How does the US Constitution create checks and balances?
This “balance of power” is detailed in the first three Articles of the US Constitution and is frequently referred to as a system of “checks and balances.” Of the three branch of government – Legislative, Executive, and Judicial, none has the power to overcome the other.
What does checks and balances in the constitution mean?
Checks and Balances - The American Constitution. What Are the Checks and Balances? Checks and balances is defined as the practice of dispersing political power and creating mutual accountability among political entities such as the courts, president, the legislature, and the citizens. What does that really mean?
What are constitutional checks and balances?
The system of checks and balances is an important part of the Constitution. With checks and balances, each of the three branches of government can limit the powers of the others. This way, no one branch becomes too powerful. the power of the other branches to make sure that the power is balanced between them.
What is the principle of checks and balances?
checks and balances, principle of government under which separate branches are empowered to prevent actions by other branches and are induced to share power. Checks and balances are applied primarily in constitutional governments. They are of fundamental importance in tripartite governments, such as that of the United States, which separate powers among legislative, executive, and judicial branches.
See more

What does Article 1 Section 4 of the Constitution say?
Section 4 Congress The Times, Places and Manner of holding Elections for Senators and Representatives, shall be prescribed in each State by the Legislature thereof; but the Congress may at any time by Law make or alter such Regulations, except as to the Places of chusing Senators.
What is Article 1 Section 3 of the Constitution?
Section 3 Senate No Person shall be a Senator who shall not have attained to the Age of thirty Years, and been nine Years a Citizen of the United States, and who shall not, when elected, be an Inhabitant of that State for which he shall be chosen. ArtI.S3.C3.1 Overview of Senate Qualifications Clause.
Did the Constitution include checks and balances?
The U.S. Constitution created a system called checks and balances to make sure that each of these three branches are also responsible for checking on the actions of other branches.
What does Article 1 Section 5 of the Constitution say?
Each House shall be the Judge of the Elections, Returns and Qualifications of its own Members, and a Majority of each shall constitute a Quorum to do Business; but a smaller Number may adjourn from day to day, and may be authorized to compel the Attendance of absent Members, in such Manner, and under such Penalties as ...
What is Article 1 Section 2 of the Constitution?
Article 1, Section 2 of the United States Constitution: The House of Representatives shall be composed of Members chosen every second Year by the People of the several States, and the Electors in each State shall have the Qualifications requisite for Electors of the most numerous Branch of the State Legislature.
What do Articles 1 2 3 of the Constitution do?
The first three articles establish the three branches of government and their powers: Legislative (Congress), Executive (office of the President,) and Judicial (Federal court system). A system of checks and balances prevents any one of these separate powers from becoming dominant.
What are 5 examples of checks and balances in the Constitution?
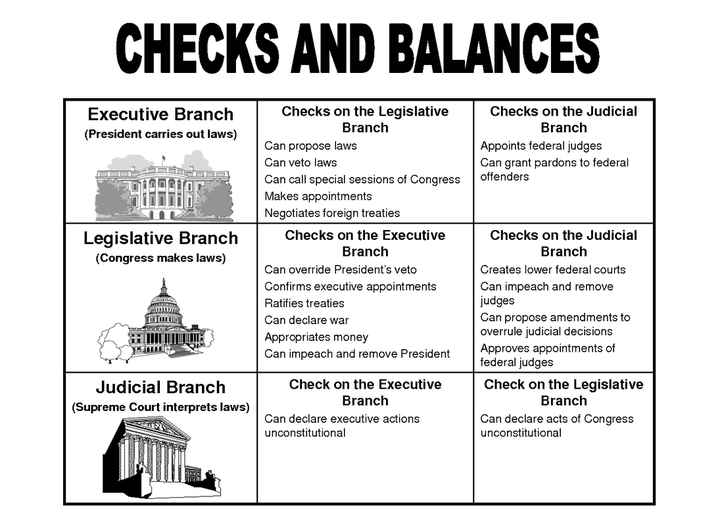
Executive BranchChecks on the Legislature. Veto power. Vice President is President of the Senate. Commander in chief of the military. ... Checks on the Judiciary. Power to appoint judges. Pardon power.Checks on the Executive. Vice President and Cabinet can vote that the President is unable to discharge his duties.
What does Article 1 Section 8 of the Constitution say?
Section 8. To make all laws which shall be necessary and proper for carrying into execution the foregoing powers, and all other powers vested by this Constitution in the government of the United States, or in any department or officer thereof.
What does Article 1 Section 7 of the Constitution mean?
Section 7 Legislation All Bills for raising Revenue shall originate in the House of Representatives; but the Senate may propose or concur with Amendments as on other Bills.
What does Article 1 Section 8 of the Constitution mean?
The Congress shall have Power To lay and collect Taxes, Duties, Imposts and Excises, to pay the Debts and provide for the common Defence and general Welfare of the United States; but all Duties, Imposts and Excises shall be uniform throughout the United States; ArtI.S8.C1.1 Taxation.
What is section 3 about in the Constitution?
Section 3. Treason against the United States, shall consist only in levying War against them, or in adhering to their Enemies, giving them Aid and Comfort. No Person shall be convicted of Treason unless on the Testimony of two Witnesses to the same overt Act, or on Confession in open Court.
What does Article 1 Section 3 Clause 7 of the Constitution mean?
Judgment in Cases of Impeachment shall not extend further than to removal from Office, and disqualification to hold and enjoy any Office of honor, Trust or Profit under the United States: but the Party convicted shall nevertheless be liable and subject to Indictment, Trial, Judgment and Punishment, according to Law.
What does Article 1 Section 3 Clause 4 of the Constitution say?
Clause 4 President The Vice President of the United States shall be President of the Senate, but shall have no Vote, unless they be equally divided.
How does the check and balance system work?
Checks and balances operate throughout the U.S. government, as each branch exercises certain powers that can be checked by the powers given to the other two branches.
Why did the Framers create checks and balances?
In addition to this separation of powers, the framers built a system of checks and balances designed to guard against tyranny by ensuring that no branch would grab too much power. “If men were angels, no government would be necessary,” James Madison wrote in the Federalist Papers, of the necessity for checks and balances.
What branch of government can impeach the Supreme Court?
By passing amendments to the Constitution, Congress can effectively check the decisions of the Supreme Court. Congress (considered the branch of government closest to the people) can impeach both members of the executive and judicial branches.
Which three branches of government were divided into?
Constitution divided the powers and responsibilities of the new federal government among three branches: the legislative branch, the executive branch and the judicial branch.
Which branch of government was divided into three branches?
Constitution divided the powers and responsibilities of the new federal government among three branches: the legislative branch, the executive branch and the judicial branch. ...
Which branch of government can declare a law unconstitutional?
The Supreme Court and other federal courts (judicial branch) can declare laws or presidential actions unconstitutional, in a process known as judicial review.
What were the three branches of government in Ancient Rome?
In his analysis of the government of Ancient Rome, the Greek statesman and historian Polybius identified it as a “mixed” regime with three branches: monarchy (the consul, or chief magistrate), aristocracy (the Senate) and democracy (the people). These concepts greatly influenced later ideas about separation of powers being crucial to a well-functioning government.
What is checks and balances?
Checks and Balances Definition. The definition of checks and balances is simply a system for distributing governmental powers. Each branch of the government has specific procedures only they can follow that help protect against fraud, errors, and illegal actions.
What was the purpose of the checks and balances system?
Once these branches were established, Congress realized they’d need to make sure no branch could simply overtake the others. This is where the system of checks and balances came in.
How often do checks and balances change?
Take a look at current events and you’ll probably see examples of checks and balances today in government proceedings. The president of the United States changes every four years, or eight years if a president is re-elected, and some government positions change more frequently. This keeps the system of checks and balances relevant as beliefs, attitudes, and opinions change. Continue exploring governmental powers by learning about the 25th Amendment.
What is the Constitution full of?
The U.S. Constitution is full of checks and balances of the three branches of government. The best example of checks and balances is that the president can veto any bill passed by Congress, but a two-thirds vote in Congress can override the veto.
What are the three branches of government?
The power of the new government was split into three branches, creating a clear separation of powers. The three branches of government are: 1 The executive branch (President, Vice President and cabinet) carries out laws. 2 The legislative branch (Congress: Senate and House of Representatives) makes laws. 3 The judicial branch (Supreme Court and other federal courts) interprets laws.
What is Article III of the Constitution?
Article III outlines the judicial powers of the judicial branch.
How to find out how the government structure was set up?
You can find out how the government structure was set up and what each branch is responsible for by looking at the Articles of the Constitution. The first three Articles tell you more details about each branch of the government: Article I outlines the powers of Congress, or the legislative branch. Article II outlines the executive branch and ...
Separation of Powers
The U.S. System of Checks and Balances
Checks and Balances Examples
- Checks and balances operate throughout the U.S. government, as each branch exercises certain powers that can be checked by the powers given to the other two branches. 1. The president (head of the executive branch) serves as commander in chief of the military forces, but Congress (legislative branch) appropriates funds for the military and votes to...
Checks and Balances in Action
- The system of checks and balances has been tested numerous times throughout the centuries since the Constitutionwas ratified. In particular, the power of the executive branch has expanded greatly since the 19th Century, disrupting the initial balance intended by the framers. Presidential vetoes—and congressional overrides of those vetoes—tend to fuel controversy, as do congressi…
Roosevelt and The Supreme Court
- The checks and balances system withstood one of its greatest challenges in 1937, thanks to an audacious attempt by Franklin D. Rooseveltto pack the Supreme Court with liberal justices. After winning reelection to his second term in office by a huge margin in 1936, FDR nonetheless faced the possibility that judicial review would undo many of his major policy achievements. From 193…
The War Powers Act and Presidential Veto
- The United States Congress passed the War Powers Act on November 7, 1973, overriding an earlier veto by President Richard M. Nixon, who called it an “unconstitutional and dangerous” check on his duties as commander-in-chief of the military. The act was created in the wake of the Korean War and during the Vietnam War and stipulates that the president has to consult Congre…
State of Emergency
- The first state of emergency was declared by President Harry Truman on December 16, 1950 during the Korean War. Congress did not pass The National Emergencies Act until 1976, formally granting congress checks on the power of the president to declare National Emergencies. Created in the wake of the Watergate scandal, the National Emergencies Act included several limits on p…
Sources
- Checks and Balances, The Oxford Guide to the United States Government. Baron de Montesquieu, Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. FDR’s Losing Battle to Pack the Supreme Court, NPR.org. State of Emergency, New York Times, Pacific Standard, CNN.