.
Which vessels travel through the apical axillary nodes?
The apical axillary nodes also receive lymph from those lymphatic vessels accompanying the cephalic vein. Efferent vessels from the apical axillary nodes travel through the cervico-axillary canal, before converging to form the subclavian lymphatic trunk.
What is lymphatic drainage?
Lymphatic drainage is an established treatment for certain medical conditions involving swelling or issues with the lymphatic system. It’s beauty benefits, however, require more research.
Why do people use lymphatic drainage?
Beauty bloggers and massage therapists alike often tout lymphatic drainage as a way to improve the appearance of the skin by reducing fine lines, wrinkles, and eye bags.
How long does lymphatic drainage last?
Bodily lymphatic drainage usually lasts up to an hour while the facial version is typically a little shorter. Deep breathing exercises, which promote better lymphatic circulation, tend to be combined with both.
What is the lymphatic system?
The lymphatic system is a crucial part of your immune system. Through a network of hundreds of lymph nodes, it drains fluid called lymph to be transported back into your bloodstream. It also removes bodily waste and carries white blood cells that help prevent infection.
Does lymphatic drainage help with skin irritation?
But in recent years, some have started incorporating facial lymphatic drainage into their beauty regimen as a weapon against puffy, dull complexion and skin irritation.
Who questioned whether people have lymphatic drainage issues in their facial area?
In an article published by the Journal of Clinical Investigation, dermatologist George Cotsarelis questioned whether people even have lymphatic drainage issues in their facial area.
Can you get lymphedema in your neck?
Keep in mind, however, that people can develop lymphedema in the head or neck. Fellow dermatologist Michael Detmar did admit in the article that the aging process, coupled with sun damage, can result in fewer lymphatic vessels and a deterioration of lymphatic function.
Which lymph nodes does the liver drain?
The liver drains its lymph into the hepatic, caval, posterior mediastinal, and celiac lymph nodes.[6] The lymphatic drainage of the kidneys is to the aortic and caval groups of lymph nodes. Nevertheless, it is not limited to these nodes, as it has been observed to have a distant reach like celiac, iliac, and even thoracic duct directly. Hence it becomes quite a challenge to treat a renal carcinoma patient. [10]
Why is lymphatic drainage important?
The lymphatic drainage of the stomach has gained much importance, primarily because of its cancer spread. [8] The carcinoma of the stomach mainly spreads through this route, thus increasing its relevance clinically, especially for staging and surgical resection. The lymphatic drainage of the stomach is initially into the hepatic, left gastric, pancreaticosplenic, gastroepiploic, and pyloric groups of lymph nodes. Finally, all these will drain into the celiac group, which opens into the cisterna chyli. [9]
Why does the lymphatic system in the abdomen have a disease?
Primary causes are essentially due to a disruption in the development of the lymphatic system itself. These causes encompass congenital or developmental conditions. Secondary causes can be due to a result of other diseases.
What is the lymphatic system?
The lymphatic system is a system that drains the leaked tissue fluid back into the circulation. Its components are lymphatic vessels, lymphatic organs, lymph nodes, and widely scattered lymphoid tissue within the connective tissue. Lymph is the tissue fluid flowing through these lymphatic channels.
What is the name of the sack of vessels that drain into the abdomen?
In the abdomen, they have an extensive network of vessels, which all finally drain into a large sack called cisterna chyle. Usually, they are so thin that they can be seen only by a microscope, except the largest one, the thoracic duct and right lymphatic duct by which the lymph finally reaches the bloodstream.
What is the lymph capillary?
The lymph capillaries are very fine vessels that form a massive network throughout the body. They begin as blind sacs in the spaces between the cells and carry the leaked tissue fluid along with the cell debris. The lymph passes through lymph nodes where it gets filtered of foreign particles like bacteria and virus and finally returns to the bloodstream. The lymph nodes are almost kidney-shaped, covered by a fibrous capsule that dips down deeper into the tissue in the form of trabeculae. The substance within will be mainly by vast aggregation of lymphocytes in the form of follicles, macrophages, and surrounded by the reticular network. Its concave part is the hilum where an artery, a vein, few nerves, and one efferent vessel are visible. Lymph vessels that carry lymph towards lymph nodes are afferent vessels, are 4 to 5 in number, and they open on the convex surface of the lymph node.
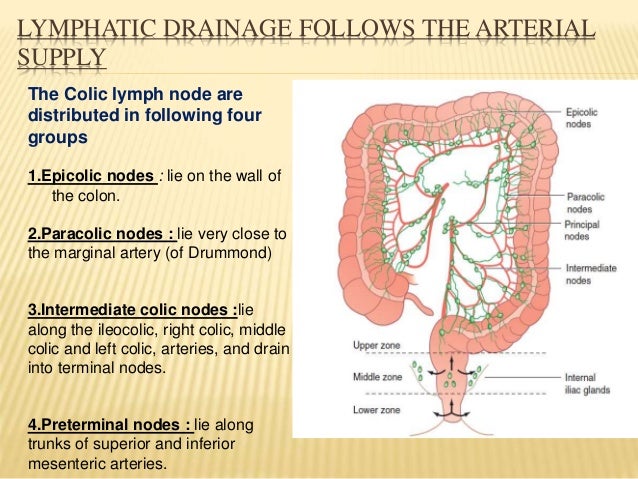
Which lymphatic system is the colon, ileum, duodenum, and upper and lower group of?
Lymphatics of the Colon, Ileum, Duodenum, Upper and Lower group of Ileocolic lymph glands, cecum, Vermiform process. Contributed by Gray's Anatomy Plates