
In What Phase of Cell Division Does DNA Synthesis Occur?
- The S Phase. The purpose of the cell's S phase is to create a new and identical double-stranded (ds) DNA molecule.
- Replicating DNA. The dsDNA strand is "unzipped" by helicase and DNA synthesis occurs at the Y-shaped replication fork in the five prime (5’) to three prime (3’) direction.
- Importance in Cell Cycle. ...
- Problems During DNA Synthesis. ...
Where is DNA found inside the cell?
Where is the DNA found in the cell? Nearly every cell in a person’s body has the same DNA. Most DNA is located in the cell nucleus (where it is called nuclear DNA), but a small amount of DNA can also be found in the mitochondria (where it is called mitochondrial DNA or mtDNA).
Where is DNA located and in what structure?
DNA is located mainly in the nucleus, but can also be found in other cell structures called mitochondria. Since the nucleus is so small, the DNA needs to be tightly packaged into bundles known as chromosomes. The DNA that is found in the cell structures, known as mitochondria, is responsible for providing the energy that the cell needs to function.
Where is the most DNA found within the nucleus?
Most DNA is located in the cell nucleus (where it is called nuclear DNA), but a small amount of DNA can also be found in the mitochondria (where it is called mitochondrial DNA or mtDNA). Mitochondria are structures within cells that convert the energy from food into a form that cells can use.
What are the steps in DNA synthesis?
- Mutation and mutagenesis studies
- DNA sequencing and identification
- Genotype and phenotype studies
- Disease diagnosis
- Metagenomic studies
- Pathogen and microbial identification
- Species and speciation studies
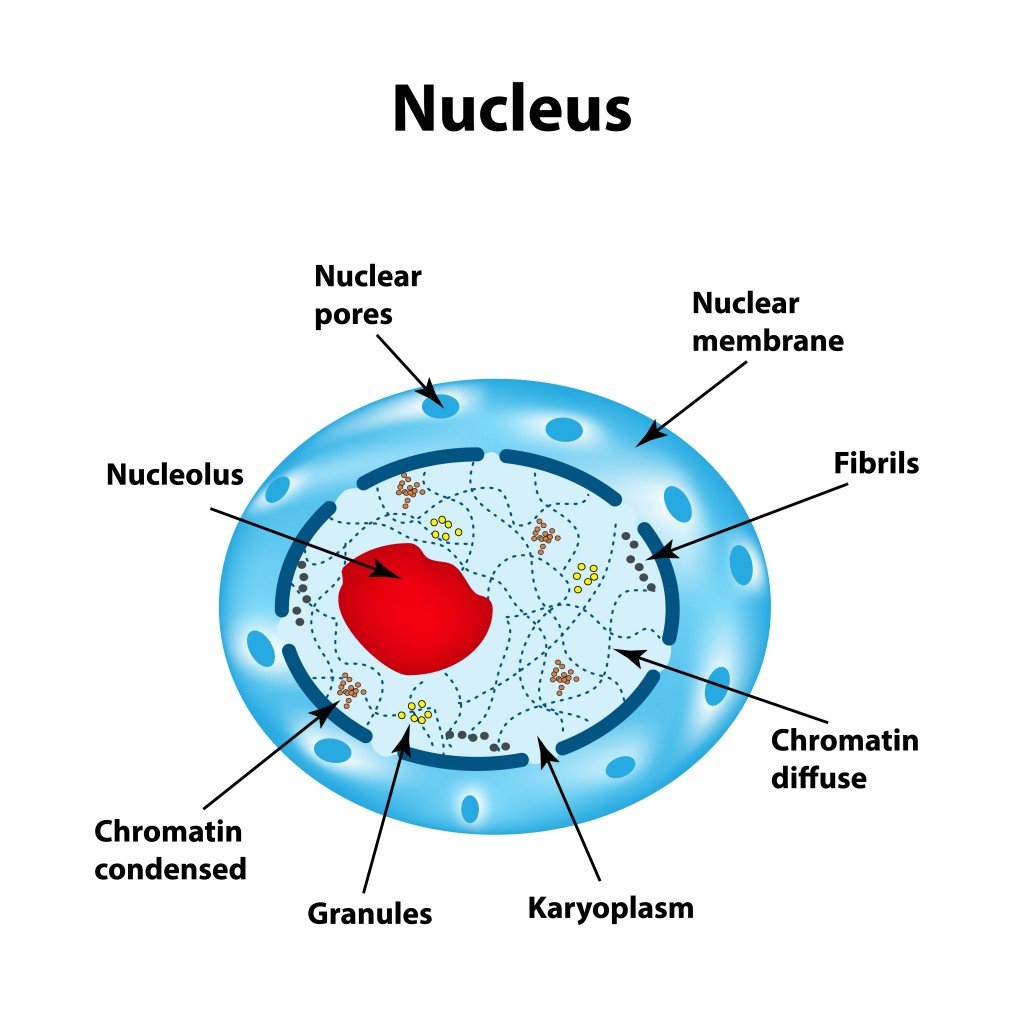
Where is DNA Synthesised in the cell?
(a) DNA synthesis starts at a specific place on a chromosome called an origin. In the first mechanism one daughter strand is initiated at an origin on one parental strand and the second is initiated at another origin on the opposite parental strand.
Where is RNA and DNA synthesized?
Synthesis takes place within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells or in the cytoplasm of prokaryotes and converts the genetic code from a gene in deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA ) to a strand of RNA that then directs protein synthesis. Three types of RNA are found in cells.
Who synthesis DNA in cell?
An enzyme called helicase unwinds and separates the bonds between the two DNA strands, and both these separated strands act as templates from which new DNA is made. DNA polymerases are a group of enzymes which make new DNA.
How are DNA synthesized?
DNA biosynthesis occurs when a cell divides, in a process called replication. It involves separation of the DNA double helix and subsequent synthesis of complementary DNA strand, using the parent DNA chain as a template.
Where is RNA synthesized?
mRNA travels to the ribosome to direct the assembly of polypeptides. RNA is synthesized on a DNA template by a process of DNA transcription in which RNA polymerase enzymes make an RNA copy of a DNA sequence. RNA polymerases are formed from multiple polypeptide chains with a molecular weight of 500,000.
Where does RNA get synthesized?
RNA is synthesized from DNA by an enzyme known as RNA polymerase during a process called transcription. The new RNA sequences are complementary to their DNA template, rather than being identical copies of the template. RNA is then translated into proteins by structures called ribosomes.
Is DNA synthesized in the nucleus?
The nucleus (plural, nuclei) houses the cell's genetic material, or DNA, and is also the site of synthesis for ribosomes, the cellular machines that assemble proteins.
During what phase is DNA synthesized?
S phaseIn the eukaryotic cell cycle, chromosome duplication occurs during "S phase" (the phase of DNA synthesis) and chromosome segregation occurs during "M phase" (the mitosis phase).
What is DNA synthesis in cell cycle?
S phase, or synthesis, is the phase of the cell cycle when DNA packaged into chromosomes is replicated. This event is an essential aspect of the cell cycle because replication allows for each cell created by cell division to have the same genetic make-up.
Where does DNA replication take place?
the nucleusDNA replication is the process of creating two identical daughter strands of DNA. DNA replication occurs in the nucleus in eukaryotic cells and in the nucleoid region in prokaryotic cells. DNA replication occurs in S phase during the cell cycle prior to cell division.
What is DNA synthesis quizlet?
the process of making identical copies of DNA before cell division. Replication Origin. Specific sequence of DNA where DNA synthesis begins. You just studied 23 terms! 1/23.
How is synthetic DNA synthesized?
(From top, clockwise) Synthetic DNA constructs are designed and manipulated using computer-aided design software. The designed DNA is then divided into synthesizable pieces (synthons) up to 1–1.5 kbp. The synthons are then broken up into overlapping single-stranded oligonucleotide sequences and chemically synthesized.
What is the synthesis of DNA and RNA?
The syntheses of RNA (transcription), DNA and proteins (translation) are fundamental processes necessary for all life. Transcription begins by uncoiling a section of DNA that will be used as the template and is initiated by RNA polymerase binding to a promoter sequence.
Is RNA used in DNA synthesis?
Abstract. Primer RNA is RNA that initiates DNA synthesis. Primers are required for DNA synthesis because no known DNA polymerase is able to initiate polynucleotide synthesis. Edited transcriptional RNA is used to initiate DNA synthesis in some phage and in metazoan mitochondria.
What is synthesis of RNA?
RNA Synthesis and Processing. RNA Synthesis. The process of synthesizing RNA from the genetic information encoded by DNA is called transcription. The enzymes involved in transcription are called RNA polymerases. Prokaryotes have one type; eukaryotes have three types of nuclear RNA polymerases.
How is DNA synthesis similar to living cells?
DNA synthesis during PCR is very similar to living cells but has very specific reagents and conditions. During PCR, DNA is chemically extracted from host chaperone proteins then heated, causing thermal dissociation of the DNA strands. Two new cDNA strands are built from the original strand, these strands can be split again to act as the template for further PCR products. The original DNA is multiplied through many rounds of PCR. More than a billion copies of the original DNA strand can be made.
What is DNA made of?
Nucleotide units are made up of a nitrogenous base ( cytosine, ...
How is DNA repaired?
Damaged DNA is subject to repair by several different enzymatic repair processes, where each individual process is specialized to repair particular types of damage. The DNA of humans is subject to damage from multiple natural sources and insufficient repair is associated with disease and premature aging. Most DNA repair processes form single-strand gaps in DNA during an intermediate stage of the repair, and these gaps are filled in by repair synthesis. The specific repair processes that require gap filling by DNA synthesis include nucleotide excision repair, base excision repair, mismatch repair, homologous recombinational repair, non-homologous end joining and microhomology-mediated end joining .
What is the term for the process of forming a new double stranded DNA molecule?
Complementary base pairing takes place, forming a new double-stranded DNA molecule. This is known as semi-conservative replication since one strand of the new DNA molecule is from the 'parent' strand. Continuously, eukaryotic enzymes encounter DNA damage which can perturb DNA replication.
Why is DNA replication so important in eukaryotic cells?
DNA replication machinery is therefore highly controlled in order to prevent collapse when encountering damage. Control of the DNA replication system ensures that the genome is replicated only once per cycle; over-replication induces DNA damage. Deregulation of DNA replication is a key factor in genomic instability during cancer development.
How does DNA replication occur?
In nature, DNA molecules are synthesised by all living cells through the process of DNA replication. This typically occurs as a part of cell division. DNA replication occurs so, during cell division, each daughter cell contains an accurate copy of the genetic material of the cell.
What is double stranded DNA?
Jump to navigation Jump to search. Structure of double-stranded DNA, the product of DNA synthesis, showing individual nucleotide units and bonds. DNA synthesis is the natural or artificial creation of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) molecules. DNA is a macromolecule made up of nucleotide units, which are linked by covalent bonds and hydrogen bonds, ...
Overview
DNA replication
In nature, DNA molecules are synthesised by all living cells through the process of DNA replication. This typically occurs as a part of cell division. DNA replication occurs so, during cell division, each daughter cell contains an accurate copy of the genetic material of the cell. In vivo DNA synthesis (DNA replication) is dependent on a complex set of enzymes which have evolved to …
Reverse Transcription
Reverse transcription is part of the replication cycle of particular virus families, including retroviruses. It involves copying RNA into double-stranded complementary DNA (cDNA), using reverse transcriptase enzymes. In retroviruses, viral RNA is inserted into a host cell nucleus. There, a viral reverse transcriptase enzyme adds DNA nucleotides onto the RNA sequence, generating cDNA that is inserted into the host cell genome by the enzyme integrase, encoding viral proteins.
Polymerase chain reaction
A polymerase chain reaction is a form of enzymatic DNA synthesis in the laboratory, using cycles of repeated heating and cooling of the reaction for DNA melting and enzymatic replication of the DNA.
DNA synthesis during PCR is very similar to living cells but has very specific reagents and conditions. During PCR, DNA is chemically extracted from host c…
Gene synthesis
Artificial gene synthesis is the process of synthesizing a gene in vitro without the need for initial template DNA samples. In 2010 J. Craig Venter and his team were the first to use entirely synthesized DNA to create a self-replicating microbe, dubbed Mycoplasma laboratorium.
Oligonucleotide synthesis is the chemical synthesis of sequences of nucleic acids. The majority of biological research and bioengineering involves synthetic DNA, which can include oligonucleotides, …