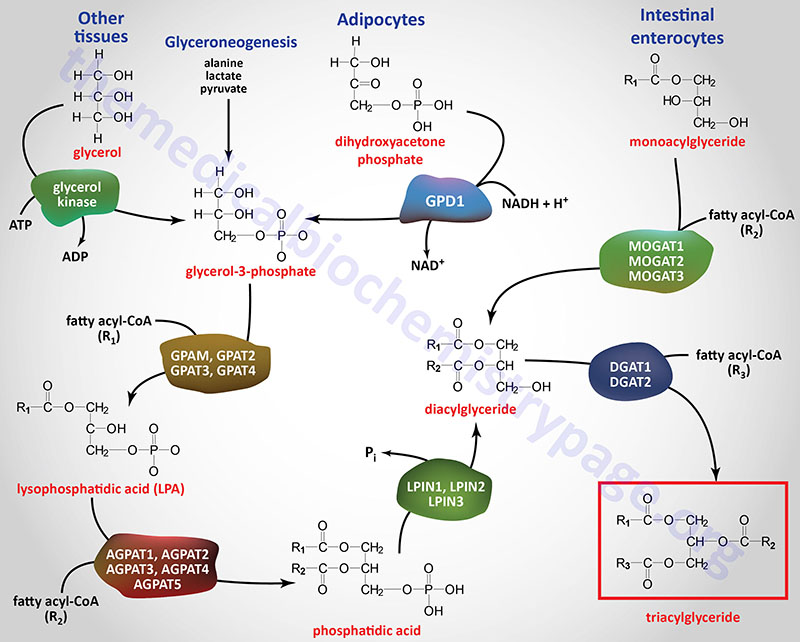
What is the component needed to synthesise a triglyceride?
Adipocytes can be considered the major cell types tasked with triglyceride synthesis as these are the primary fatty acid storage cells the body. Fatty acid, triglyceride, and phospholipid synthesis are reductive biosynthetic processes and as such utilize NADPH as the co-factor for the reductive reactions.
What is the formation of triglycerides?
Triglycerides are formed by condensation from three fatty acids and one glycerol. What is a Triglyceride ? Triglycerides are a kind of fat (lipid). They are located inside the blood. Upon consumption the body converts the calories which are unneccessary into trigylcerides. They are stored in the form of fat cells.
What is the structure and function of a triglyceride?
What Is the Function of Triglycerides?
- Characteristics. Triglycerides are the most common lipid found in the body. ...
- Energy Storage. Triglycerides provide your body with energy, but their main function is to store energy for later use.
- Health Impact. ...
- Healthy Levels. ...
- Lifestyle Changes. ...
Do triglycerides contain ester bonds?
Triglycerides. Triglycerides are lipids consisting of one glycerol molecule bonded with three fatty acid molecules. The bonds between the molecules are covalent and are called Ester bonds. They are formed during a condensation reaction. An exmample of a triglyceride. Credit: Wolfgang Schaefer. Triglycerides are hydrophobic and so insoluble in water. The charges are evenly distributed around the molecule so hydrogen bonds to not form with water molecules.

Where does triglyceride synthesis occur in the cell?
the endoplasmic reticulum membraneTriacylglycerol synthesis, on the other hand, occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane of cells by bonding three fatty acid molecules to a glycerol molecule. Both processes take place mainly in liver and adipose tissue.
What is triglyceride synthesis?
Synthesis of Triglycerides ++ Triglycerides (TGs) constitute molecules of glycerol to which 3 fatty acids have been esterified. The fatty acids present in TGs are predominantly saturated. The major building block for the synthesis of TGs, in tissues other than adipose tissue, is glycerol.
In which organelle are triglycerides synthesized?
So, the correct answer is 'Peroxisome'.
Where does triglyceride metabolism occur?
The liver is the central organ that controls lipid homeostasis by means of complex, but precisely regulated biochemical, signaling and cellular pathways. Hepatocytes are the main liver parenchymal cells, which control hepatic biochemical and metabolic functions in the liver, including triglyceride metabolism.
Are triglycerides made in the liver?
The source of triglycerides Food is one source of triglycerides. Your liver also makes them. When you eat extra calories — especially carbohydrates — your liver increases the production of triglycerides. When you consume — or your body creates — excess triglycerides, they're stored in fat cells for later use.
How are triglycerides formed in the liver?
Under fasting conditions, fatty acids are released from adipose tissue and return to the liver, where they are assembled into triglycerides and packaged to form VLDL particles that are secreted into the plasma. Fatty acids may also be oxidized in situ by mitochondria within the liver.
Does rough ER synthesize phospholipids?
The RER also makes phospholipids for cellular membranes. If the phospholipids or modified proteins are not destined to stay in the RER, they will reach their destinations via transport vesicles that bud from the RER's membrane.
What is the site for lipid synthesis?
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER)The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is the main site for lipid synthesis. Intracellular lipid trafficking is necessary to maintain most other organelle membranes as they lack the capability to synthesize lipids de novo (van Meer et al. 2008).
Where does fatty acid synthesis occur?
Fatty acid synthesis occurs in the liver and in adipose cells. The rate-limiting reaction in fatty acid biosynthesis is that of acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) that catalyzes the reaction of acetyl-CoA to malonyl-CoA in two steps shown in Fig. 9.45.
Can adipose tissue synthesize triglycerides?
The synthesis and breakdown of triglycerides in adipose tissue and muscle is a crucial element of energy metabolism because it ensures that adequate fuel is available during starvation.
How do triglycerides travel in the blood?
Cholesterol and triglycerides cannot circulate loosely in the blood, so they travel in “round parcels” called lipoproteins. Lipoproteins contain a special mix of fats and proteins which allow them to flow freely in the blood. The are four main lipoproteins (sometimes called apolipoproteins).
What is the function of triglycerides?
Triglycerides store unused calories and provide your body with energy. Cholesterol is used to build cells and certain hormones.
What is triglyceride?
Triglycerides are a type of fat that circulates in your blood. Your body makes triglycerides or gets them from the foods you eat. Your body needs some triglycerides for good health. However, high triglycerides in your blood can raise your risk of heart disease and stroke.
What are the 3 types of triglycerides?
The three types of triglycerides which arise from these types of fatty acids; are saturated, monounsaturated and polyunsaturated triglycerides.
What is the function of a triacylglycerol?
Triacylglycerols (TAGs) are one of the major constituents of the glycerolipid family. Their main role in cells is to store excess fatty acids, and they are mostly found within lipid droplets. TAGs contain acyl chains that vary in length and degree of unsaturation, resulting in hundreds of chemically distinct species.