
How does RNA polymerase know where to start transcribing?
- TATA box - A TATA box is a DNA sequence that indicates where a genetic sequence can be read and decoded. ...
- Transcription Start Site- The transcription start site is the location where transcription starts at the 5'-end of a gene sequence.
- RNA pol Binding Sites .
Where does RNA go after it leaves the nucleus?
This particular one, like most RNAs, are made in the nucleus and then exported to the cytoplasm where the translation machinery, the machinery that actually makes proteins, binds to these mRNA molecules and reads the code on the mRNA to make a specific protein.
What three types of RNA are present during translation?
What types of RNA are involved in translation quizlet?
- Messenger RNA (mRNA) Carries information specifying amino acid sequences of proteins from DNA to ribosomes.
- Transfer RNA (tRNA) Serves as adapter molecule in protein synthesis; translates mRNA codons into amino acids.
- Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
- Primary transcript.
- Small nuclear RNA (snRNA)
Where is RNA molecule formed during transcription?
Transcription begins with the opening and unwinding of a small portion of the DNA double helix to expose the bases on each DNA strand. One of the two strands of the DNA double helix then acts as a template for the synthesis of an RNA molecule.
What occurs during transcription of DNA and RNA?
Transcription is the first step in gene expression. It involves copying a gene's DNA sequence to make an RNA molecule. Transcription is performed by enzymes called RNA polymerases, which link nucleotides to form an RNA strand (using a DNA strand as a template).
How do you transcribe from DNA to RNA?
2:567:49Transcription Made Easy- From DNA to RNA (2019) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipOnce the RNA polymerase binds to the promoter region it separates. These two strands of DNAMoreOnce the RNA polymerase binds to the promoter region it separates. These two strands of DNA providing the single-stranded template needed for transcription.
Where does DNA transcription and translation occur?
The eukaryotic nucleus therefore provides a distinct compartment within the cell, allowing transcription and splicing to proceed prior to the beginning of translation. Thus, in eukaryotes, while transcription occurs in the nucleus, translation occurs in the cytoplasm.
Where does transcription occur occur?
the nucleusWith the genes bound in the nucleus, transcription occurs in the nucleus of the cell and the mRNA transcript must be transported to the cytoplasm. The prokaryotes, which include bacteria and archaea, lack membrane-bound nuclei and other organelles, and transcription occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell.
Why does transcription occur in the nucleus?
In prokaryotes, there is no nucleus and the DNA is in the cytoplasm. Thus, transcription can occur in the cytoplasm as well. But, in eukaryotes the DNA is in the nucleus. Thus, in order to copy DNA to mRNA the process of transcription must also occur in the nucleus.
What is the process from DNA to RNA to protein?
The process by which DNA is copied to RNA is called transcription, and that by which RNA is used to produce proteins is called translation.
Does transcription occur in the nucleus?
mRNA levels are determined by two distinct processes: transcription, catalyzed by RNA polymerase II (Pol II), and mRNA decay. Transcription occurs in the nucleus whereas the major mRNA decay pathways operate in the cytoplasm.
How does DNA transcription occur?
Transcription begins when RNA polymerase binds to a promoter sequence near the beginning of a gene (directly or through helper proteins). RNA polymerase uses one of the DNA strands (the template strand) as a template to make a new, complementary RNA molecule. Transcription ends in a process called termination.
What is the specific site for transcription and translation in the cell?
1 Answer. The site for transcription and translation are cell nucleus and cell cytoplasm respectively.
Does transcription occur in the ribosome?
Transcription occurs in the nucleus in eukaryotic organisms, while translation occurs in the cytoplasm and endoplasmic reticulum. Both processes occur in the cytoplasm in prokaryotes. The factor controlling these processes is RNA polymerase in transcription and ribosomes in translation.
Where in the cell does transcription occur quizlet?
Where does the transcription process occur? Transcription occurs in the nucleus. What is mRNA? mRNA, or Messenger RNA, is the copy of the DNA that transfers the information from the nucleus to the ribosomes.
Where does RNA translation occur in eukaryotes?
the ribosomeWhere Translation Occurs. Within all cells, the translation machinery resides within a specialized organelle called the ribosome. In eukaryotes, mature mRNA molecules must leave the nucleus and travel to the cytoplasm, where the ribosomes are located.
What are the steps of transcription?
Transcription takes place in three steps: initiation, elongation, and termination.
Which strand of DNA is transcribed into mRNA?
DNA is double-stranded, but only one strand serves as a template for transcription at any given time. This template strand is called the noncoding strand. The nontemplate strand is referred to as the coding strand because its sequence will be the same as that of the new RNA molecule.
How is mRNA made from DNA?
mRNA is synthesized in the nucleus using the nucleotide sequence of DNA as a template. This process requires nucleotide triphosphates as substrates and is catalyzed by the enzyme RNA polymerase II. The process of making mRNA from DNA is called transcription, and it occurs in the nucleus.
What are the three major steps of transcription?
Transcription takes place in three steps: initiation, elongation, and termination.
Where does RNA bind to DNA?
To begin transcribing a gene, RNA polymerase binds to the DNA of the gene at a region called the promoter. Basically, the promoter tells the polymerase where to "sit down" on the DNA and begin transcribing.
Which direction does RNA polymerase read DNA?
It synthesizes the RNA strand in the 5' to 3' direction, while reading the template DNA strand in the 3' to 5' direction. The template DNA strand and RNA strand are antiparallel.
What is the process of RNA polymerase?
Transcription ends in a process called termination. Termination depends on sequences in the RNA, which signal that the transcript is finished.
What is the process of copying a gene's DNA sequence to make an RNA molecule?
Transcription is the process in which a gene's DNA sequence is copied (transcribed) to make an RNA molecule.
Why is RNA polymerase important?
RNA polymerase is crucial because it carries out transcription, the process of copying DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid, the genetic material) into RNA (ribonucleic acid, a similar but more short-lived molecule). Transcription is an essential step in using the information from genes in our DNA to make proteins.
How does RNA polymerase open up DNA?
Once the RNA polymerase has bound, it can open up the DNA and get to work . DNA opening occurs at the element, where the strands are easy to separate due to the many As and Ts (which bind to each other using just two hydrogen bonds, rather than the three hydrogen bonds of Gs and Cs).
Why is transcription important?
Transcription is an essential step in using the information from genes in our DNA to make proteins. Proteins are the key molecules that give cells structure and keep them running. Blocking transcription with mushroom toxin causes liver failure and death, because no new RNAs—and thus, no new proteins—can be made.
What is the process of transcribed DNA into mRNA?
Let's Work Together! Transcription is a process in which the DNA is transcribed into mRNA. This is a very important part of the protein synthesis process.
What is transcription in biology?
Transcription is an important part of protein synthesis, which takes place within the cell. Read this article to gain more information about this subject. Living beings are made up of cells, which conduct many functions that help in sustaining a healthy and normal life. One of the most important functions of the cell is called protein synthesis.
What happens to RNA transcripts during initiation?
In initiation, the RNA polymerase binds to the sigma factor to form holoenzyme. This enzyme recognizes the promoter region in the DNA to form a closed complex. The RNA then starts proceeding towards the elongation stage. Thus, the RNA transcript increases in length.
What are the stages of transcription in prokaryotes?
Transcription process in prokaryotes can be divided into three stages – initiation, elongation, and termination. In initiation, the RNA polymerase binds to the sigma factor to form holoenzyme. This enzyme recognizes the promoter region in the DNA to form a closed complex. The RNA then starts proceeding towards the elongation stage. Thus, the RNA transcript increases in length. Then finally, in the termination stage, the RNA polymerase pauses, and the mRNA molecule is terminated from the DNA molecule.
How does translation occur in DNA?
This process is initiated when the DNA molecule uncoils its strands by breaking the hydrogen bonds, which hold the complementary base pairs together.
What is the name of the enzyme that recognizes the DNA template?
The other leftover part is the sense strand. Then RNA polymerase enzyme, which has the sigma factor recognizes the DNA template.
Why is protein synthesis important?
Protein synthesis is an important function of the cell, and hence, an important part of DNA research and studies.
Overview of transcription
Transcription is the process of making an RNA copy of a DNA segment. This copy is called a messenger RNA ( mRNA) molecule. This mRNA will be transported from the cell nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm, where the mRNA directs the synthesis of the protein.
What kinds of RNA can be transcribed (produce)?
When talking about RNA and transcription, we usually refer to messenger RNA (mRNA). An mRNA is transcribed from a protein-encoding gene and subsequently is translated to a protein. But there is a whole set of other RNAs that get transcribed, like transfer RNA (tRNA) and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), that do different functions in the cells.
Stages of transcription
Transcription of a gene takes place in three stages: initiation, elongation, and termination. Here, we will briefly see how these steps happen.
Eukaryotic RNA modifications after transcription
In prokaryotic cells, the RNA transcripts can act as messenger RNAs (mRNAs) right away. However, in eukaryotic cells, the RNA transcripts produced by transcription are only pre-mRNAs. These pre-mRNAs must go through extra processing before they can be used in translation.
The regulation of Individual genes
Not all genes are transcribed all the time. Instead, transcription is controlled spatially (in different cells) and temporarily (in different timing) for each gene. For example, some growth hormones express only when we are young. Some proteins which can wake our immune system up will only be produced when our bodies sense pathogen invasion.
Transcription in bacteria
In this article, we mainly discuss the transcription in eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotes produce RNA in a very similar way. However, there are some differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic gene expression. In bacteria, all transcription is performed by a single type of RNA polymerase.
Where does transcription occur?
Transcription takes place in the cell’s nucleus and starts when an enzyme called RNA polymerase binds to the section of DNA it needs and opens the double helix. RNA polymerase binds at an area called the promoter, which is a found a short distance “upstream” from the gene itself. The promoter sequence is found on one strand only – this indicates not only where to start transcribing but also which strand of DNA to use.
What is transcription in a library?
What is transcription? Libraries often have large reference books that can’t be taken out of the library – they hold a vast amount of information, of which you only need a small portion. So, you make a photocopy of the needed information and take THAT home instead. This is the idea behind protein transcription.
What happens if the DNA template strand says A T C G A T C G?
So, if the DNA template strand says A T C G A T C G, the RNA will read U A G C U A G C. RNA polymerase continues to build the strand of mRNA until it finds a terminator sequence at the end of the gene. The enzyme then leaves the DNA strand, and is now free to transcribe another gene.
What is the strand of mRNA called?
RNA polymerase starts to build a strand of mRNA using the DNA as a template. Thus, the DNA strand being used is called the template strand and the strand not used is called the coding strand (which contains the gene itself). The mRNA is made using complementary base pairing.
How is mRNA made?
The mRNA is made using complementary base pairing. As the DNA strand is unwound and its bases exposed, the corresponding RNA base is put in place by RNA polymerase. Adenine always pairs with thymine (or uracil, in the case of RNA), and cytosine always pairs with guanine.
What happens to the mRNA strand before it leaves the nucleus?
The enzyme then leaves the DNA strand, and is now free to transcribe another gene. Some mRNA strands need modifications before they can leave the nucleus: 1) a “cap” is put on one end, 2) a string of about 200 adenines is added to other end, and 3) junk sequences, called introns, are removed.
Why can't DNA leave the nucleus?
This is the idea behind protein transcription. Cellular DNA cannot leave the nucleus (for fear of damage, lack of efficiency, and getting it back into the nucleus).
When does DNA replication occur?
Replication of a cell’s DNA occurs before a cell prepares to undergo division —either mitosis or meiosis I.
What is the basic of DNA and RNA?
DNA and RNA Basics: Replication, Transcription, and Translation. Posted on 6/22/21 by Laura Snider. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is one of the most important molecules in your body, and though around 99.9% of your DNA is the same as that of every other human, the 0.1% that’s different is what makes you genetically unique!
What are the four nitrogenous bases found in DNA?
Learn more on Visible Body's Biology Learn Site. Four nitrogenous bases—cytosine, thymine, adenine, and guanine —can be found on strands of DNA. In terms of their chemical structure, cytosine and thymine are pyrimidines and adenine and guanine are purines. Adenine and thymine (A and T) always pair together, and guanine and cytosine (G and C) ...
How many strings of DNA are there in the human body?
DNA structure and storage. Learn more on Visible Body's Biology Learn Site. There are 46 separate strings of DNA in each somatic cell of the human body.
How does RNA polymerase clean up DNA?
As the RNA polymerase travels down the string of DNA, it closes the helical structure back up after it. Before the new m RNA can go out to deliver its protein fabrication instructions, it gets “cleaned up” by enzymes. They remove segments called introns and then splice the remaining segments, called exons, together.
What is the process of replicating DNA?
Replication of a cell’s DNA occurs before a cell prepares to undergo division —either mitosis or meiosis I. It takes place in three (ish) steps. DNA unwinds from the histones. An enzyme called DNA helicase opens up the helix structure on a segment of DNA, breaking the bonds between the nitrogenous bases.
How much DNA is in a human cell?
Did you know that in the average human cell, there is about 2m (6ft) of DNA? That’s pretty impressive, considering that even the largest cells are just over 100µm in diameter. (That’s really tiny, by the way—1µm is one millionth of a meter.)
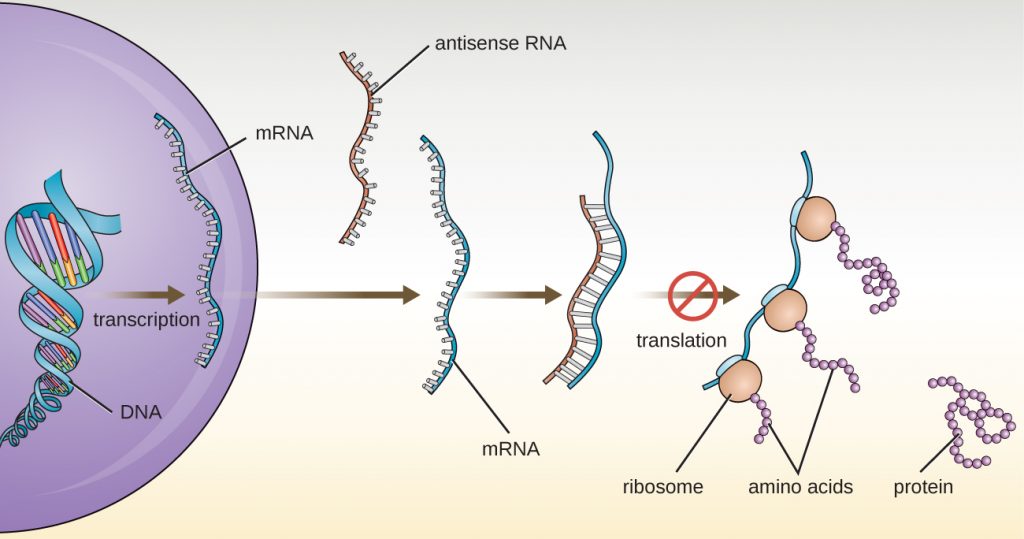
Overview of Transcription
- Transcription is the process of making an RNA copy of a DNA segment. This copy is called a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule. This mRNA will be transported from the cell nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm, where the mRNA directs the synthesis of the protein. [In this image] Overview of transcription. You can see in this diagram that a piece of u...
Gene Expression
- Genes contain the information to build proteins that cells need. Our genes are written as the nucleotide base pairs (A, T, G, C) in the DNA. For a gene to exert its function, the genetic information must read out to build a protein. This process is called gene expression. There are two steps for making proteins from genes: First, inside the cell nucleus, the transcription makes …
What Does “Transcription” Mean?
- Transcription is a process in which information is rewritten. For example, you took draft notes in class, and then you rewrote them neatly in a notebook to help you review. Or your friend left a message on your voicemail, and you had to rewrite it down on paper. If you made a mistake while you rewrote or “transcribed” the critical information (i.e., phone number, address, next exam dat…
What Kinds of RNA Can Be Transcribed (Produce)?
- When talking about RNA and transcription, we usually refer to messenger RNA (mRNA). An mRNA is transcribed from a protein-encoding gene and subsequently is translated to a protein. But there is a whole set of other RNAs that get transcribed, like transfer RNA (tRNA) and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), that do different functions in the cells. [In this image] Types of RNA molecules. Transcri…
Stages of Transcription
- Transcription of a gene takes place in three stages: initiation, elongation, and termination. Here, we will briefly see how these steps happen.
Eukaryotic RNA Modifications After Transcription
- In prokaryotic cells, the RNA transcripts can act as messenger RNAs (mRNAs) right away. However, in eukaryotic cells, the RNA transcripts produced by transcription are only pre-mRNAs. These pre-mRNAs must go through extra processing before they can be used in translation. [In this image] The difference in gene expression between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. In eukar…
The Regulation of Individual Genes
- Not all genes are transcribed all the time. Instead, transcription is controlled spatially (in different cells) and temporarily (in different timing) for each gene. For example, some growth hormones express only when we are young. Some proteins which can wake our immune system up will only be produced when our bodies sense pathogen invasion. Cells carefully regulate transcription, jus…
Transcription in Bacteria
- In this article, we mainly discuss the transcription in eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotes produce RNA in a very similar way. However, there are some differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic gene expression. In bacteria, all transcription is performed by a single type of RNA polymerase. Because bacteria have no nucleus, their transcription and translation can occur simultaneously i…
Summary
- 1. Transcription copies a gene’s DNA sequence to make an RNA molecule. Transcription is the first step of gene expression. 2. Transcription is done in the cell nucleus by an enzyme called RNA polymerase. RNA polymerase uses a DNA strand as a template to make an RNA copy. 3. Transcription can be divided into three stages: (1) initiation, (2) elongation, and (3) termination. …