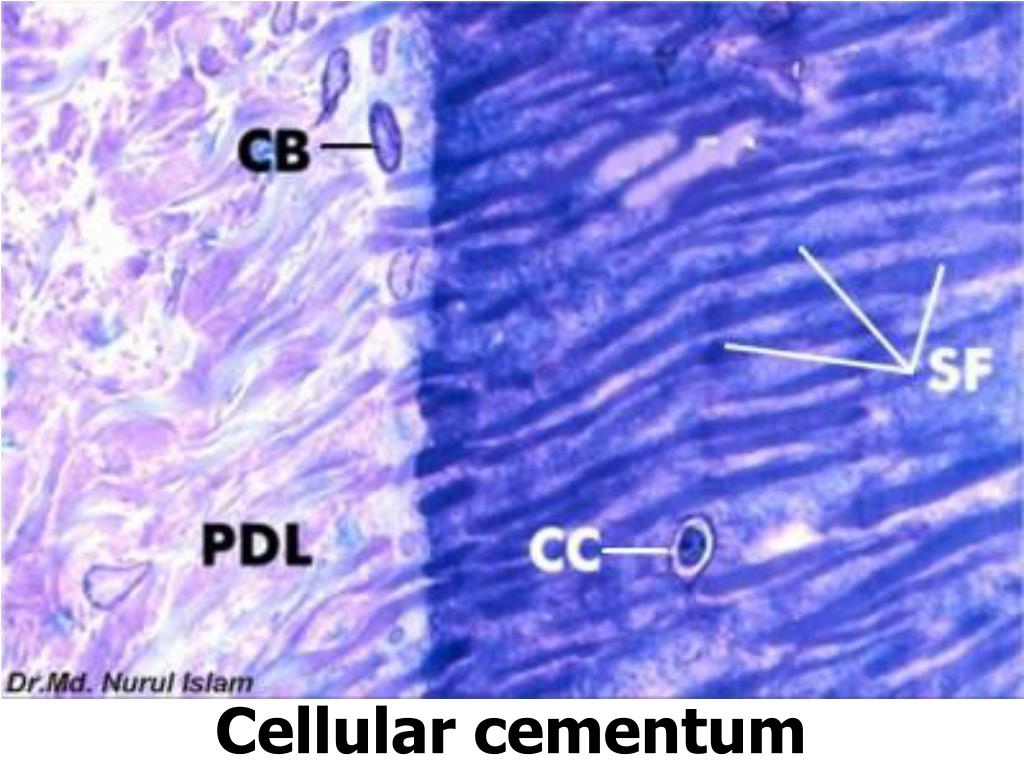
Cellular, mixed fiber cementum
- Found on the apical third of the root and in furcations
- Mineralized, extrinsi_c collagen fibers (Sharpey’s fibers) run a more irregular course
- Intrinsic fibers are found interspersed with extrinsic fibers (individual Sharpey’s fibers are readily identifiable)
- Cementoblasts are trapped in lacunae where they become cementocytes
Where is the cellular cementum located in a root?
Cellular cementum is found in the apical half of the root. , and can be found in the coronal half of the root as well as underneath cellular cementum in the apical portion (cementum is around 50 μM thick in the coronal region and 200 μM thick in the apical region). .
What is the difference between acellular and cellular cementum?
The cementum attached to the root dentin and covering the upper (cervical) portion of the root is acellular and thus is called acellular, or primary, cementum. The lower (apical) portion of the root is covered by cellular, or secondary, cementum.
Where is the cementum located in a pulp canal?
Cementum on the root ends surrounds the apical foramen and may extend slightly onto the inner wall of the pulp canal. Cementum is secreted by cells called cementoblasts within the root of the tooth and is thickest at the root apex.
What is the function of the cementum?
Cementum is a bone-like mineralized tissue lining the dentin of the root that protects the root and also serves as an attachment surface to anchor the PDL to the tooth (Diekwisch, 2001). Cementum covers the roots of the teeth and is interlocked firmly with the dentin of the root (see Figures 1-1, 1-2, and 1-5, B ).

What is cellular cementum?
Cementum is a thin layer of hard dental tissue covering the anatomic roots of teeth. It is formed by cells known as cementoblasts, which develop from undifferentiated mesenchymal cells in the connective tissue of the dental follicle.
What is cellular and acellular cementum?
Summary – Cellular vs Acellular Cementum Cementum is a bone-like mineralized tissue that lines the dentin of the root while protecting the root. Cellular cementum is relatively thick and covers the apical half of the root, while acellular cementum is relatively thin and covers the cervical half of the root.
How is cellular cementum formed?
The development of acellular cementum seems to be associated with secretion of enamel-related proteins by cells of the epithelial root sheath. Formation of the matrix for cellular cementum appears to be induced by exposure of the inner layer of the epithelial root sheath to the mesenchymal cells in the dental follicle.
What is difference between acellular and cellular?
The main difference between acellular and cellular organism is that acellular organism doesn't contain cells and cellular organism contain cells. ... The main properties of living beings are self-regulation, self-reproduction and self-renewal which doesn't occur in case of acellular organism.
What are the types of cementum?
There are three types of cementum: acellular cementum, cellular cementum and afibrillar cementum. Acellular cementum covers about 1/3-1/2 of the root and has little to no cellular components. Cellular cementum covers about 1/3-1/2 of the apex and is permeable.
What is primary and secondary cementum?
Primary cementum is frequently the only type of cementum found on the roots of incisors and canines (single-rooted teeth). Secondary cementum is found chiefly in the apical regions of the roots of premolars and molars (multi-rooted teeth).
What is primary cementum?
Primary cementum (PC), which covers the coronal two-thirds of the root is the major contributor for attachment of dentition to alveolar bone [1, 2].
What is tooth cementum made of?
cementum, also called Cement, in anatomy, thin layer of bonelike material covering the roots and sometimes other parts of the teeth of mammals. Cementum is yellowish and softer than either dentine or enamel. It is made by a layer of cementum-producing cells (cementoblasts) adjacent to the dentine.
What is meant by acellular?
Definition of acellular 1 : containing no cells acellular vaccines. 2 : not divided into cells : consisting of a single complex cell —used especially of protozoa and ciliates.
What is the difference between acellular microbes and cellular microorganisms?
Cellular microbes include bacteria, the archaea, the fungi, and the protists ( algae, protozoa, slime molds, and water molds). Cellular microbes can be either unicellular or multicellular. Acellular microbes include viruses and other infectious agents, such as prions and viroids.
What is primary and secondary cementum?
Primary cementum is frequently the only type of cementum found on the roots of incisors and canines (single-rooted teeth). Secondary cementum is found chiefly in the apical regions of the roots of premolars and molars (multi-rooted teeth).
What is the function of cementum?
This connective tissue, called cementum, forms along a tooth's root and helps solidify it by connecting to fibers that support the tooth's place in the jawbone. It is like enamel but softer. Cementum also functions to cover the tooth's dentin, a bone-like substance that makes up most of our tooth structure.
What Is Cementum?
This connective tissue, called cementum, forms along a tooth's root and helps solidify it by connecting to fibers that support the tooth's place in the jawbone. It is like enamel but softer. Cementum also functions to cover the tooth's dentin, a bone-like substance that makes up most of our tooth structure.
What is the purpose of acellular cementum?
Acellular cementum has only extrinsic fibers, covers the part of the tooth where the root meets the crown, and serves the purpose of anchoring the tooth in the gum.
What Are The Different Types of Cementum?
Cementum has two main categories, cellular and acellular. As noted in a 2016 study published in the Public Library of Science, cellular cementum is thick, contains collagen fibers (both extrinsic and intrinsic), and covers the bottom half of the root. Acellular cementum has only extrinsic fibers, covers the part of the tooth where the root meets the crown, and serves the purpose of anchoring the tooth in the gum.
What Are Issues Affecting Cementum?
In addition to affecting tooth sensitivity and being affected by gum disease, cementum plays an essential role in a few oral health issues.
What is the cementoenamel junction?
The cementoenamel junction is the specific line around the tooth's perimeter, where the enamel covering the crown of the tooth meets the cementum protecting the root. In most cases, the cementum overlaps the enamel around the tooth. Still, in some people, this area contains a thin band of exposed dentin. At this location, the hard, mineralized ...
What causes cementum to be lost?
While cementum loss can cause issues, other issues like dental diseases can also contribute to cementum loss. Gum disease, or periodontitis, can cause cementum loss, for example. This loss happens when the bones and fibers that hold the teeth in place are irreversibly damaged. The destruction of bones and cementum takes place in advanced gum ...
How to treat cementoblastoma?
Treatment of a cementoblastoma involves removing the growth and the affected tooth or teeth. The best treatment includes the surgical removal of the cementoblastoma and the affected tooth, usually a lower premolar or molar. While extracting a tooth is never ideal, the risk of the growth reappearing makes it essential.
Where is cementum secreted?
Cementum is secreted by cells called cementoblasts within the root of the tooth and is thickest at the root apex. These cementoblasts develop from undifferentiated mesenchymal cells in the connective tissue of the dental follicle or sac.
What is the cementum of a tooth?
Anatomical terminology. Cementum is a specialized calcified substance covering the root of a tooth. The cementum is the part of the periodontium that attaches the teeth to the alveolar bone by anchoring the periodontal ligament.
Why is cementum formed continuously throughout life?
It is formed continuously throughout life because a new layer of cementum is deposited to keep the attachment intact as the superficial layer of cementum ages.
What is the surface layer of the tooth root?
Cementum. The cementum is the surface layer of the tooth root, covering the dentin (which is labeled B ). Rather than being a passive entity like paint on a wall, cementum is a dynamic entity within the periodontium.
What type of fibers are used to attach tooth to alveolar bone?
These cementoblasts can form subsequent layers of cementum if the tooth is injured. Sharpey fibers are part of the principal collagenous fibers of the periodontal ligament embedded in the cementum and alveolar bone to attach the tooth to the alveolus.
Why is the crown bigger than the anatomical crown?
This is often due to gingival recession and may be an indication of periodontal disease.
Which type of ligament connects the tooth to the alveolar bone?
The extrinsic fibres within acellular extrinsic fibre cementum, travel perpendicular to the surface of the root and allow the tooth to attach to the alveolar bone by the periodontal ligament (PDL), continuous with the cementodentinal junction (CDJ). Acellular cementum only contains extrinsic collagen fibres.
Which cells can deposit cementum?
Interestingly, cells other than cementoblasts and odontoblasts derived from dental papillae can deposit cementum. Calvarial cells – which, like cementoblasts, are of neural crest origin – can produce a cementum-like tissue when cocultured with slices of tooth root, presumably as a result of an inductive interaction ( Melcher et al., 1987 ), and cementum is deposited onto existing dentine.
Where do collagenous fibres insert into the cementum?
Figure 1.11. The collagenous fibres of a murine periodontal ligament insert into the cementum (bottom) of the first molar tooth.
What is the cementum of dentine?
Cementum is deposited by cementoblasts onto existing dentine, a site that gives cementum features of dentine. Cementoblasts, along with the odontoblasts that deposit dentine, osteoblasts that deposit supporting (alveolar) bone and the fibroblasts that deposit pulp and periodontal ligament ( Figure 1.11) arise from the dental papilla, which is a neural crest cell derivative ( Chapter 17 ). Acellular and cellular cementum are well recognised and ancient supporting tissue for teeth ( Poole, 1967; Diekwisch, *2001; Luan et al., 2009 ).
How many types of cementum are there?
In addition, cementum has been further classified according to the nature of its organic matrix [ 4 ]. Thus, generally, four types of cementum are recognized:
What is the bone tissue that anchors the periodontal ligament to the tooth?
Cementum. Cementum is a bone-like mineralized tissue lining the dentin of the root, which functions both to protect the root and as an attachment surface used to anchor the periodontal ligament to the tooth. From: Handbook of Stem Cells, 2004. Download as PDF. About this page.
Why is cementum ignored?
Cementum is often ignored by skeletal biologists, probably because it is associated in our minds and in the organism with teeth, rather than the skeleton. However, like dentine, cementum exists in a variety of forms, some of which reflect deposition of odontoblast products into the cementum matrix. Consequently, cementum can stand alone as a tissue, or present as an admixture of tissues an intermediate tissue. Variation exists even within individuals; cementum can be acellular distally but cellular proximally. On the other hand, the teeth of extinct mosasaurs were supported by acellular cementum, cellular cementum, a mineralised periodontal ligament and alveolar bone ( Luan et al., 2009 ), indicating that cementum can exist as a stable skeletal tissue.
What is the supporting tissue that anchors the teeth of many vertebrates into their sockets?
Cementum . Cementum , the supporting tissue that anchors the teeth of many vertebrates into their sockets has features specific to cementum, features of dentine (see Chapter 5 ), and in some locations, such as on the coronal surface of the molar teeth in guinea pigs, Cavia porcellus, has features of calcified cartilage.
Where is cellular cementum found?
Cellular cementum is found in the apical half of the root. Acellular cementum. does not contain. cementocytes. , and can be found in the coronal half of the root as well as underneath cellular cementum in the apical portion (cementum is around 50 μM thick in the coronal region and 200 μM thick in the apical region).
What connects the cementum to the alveolar bone?
The Periodontal Ligament () is a region of#N#dense regular connective tissue#N#← that connects the cementum to#N#alveolar bone#N#.#N#Sharpey's fibers#N#extend from one side of the PDL into cementum, and on the other side of the PDL into alveolar bone. Like the , the border between cementum and PDL is blurred due to their shared lineage. Clusters of rogue epithelial cells can be found within the PDL which are named the#N#epithelial rests of Malassez#N#. The PDL has a much higher degree of#N#vascularity#N#than other ligaments. It also has a more diverse and numerous population of cells (compare Fig. 4.14 to the link to dense regular connective tissue above).
How many cells are in each rod of enamel?
Figure 4.2: The ECM of enamel is laid down in rods next to other rods, each rod is secreted by one cell. In contrast, bone tissue is deposited in a circular layer upon circular layer, each cell working only in one layer.
What is the extracellular matrix?
Extra-Cellular Matrix: Materials in the body, but outside of cells. A network of macromolecules, such as fibers, enzymes, and glycoproteins, that provide structural and biochemical support to surrounding cells.
What is the name of the group of connective tissue fibers that attach a tooth to alveolar bone?
Periodontal Ligament , a group of specialized connective tissue fibers that attach a tooth to alveolar bone. A hard connective tissue which is mostly ECM, including collagen fibers and a calcium-phosphate crystal. A differentiated connective tissue cell that secretes bone ECM, including collagen, calcium and phosphate.
What is the porous surface of the ethmoid bone called?
The porous surface is called the. cribriform plate. , which is not to be confused with the other region of compact bone riddled with tiny holes, the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone (whose holes are for olfactory nerve endings, connecting the nasal cavity to the brain).
What is the histology of alveolar bone?
Alveolar bone. contains compact bone tissue, with a semi-unique feature of many tiny holes through which. Sharpey's fibers. from the insert , as well as larger holes for the nerves, blood and lymphatic vessels that exit bone tissue and enter the apical foramen of a tooth.
What are the cells that are present in the cementum?
The cells which are present within the cementum are the entrapped cementoblasts, or the cementocytes. Each cementocyte lies in its lacuna, which is similar to the pattern found in the bone. In addition, these lacunae have canals. However, unlike those which are found in bone, the canals which are in the cementum do not contain nerves, nor do they radiate outward. These canals orient toward the periodontal ligament. They contain cementocytic processes which diffuse nutrients from the ligament.
What is the cementum of the tooth?
The cementum is a special type of calcified substance which covers the tooth’s roots. The cementum is included as part of the periodontium. It anchors the periodontal ligament and attaches the teeth to the alveolar bone.
What is the cementoid that surrounds the cementocytes?
Once the cementoid reaches the necessary thickness, the cementoid which surrounds the cementocytes is mineralized and is considered to be cementum. As a result of the apposition of cementum on the dentin, the dentinocemental junction (DCJ) forms. This interface is not as defined compared to the dentinoenamel junction (DEJ). The cementum and dentin are from a similar embryological background, which differs from that of the enamel and dentin.
Why is my cementum visible?
When the cementum is visible on the teeth, this suggests that there is root exposure. This often occurs as a result of gingival recession. It may also be sign of periodontal disease.
Where do cementoblasts collect?
This occurs on the outer covering of the periodontal ligament. These cementoblasts are able to form additional layers of cementum in the event the tooth suffers an injury.
What is the dentinocemental junction?
The dentinocemental junction (DCJ) is a relatively smooth area which exists in permanent teeth. While the attachment of cementum to the dentin is firm, it is not fully understood.
