What are thrombocytes formed from?
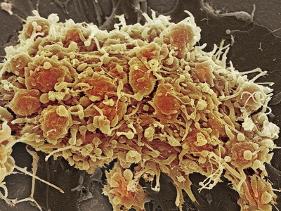
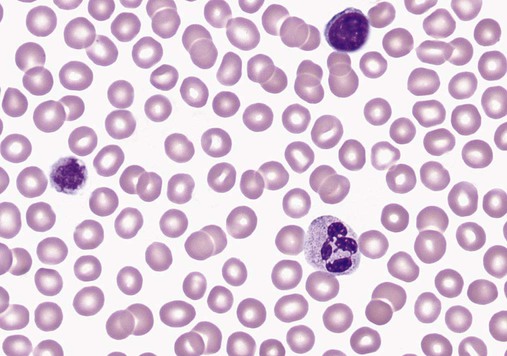
Platelets (thrombocytes) are derived from bone marrow megakaryocytes (see Bone Marrow) (Figure 20). In mice, platelets are often clustered together but may occur as individual platelets. In both species, the diameter of platelets seen on a blood smear ranges from 1 to 4 µm.
How do thrombocytes grow?
8 Things That Can Increase Your Blood Platelet CountEating more leafy greens. ... Eating more fatty fish. ... Increasing folate consumption. ... Avoiding alcohol. ... Eating more citrus. ... Consuming more iron-rich foods. ... Trying a chlorophyll supplement. ... Avoiding vitamin E and fish oil supplements.
What stimulates production of thrombocytes?
Thrombopoiesis is stimulated and regulated by the hormone thrombopoietin. Platelets have an average life span of five to ten days. Old platelets are destroyed by phagocytosis. The spleen holds a reservoir of additional platelets. Abnormal numbers of platelets result from problems in thrombopoiesis.
Where are thrombocytes made in the body?
Platelets, or thrombocytes, are small, colorless cell fragments in our blood that form clots and stop or prevent bleeding. Platelets are made in our bone marrow, the sponge-like tissue inside our bones.
What foods increase thrombocytes?
That being said, if you are looking for how to increase platelet counts naturally, then the list of foods below should help you to some extent.Milk. ... Green Leafy Vegetables: ... Papaya Leaf Extract: ... Pomegranate: ... Pumpkin: ... Wheatgrass: ... Vitamin B-12. ... Iron.More items...
What is the difference between platelet and Thrombocyte?
Platelets are made in your bone marrow along with your white and red blood cells. Your bone marrow is the spongy center inside your bones. Another name for platelets is thrombocytes. Healthcare providers usually call a clot a thrombus.
Why do platelets get destroyed?
Severe bacterial infections involving the blood (bacteremia) can destroy platelets. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. This is a rare condition that occurs when small blood clots suddenly form throughout your body, using up large numbers of platelets.
How long does it take for platelets to replenish?
within 72 hoursWhen you give platelets, your body immediately begins converting more stem cells into platelets and will replace the donated platelets within 72 hours.
Why do thrombocytes increase?
Some conditions that can raise your risk of thrombocytosis are listed below. Anemia: Iron-deficiency anemia and hemolytic anemia can cause thrombocytosis. Cancer: Many people who have high platelet counts also have cancer — mostly lung, gastrointestinal, breast, or ovarian cancer or lymphoma.
Can platelets grow?
People with a low platelet count may be able to improve their condition by eating specific foods and taking certain supplements. Foods that may be of benefit include those containing folate and those rich in vitamins B12, C, D, or K. Supplements that may help include chlorophyll and papaya leaf extract.
Do thrombocytes reproduce?
Summary: Scientists have discovered that platelets are able to reproduce themselves in the circulation. University of Utah researchers led an international team of scientists that is the first to report on the previously undescribed ability of platelets to reproduce themselves in the circulation.
What is the life cycle of thrombocytes?
Platelets, also called thrombocytes, are blood cells whose function is to stop bleeding. The average life span of circulating platelets is 7 to 10 days.
How do platelets help with hemostasis?
Thrombocytes (platelets) play an important role in hemostasis, by plugging and repairing damaged blood vessels, thus preventing blood loss. They also participate in a cascade of events that leads to blood clotting by triggering the release of a series of coagulation factors. In the first step, platelets are activated by various substances, including collagen from damaged tissue, as well as ADP (adenosine diphosphate) and thromboxane A2, secreted by activated platelets. Activation causes platelets to become adhesive, which facilitates their attachment to damaged tissues and to each other to form clumps. The penultimate step in coagulation is the formation of fibrin from fibrinogen. Fibrin filaments enmesh platelets and red and white blood cells to form a plug, which contracts to form a clot. Because this is a multi-step process, separate in vitro tests are often carried out for inhibition of platelet aggregation by collagen, ADP, arachidonic acid, or other substrates.
How long do platelets live?
They are small, irregularly shaped clear cell fragments, which are derived from megakaryocytes. The average lifespan of a platelet is approximately 5–9 days. Platelets are at the balance of bleeding or clotting events: when platelet numbers are low (thrombocytopenia), excessive bleeding can occur, and when platelet numbers are high (thrombocytosis), thrombosis can occur. Disorders that reduce the number of platelets but typically cause thrombosis instead of bleeding are heparin-induced thrombocytopenia and thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.
What is the time of activation of thromocytes?
Thrombocytes are also called platelets and are cell fragments which circulate within the blood with a life span of about 10 days. The middle of the night and morning hours are time of platelet activation, when they can be a causative factor of serious cardiovascular disease such as in myocardial infarction or stroke. Generally, they are useful in cases of injury and will adhere at the site of a wound or to the walls of damaged vessels to release chemicals which clot and close the wound or vessel. Immediately the 13 different clotting factors are triggered in a cascading sequence.
What is the function of fibrin filaments?
Fibrin filaments enmesh platelets and red and white blood cells to form a plug, which contracts to form a clot. Because this is a multi-step process, separate in vitro tests are often carried out for inhibition of platelet aggregation by collagen, ADP, arachidonic acid, or other substrates.
Why are platelets important for immune cells?
Because of their abundance in blood and their adhesive receptors, platelets are perfectly positioned to have an impact on immune cell extravasation. Platelet P-selectin interacts with leukocyte P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 (PSGL-1), allowing leukocytes to roll on adherent activated platelets.
How many platelets are released in a megakaryocyte?
Megakaryocytes mature in the bone marrow, and platelets are released into the circulation when megakaryocytes undergo fragmentation that results in the release of over 1,000 platelets per megakaryocyte. Mature platelets then bind and clear thrombopoietin from the circulation, closing the feedback loop.
What essential oils are antiplatelet?
Among all 23 essential oils, antiplatelet and clot dissolving activity correlated with their content of phenylpropanoid or phenolic constituents. Essential oils with a negligible action included clary sage, cypress, lemongrass, rosemary, Dalmatian sage Scots pine and turmeric ( Tognolini et al 2006 ).
How do megakaryocytes produce thrombocytes?
Megakaryocytes are stimulated to produce thrombocytes in response to thrombopoietin from the kidneys and liver. A single megakaryocyte can generate a couple of thousand platelets during its lifespan. There is constant turnover and production of thrombocytes, with upwards of 100 billion cells being generated daily. Reserve thrombocytes are contained within the spleen and sympathetic innervation stimulates the spleen to contract and release them into the bloodstream. Each thrombocyte only lives approximately 8-9 days. Macrophages in the spleen and liver will phagocytose old and effete thrombocytes. However, reductions in circulating thrombocytes stimulate the kidney and liver to produce more thrombopoietin, which leads to increased generation of thrombocytes from megakaryocytes.
What are platelets in mammals?
They aggregate, or clump, together at sites of hemorrhage or tissue injury. In mammals, they are anucleated (lacking a nucleus), discoid and biconvex in shape , and approximately 2-3 microns in diameter. In reptiles and birds, they are solely referred to as thrombocytes as they contain a nucleus, are more round to polyhedral, and often found in blood smears in aggregates. Thrombocytes represent pinched off portions of cytoplasm from megakaryocytes in the bone marrow and other hematopoietic organs (those that contain stem or progenitor cells for cells circulating in the blood, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and thrombocytes), such as the spleen.
What is the largest cell in the bone marrow?
Thrombocytes are derived from megakaryocytes, which in turn are derived from megakaryoblasts. Megakaryocytes are one of the largest cells in the bone marrow; they are approximately 50-100 microns in diameters. They are considered multi-segmented as their nucleus is lobated. While these cells contain a single nucleus, they may contain many copies of DNA, up to 32x normal complement of DNA as other somatic cells.
What blood cells are derived from megakaryoblasts?
This diagram shows the different blood cell lineage. As shown, megakaryocytes are derived from megakaryoblasts and will pinch off part of their cytoplasm to generate thrombocytes (platelets).
What is the term for a thrombocyte that is produced in the bloodstream?
Increased production of thrombocytes is called thrombocytosis and is less common than thrombocytopenia. It can cause arterial or venous thrombosis (blockage of the vessel). It is important to establish the underlying cause of this disorder and treat accordingly.
What is the main disease of thrombocytes?
The main disease of thrombocytes is thrombocytopenia, which is a reduction in the number of thrombocytes. This can be due to the following:
Where are thromocytes derived from?
Thrombocytes, also called platelets, are derived from megakaryocytes in the bone marrow and essential for blood clotting. This lesson discusses how they are formed, their life cycle, and function. Updated: 11/04/2020
What are Platelets (Thrombocytes)?
Platelets or thrombocytes are anucleated cells derived from the megakaryocytic cells in the bone marrow that, besides being one of the key players in maintaining hemostasis, are involved in developing non-hemostatic immune functions.
How do platelets affect the immune system?
Platelets also influence the adaptive immune responses as these express a wide range of immune receptors that can interact with immune cells as the vascular endothelium.
Why are platelets important for innate immunity?
The involvement of platelets in innate immunity is the result of their ability to release a group of inflammatory mediators as a result of activation. Besides, platelets can also function as effector cells by interacting with pathogens like bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoans.
What is platelet activation?
The activation of platelets is accompanied by the release of several molecules into the bloodstream. These molecules are capable of inducing inflammation or other immune responses in the body. Platelet Activation.
What is the size of a platelet?
Structure of Platelets (Thrombocytes) Platelets are anucleated cells with a diameter of 1-3 µm, but the size can increase up to 6 µm after activation. Platelets are often considered fragments of cells instead of an actual cell as these lack many components of a normal cell. The outermost region of the cell contains a membrane and its invaginations, ...
What are the organelles that make up platelets?
Even though platelets are anuclear, they contain cellular organelles like RNA, ribosomes, mitochondria, and granules that are essential for the function of the cell. Granules occurring in platelets are of three different types; α-granules, dense granules, and lysosomes. α-granules are the most abundant and largest granules occurring in ...
What are the most abundant and largest granules occurring in the platelets?
α-granules are the most abundant and largest granules occurring in the platelets. These contain platelet factors that are responsible for hemostasis. The dense granules are the smallest granules that appear as dense bodies under an electron microscope. These contain ADH, serotonin, and high levels of calcium.
What are the small, colorless cells that form clots and stop bleeding?
Platelets, or thrombocytes, are small, colorless cell fragments in our blood that form clots and stop or prevent bleeding. Platelets are made in our bone marrow, the sponge-like tissue inside our bones. Bone marrow contains stem cells that develop into red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
How many platelets are needed in a year?
Every 15 seconds someone needs platelets – that’s about 2 million units of platelets being transfused each year in the U.S. Since platelets must be used within 5 days of donation, platelet donors are constantly needed. Making a platelet-only donation means your generosity can help one, two, or even three patients!
How does platelet donation work?
In a platelet-only donation, blood is drawn from your arm into a machine. The platelets are separated from the other blood components, which are returned to you through your other arm. This cycle repeats several times.
Why is my bone marrow not making enough platelets?
This can be caused by certain cancers, such as Leukemia – and it can also be caused by cancer treatments.
What is bone marrow?
Bone marrow contains stem cells that develop into red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Platelets and other blood components are always needed. One donation could help save more than one life. Be a hero!
Why are platelets important?
Platelets control bleeding in our bodies, so they can be essential to surviving surgeries such as organ transplant, as well as fighting cancer, chronic diseases, and traumatic injuries.
Does chemotherapy cause low platelet count?
Low platelet count is a major side effect of cancer treatment. Some types of chemotherapy can damage bone marrow, reducing platelet production. ( This damage is usually temporary.) Other times, the cancer itself causes the problem. Leukemia and lymphoma can invade the bone marrow and prevent the patient’s body from producing the platelets it needs.