
When Is A Tracheostomy considered?
A tracheostomy may be performed for the following conditions: 1. Obstruction of the mouth or throat 2. Breathing difficulty caused by edema (swelli...
What Is A Tracheostomy Tube?
A tracheostomy (trach) tube is a small tube inserted into the tracheostomy to keep the stoma (opening) clear.Tracheostomy tubes are available in se...
What Do I Need to Know After Going Home With A Tracheostomy?
1. Immediately after the tracheostomy, you will communicate with others by writing until your healthcare provider gives you instruction for communi...
When Should I Call My Healthcare Provider?
Contact your healthcare provider or physician immediately: 1. If you have an irregular heart rate. 2. If you feel increased pain or discomfort.Note...
How Do I Take Care of My Tracheostomy Tube?
Your nurse will teach you the proper way to care for your tracheostomy tube before you go home. Routine tracheostomy care should be done at least o...
Why Is A Tracheostomy Performed?
A tracheostomy is performed to provide an airway in people who need to be on a mechanical ventilator, or who have trouble swallowing and are at ris...
Types of Tracheostomy Tubes
There are different types and sizes of tracheostomy tubes used for different reasons.Outer Cannula: The outer cannula is the main body of the tube....
Allowing For Speech When A Trach Tube Is Present
Cuff Deflations: A person can speak with a trach tube by deflating the cuff and placing a speaking valve. The Pulmonologist or Nurse Practioner wil...
How Long Will A Patient Have A Tracheostomy Tube?
The length of time a tracheotomy tube stays in place depends on why it was required in the first place. For individuals on a ventilator, it will ne...
Decannulation (Trach Tube Removal)
A tracheotomy tube can be removed if breathing or the airway improves to the point where the tube is no longer needed. During removal, the tube wil...
How long does it take for a tracheal tube to mature?
The tract between the skin and the tracheal lumen takes a little longer (10-14 days) to mature as there is no formal layer by layer dissection involved. We, therefore, perform the first tube change on Day 10-12 postoperatively.
What is the decision to perform a tracheostomy?
Once the decision to perform a tracheostomy has been made, the surgeon must determine if the patient is a good candidate for the surgery and obtain written informed consent. In addition, the range of motion of the neck needs to be assessed. The tracheostomy team, including the surgeons and anesthesiologists need to discuss the entire sequence and alternatives to the procedure. All equipment must be available and functioning properly.
How to identify cricothyroid space?
The cricothyroid space can be identified by palpating a slight indentation immediately below the inferior edge of the thyroid cartilage. Cricothyroid arteries traverse the superior aspect of this space on each side and anastomose near ...
What is the vertical incision for cricoid cartilage?
A horizontal or vertical incision centered on the inferior border of the cricoid cartilage may be used. We routinely use a 3-4 cm vertical incision.
Where is the introducer needle placed in bronchoscopy?
Placing the needle at the inferior edge of the light reflex, the tip of the needle is directed caudad into the tracheal lumen avoiding the posterior tracheal wall at all cost.
Is chest X-ray postoperative?
Postoperative Consideration. A chest X-ray is not routinely required as long as the entire procedure was done under direct visualization and there were no adverse events intraoperatively 6. The postoperative care is same as for the open procedure.
Is a tracheostomy the same as a routine tracheostomy?
They are the same as a routine open operative tracheostomy with particular attention to contraindications. 1
Where to take care of trach tube?
Stand or sit in a comfortable position in front of a mirror (in the bathroom over the sink is a good place to care for your trach tube).
What is a tracheostomy tube?
A tracheostomy (trach) tube is a small tube inserted into the tracheostomy to keep the stoma (opening) clear.
How do I take care of my tracheostomy tube?
Your nurse will teach you the proper way to care for your tracheostomy tube before you go home. Routine tracheostomy care should be done at least once a day after you are discharged from the hospital.
What is the opening of the neck called?
A tracheostomy is an opening (made by an incision) through the neck into the trachea (windpipe). A tracheostomy opens the airway and aids breathing.
Why do you need a tracheostomy cover?
Use tracheostomy covers to protect your airway from outside elements (such as dust, cold air, etc.) Ask your healthcare provider for more information about tracheostomy covers and where to purchase them.
How to clean a cannula?
Clean the inner cannula with pipe cleaners or a small brush. Thoroughly rinse the inner cannula with normal saline, tap water or distilled water (if you have a septic tank or well water). Dry the inside and outside of the inner cannula completely with a clean 4 x 4 fine mesh gauze pad.
What are the conditions that require a tracheostomy?
A tracheostomy may be performed for the following conditions: Obstruction of the mouth or throat. Breathing difficulty caused by edema (swelling), injury or pulmonary (lung) conditions. Airway reconstruction following tracheal or laryngeal surgery. Airway protection from secretions or food because of swallowing problems.
How is a trach tube held in place?
It is held in place with a Velcro strap, which wraps around the patient’s neck. The trach tube pictured here has a “cuff”. A cuff is a balloon attached around the outside of the tube. The cuff is inflated by filling the pilot balloon with air, which fills the cuff.
What is a tracheostomy tube?
What is a Tracheostomy? A tracheostomy is a hole in the windpipe (trachea) created by a surgeon. This hole, called a stoma, replaces a person’s nose and mouth as the pathway for breathing. A tracheostomy tube is inserted into the stoma to keep the hole open and provide an entryway into the lungs.
What is a Bivona trach tube?
Bivona® Trach Tubes: Traditional tracheostomy tubes are generally made of rigid plastic or metal. However, Bivona® trach tubes are made of soft silicone. This allows for greater movement and comfort with less irritation. Silicone is less porous than plastic and less likely to grow bacteria.
How often should you change a trach tube?
After the stoma is clean, place a gauze pad under the trach tube. A plastic trach tube should be replaced every two weeks. A Bivona® or a metal trach can be changed once a month. Keeping the trach site clean and replacing the tubes regularly will help keep your patient healthy and free from infection.
What is the function of the inner cannula?
The tube then functions as a port for suctioning to clean out the lungs. Inner Cannula: The inner cannula fits inside the trach tube and acts as a liner. This liner can be removed and cleaned to help prevent the build-up of mucus inside the trach tube. The inner cannula locks into place to prevent accidental removal.
Why does a tracheostomy interfere with speech?
Speech. A tracheostomy will interfere with a person’s ability to speak. This happens because the trach is located below the vocal cords. Air must be allowed to pass over and vibrate the vocal cords to create sound. However, with a trach tube, air moves in and out of the tube and does not reach the vocal cords.
Why do people need a tracheostomy?
A tracheostomy is performed to provide an airway in people who need to be on a mechanical ventilator or who have trouble swallowing and are at risk for aspiration. Aspiration is the act of breathing in a foreign object, such as, saliva, liquids or food. A tracheostomy is also done when a patient is unable cough up their own mucus and provides an easy way to suction mucus from the lungs.
How does a tracheostomy work?
A tracheostomy is a medical procedure — either temporary or permanent — that involves creating an opening in the neck in order to place a tube into a person’s windpi pe. The tube is inserted through a cut in the neck below the vocal cords. This allows air to enter the lungs.
Why do people cover their tracheostomy tubes?
This is because the air you breathe no longer passes through your voice box. For some people, covering the tube helps them talk. Alternately, special valves can be attached to the tracheostomy tube. While still taking in air through the tube, these valves allow air to exit the mouth and nose, permitting speech.
What is the name of the hole in the neck that the tube passes through?
Breathing is then done through the tube, bypassing the mouth, nose, and throat. A tracheostomy is commonly referred to as a stoma. This is the name for the hole in the neck that the tube passes through.
What are the risks of a tracheostomy?
Risks specific to a tracheostomy include: 1 damage to the thyroid gland in the neck 2 erosion of the trachea, which is rare 3 lung collapse 4 scar tissue in the trachea
What conditions require a tracheostomy?
Conditions that may require a tracheostomy include: anaphylaxis. birth defects of the airway. burns of the airway from inhalation of corrosive material. cancer in the neck. chronic lung disease. coma. diaphragm dysfunction. facial burns or surgery.
Where does the cut go in the neck?
Your surgeon will make a cut into your neck just below your Adam’s apple. The cut will go through the cartilaginous rings of the outer wall of your trachea , also known as your windpipe.
Can a tracheostomy cause an allergic reaction?
Every medical procedure where the skin is broken carries the risk of infection and excessive bleeding. There’s also a chance of an allergic reaction to anesthesia, although it’s rare. Tell your doctor if you’ve had an allergic reaction to anesthesia in the past. Risks specific to a tracheostomy include: damage to the thyroid gland in the neck.
How is a tracheostomy tube placed?
Tracheostomy tube placement can be performed surgically via open surgical tracheostomy (OST), or percutaneously via percutaneous dilational tracheostomy (PDT). PDTs are increasingly being performed at bedside in the intensive care unit rather than in operating rooms as there is no significant difference in postprocedure complications. 1,2 Procedure time is significantly decreased through placement with PDT and generally preferred over OST for elective tracheotomies. 2 The percutaneous approach performed with the single-step dilatation technique is more reliable than guidewire dilating forceps with regards to safety and success. 3 In addition, observational studies suggest that preprocedure use of ultrasound and bronchoscopy appears to reduce periprocedural complications such as bleeding, posterior membrane laceration, and false tract formation. 4,5
Why do you need a tracheostomy tube?
Placement of a tracheostomy tube is performed to bypass airway obstruction, aid in the management of secretions, to a reduction of anatomic dead space, and to aid in weaning from mechanical ventilation in patients with chronic respiratory failure. Complications of tracheostomy placement are infrequent, but can be life threatening.
How long does it take for a tracheostomy to mature?
Early complications of tracheostomy are those occurring within the first week following placement, as the tracheosto my stoma takes approximately 1 week to mature. Stomal infections and bleeding are the most common complications following OST, while PDT has a higher incidence of injury to the posterior wall of the trachea. There is no significant difference in complications between PDT and OST 2 ( Table 2 ).
Why do tracheostomy tubes have TIFs?
TIFs are due to erosion into the innominate artery by the tracheostomy tube because of elevated pressure from the tracheostomy tube cuff or contact between the distal end of the tracheostomy tube and the innominate artery . Formation of a tracheoinnominate fistula following tracheostomy placement is a medical emergency.
What are the contraindications for tracheostomy?
Indications for tracheostomy placement using either the surgical or percutaneous approach include upper respiratory tract obstruction, prolonged ventilation, copious secretions, severe obstructive sleep apnea, and head/neck surgery ( Table 1 ). Absolute contraindications for PDT include placement in pediatric patients, the presence of a midline neck mass, inability to palpate the laryngeal cartilages and tracheal rings, and uncorrectable coagulopathy. Relative contraindication for PDT include an unstable cervical spine, morbid obesity, anatomic distortion of the neck, previous neck surgery/radiation, active infection/burn/traumatic injury over neck, elevated intracranial pressure, significant ventilator requirements, and the need to secure the airway in an emergency situation in inexperienced hands. 6
How much pressure should a tracheostomy tube cuff be?
8 Tracheostomy tube cuff pressures should be measured on a regular basis and should range from 20 to 25 mm Hg.
How common is subcutaneous emphysema after tracheostomy?
The incidence of subcutaneous emphysema following tracheostomy vary from 0% to 5%. 11 Subcutaneous emphysema is caused by formation of a tissue tract anterior to trachea secondary to positive pressure ventilation or forced coughing against a tightly sutured or packed wound. Air driven by positive pressure ventilation can extend into to pleural space, leading to development of pneumothorax. This can be prevented by not suturing tissue around the wound tightly. Chest x-ray to identify subcutaneous air is recommended only when placement of the tracheostomy tube is technically challenging or in patients with signs and symptoms of subcutaneous air. Such complications are treated conservatively and are typically self-limited.
How is a Tracheostomy Tube Inserted?
Tracheotomies (the procedure that creates the opening or stoma in the patient’s neck where a tracheostomy tube will be placed through) are performed by surgeons or doctors.
What is a Tracheostomy Tube?
A tracheostomy tube is an artificial airway that bypasses the patient’s upper airway and is inserted directly into the trachea via a stoma. The tube is most often made from silicone or polyvinyl material.
What is a Fenestrated Tracheostomy Tube?
A fenestrated tracheostomy tube is a tracheostomy tube that has a hole above the tube’s cuff. This hole, combined with removal of the patient’s inner cannula, can allow airflow through the patient’s upper airway. Capping a fenestrated tube with the inner cannula removed and the cuff deflated can allow you to gauge the function of the patient’s upper airway.
How to Perform Tracheostomy Care?
Properly cleaning and caring for a tracheostomy is an essential step in preventing the tracheostomy from becoming infected or accidentally decannulated. Below are the steps to tracheostomy care:
Why is a trach airborne?
Because we have to remove anything that is covering a trach prior to cleaning it (such as an HME), any secretions the patient expectorates during trach care is liable to become airborne.
What are the risks of a tracheostomy?
The most common risks and complications of a tracheostomy include: Damage to the larynx or trachea, such as tracheal or laryngeal lesions, the formation of granulomas, etc. Obstruction to the tracheostomy tube from secretions or blood clots that prevent ventilation.
What is a fenestrated tube?
Fenestrated tracheostomy tubes (tubes with a hole above the cuff to help the patient with weaning or speaking)
How is a tracheostomy performed?
The tracheostomy procedure is performed in the operating room under general anesthesia. A small incision is made in the skin overlying the trachea in the middle of the neck. The surgeon exposes the airway and makes a small incision into the trachea. The tracheostomy tube is placed in the hole, and secured to the neck.
How long does it take to change a tracheostomy tube?
The tracheostomy tube is changed to a new tube by the surgeon several days after the operation. Occasionally, the ties around the neck are changed during the first week after the operation.
What is a tracheostomy?
The term tracheostomy is used to describe a surgically created hole in the neck that extends to the trachea (windpipe) to allow for safe breathing. A tracheostomy tube is the plastic breathing tube that is placed into the hole.
Who needs a tracheostomy?
There are many reasons why a child may need a tracheostomy. Two common reasons include:
Can a child eat with a tracheostomy tube?
As a general rule, the tracheostomy tube will not keep your child from being able to eat normally or use their voice, although some children may not be able to eat orally or speak for other reasons . Many children with a tracheostomy tube are able to lead happy lives.
Can you swim with a tracheostomy?
When a tracheostomy is present, care must be taken to prevent water or sand from getting into the tracheostomy tube (no swimming.)
Is a tracheostomy permanent?
For most children the tracheostomy is not permanent. The length of time it stays in place depends on the individual patient and the reason it was initially placed. Although some tracheostomy tubes stay in place for many months or years, many are temporary and can be removed after a shorter period of time. After the tracheostomy tube is removed, the hole frequently closes by itself. If it does not close by itself, the hole can be surgically closed.
Why do you need a tracheostomy tube in the neck?
If a patient has been on prolonged ventilation through a tube in the mouth, a tracheostomy tube in the neck may allow the patient to be wide awake and more comfortable as they work towards becoming unhooked from the ventilation equipment and breathe on their own.
How to do a percutaneous tracheostomy?
During a percutaneous tracheostomy, the doctor will insert a needle through the lower front part of your neck and into your trachea followed by a small incision. Then, a catheter is threaded through the needle into the windpipe, and the opening is successively dilated until a tracheotomy tube can be inserted over the catheter.
What should I expect during a tracheostomy?
To create a surgical tracheostomy, a surgeon makes a cut through the lower front part of your neck and then another into your trachea, or windpipe. A tube is then placed through the hole and into the windpipe. Held in place with stitches, surgical tape or a Velcro band, the tube will help keep the hole open. The procedure to make a tracheostomy usually takes between 20 and 45 minutes.
What are potential complications from a tracheostomy?
However, the two complications doctors see most often are profuse bleeding or a dislodged tracheotomy tube. Yale Medicine doctors address severe bleeding immediately with anti-hemorrhagic dressing to stem the blood. Our doctors also take extra precautions to prevent the tube from falling out typically by suturing the tube in four quadrants and tying it in place.
Why do you need a tracheostomy?
There are three major reasons why someone may need a tracheostomy, says Dr. Mehra. They include: 1 To help patients loosen and remove mucus or phlegm from the bronchioles to the upper airways to prevent lung infections. A tracheostomy allows doctors to insert a suction catheter into the lungs to remove mucus. 2 If a patient has been on prolonged ventilation through a tube in the mouth, a tracheostomy tube in the neck may allow the patient to be wide awake and more comfortable as they work towards becoming unhooked from the ventilation equipment and breathe on their own. 3 If a patient has an obstructed upper airway because of a tumor, inflammation, infection, or other blockage, a tracheotomy can easily and safely deliver oxygen directly to the lungs, bypassing the obstruction.
What is the name of the procedure that is done through the neck into the trachea?
One solution to this problem is a tracheostomy. A tracheostomy is a temporary or permanent opening surgically created through the neck into the trachea (or windpipe) where a tube is then placed so that the patient can breathe. The procedure is also called a tracheotomy, but both terms are often used interchangeably.
How long does it take to make a tracheostomy?
The procedure to make a tracheostomy usually takes between 20 and 45 minutes.
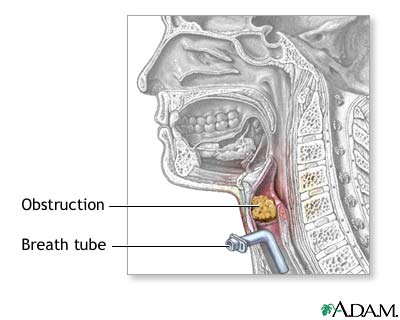
Why It's Done
- Situations that may call for a tracheostomy include: 1. Medical conditions that make it necessary to use a breathing machine (ventilator) for an extended period, usually more than one or two weeks 2. Medical conditions that block or narrow your airway, such as vocal cord paralysis or thr…
Risks
- Tracheostomies are generally safe, but they do have risks. Some complications are particularly likely during or shortly after surgery. The risk of such problems greatly increases when the tracheotomy is performed as an emergency procedure. Immediate complications include: 1. Bleeding 2. Damage to the trachea, thyroid gland or nerves in the neck 3. Misplacement or displ…
How You Prepare
- How you prepare for a tracheostomy depends on the type of procedure you'll undergo. If you'll be receiving general anesthesia, your doctor may ask that you avoid eating and drinking for several hours before your procedure. You may also be asked to stop certain medications.
What You Can Expect
- During the procedure
A tracheotomy is most commonly performed in an operating room with general anesthesia, which makes you unaware of the surgical procedure. A local anesthetic to numb the neck and throat is used if the surgeon is worried about the airway being compromised from general anesthesia or i… - After the procedure
You'll likely spend several days in the hospital as your body heals. During that time, you'll learn skills necessary for maintaining and coping with your tracheostomy: 1. Caring for your tracheostomy tube.A nurse will teach you how to clean and change your tracheostomy tube to h…
Results
- In most cases, a tracheostomy is temporary, providing an alternative breathing route until other medical issues are resolved. If you need to remain connected to a ventilator indefinitely, the tracheostomy is often the best permanent solution. Your health care team will help you determine when it's appropriate to remove the tracheostomy tube. The hole may close and heal on its own…
Surgical Anatomy
Indications For PDT
- They are the same as a routine open operative tracheostomy with particular attention to contraindications.1
Preparation For Tracheostomy
- Once the decision to perform a tracheostomy has been made, the surgeon must determine if the patient is a good candidate for the surgery and obtain written informed consent. In addition, the range of motion of the neck needs to be assessed. The tracheostomy team, including the surgeons and anesthesiologists need to discuss the entire sequence and alternatives to the pro…
Equipment
- A regimented approach to preparation and performance of the procedure has been shown to significantly reduce the incidence of procedural complications4. Our approach includes the following equipment and protocols: 1. We routinely use Cook Blue Rhino single dilator kit and videobronchoscopy to perform the procedure. 2. The following must be available: 2.1. An attendi…
Technique
- The technique described here is based on Seldinger’s principle 2. The technique we use was first described and later modified by Ciaglia 3. The use of bronchoscopy was first introduced by Marelli et al and has subsequently been adopted by many centers 4, 5. Positioning 1. The patient’s neck is extended over a shoulder roll (unless there is a contraindication). 2. The anesthesiologist stan…
Postoperative Consideration
- A chest X-ray is not routinely required as long as the entire procedure was done under direct visualization and there were no adverse events intraoperatively6. The postoperative care is same as for the open procedure. The tract between the skin and the tracheal lumen takes a little longer (10-14 days) to mature as there is no formal layer by layer dissection involved. We, therefore, pe…
Bibliography
- Goldenberg D, Bhatti .N. Management of the Impaired Airway in the Adult, in Otolaryngology: Head & Neck Surgery, Cummings CW, Editor. 2005, Mosby
- Seldinger, S.I., Catheter replacement of the needle in percutaneous arteriography; a new technique. Acta Radiol, 1953. 39(5): p. 368-76.
- Ciaglia, P., R. Firsching, and C. Syniec, Elective percutaneous dilatational tracheostomy. A n…
- Goldenberg D, Bhatti .N. Management of the Impaired Airway in the Adult, in Otolaryngology: Head & Neck Surgery, Cummings CW, Editor. 2005, Mosby
- Seldinger, S.I., Catheter replacement of the needle in percutaneous arteriography; a new technique. Acta Radiol, 1953. 39(5): p. 368-76.
- Ciaglia, P., R. Firsching, and C. Syniec, Elective percutaneous dilatational tracheostomy. A new simple bedside procedure; preliminary report. Chest, 1985. 87(6): p. 715-9.
- Bhatti N, Mirski M, Tatlipinar A, Koch WM, Goldenberg D. Reduction of complication rate in percutaneous dilation tracheostomies. Laryngoscope, 2007. 117(1):172-5.