
What is the location and function of the Basil nuclei?
The basal ganglia, or basal nuclei, are a group of subcortical structures found deep within the white matter of the brain. They form a part of the extrapyramidal motor system and work in tandem with the pyramidal and limbic systems.
How is the basal ganglia connected to the prefrontal cortex?
While the basal ganglia are primarily involved in movement, they are also connected to the prefrontal cortex. Since the prefrontal cortex helps regulate our behavior, it seems that the basal ganglia may play a role in that as well. This explains why many people with basal ganglia damage develop obsessive-compulsive disorder.
What is the function of dorsal root ganglia?
The dorsal nerve root[3]:
- Controls pain (nociception) and temperature sensations
- It lowers the voltage threshold needed and consequently allows it to fire action potentials; this occurs when a mechanical stimulus compresses the DRG.
- Can be affected by traumatic injury, degenerative disc disease, a herniated disc, bulging disc, and/or other spinal abnormalities
What does the basal ganglia control in the brain?
- The subcortical basal ganglia nuclei receive information from the cortex and send output to the thalamus
- Motor control through the basal ganglia occurs through both the direct and indirect pathways
- Disinhibition is when an inhibitory region is itself inhibited
What transmits signals to basal ganglia?
The striatum is the main recipient of afferents to the basal ganglia (Figure 4.2). These excitatory afferents arise from the entire cerebral cortex and from the intralaminar nuclei of the thalamus (primarily the centromedian nucleus and parafascicularis nucleus).
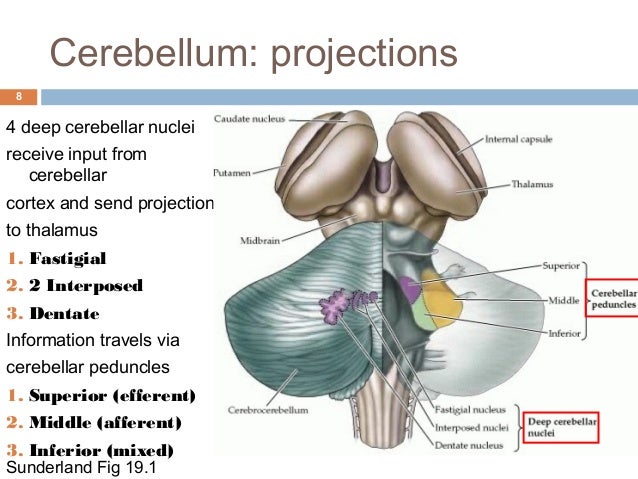
Does the basal ganglia receive input from the cerebellum?
The basal ganglia and cerebellum are major subcortical structures that influence not only movement, but putatively also cognition and affect (1, 2). Both structures receive input from and send output to the cerebral cortex. Thus, the basal ganglia and cerebellum form multisynaptic loops with the cerebral cortex.
What is the direct pathway of the basal ganglia?
The direct pathway starts from the cortex and projects to the striatum (caudate nucleus and putamen) with excitatory glutamatergic (glu) neurons. The neurons from the striatum, which are inhibitory GABAergic, send their axons to the medial (internal) globus pallidus and substantia nigra, pars reticulata (SNr).
Which part of the brain receives and interprets sensory information?
Parietal lobes: The parietal lobes are near the center of your brain. They receive and interpret signals from other parts of your brain. This part of your brain integrates many sensory inputs so that you can understand your environment and the state of your body.
How are the cerebellum and the basal ganglia involved in memory?
The cerebellum and basal ganglia are parts of the brain network dedicated to implicit memory formation. The cerebellum is important for storing classically conditioned memories. The basal ganglia are involved in motor movement and help form procedural memories for skills.
How does the basal ganglia differ from the cerebellum?
The basal ganglia are specialized for reinforcement (reward-based) learning, guided by the reward signals from midbrain dopaminergic neurons. The cerebellum is specialized for supervised (error-based) learning, guided by error signals from the inferior olive.
Whats the difference between the cerebellum and the basal ganglia?
The key difference between basal ganglia and cerebellum is that basal ganglia are found deep within the cerebral hemispheres while cerebellum is found below the pones attached to the bottom of the brain. The brain is a complex structure. It is one of the two components of the central nervous system.
Is the basal ganglia in the cerebrum?
The basal ganglia are a group of structures found deep within the cerebral hemispheres. The structures generally included in the basal ganglia are the caudate nucleus, putamen, and globus pallidus in the cerebrum, the substantia nigra in the midbrain, and the subthalamic nucleus in the diencephalon.
What is the function of the basal ganglia?
The function of the basal ganglia is to fine-tune the voluntary movements. They do so by receiving the impulses for the upcoming movement from the cerebral cortex, which they process and adjust. They convey their instructions to the thalamus, which then relays this information back to the cortex.
How many nuclei are in the basal ganglia?
The basal ganglia consist of five pair s of nuclei: caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus, subthalamic nucleus, and substantia nigra. These nuclei are grouped into broader clusters; Striatum, which further consists of the: Dorsal striatum, made by the caudate nucleus and putamen.
Which part of the brain receives excitatory inputs from the cerebral cortex?
The striatum is the main input unit of the basal ganglia. It receives excitatory glutamatergic inputs from the cerebral cortex, whose synapsing pattern reflects the topography of the cortex. This means that the caudal parts of the cortex project to the caudal part of the striatum, while the rostral parts of the cortex project to the rostral part of the striatum.
Where is the striatum located?
The striatum is a complex nucleus located deep in subcortical structures of the forebrain, inside the insular lobe .#N#In the introduction, we mentioned that the striatum is composed of the dorsal and ventral parts. The ventral striatum is considered part of the limbic system, thus we will not describe it furthermore.
Which part of the brain controls voluntary motor activity?
The basal ganglia are one of the components in the neural chain that controls the voluntary motor activity. The supreme component of this chain is the cerebral cortex. It generates the commands that define the motor activity of all skeletal muscles in the body.
Where is the caudate nucleus located?
The caudate nucleus is an elongated C-shaped nucleus that lies anterior to the thalamus, just lateral to the lateral ventricles and medial to the internal capsule.
Is the subthalamic nucleus anatomical?
The subthalamic nucleus is not an anatomical part of the basal ganglia. However, given their functional connection, the subthalamus is listed as a functional part of the basal ganglia.
How do basal ganglia receive information?
The basal ganglia receive information from the cerebral cortex and thalamus through input nuclei. After the information has been processed, it is passed along to intrinsic nuclei and sent to output nuclei. From the output nuclei, the information is sent to the thalamus. The thalamus passes the information on to the cerebral cortex.
What is the basal ganglia?
The basal ganglia consist of the corpus striatum (a major group of basal ganglia nuclei) and related nuclei. The basal ganglia are involved primarily in processing movement-related information. They also process information related to emotions, motivations, and cognitive functions. Basal ganglia dysfunction is associated with a number ...
What is the effect of Gaba on the pallidus?
GABA has an inhibitory effect on motor function . The external segments of the pallidus are intrinsic nuclei, relaying information between other basal ganglia nuclei and internal segments of the pallidus. The globus pallidus is involved in the regulation of voluntary movement.
What are some examples of basal ganglia disorders?
Examples of these disorders include Parkinson's disease, Huntington disease, dystonia ( involuntary muscle contractions), Tourette syndrome, and multiple system atrophy ( neurodegenerative disorder). Basal ganglia disorders are commonly the result of damage to the deep brain structures of the basal ganglia.
Why is my basal ganglia slow to walk?
This damage may be caused by factors such as head injury, drug overdose, carbon monoxide poisoning, tumors, heavy metal poisoning, stroke, or liver disease. Individuals with basal ganglia dysfunction may exhibit difficulty in walking with uncontrolled or slow movement.
Where are the globus pallidus located?
Globus Pallidus: These paired nuclei (one in each hemisphere) are located near the caudate nucleus and putamen. The globus pallidus is divided into internal and external segments and acts as one of the major output nuclei of the basal ganglia. It sends information from basal ganglia nuclei to the thalamus.
Which segment of the basal ganglia is responsible for motor control?
The pars reticulata segment forms one of the major inhibitory outputs of the basal ganglia and assists in the regulation of eye movements. The pars compacta segment is composed of intrinsic nuclei that relay information between input and output sources. It is involved mainly in motor control and coordination.
Where does information from the basal ganglia go?
Information that exits the basal ganglia goes to the thalamus, primarily the ventroanterior and ventromedial motor thalamic nuclei for the motor pathway and the mediodorsal thalamic nucleus for the limbic pathway, and then is sent back to the appropriate part of the cortex.
Where are the basal ganglia located?
Basal ganglia, group of nuclei (clusters of neurons) in the brain that are located deep beneath the cerebral cortex (the highly convoluted outer layer of the brain).
What is the input nucleus of the basal ganglia?
The major input nucleus of the basal ganglia is the striatum (collectively including the dorsal and ventral divisions), which receives information from almost all areas of the cortex. The dorsal striatum (upper region of the striatum) receives information from areas below the cortex (e.g., the midbrain) via the thalamus. In the motor circuit the subthalamic nucleus serves as an input nucleus, receiving information from the cortex and thalamus and influencing the conventional route of basal ganglia outflow from the striatum to the output nuclei of the thalamus. The output nuclei of the basal ganglia are the globus pallidus internus and substantia nigra pars reticulata in the motor pathway and the ventral pallidum in the limbic pathway. Information that exits the basal ganglia goes to the thalamus, primarily the ventroanterior and ventromedial motor thalamic nuclei for the motor pathway and the mediodorsal thalamic nucleus for the limbic pathway, and then is sent back to the appropriate part of the cortex.
How do basal ganglia work?
Although the basal ganglia are a distinct part of the motor system, they appear to work in concert with the pyramidal motor pathway—the path that conducts signals for action directly along nerve tracts that descend from the cerebral cortex to the motor neurons that activate skeletal muscles. The basal ganglia refine action signals from the cortex, thereby ensuring that an appropriate motor plan is communicated to the muscles. Unlike the pyramidal pathway, the basal ganglia process information indirectly in a set of loops, whereby they receive input from the cortex and return it to the cortex via the thalamus. In that way the basal ganglia modify the timing and amount of activity that leaves the cortex and travels down the pyramidal pathway, amplifying activity that leads to a positive outcome and suppressing activity that leads to a deleterious outcome in a particular situation.
What is the basal ganglia?
anatomy. ... (Show more) ... (Show more) Basal ganglia, group of nuclei (clusters of neurons) in the brain that are located deep beneath the cerebral cortex (the highly convoluted outer layer of the brain). The basal ganglia specialize in processing information on movement and in fine-tuning the activity of brain circuits ...
What are the functions of parallel pathways in the basal ganglia?
Parallel pathways within the basal ganglia circuits facilitate signal promotion and signal inhibition. Neighbouring pathways carrying information about elements of the same desired movement successively amplify the promoted signal as it progresses through the basal ganglia. More often, however, neighbouring pathways act to reduce unwanted signals, ensuring that an accurate, precise, and optimized action plan is developed. In the absence of action selection, all motor plans are promoted and many muscles around the body are activated, leading to a failure to execute desired actions.
Which part of the brain controls the signaling pathways?
The striatum, which serves as a gateway for the regulation of signals through the basal ganglia during the learning of actions and the selection of desirable actions, has the most-complex signaling architecture. In addition to receiving vast external excitatory input from the cortex and thalamus, it also contains several types of interneurons (neurons that connect sensory and motor circuits) and some of the highest levels in the brain of the neurochemicals dopamine and acetylcholine. Collectively, these substances modulate the way in which excitatory inputs are processed and contribute to the final output from the striatum.
Where does the information from the basal ganglia come from?
The principal source of input to the basal ganglia is from the cerebral cortex. This input is glumatergic and therefore, excitatory.
What are the functions of the basal ganglia?
There are multiple circuits that pass through the basal ganglia: 1 The motor circuit, which plays a role in voluntary movement 2 The oculomotor circuit, which plays a role in eye movement 3 The associative circuit, which plays a role in executive functions like behavioral inhibition (preventing impulsive behaviors) planning and problem solving, and mediating socially appropriate behaviors 4 The limbic or emotional circuit, which plays a role in the processing of emotion and reward.
What is the primary output region of the basal ganglia?
The primary output region of the basal ganglia is the internal segment of the globus pallidus. This region sends inhibitory GABAergic projections to nuclei in the thalamus. This inhibitory output has a tonic, constant firing rate, which allows the basal ganglia output to both increase and decrease depending on the situation. The thalamus then projects back out to the cerebral cortex, primarily to motor areas.
What are the subcortical structures located at the base of the forebrain?
The basal ganglia are subcortical structures located at the base of the forebrain. They are comprised of the caudate and putamen, which both make up the striatum, as well as the globus pallidus, substantia nigra, and subthalamic nucleus.
Which pathway is activated when input from the cortex or substantia nigra increases in intensity?
Activation of the Direct Pathway. When input from either the cortex or substantia nigra increases in intensity, the direct pathway is activated. The neurons in the striatum involved in the direct pathway express the D1 metabotropic dopamine receptor, and the activation of this receptor is excitatory.
Which part of the brain sends glutamate projections to the thalamus?
Figure 27.7. The cortex sends glutamate projections to the striatum. The substantia nigra sends dopamine projections to the striatum, which are excitatory, acting on D1 receptors in the neurons involved in the direct pathway. The striatum sends GABA projections to the internal segment of the globus pallidus (GPi). The GPi sends GABA projections to the thalamus. The thalamus sends glutamate projections to the cortex. ‘Basal Ganglia Direct Pathway – Text’ by Casey Henley is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial Share-Alike (CC BY-NC-SA) 4.0 International License.
Which segment of the globus pallidus sends glutamate projections to the cortex?
Figure 27.5. The internal segment of the globus pallidus sends GABA projections to the thalamus. The thalamus sends glutamate projections to the cortex. ‘Basal Ganglia Output – Text’ by Casey Henley is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial Share-Alike (CC BY-NC-SA) 4.0 International License.
What are the functions of the basal ganglia?
The most prominent functions of the. basal ganglia include: Represents the accessory motor system. Mediates between neocortical motor centers and the "elderly" motor areas of the brainstem Selects the purposeful and desired motor activity and suppresses unwanted movements.
Which part of the brain gives projections to the basal ganglia?
Portions of the cerebral cortex that give projections to the basal ganglia. Parts of the cerebellum that give projections to the basal ganglia. Parts of the reticular formation that are connected to the basal ganglia and cerebral cortex. Thalamus nuclei associated with the basal ganglia and reticular formation.
What is the brain capsule?
Almost all the motor and sensory nerve fibers that connect the cerebral cortex to the spinal cord pass between the major masses of the basal ganglia ( nucleus caudatus and putamen) and are called the internal brain capsule.
What is the role of the extrapyramidal system?
The role of the extrapyramidal system is to control automatic movements, skeletal muscle tone, and maintenance of postural reflexes. The basal ganglia exert their role in motor control through constant interaction with the c erebral cortex and the corticospinal pathway ( 1 ).
What is the main circuit of the basal ganglia system?
Namely, the main circuit of the basal ganglia system involves a huge number of connections between the basal ganglia themselves, as well as numerous entry and exit pathways between the motor regions of the brain and the basal ganglia . The most prominent functions of the. basal ganglia include:
What is the dorsal part of the striped body?
The striped body is divided into dorsal and ventral parts. The dorsal part is associated with the somatosensory and somatomotoric systems, and the ventral one is associated with the limbic system. All information aimed at the basal ganglia goes through the striatum.
Which part of the brain is responsible for motion planning?
The basal ganglia are a set of brain structures located beneath the cerebral cortex that receive information from the cortex, transmit it to the motor centers, and return it to the part of the cerebral cortex that is in charge of motion planning.
Where is the basal ganglia located?
The basal ganglia are located in the inferior (lower/-est or underneath) portion of the brain. Where you should exercise caution, however, is with the term “ganglia.”. Ganglia is said to be a bit of a misnomer in that this term refers to an assemblage of neurons specifically in the peripheral nervous system.
What is the significance of the basal ganglia?
The basal ganglia are an assemblage of structures positioned within the cerebral hemispheres. Within the basal ganglia are even more fun things! Firstly, note that the basal ganglia extend over more than just the cerebrum.
What is the role of the basal ganglia in the skeletal muscle?
This pathway functions by conducting signals for action (movement) to the nerves that connect the cerebral cortex to the motor neurons, which then activate the skeletal muscles.
Why are basal ganglia important?
As you’ve seen, the basal ganglia are heavily involved in many different functions that are vital to survival and human cognition. This is why any damage to the basal ganglia can result in many different types of neurological disorders.
What is the effect of repeated exposure to a stimulus on the basal ganglia?
With repeated exposure to a certain stimulus, a person is able to refine their reaction and the basal ganglia work to increase the frequency with which this action is performed.
Which pathway excites the thalamic structures that then excite the cortical neurons?
The direct pathway excites the thalamic structures which then excite the cortical neurons; whereas the indirect pathway inhibits thalamic neurons, suppressing their ability to excite motor cortex neurons. The standard functioning of the basal ganglia requires the perfect balance between these two pathways.
Which ganglia control muscle memory?
The basal ganglia play their role in muscle memory because they can directly control the intensification and suppression of activities based on their outcome.
Where is the basal ganglia located?
The basal ganglia are situated at the base of the forebrain and top of the midbrain. Basal ganglia are strongly interconnected with the cerebral cortex, thalamus, and brainstem, as well as several other brain areas.
What is the role of the basal ganglia in the brain?
Experimental studies show that the basal ganglia exert an inhibitory influence on a number of motor systems, and that a release of this inhibition permits a motor system to become active. The "behavior switching" that takes place within the basal ganglia is influenced by signals from many parts of the brain, including the prefrontal cortex, which plays a key role in executive functions. It has also been hypothesized that the basal ganglia are not only responsible for motor action selection, but also for the selection of more cognitive actions. Computational models of action selection in the basal ganglia incorporate this.
What is the function of the subthalamic nucleus?
The role of the subthalamic nucleus is to stimulate the SNr-GPi complex and it is part of the indirect pathway. The subthalamic nucleus receives inhibitory input from the external part of the globus pallidus and sends excitatory input to the GPi.
What are the components of the basal ganglia?
The main components of the basal ganglia – as defined functionally – are the striatum, consisting of both the dorsal striatum ( caudate nucleus and putamen) and the ventral striatum ( nucleus accumbens and olfactory tubercle ), the globus pallidus, the ventral pallidum, the substantia nigra, and the subthalamic nucleus.
What is the TA2 ganglia?
TA2. 5559. FMA. 84013. Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy. The basal ganglia (or basal nuclei) are a group of subcortical nuclei, of varied origin, in the brains of vertebrates. In humans, and some primates, there are some differences, mainly in the division of the globus pallidus into an external and internal region, ...
Which part of the brain receives input from the basal ganglia?
The largest component, the striatum (dorsal and ventral), receives input from many brain areas beyond the basal ganglia, but only sends output to other components of the basal ganglia. The globus pallidus receives input from the striatum, and sends inhibitory output to a number of motor-related areas.
Which ganglia regulates what enters and what doesn't enter working memory?
The basal ganglia has been proposed to gate what enters and what doesn't enter working memory. One hypothesis proposes that the direct pathway (Go, or excitatory) allows information into the PFC, where it stays independent of the pathway, however another theory proposes that in order for information to stay in the PFC the direct pathway needs to continue reverberating. The short indirect pathway has been proposed to, in a direct push pull antagonism with the direct pathway, close the gate to the PFC. Together these mechanisms regulate working memory focus.
