What are the stages in cellular respiration in the correct order?
4 distinct steps of cellular respiration include: Glycolysis pathway (Embden-Meyerhof pathway) The transition reaction (oxidative decarboxylation) Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle) Oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria
What are the 4 stages of respiration?
what are the stages of aerobic respiration
- Aerobic Cellular Respiration, Glycolysis, Prep Steps
- Cellular Respiration (UPDATED)
- The stages of aerobic respiration
What is stage one of cellular respiration?
The first stage of cellular respiration, called glycolysis, takes place in the cytoplasm. In this step, enzymes split a molecule of glucose into two molecules of pyruvate, which releases energy that is transferred to ATP. Where does stage 1 of cellular respiration glycolysis occur?
What are the three steps of cellular metabolism?
- The production of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH). ...
- It synthesises pentose sugars which are precursors for nucleotide synthesis DNA, RNA, FADH2, ATP, NADH and CoA.
- It establishes a way to breakdown 5-carbon sugars which are consumed within the diet.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/aerobic_cellular_respiration-5c37aa17c9e77c0001c3f665.jpg)
What are the 4 stages of cellular respiration and where do they occur?
In eukaryotes, the 4 stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, transition reaction (pyruvate oxidation), the Krebs cycle (also known as the citric acid cycle), and oxidative phosphorylation through the electron transport chain.
Where do Stages 3 of cellular respiration occur?
the mitochondrionThe third and final stage of cellular respiration, called electron transport , takes place on the inner membrane of the mitochondrion. Electrons are transported from molecule to molecule down an electron-transport chain.
Where does step 2 of cellular respiration take place?
The second stage of cellular respiration, the Krebs cycle, takes place in the matrix. The third stage, electron transport, takes place on the inner membrane.
Where does cellular respiration occur in the mitochondria?
In the mitochondria, cellular respiration occurs in the mitochondrial matrix through the Krebs cycle to form ATP, FADH2 and NADH. The formed FADH2 and NADH then go into the inner mitochondrial membrane where they are involved in the electron transport chain to form more ATP molecules.
Where in a cell does stage 1 occur?
Stage one of cellular respiration is glycolysis. Glycolysis is the splitting, or lysis of glucose. Glycolysis converts the 6-carbon glucose into two 3-carbon pyruvate molecules. This process occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell, and it occurs in the presence or absence of oxygen.
What are the 3 main stages of cellular respiration?
The three stages of cellular respiration are glycolysis, Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation by the electron transport system (ETS).
Where in the cell does glycolysis occur?
the cytoplasmGlycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm. Within the mitochondrion, the citric acid cycle occurs in the mitochondrial matrix, and oxidative metabolism occurs at the internal folded mitochondrial membranes (cristae).
How does cellular respiration occur?
In cellular respiration, glucose and oxygen react to form ATP. Water and carbon dioxide are released as byproducts. The three stages of aerobic cellular respiration are glycolysis (an anaerobic process), the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
What are the three stages of cellular respiration quizlet?
The cellular respiration process consists of three stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain. glycolysis, the six-carbon sugar molecule (glucose) breaks down into 2 three-carbon molecules (pyruvic acid).
Which steps occur in the mitochondria?
What two processes occur in the mitochondria? The Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation are the two processes of cellular respiration that occur in the mitochondria. Glycolysis, the first process in cellular respiration, occurs in the cytoplasm.
Which process occur in mitochondria?
Mitochondria, using oxygen available within the cell convert chemical energy from food in the cell to energy in a form usable to the host cell. The process is called oxidative phosphorylation and it happens inside mitochondria.
What process occurs in the cytoplasm?
Cytoplasm Functions Many cellular processes also occur in the cytoplasm, such as protein synthesis, the first stage of cellular respiration (known as glycolysis), mitosis, and meiosis. The cytoplasm helps to move materials, such as hormones, around the cell and also dissolves cellular waste.
Do all three stages of cellular respiration occur in the mitochondria?
In general, cellular respiration can be divided into four stages: Glycolysis, which does not require oxygen and occurs in the mitochondria of all cells, and the three stages of aerobic respiration, all of which occur in mitochondria: the bridge (or transition) reaction, the Krebs cycle and the electron transport chain ...
What are the 3 main stages of cellular respiration which produces the majority of the ATP?
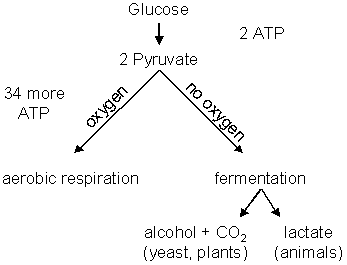
Cellular respiration has three main stages: the glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the Electron transport chain. Whereas the glycolysis and the Krebs cycle result in a net gain of 2 ATPs each, the bulk of the ATP is produced during the last stage (Electron transport chain), which results in up to 34 more ATP molecules.
What are the three stages of cellular respiration quizlet?
The cellular respiration process consists of three stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain. glycolysis, the six-carbon sugar molecule (glucose) breaks down into 2 three-carbon molecules (pyruvic acid).
Where does citric acid cycle occur?
the mitochondriaThe TCA cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or Krebs cycle, occurs in the mitochondria and provides large amounts of energy in aerobic conditions by donating electrons to three NADH and one FADH (flavin adenine dinucleotide), which donate electrons to the electron transport chain, creating the proton gradient ...
What is cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that uses glucose to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), an organic compound the body can use for ene...
What is the purpose of cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is used to generate usable ATP energy in order to support many other reactions in the body. ATP is particularly important for...
What are the main steps of cellular respiration?
There are three main steps of cellular respiration: glycolysis; the citric acid (TCA) or the Krebs cycle; and the electron transport chain, where o...
Where does cellular respiration take place?
Cellular respiration takes place in the cytoplasm and mitochondria of each cell of the body. Glycolysis occurs inside the cytoplasm, while the TCA...
What are the reactants of cellular respiration?
The reactants of cellular respiration vary at each stage, but initially, it requires an input of glucose, ATP, and NAD+. NAD+, a nicotinamide deriv...
What are the products of cellular respiration?
The final end products of cellular respiration are ATP and H2O. Glycolysis produces two pyruvate molecules, four ATPs (a net of two ATP), two NADH,...
What are the rate-determining enzymes in cellular respiration?
There are three primary rate-determining enzymes in cellular respiration. These enzymes catalyze the rate-limiting steps, which are the slowest rea...
What diseases can affect cellular respiration?
Several diseases can affect cellular respiration. Since cellular respiration is so vital to bodily functions, many of these diseases severely affec...
What are the most important facts to know about cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is a series of chemical reactions that break down glucose to produce ATP, which may be used as energy to power many reactions...
What is cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that uses glucose to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), an organic compound the body can use for energy. One molecule of glucose can produce a net of 30-32 ATP.
What is the purpose of cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is used to generate usable ATP energy in order to support many other reactions in the body. ATP is particularly important for energetically unfavorable reactions that would otherwise not occur without an energy input.
What are the main steps of cellular respiration?
There are three main steps of cellular respiration: glycolysis; the citric acid (TCA) or the Krebs cycle; and the electron transport chain, where oxidative phosphorylation occurs. The TCA cycle and oxidative phosphorylation require oxygen, while glycolysis can occur in anaerobic conditions.
Where does cellular respiration take place?
Cellular respiration takes place in the cytoplasm and mitochondria of each cell of the body. Glycolysis occurs inside the cytoplasm, while the TCA cycle occurs inside the matrix of the mitochondria.
What are the reactants of cellular respiration?
The reactants of cellular respiration vary at each stage, but initially, it requires an input of glucose, ATP, and NAD+. NAD+, a nicotinamide derived from vitamin B3, is a universal electron acceptor that is crucial in the process of cellular respiration. Another important universal electron acceptor is FAD, a flavin nucleotide from vitamin B2.
What are the products of cellular respiration?
The final end products of cellular respiration are ATP and H 2 O. Glycolysis produces two pyruvate molecules, four ATPs (a net of two ATP), two NADH, and two H 2 O. Therefore, without the presence of oxygen, glycolysis is the only process that can occur, and only two ATP molecules may be produced for each glucose molecule.
What are the rate-determining enzymes in cellular respiration?
There are three primary rate-determining enzymes in cellular respiration. These enzymes catalyze the rate-limiting steps, which are the slowest reactions in the series.
What are the steps of cellular respiration?
Steps of cellular respiration 1 (Glycolysis): Steps of cellular respiration 2 (Krebs cycle or Citric Acid Cycle): Steps of cellular respiration 3 (Electron Transport Chain): Catabolism of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates in the 3 steps of cellular respiration.
How does cellular respiration help the body?
Cellular respiration plays an important role in releasing the energy to break down glucose to make ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate). Adenosine Triphosphate, also knew as, ATP is an organic compound, which provides energy in living cells in the body. In this process, each molecule of glucose makes 38 molecules of ATP. Here is the equation below:
What is the name of the enzyme that splits glucose into two molecules?
A glucose molecule split by the enzymes and forms into two- molecules of pyruvate as known as pyruvic acid. When the two molecules of pyruvate formed, the energy released four molecules of ATP and the two-electron carriers NADH (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide + Hydrogen) made.
How many ATPs can be produced from glucose?
Glucose plays a vital role in the Glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, ETC (Electron Transport Chain). One molecule of glucose can potentially cause 38 molecules of ATPs from cellular respiration .
How do reactants transfer electrons from the electron carrier molecules from high to low transport chain?
Furthermore, these reactants will transfer the electrons from the electron carrier molecules from high to low transport chain by using active transport. The NADH and FADH2 discharged highly potential energy electrons. On the other hand, the electron transport chain is from the central membrane of the mitochondrion, which occupied the high potential energy electrons along the way.
What is the process of releasing glucose to make ATP?
Now, you might have a few questions about living things. Living things make use of this energy by a process called cellular respiration. Cellular respiration plays an important role in releasing the energy to break down glucose to make ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate).
What are the two electron carrier molecules?
Two molecules of ATPs need splitting glucose molecule and the two-electron carrier molecules are 2NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide). Next, four molecules of ADP+P (Adenosine Diphosphate) will become four ATP molecules.
Where do most of the steps of cellular respiration occur?
Most of the steps of cellular respiration take place in the mitochondria. Oxygen and glucose are both reactants in the process of cellular respiration.
What are the 4 stages of cellular respiration and where do they occur?
The cellular respiration process includes four basic stages or steps: Glycolysis, which occurs in all organisms, prokaryotic and eukaryotic; the bridge reaction, which stets the stage for aerobic respiration; and the Krebs cycle and the electron transport chain, oxygen-dependent pathways that occur in sequence in the …
What are the 3 steps of cellular respiration and where does each occur?
The three main stages of cellular respiration (aerobic) would include Glycolysis in the cytoplasm, the Kreb’s Cycle in the Mitochondrial Matrix and the Electron Transport Chain in the Mitochondrial Membrane.
Which of the following occurs during cellular respiration?
cellular respiration, the process by which organisms combine oxygen with foodstuff molecules, diverting the chemical energy in these substances into life-sustaining activities and discarding, as waste products, carbon dioxide and water.
Which part of cellular respiration takes place in the mitochondria?
The citric acid cycle (also known as the Krebs cycle) is the second pathway in cellular respiration, and it also takes place in the mitochondria.
What are the 3 major steps in cellular respiration?
The transition from glucose to ATP doesn’t take place all at once, though. Cellular respiration is made up of three sub-processes: glycolysis, the Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs Cycle), and the Electron Transport Chain (ETC).
What are the 3 main parts of cellular respiration?
The reactions of cellular respiration can be grouped into three main stages and an intermediate stage: glycolysis, Transformation of pyruvate, the Krebs cycle (also called the citric acid cycle), and Oxidative Phosphorylation.
How many ATP molecules are produced in cellular respiration?
When a molecule of glucose undergoes aerobic cellular respiration, 36 molecules of ATP are produced. Glucose is an energy-rich molecule. The breakdown of glucose results in the ...
Where does anaerobic cytosol occur?
This process is anaerobic (without oxygen) and occurs in the cytosol of cells.
What happens when oxygen is present in the mitochondria?
If oxygen is present, the pyruvate molecules enter the mitochondria and the process of aerobic cellular respiration can occur.
What percentage of the energy in glucose is converted into energy in ATP molecules?
This coupling of reactions results in about 40 percent of the chemical energy in the glucose molecule being transformed into energy in ATP molecules. The rest of the energy is waste thermal energy.
Where is oxidative phosphorylation located?
Oxidative phosphorylation relies on the electron transport chain. This is a series of molecules that are embedded on the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.
Where is the Krebs cycle located?
The Krebs cycle is a cyclical metabolic pathway located in the matrix of a mitochondrion. Only one ATP molecule results from one cycle of this metabolic pathway.
What is the breakdown of glucose?
The breakdown of glucose results in the formation of low-energy molecules and energy. ATP synthesis requires energy; it involves a series of endothermic reactions. The exothermic breakdown of glucose is coupled (linked) to the endothermic reactions involved in the synthesis of ATP.
Where does cellular respiration occur and what are its products?
Most of the steps of cellular respiration take place in the mitochondria. Oxygen and glucose are both reactants in the process of cellular respiration. The main product of cellular respiration is ATP; waste products include carbon dioxide and water.
Why does cellular respiration occur?
Cells do cellular respiration to extract energy from the bonds of glucose and other food molecules. Cells can store the extracted energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
What are the 4 stages of cellular respiration and where do they occur?
In eukaryotes, the 4 stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, transition reaction (pyruvate oxidation), the Krebs cycle (also known as the citric acid cycle), and oxidative phosphorylation through the electron transport chain.
Which cells in your body do cellular respiration?
All living cells must carry out cellular respiration. It can be aerobic respiration in the presence of oxygen or anaerobic respiration. Prokaryotic cells carry out cellular respiration within the cytoplasm or on the inner surfaces of the cells.
What is cellular respiration in biology?
cellular respiration, the process by which organisms combine oxygen with foodstuff molecules, diverting the chemical energy in these substances into life-sustaining activities and discarding, as waste products, carbon dioxide and water.
What is cellular respiration short answer?
Cellular respiration is the process by which organisms use oxygen to break down food molecules to get chemical energy for cell functions. Cellular respiration takes place in the cells of animals, plants, and fungi, and also in algae and other protists.
Why does cellular respiration occur in the mitochondria?
Cellular respiration takes place (mainly) in the mitochondria because it is the cell’s “powerhouse”. It is where the energy (ATP) is produced in the cell, and the process of cellular respiration is the way the cells form that energy.