
What is translocation in a plant?
It is the movement of materials like sugars and nutrients from the leaves to other parts of the plant. For translocation to occur, Food molecules enter the part of the phloem called sieve tubes from where they can be transported to all parts of the plant including roots.
What does chromosomal translocation mean in pregnancy?
More in Pregnancy Loss. A balanced or chromosomal translocation is a condition in which part of a chromosome has broken off and reattached in another location. In other words, it means that sections of two chromosomes have switched places.
What is balanced translocation?
In a balanced translocation, a person usually has all the genetic material necessary for normal growth -- a piece of a chromosome is merely broken off and attached to another one.
Can translocations be harmful?
Translocations can be completely harmless or they can cause serious health problems, depending on the circumstances. In the case of the former, many people can have translocations without being aware of the condition.
How Does It Move?
How does water move through a plant?
How do materials move in the phloem?
How do nutrients flow through plants?
What is the process of water moving from an area where there is more of it to an area where there is less?
What is the process of transporting materials from the leaves to other parts of the plant?
How does food get to where it needs to go?
See 4 more
About this website
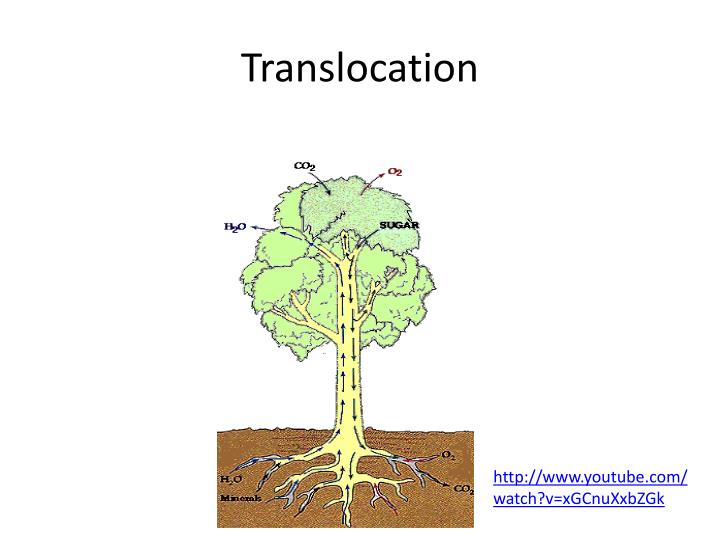
What is translocation and where does it occur?
Translocation is the movement of sugar produced in photosynthesis to all other parts of the plant for respiration and the other processes described above. This occurs in phloem cells.
Where does translocation occur in phloem?
Translocation occurs in the phloem tissue, which consists of tube-like structures called phloem vessels. These phloem vessels run from the leaves into every other part of the plant and are responsible for transporting dissolved organic solutes, such as sucrose and amino acids, from the sources to the sinks.
How does translocation take place in plants?
For translocation, food molecules enter the part of the phloem called the sieve tubes where they can be transported upwards or downwards to all parts of the plant including roots. Translocation is achieved by utilising energy from the ATP that provides osmotic pressure required for upward and downward movement of food.
What is moved by translocation?
The movement of sucrose and other substances like amino acids around a plant is called translocation . In general, this happens between where these substances are made (the sources) and where they are used or stored (the sinks): from sources in the root to sinks in the leaves in early spring time.
Is translocation is for phloem or xylem?
phloemXylem is associated with translocation of mainly water, mineral salts, some organic nitrogen and hormones from roots to the aerial parts of the plants. While the phloem translocates a variety of organic and inorganic solutes mainly from the leaves to other parts of the plants.
Does translocation occur in xylem?
Xylem transports water and mineral salts from the roots up to other parts of the plant, while phloem transports sucrose and amino acids between the leaves and other parts of the plant....Xylem and phloem.TissueWhat is movedProcessXylemWater and mineralsTranspiration streamPhloemSucrose and amino acidsTranslocation
Does translocation take place in sieve tube?
The transportation occurs in the direction of the source to sink. Transport of organic solutes from one part of the plant to the other through phloem sieve tubes is called translocation of organic solvents.
What phase does translocation occur?
Translocations. Translocations occur when chromosomes become broken during meiosis and the resulting fragment becomes joined to another chromosome.
What is translocation process in biology?
(TRANZ-loh-KAY-shun) A genetic change in which a piece of one chromosome breaks off and attaches to another chromosome.
How does cell body translocation happen?
A translocation occurs when a piece of one chromosome breaks off and attaches to another chromosome. This type of rearrangement is described as balanced if no genetic material is gained or lost in the cell. If there is a gain or loss of genetic material, the translocation is described as unbalanced .
What moves down in translocation?
Translocation is the movement of organic compounds (e.g. sugars, amino acids) from sources to sinks. Organic molecules such as sucrose and amino acids move from a source to a sink via phloem tubes in plants.
What causes translocation to occur?
Translocations generally result from swapping of chromosomal arms between heterologous chromosomes and hence are reciprocal in nature (Figure 1) (8,9). DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) are prerequisites for such translocations, although little is known about their generation.
What is the path of translocation of food in phloem?
The transportation of food in plants through phloem is bidirectional i.e., in both upward and downward directions.
What phase does translocation occur?
Translocations. Translocations occur when chromosomes become broken during meiosis and the resulting fragment becomes joined to another chromosome.
What is translocation through phloem?
Sugars produced in sources, such as leaves, need to be delivered to growing parts of the plant via the phloem in a process called translocation, or movement of sugar. The points of sugar delivery, such as roots, young shoots, and developing seeds, are called sinks.
How is translocation achieved in phloem?
Phloem translocation is generally believed to be driven by pressure and is achieved by utilizing energy. Material like sucrose is transferred into phloem tissue using energy from ATP. This increases the osmotic pressure of the tissue causing water to move into it.
Mechanism of Translocation in Plants
Several hypotheses have been proposed to explain the mechanism of translocation. Some of them are given below:...
Explain the process of translocation of food materials in plants.
Translocation occurs through part of vascular tissue known as phloem that also transports carbohydrates, amino acids and other substances such as plant hormone which are made in tips of roots and shoots to the storage and growing organs.
Translocation (A Level) — the science hive
Translocation. Translocation is the movement of dissolved substances, such as sucrose and amino acids, from parts of the plant where the substances are made to other parts of the plant where they’re needed.Translocation takes place in the phloem - transport vessels made up of two types of cell, sieve tube elements and companion cells.The parts of the plant which make these substances are ...
Plant Translocation Biology & Process - Study.com
Understand translocation in plants. Comprehend the process plants use to translocate glucose to where they need it. Find out about translocation in biology.
Translocation...... Starter ........ Plenary.......Activity ...
Attached files are consist of ppt on translocation with starter and plenary. Activity sheet is with success criteria. this activity could be done at home or in school but I prefer to give as biology project work to complete at home.
How Does It Move?
In some plants, it's directly transported into the phloem using sugar transport proteins. In others, it makes its way in through small openings in the phloem cell walls and is then converted into larger forms so that it cannot move back out.
How does water move through a plant?
The entrance of the water causes pressure to build and forces the water and dissolved materials to move through the phloem from the leaves into the rest of the plant, where it can be stored or turned into energy. The materials move from sugar sources, which have an abundance of sugar following photosynthesis (such as leaves), into sugar sinks, which are areas where there's a lack of sugar (such as the stems and flowers).
How do materials move in the phloem?
The most widely accepted hypothesis about how these materials move within the phloem is the mass flow hypothesis . Sugars enter the phloem either through sugar transport proteins or by going through small openings and then being transformed to larger forms so they cannot move back out. This causes sugar to build up in the phloem in the leaves, and water enters via osmosis, or when a material, such as water, moves from an area where there is more of it into an area where there is less.
How do nutrients flow through plants?
The nutrients the plant creates can't simply stream through the leaves to the other parts of the plant. They're moved through special tubes that run all throughout the plant, known as phloem. These long, continuous tubes extend from the leaves into every part of the plant, and new phloem are added as the plant grows, so the flow of nutrients is never interrupted.
What is the process of water moving from an area where there is more of it to an area where there is less?
Osmosis is when a material (such as water) moves from an area where there is more of it into an area where there is less. The entrance of the water causes pressure to build inside the phloem. This, in turn, forces the water and dissolved materials to begin moving out of the leaves and into the areas where the sugar is needed.
What is the process of transporting materials from the leaves to other parts of the plant?
Translocation is the movement of materials in plants from the leaves to other parts of the plant. Nutrients, mainly sugars, are created in the leaves during photosynthesis. These are then transported throughout the plant through phloem, which are a long series of connected cells.
How does food get to where it needs to go?
When you eat, how does the food get where it needs to go? It starts at your mouth and is moved by a series of mechanisms that turn it into energy and transport nutrients throughout your body. A similar thing happens in plants. Even though plants don't have mouths, they still need to transport nutrients throughout their system, just as people do.
How many parts does a ribosome have?
Each ribosome has 2 parts: a small subunit and a large subunit. The small subunit is called the 40S subunit and the large the 60S subunit. The two parts of the ribosomes enclose the mRNA strand, almost like the two pieces of bread on a sandwich.
What is the name of the triplet of bases in mRNA?
Information in mRNA is stored in the form of sequences of nucleotide bases (A, C, G, and U) that are read in threes. A triplet of bases is called a codon. Each codon refers to a specific amino acid. For example, the codon ACG specifies the amino acid threonine.
How many codons are there in RNA?
In human RNA, there are 61 codons that encode for about 20 amino acids. There is also the special codon AUG called a “start codon” that tells where the gene begins. Lastly, there are three special codons that do not code for amino acids (UAA, UAG, UGA) that are called “stop codons”.
How to understand translation?
To understand translation we must first understand how information for proteins is stored in mRNA. Strictly speaking, mRNA does not encode for a protein. Rather, mRNA encodes—gives instructions for—a sequence of amino acids called a polypeptide chain. Proteins are made out of numerous polypeptide chains.
Where do mRNA strands go?
mRNA strands are fed into ribosomes which read the codons. Ribosomes contain compartments for tRNA anticodons to bind to their corresponding mRNA codons. The three binding sites for tRNA on ribosome are called the A, P, and E sites. Ribosomes also contain enzymes that catalyze the reaction that binds amino acids together into a polypeptide chain.
Which molecule binds to the small subunit of mRNA?
In eukaryotes, a tRNA molecule containing methionine binds to the small subunit and together they move down the mRNA strand until they reach the start codon, which is almost always the AUG codon. Once reached, the large ribosomal subunit encloses the rest of the strand, forming the completed initiation complex.
What are the steps of gene expression?
Fundamentally, gene expression has two steps: 1 Transcription – During transcription, information in DNA is “copied” into the form of messenger RNA (mRNA) 2 Translation – In this stage, mRNA is “read” by cellular machinery and the encoded proteins are made
How many couples have a balanced translocation?
In about 4.5% of all couples with recurrent miscarriages, one or both parents has a balanced translocation. 2 Research has shown that couples with balanced translocations are more likely to have miscarriages than couples without balanced translocations. There's some evidence that balanced translocations involving specific chromosomes are more likely to cause miscarriages than others. 3
What is a balanced translocation?
A balanced or chromosomal translocation is a condition in which part of a chromosome has broken off and reattached in another location. In other words, it means that sections of two chromosomes have switched places.
How much of your adjusted gross income is tax deductible for IVF?
That being said, you may be able to obtain loans that will help pay for these procedures, apply for grants for couples in need of IVF or save up the money yourself and report your medical expenses as a tax deduction if they exceed 7.5% of your adjusted gross income.
Can translocations be harmful?
Translocations can be completely harmless or they can cause serious health problems, depending on the circumstances. In the case of the former, many people can have translocations without being aware of the condition. This is usually the case for reciprocal (or balanced) translocation, a type of chromosomal translocation that increases the risk ...
Can a miscarriage cause scar tissue?
For some women, repeated miscarriages can cause complications, such as build up of scar tissue after a D&C. Accordingly, couples with a known balanced translocation who fear both the emotional and physical trauma repeated pregnancy loss can cause may want to explore more high-tech means to carry a pregnancy to term. 1 .
Can you cure a miscarriage from a balanced translocation?
There is no cure for balanced translocation, and in most cases, the only adverse effect on health is recurrent miscarriages. 1 For couples affected by balanced translocation, odds are in favor of a successful pregnancy at some point, but repeated miscarriages can obviously be difficult to cope with emotionally.
Does Verywell Family use peer reviewed sources?
Verywell Family uses only high-quality sources , including peer-reviewed studies, to support the facts within our articles. Read our editorial process to learn more about how we fact-check and keep our content accurate, reliable, and trustworthy.
How Does It Move?
In some plants, it's directly transported into the phloem using sugar transport proteins. In others, it makes its way in through small openings in the phloem cell walls and is then converted into larger forms so that it cannot move back out.
How does water move through a plant?
The entrance of the water causes pressure to build and forces the water and dissolved materials to move through the phloem from the leaves into the rest of the plant, where it can be stored or turned into energy. The materials move from sugar sources, which have an abundance of sugar following photosynthesis (such as leaves), into sugar sinks, which are areas where there's a lack of sugar (such as the stems and flowers).
How do materials move in the phloem?
The most widely accepted hypothesis about how these materials move within the phloem is the mass flow hypothesis . Sugars enter the phloem either through sugar transport proteins or by going through small openings and then being transformed to larger forms so they cannot move back out. This causes sugar to build up in the phloem in the leaves, and water enters via osmosis, or when a material, such as water, moves from an area where there is more of it into an area where there is less.
How do nutrients flow through plants?
The nutrients the plant creates can't simply stream through the leaves to the other parts of the plant. They're moved through special tubes that run all throughout the plant, known as phloem. These long, continuous tubes extend from the leaves into every part of the plant, and new phloem are added as the plant grows, so the flow of nutrients is never interrupted.
What is the process of water moving from an area where there is more of it to an area where there is less?
Osmosis is when a material (such as water) moves from an area where there is more of it into an area where there is less. The entrance of the water causes pressure to build inside the phloem. This, in turn, forces the water and dissolved materials to begin moving out of the leaves and into the areas where the sugar is needed.
What is the process of transporting materials from the leaves to other parts of the plant?
Translocation is the movement of materials in plants from the leaves to other parts of the plant. Nutrients, mainly sugars, are created in the leaves during photosynthesis. These are then transported throughout the plant through phloem, which are a long series of connected cells.
How does food get to where it needs to go?
When you eat, how does the food get where it needs to go? It starts at your mouth and is moved by a series of mechanisms that turn it into energy and transport nutrients throughout your body. A similar thing happens in plants. Even though plants don't have mouths, they still need to transport nutrients throughout their system, just as people do.

How Does mRNA Store Information?
Overview of Translation
- Translation is a complex process that requires some specialized machinery. Two types of molecules are involved in the translation process: tRNA and ribosomes. tRNA tRNAs (“transfer” RNAs) are molecules that bridge the gap between codons in mRNA and the amino acids they specify. One end of tRNA contains a sequence of bases called an anticodon that can bind to a s…
Post-Translation Modification
- Now that we have a complete polypeptide chain, it can go out and start doing work in the body, right? Well, not quite. In prokaryotes, proteins are generally ready to go as soon as they are translated. In eukaryotes, however, polypeptide chains must often go through a handful of modifications before they are a full-blown functioning mature protein. These post-translation edi…