Where are Chaco people from?
The indigenous Gran Chaco people consist of approximately thirty-five tribal groups in the Gran Chaco of South America. Because, like the Great Plains of North America, the terrain lent itself to a nomadic lifestyle, there is little to no archaeological evidence of their prehistoric occupation.
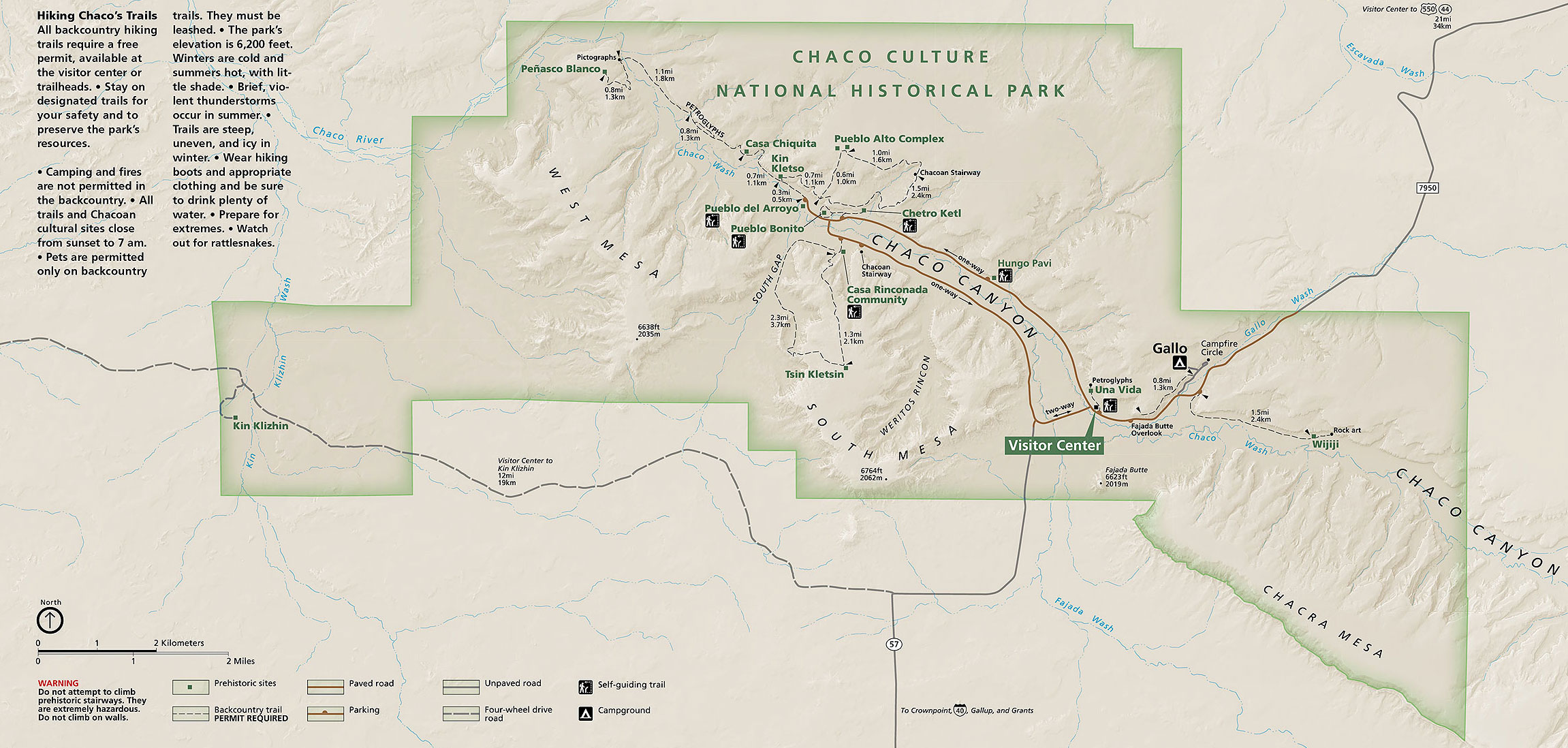
Where in the US is Chaco Canyon?
northwestern New MexicoChaco Canyon is located in northwestern New Mexico. The park can only be accessed by driving on dirt roads.
What city is Chaco Canyon near?
Bloomfield, Aztec and Farmington, New Mexico, are the closest towns to Chaco Canyon National Historical Park's main north road. Each is about an hour and a half from the park's entrance.
What is Chaco known for?
Chaco Canyon served as a major center of ancestral Puebloan culture. Remarkable for its monu mental buildings, distinctive architecture, astronomy, artistic achievements, it served as a hub of ceremony, trade, and administration for the Four Corners Area unlike anything before or since.
What does Chaco mean?
Chaco refers to a place—Chaco Canyon—and to an ancient Puebloan society that developed in that place. Chacoan society arose in an isolated canyon setting without highly visible resources. Chacoans developed ritual-ceremonial system that quickly spread across a large portion of the ancient Puebloan landscape.
How hard is it to get to Chaco Canyon?
It's a long drive over rough road to reach the park and pueblos. First 6 miles are ok but next 7 miles are over roadbed as rough as a washboard. You have to drive slowly as the road is so rutted and even then your bones are jarred.
How many days do you need in Chaco Canyon?
To get a good feel for Chaco takes about 3 days 2 nights. We usually get their early on the first day and tour the loop buildings all day, go back to the campground and build a nice relaxing fire to sit near and wait for the chile con carne to warm up.
Do you need reservations for Chaco Canyon?
Group stays are limited to seven days at a time. Group campground reservations must be made in advance by visiting www.recreation.gov or by calling 1-877-444-6777. All groups making reservations must call and inform the Visitor Center of their stay (505-786-7014 ext 253).
Is there cell service at Chaco Canyon?
Internet & Cellular Access There is limited cell service inside the Visitor Center. Does not work with all carriers and not strong enough to use the internet. Chaco Culture National Historical Park preserves a major center of ancestral Puebloan culture dating between 850 and 1250 CE.
Why did people leave Chaco?
It's not completely clear why the people left Chaco Canyon, but prolonged drought is one possible explanation. It was around this time that communities in other places in the region, such as Mesa Verde and the Chuska Mountains, grew in size and importance.
Why was Chaco abandoned?
But by the end of the 12th century, Chaco Canyon had been abandoned. No one knows why for sure, but the thinking among archaeologists has been that excessive logging for firewood and construction caused deforestation, which caused erosion, which made the land unable to sustain a large population.
What does Anasazi mean in Navajo?
“ancient enemyThe term is Navajo in origin, and means “ancient enemy.” The Pueblo peoples of New Mexico understandably do not wish to refer to their ancestors in such a disrespectful manner, so the appropriate term to use is “Ancestral Pueblo” or “Ancestral Puebloan.”
Is Chaco Canyon open to public?
Chaco Culture National Historical Park has one Visitor Center that is open from 9:00am-5:00pm daily from May through October; and from 8:00am-4:00pm from November through April. Hiking trails and archaeological sites are open daily from 7:00am to 9:00pm.
Why was the Chaco Canyon abandoned?
But by the end of the 12th century, Chaco Canyon had been abandoned. No one knows why for sure, but the thinking among archaeologists has been that excessive logging for firewood and construction caused deforestation, which caused erosion, which made the land unable to sustain a large population.
What happened to the people that lived in Chaco Canyon?
By the 1300s, all of the villages and pueblos of Chaco Canyon were abandoned. As the ancient Indians left, their kivas were ceremonially burned, and most of their possessions were left behind.
Why is Chaco Canyon sacred?
This history is of deep importance to the living ancestors of the ancient Pueblo people who live in communities in New Mexico and Arizona. Chaco Canyon is a sacred pilgrimage site for those who believe their ancestors still dwell in the ancient city.
Where is Chaco located?
The province of Chaco lies within the southern part of the Gran Chaco region, a vast lowland plain that covers territories in Argentina, Paraguay, and Bolivia .
What is Chaco in Argentina?
Chaco ( Spanish pronunciation: [ˈtʃako]; Wichi: To-kós-wet ), officially the Province of Chaco ( Spanish: provincia del Chaco [pɾoˈβinsja ðel ˈtʃako] ), is one of the 23 provinces in Argentina. Its capital and largest city, is Resistencia. It is located in the north-east of the country.
What language does Chaco speak?
In 2010, Chaco became the second province in Argentina to adopt more than one official language. These languages are the Kom, Moqoit and Wichí languages, spoken by the Toba, Mocovi and Wichí peoples respectively.
How many hunters would enter the Chaco Gualamba?
Annually, large groups of up to thirty thousand hunters would enter the territory, forming columns and circling their prey. Jesuit missioner Pedro Lozano wrote in his book Chorographic Description of the Great Chaco Gualamba, published in Cordoba, Spain in 1733: "Its etymology indicates the multitude of nations that inhabit that region. When they go hunting, the Indians gather from many parts the vicuñas and guanacos; that crowd is called chacu in the Quechua language, which is common in Peru, and that Spaniards have corrupted into Chaco ".
What river separates Chaco from Corrientes?
The Paraná and Paraguay rivers separate Chaco province from Corrientes Province and the Republic of Paraguay. To the north, the river Bermejo forms another natural border, dividing Chaco Province from Formosa Province .
What river runs through Santa Fe?
Other important rivers include: the Negro, Tapenagá, Palometa, and Salado, all tributaries or anabranches of the river Paraná .
When was Gran Chaco established?
The Territorio Nacional del Gran Chaco was established in 1872. This territory, which included the current Formosa Province and lands presently inside Paraguay, was superseded by Territorio Nacional del Chaco upon its administrative division, in 1884.
Where is Chaco located?
The Chaco’s northern and southern boundaries are not as precise: it generally is said to reach northward to the Izozog Swamps in eastern Bolivia and southward to about latitude 30° S, or roughly the Salado River in Argentina.
What type of soil is Chaco?
Chaco soils range from sandy to heavy clay. Soils in the more humid east have more organic material and lateritic subsoils, whereas in the west the soils contain less surface organic material and have predominately calcareous subsoils. The local determining factor is drainage, whether a function of soil texture or of relative relief. Sometimes differences in elevation of less than three feet result in different soil types. Grasslands, or savannas, generally tend to be associated with sandier soils, bushlands with poorly drained clay soils, and the forestland with better-drained clay soils. In many cases, the high concentration of dissolved salts in the groundwater creates conditions in swampy sites that are intolerable to most plants, thus extending an arid appearance even into many areas where water is abundant.
What river drains the Gran Chaco?
Drainage. All but the extreme northwestern sector of the Gran Chaco is drained by west-bank tributaries of the Paraguay and Paraná rivers. The Bermejo and the Pilcomayo, even though they manage to traverse the Chaco, remain typical of most Chaco streams.
Which river flows through Paraguay?
The two permanent rivers of the Gran Chaco, the Pilcomayo and the Bermejo (Teuco), flow southeastward across the plain from their Andean headwaters to the Paraguay River and demarcate the three main regional divisions of the Chaco in Paraguay and Argentina: the Chaco Boreal north of the Pilcomayo, the Chaco Central between the two rivers, and the Chaco Austral south of the Bermejo; the portion of the Chaco in Bolivia commonly is called the Bolivian Chaco.
What is the climate of Gran Chaco?
With its considerable north-south extent, the Gran Chaco is subject to climates that vary from tropical in the north to warm-temperate in the south. Most of the region, however, is subtropical. Average temperatures vary from 60 to 85 °F (16 to 29 °C), with an average relative humidity between 50 and 75 percent.
How deep is Gran Chaco?
Because of its alluvial character, the Gran Chaco is nearly stone-free and is composed of unconsolidated sandy and silty sediments that are up to 10,000 feet (3,050 metres) deep in some places.
How many miles is the Gran Chaco?
Thus defined, the Gran Chaco extends some 450 miles (725 km) from east to west and about 700 miles (1,100 km) from north to south and covers about 280,000 square miles (725,000 square kilometres); of this total, slightly more than half lies within Argentina, a third in Paraguay, and the remainder in Bolivia. The two permanent rivers of the Gran ...

Overview
Chaco , officially the Province of Chaco (Spanish: provincia del Chaco [pɾoˈβinsja ðel ˈtʃako]), is one of the 23 provinces in Argentina. Its capital and largest city, is Resistencia. It is located in the north-east of the country.
It is bordered by Salta and Santiago del Estero to the west, Formosa to the north, Corrientes to the east, and Santa Fe to the south. It also has an international bor…
Etymology
Chaco derives from chaku, the Quechua word used to name a hunting territory or the hunting technique used by the people of the Inca Empire.
Annually, large groups of up to thirty thousand hunters would enter the territory, forming columns and circling their prey. Jesuit missioner Pedro Lozano wrote in his book Chorographic Description of the Great Chaco Gualamba, published in Cordoba, Spain in 1733: "Its etymology indicates the …
Geography
The province of Chaco lies within the southern part of the Gran Chaco region, a vast lowland plain that covers territories in Argentina, Paraguay, and Bolivia.
Chaco Province covers an area of 99,633 km (38,469 sq mi) and ranks as the twelfth largest Argentinian province. The highest ground in the province is also the most western, near the municipality of Taco Pozo, at an elevation of 272 …
History
The area was originally inhabited by various hunter-gatherers speaking languages from the Mataco-Guaicru family. Native tribes including the Toba, and Wichí survive in the region and have important communities in this province as well as in Formosa Province.
In 1576, the governor of a province in Northern Argentina commissioned the m…
20th century
Between the end of the nineteenth and the first decades of the twentieth centuries, the province received a variety of immigrants, among them Volga Germans and Mennonites from Russia, Germany, and Canada. They, alongside other immigrants, transformed Chaco into a productive farming region known for its dairy and beef production.
Economy
Chaco's economy, like most in the region, is relatively underdeveloped, yet has recovered vigorously since 2002. It was estimated to be US$4.397 billion in 2006, or US$4,467 per capita (half the national average and the third-lowest in Argentina). Chaco's economy is diversified, but its agricultural sector has suffered from recurrent droughts over the past decade.
Government
The provincial government is divided into the usual three branches: the executive, headed by a popularly elected governor, who appoint the cabinet; the legislative; and the judiciary, headed by the Supreme Court and completed by several inferior tribunals.
The Constitution of Chaco Province forms the formal law of the province.
In Argentina, the most important law enforcement organization is the Argentine Federal Police bu…
Villages
• Colonia Aborigen El Pastoril
• Colonia Baranda
• Colonias Unidas
• El Espinillo
• El Sauzal