What are the steps in the citric acid cycle?
Feb 14, 2020 · Where does the citric acid cycle occur? Overview of the citric acid cycle. In eukaryotes, the citric acid cycle takes place in the matrix of the mitochondria, just like the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoAstart text, C, o, A, end text. In prokaryotes, these steps both take place in the cytoplasm. Click to see full answer.
Where does the Krebs cycle occur?
Jun 21, 2020 · In prokaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the cytoplasm; in eukaryotic cells the citric acid cycle takes place in the matrix of the mitochondria. Popular Trending
Where does Krebs cycle take place?
Practice: Krebs (citric acid) cycle and oxidative phosphorylation questions. Practice: Oxidative phosphorylation questions. The citric acid cycle. This is the currently selected item. Krebs / citric acid cycle. Regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase. Regulation of Krebs-TCA cycle. Electron transport chain.
What molecule enters the citric acid cycle?
Where does citric acid cycle occur occur?
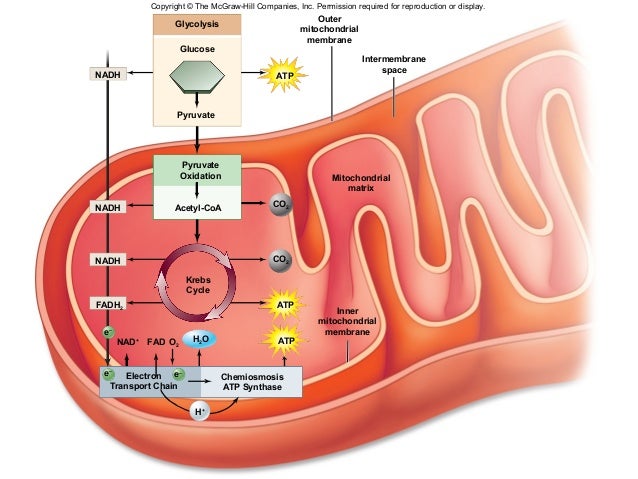
the mitochondriaThe TCA cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or Krebs cycle, occurs in the mitochondria and provides large amounts of energy in aerobic conditions by donating electrons to three NADH and one FADH (flavin adenine dinucleotide), which donate electrons to the electron transport chain, creating the proton gradient ...
Where does citric acid cycle occur quizlet?
The Citric acid cycle occurs in the mitochondria. The most important structural feature of mitochondria are the inner membrane, the matrix (where the enzymes are dissolved), and the cristae (the infoldings of the inner membrane).
Does the citric acid cycle occur in the cytoplasm?
In prokaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the cytoplasm; in eukaryotic cells the citric acid cycle takes place in the matrix of the mitochondria.Apr 9, 2022
Where does the citric acid cycle occur in eukaryotes quizlet?
Where do the reactions of the citric acid cycle occur in eukaryotic cells? The citric acid cycle, which takes place in mitochondria, completes the degradation of glucose.
Where does the citric acid cycle occur in the mitochondria quizlet?
The Citric Acid Cycle occurs in the inner mitochondrial matrix.
Where does the citric acid cycle occur inside the mitochondria?
Explanation: The citric acid cycle takes place in the mitochondrial matrix. Glycolysis takes place in the cytosol, and the electron transport chain involves both the intermembrane space and the inner mitochondrial membrane. Pyruvate from glycolysis is transported into the mitochondrial matrix for the citric acid cycle.
What occurs in the first step of the citric acid cycle?
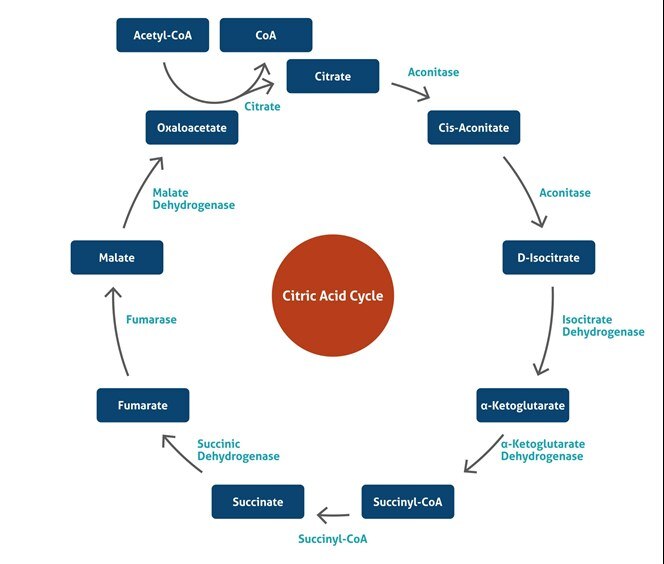
The citric acid cycle utilizes mitochondrial enzymes. The first step is fusion of the acetyl group of acetyl-CoA with oxaloacetate, catalyzed by citrate synthase. CoA-SH and heat are released and citrate is produced.
Why citric acid cycle is called TCA cycle?
Citric acid is a so-called tricarboxylic acid, containing three carboxyl groups (COOH). Hence the Krebs cycle is sometimes referred to as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle.
What is the Krebs Cycle?
Also known as the citric acid cycle, the Krebs cycle is a chain of reactions occurring in the mitochondria, through which almost all living cells p...
How Many ATPs are Produced In the Krebs Cycle?
2 ATPs are produced in one Krebs Cycle. For complete oxidation of a glucose molecule, the Krebs cycle yields 4 CO2, 6NADH, 2 FADH2 and 2 ATPs.
Where Does Krebs Cycle Occur?
Mitochondrial matrix. In all eukaryotes, mitochondria are the site where the Krebs cycle takes place. The cycle takes place in a mitochondrial mat...
How The Krebs Cycle Works?
It is an eight-step process 1) Condensation of acetyl CoA with oxaloacetate (4C) forming citrate (6C), coenzyme A is released. 2) Conversion of Ci...
Why Is Krebs Cycle Called As Amphibolic Pathway?
It is called amphibolic as in the Krebs cycle both catabolism and anabolism take place. The amphibolic pathway indicates the one involving both cat...
How Many NADH are Produced In The Krebs Cycle?
3 NADH molecules In one turn of the Krebs cycle, 3 molecules of NADH are produced. For complete oxidation of a glucose molecule, Krebs cycle yield...
What Is The Krebs Cycle Also Known As?
Krebs cycle is also known as Citric acid cycle (CAC) or TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle)
Why Krebs Cycle Is Called the Citric Acid Cycle?
Krebs cycle is also referred to as the Citric Acid Cycle. Citric acid is the first product formed in the cycle.
What is the citric acid cycle?
The citric acid cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a series of chemical reactions in the cell that breaks down food molecules into carbon dioxide, water, and energy. In plants and animals (eukaryotes), these reactions take place in the matrix of the mitochondria of the cell as part of cellular respiration.
What happens to the citric acid molecule at the end of the cycle?
At the end of the cycle, a molecule of oxaloacetate remains, which can combine with another acetyl group to begin the cycle again.
What are the functions of the Krebs cycle?
The Krebs cycle is the key set of reactions for aerobic cellular respiration. Some of the important functions of the cycle include: 1 It is used to obtain chemical energy from proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. ATP is the energy molecule that is produced. The net ATP gain is 2 ATP per cycle (compared with 2 ATP for glycolysis, 28 ATP for oxidative phosphorylation, and 2 ATP for fermentation). In other words, the Krebs cycle connects fat, protein, and carbohydrate metabolism. 2 The cycle can be used to synthesize precursors for amino acids. 3 The reactions produce the molecule NADH, which is a reducing agent used in a variety of biochemical reactions. 4 The citric acid cycle reduces flavin adenine dinucleotide (FADH), another source of energy.
What is the name of the reaction that occurs in citric acid?
Another name for citric acid is tricarboxylic acid, so the set of reactions is sometimes called the tricarboxylic acid cycle or TCA cycle.
What is the name of the compound that breaks down food in the citric acid cycle?
At the start of the citric acid cycle, an acetyl group combines with a four-carbon molecule called oxaloacetate to make a six-carbon compound, citric acid. During the cycle, the citric acid molecule is rearranged and stripped of two ...
What is the Krebs cycle?
The Krebs cycle is the key set of reactions for aerobic cellular respiration. Some of the important functions of the cycle include: It is used to obtain chemical energy from proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. ATP is the energy molecule that is produced.
What is the function of itric acid?
It is a weak acid found in citrus fruits and used as a natural preservative and to impart a sour flavoring. LAGUNA DESIGN / Getty Images.
What are the components of the citric acid cycle?
Vitamins play an important role in the citric acid cycle. Riboflavin, niacin, thiamin and pantothenic acid as a part of various enzymes cofactors (FAD, NAD) and coenzyme A. Regulation of Krebs cycle depends on the supply of NAD + and utilization of ATP in physical and chemical work.
What is the role of vitamin in the citric acid cycle?
It plays an important role in gluconeogenesis and lipogenesis and interconversion of amino acids. Many intermediate compounds are used in the synthesis of amino acids, nucleotides, cytochromes and chlorophylls, etc. Vitamins play an important role in the citric acid cycle.
What is the role of fatty acids in the Krebs cycle?
Fatty acids undergo 𝞫-oxidation to form acetyl CoA, which enters the Krebs cycle. It is the major source of ATP production in the cells. A large amount of energy is produced after complete oxidation of nutrients. It plays an important role in gluconeogenesis and lipogenesis and interconversion of amino acids.
What reactants are produced in the Krebs cycle?
Krebs cycle reactants: Acetyl CoA , which is produced from the end product of glycolysis, i.e. pyruvate and it condenses with 4 carbon oxaloacetate, which is generated back in the Krebs cycle
What is the first step in the formation of acetyl CoA?
Step 1: The first step is the condensation of acetyl CoA with 4-carbon compound oxaloacetate to form 6C citrate, coenzyme A is released. The reaction is catalysed by citrate synthase. Step 2: Citrate is converted to its isomer, isocitrate. The enzyme aconitase catalyses this reaction.
How many steps are there in acetyl-CoA?
It is a series of eight-step processes, where the acetyl group of acetyl-CoA is oxidised to form two molecules of CO 2 and in the process, one ATP is produced. Reduced high energy compounds, NADH and FADH 2 are also produced.
What is the Krebs cycle?
Krebs cycle or Citric acid cycle is the final pathway of oxidation of glucose, fats and amino acids. Many animals are dependent on nutrients other than glucose as an energy source. Amino acids (metabolic product of proteins) are deaminated and get converted to pyruvate and other intermediates of the Krebs cycle.
Where does the citric acid cycle take place?
In prokaryotic cells, the citric acid cycle occurs in the cytoplasm; in eukaryotic cells the citric acid cycle takes place in the matrix of the mitochondria. Click to see full answer.
Where does glycolysis take place?
Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm. Within the mitochondrion, the citric acid cycle occurs in the mitochondrial matrix, and oxidative metabolism occurs at the internal folded mitochondrial membranes (cristae).
Where does glycolysis take place in eukaryotic cells?
Both types of metabolism share the initial pathway of glycolysis, but aerobic metabolism continues with the Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. In eukaryotic cells, the post-glycolytic reactions take place in the mitochondria, while in prokaryotic cells, these reactions take place in the cytoplasm. Likewise, where does glycolysis take place ...
What is the end product of glycolysis?
The net end products of glycolysis are two Pyruvate, two NADH, and two ATP (A special note on the "two" ATP later).
Where are the products of the citric acid cycle made?
These products from the citric acid cycle are made in the mitochondria of your cells.. Step 4: Oxidative phosphorylation.
Which step of the citric acid cycle produces ATP?
Oxidative phosphorylation, the process where electron transport from the energy precursors from the citric acid cycle (step 3) leads to the phosphorylation of ADP, producing ATP.
What happens to oxaloacetate at the end of the citric acid cycle?
Throughout the citric acid cycle, oxaloacetate is progressively transformed into several different molecules (as carbon atoms are added to and removed from it), but at the end of the cycle it always turns back into oxaloacetate to be used again.
How does the enzyme start the cycle?
To start the cycle, an enzyme fuses acetyl CoA and oxaloacetate together so that citric acid is formed (a 2-carbon molecule + a 4-carbon molecule = a 6-carbon molecule!). This is the first molecule that is made in the cycle and is where the cycle gets its name.
What is the step 2 of glycolysis?
Step 2: The transformation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA. This is a very short step in between glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. The 3-carbon pyruvate molecule made in glycolysis loses a carbon to produce a new, 2-carbon molecule called acetyl CoA.
What is the energy stored in the chemical bonds of acetyl CoA?
The citric acid cycle captures the energy stored in the chemical bonds of acetyl CoA (processed glucose) in a step-by-step process, trapping it in the form of high-energy intermediate molecules.
What do we need to fuel our citric acid cycle?
What types of foods do we need to be eating in order to fuel our citric acid cycles? Our bodies are capable of digesting complex carbs, proteins, and fats to provide energy for the citric acid cycle. Carbs can be broken down into glucose, the first molecule used during glycolysis. Similarly, proteins can be broken down into their basic parts to form acetyl CoA, the molecule that enters the citric acid cycle. Components of many fats can be transformed into acetyl CoA, or converted to glucose so they can enter the citric acid cycle as well. Essentially, all of the different types of food we eat can end up in the citric acid cycle.
