Does RNA contain genetic material?
RNA in humans does not act as a genetic material but play various other roles such as an adapter, enzyme, helps in protein synthesis, etc. RNA functions as a messenger for information to be transferred. Test your Knowledge on DNA and RNA! Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs.
Why does nature need RNA?
When living things first arose, they must have used a simpler system for creating the machinery they need. Very likely they used RNA for many of the things proteins and DNA do now. Gradually, those RNA based organisms found it useful to use bits of proteins (amino acids) and that, in turn, led to the evolution of our modern genetic machinery.
What does DNA have that RNA does not have?
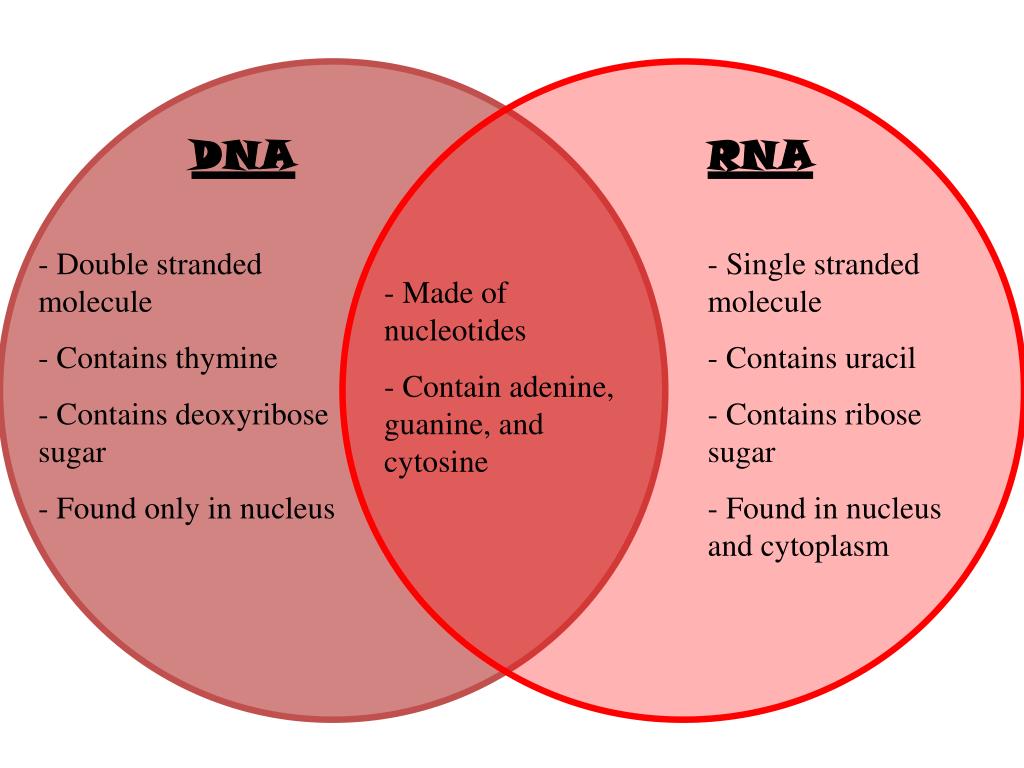
DNA is a double-stranded molecule, with two nucleotide strands consisting of a phosphate backbone, deoxyribose sugar, and has adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine as bases; whereas RNA is a ...
What are the 4 main differences between DNA and RNA?
Main Differences Between DNA and RNA. DNA is a double-stranded helix structure with long chains of nucleotides. Whereas, RNA molecules are single-stranded helix structures with shorter chains of nucleotides. The bases present in DNA are Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, and Cytosine. RNA also shares the same bases, but instead of Thymine is contains ...
Does RNA carries genetic information?
The two strands of DNA contain complementary information, so that one strand of DNA contains the information to specify the other strand. Normally, only one of the two DNA strands is copied to make RNA, in the process called transcription.
Where is genetic information carried?
Genetic information is carried in the linear sequence of nucleotides in DNA. Each molecule of DNA is a double helix formed from two complementary strands of nucleotides held together by hydrogen bonds between G-C and A-T base pairs.
What info does RNA carry?
Specifically, messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the protein blueprint from a cell's DNA to its ribosomes, which are the "machines" that drive protein synthesis. Transfer RNA (tRNA) then carries the appropriate amino acids into the ribosome for inclusion in the new protein.
Why is RNA a carrier of information?
RNA is considered a carrier of information because the DNA has the genetic codes, technically known as codons that consist of three nucleotides, to synthesize the amino acids that will be used to form the proteins necessary for cell and body functions.
What is the main carrier of genetic information?
Nucleic acid is the carrier of genetic information, and it is of two principal types: DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid).
Where are messenger RNAs made?
Messenger RNAs, also known as mRNA, are one of the types of RNA that are found in the cell. This particular one, like most RNAs, are made in the nucleus and then exported to the cytoplasm where the translation machinery, the machinery that actually makes proteins, binds to these mRNA molecules and reads the code on the mRNA to make a specific protein. So in general, one gene, the DNA for one gene, can be transcribed into an mRNA molecule that will end up making one specific protein.
What is messenger RNA?
Messenger RNA (mRNA) =. Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a single-stranded RNA molecule that is complementary to one of the DNA strands of a gene.
What organelle reads the amino acid sequence?
During protein synthesis, an organelle called a ribosome moves along the mRNA, reads its base sequence, and uses the genetic code to translate each three-base triplet, or codon, into its corresponding amino acid.
What is the process of RNA?
Normally, only one of the two DNA strands is copied to make RNA, in the process called transcription.
What is the transfer of RNA?
Transfer RNA. Transfer RNA (tRNA) is the adaptor between mRNA and protein information. tRNA provides the specificity for the genetic code, so each codon doesn't have to specify a particular amino acid. Transfer RNA contains two active sites. The anticodon consists of three nucleotides that form base‐pairs with the three nucleotides of a codon.
What are ribosomes made of?
Ribosomes are large particles composed of about two‐thirds RNA and one‐third protein by weight . Ribosomes facilitate several reactions: Initiation of the synthesis of a protein. Base‐pairing between the codon in mRNA and the anticodon in tRNA. Synthesis of the peptide bond.
How many codons are in a protein?
The mRNA sequence is read in groups of three, called codons. Because there are four bases in DNA or RNA, there are 64 (4 3) codons.
What are the three codons in the genetic code?
In other words, the genetic code is redundant. The code also contains punctuation marks. Three codons, UAG, UAA, and UGA, specify stop signals (like the periods in a sentence). One amino acid, methionine, coded by AUG, is used to initiate each protein (like a capital letter at the beginning of a sentence).
How many subunits are in ribosomes?
Ribosomes consist of two subunits: a small subunit primarily involved with initiation, codon‐anticodon interaction, and protein release; and a large subunit primarily concerned with the actual synthetic process: Previous Introduction to Biological Energy Flow. Next Base Pairing and the Central Dogma.
Is RNA disposable?
Unlike DNA, RNA is disposable: Many copies of an RNA sequence are made from a single DNA sequence. These copies are used and recycled back to their constituent nucleotides. This allows the cell to respond quickly to changing conditions by transcribing different sequences into RNA.
How would RNA have evolved?
They would have consisted of little more than a simple membraneenclosing a set of self-replicating molecules and a few other components required to provide the materials and energy for their replication. If the evolutionary speculations about RNA outlined above are correct, these early cells would also have differed fundamentally from the cells we know today in having their hereditary information stored in RNA rather than in DNA(Figure 6-101).
How did the transition between pre-RNA and RNA occur?
The transition between the pre-RNAworld and the RNA world would have occurred through the synthesis of RNA using one of these simpler compounds as both templateand catalyst. The plausibility of this scheme is supported by laboratory experiments showing that one of these simpler forms (PNA—see Figure 6-93) can act as a template for the synthesis of complementaryRNA molecules, because the overall geometry of the bases is similar in the two molecules. Presumably, pre-RNA polymers also catalyzed the formation of ribonucleotide precursors from simpler molecules. Once the first RNA molecules had been produced, they could have diversified gradually to take over the functions originally carried out by the pre-RNA polymers, leading eventually to the postulated RNA world.
Why are polynucleotides self-replicating?
Therefore, certain polynucleotides will be especially successful in any self-replicating mixture. Because errors inevitably occur in any copying process, new variant sequences of these polynucleotides will be generated over time.
What is RNA catalyzed?
An RNA molecule that can catalyze its own synthesis. This hypothetical process would require catalysis of the production of both a second RNA strand of complementary nucleotide sequence and the use of this second RNA molecule as a template to form many (more...)
How were membrane bound cells formed?
Presumably, the first membrane-bounded cells were formed by the spontaneous assembly of a set of amphipathicmolecules, enclosing a self-replicating mixture of RNA(or pre-RNA) and other molecules. It is not clear at what point in the evolution of biological catalysts this first occurred. In any case, once RNA molecules were sealed within a closed membrane, they could begin to evolve in earnest as carriers of genetic instructions: they could be selected not merely on the basis of their own structure, but also according to their effect on the other molecules in the same compartment. The nucleotidesequences of the RNA molecules could now be expressed in the character of a unitary living cell.
How did RNAarose before DNA?
Evidence that RNAarose before DNAin evolution can be found in the chemical differences between them. Ribose, like glucoseand other simple carbohydrates, can be formed from formaldehyde (HCHO), a simple chemical which is readily produced in laboratory experiments that attempt to simulate conditions on the primitive Earth. The sugardeoxyribose is harder to make, and in present-day cells it is produced from ribose in a reactioncatalyzed by a proteinenzyme, suggesting that ribose predates deoxyribose in cells. Presumably, DNA appeared on the scene later, but then proved more suitable than RNA as a permanent repository of genetic information. In particular, the deoxyribose in its sugar-phosphate backbone makes chains of DNA chemically more stable than chains of RNA, so that much greater lengths of DNA can be maintained without breakage.
What are the red rings in RNA?
Common elements of RNA secondary structure. Conventional, complementary base-pairing interactions are indicated by red“rungs” in double-hel ical portions of the RNA.
Who developed the idea to explain how DNA and RNA related in protein production?
James Watson and Francis Crick developed the idea to explain how DNA and RNA related in protein production.
Who is the scientist who worked on the Rous sarcoma virus?
David Baltimore and Howard Temin explain work on the Rous sarcoma virus.
