
Precautions
D igoxin absorption has been studied in four normal volunteers. Whereas the digoxin (Lanoxin) administered in an oral solution is completely absorbed, that in tablet form is only 75% absorbed.
What is the absorption rate of Digoxin Tablets?
Widely distributed in body tissues; highest concentrations in the heart, kidneys, intestine, stomach, liver, and skeletal muscle. In the myocardium, digoxin is found in the sarcolemma-T system bound to a receptor. Crosses the placenta.
Where is digoxin found in the human body?
Drugs that alter GI transit time and/or motility of the GI tract (e.g., antimuscarinics, diphenoxylate) may alter the rate of digoxin absorption. Concurrent use of antimuscarinics and slow-dissolving digoxin tablets may result in increased digoxin concentrations.
What drugs interfere with digoxin absorption?
After intravenous (IV) administration to healthy subjects, 50-70% of the dose is measured excreted as unchanged digoxin in the urine. Approximately 25 to 28% of digoxin is eliminated outside of the kidney. Biliary excretion appears to be of much less importance than renal excretion. 6
How is digoxin excreted from the body after IV administration?

Is digoxin metabolized by the liver?
Digoxin is minimally metabolized in the liver and does not materially affect the activity of cytochrome P450 enzymes.
How is digoxin distributed in the body?
This drug is widely distributed in the body, and is known to cross the blood-brain barrier and the placenta. The apparent volume of distribution of digoxin is 475-500 L. A large portion of digoxin is distributed in the skeletal muscle followed by the heart and kidneys.
What enzyme is digoxin metabolized by?
It is primarily metabolized through the CYP2C19 enzyme, a member of the P450 mixed-function oxidase group, although a minor pathway of metabolism is through CYP3A4, another P450 enzyme. Digoxin is primarily metabolized outside the P450 system, but a minor pathway of metabolism is by CYP3A4.
What factors may affect the absorption of digoxin?
Propantheline and diphenoxylate, by decreasing gut motility, may increase digoxin absorption. Antacids, kaolin-pectin, sulfasalazine, neomycin, cholestyramine, certain anticancer drugs, and metoclopramide may interfere with intestinal digoxin absorption, resulting in unexpectedly low serum concentrations.
What is the main action of digoxin?
Mechanism of action Digoxin binds to and inhibits the sodium/potassium-ATPase (sodium pump) within the plasma membrane of cardiac myocytes. This inhibition increases the intracellular sodium content which in turn increases the intracellular calcium content which leads to increased cardiac contractility.
Which medication can interfere with absorption of digoxin?
Drugs which reduce digoxin absorption include the antacids aluminium hydroxide, magnesium hydroxide and magnesium trisilicate, the antidiarrhoeals kaolin and pectin, the hypocholesterolaemic agent cholestyramine and the chemotoxins cyclophosphamide, vincristine and bleomycin.
What is the relationship between digoxin and potassium?
Because digoxin binds to the K+ site of the Na+/K+-ATPase pump, low serum potassium levels increase the risk of digoxin toxicity. Conversely, hyperkalemia diminishes digoxin's effectiveness.
How is digoxin eliminated?
The main route of elimination is renal excretion of digoxin, which is closely correlated with the glomerular filtration rate. In addition, some tubular secretion and perhaps tubular reabsorption occurs. Nearly all of the digoxin in the urine is excreted unchanged, with a small part as active metabolites.
What is the volume of distribution of digoxin?
Digoxin has a volume of distribution of about 7.3 L/kg but this decreases in renal disease and hypothyroidism (increases in hyperthyroidism) [4].
What is volume of distribution of drugs?
Volume of distribution (Vd), represents the apparent volume into which the drug is distributed to provide the same concentration as it currently is in blood plasma. It is calculated by the amount of the drug in the body divided by the plasma concentration [19].
What is the relationship between digoxin and potassium?
Because digoxin binds to the K+ site of the Na+/K+-ATPase pump, low serum potassium levels increase the risk of digoxin toxicity. Conversely, hyperkalemia diminishes digoxin's effectiveness.
Where does digoxin come from?
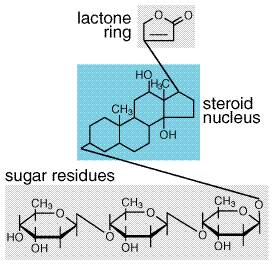
Digoxin is obtained from the leaf of the woolly or Balkan foxglove, D lanata,2 from which it was first isolated by Dr Sydney Smith at Burroughs Wellcome in Britain in 1930. It is still extracted from the plant because, although it can be made synthetically, this is a difficult and expensive process.
How long should digoxin be used before cardioversion?
Reduce dosage or withhold digoxin therapy for 1–2 days before elective cardioversion in patients with atrial fibrillation; consider consequences of increasing the ventricular response. Postpone elective cardioversion in patients with manifestations of digoxin toxicity.
What is Digoxin immune fab?
Digoxin immune Fab is a specific antidote that binds to digoxin ( preventing and reversing pharmacologic and toxic effects and enhancing elimination) and can be used in the treatment of potentially life-threate ning acute or chronic digoxin toxicity.
What can be used to guide dosing?
Serum digoxin concentrations can be used to guide dosing.
Can digoxin be used for a patient who cannot take a preferred therapy?
Because of potential for adverse effects, use of digoxin is generally reserved for patients who fail or cannot take preferred therapies (e.g., β-blockers, nondihydropyridine calcium-channel blocking agents, flecainide, propafenone).
Can you give digoxin with 5% dextrose?
May administer digoxin injection either undiluted or diluted with a fourfold or greater volume of sterile water for injection, 5% dextrose injection, or 0.9% sodium chloride injection; use of a smaller volume of diluent may cause precipitation of digoxin.
When to administer IV?
May administer IV when oral therapy is not feasible or when rapid therapeutic effect is necessary.
Is digoxin safe for heart failure?
Although digoxin has been used extensively in the management of heart failure, current use is generally limited because of lack of demonstrated survival benefit, potential for serious adverse effects, and availability of other drugs that have been shown to substantially reduce morbidity and mortality.
How is digoxin absorbed?
Digoxin is approximately 70-80% absorbed in the first part of the small bowel. 6 The bioavailability of an oral dose varies from 50-90%, however, oral gelatinized capsules of digoxin are reported to have a bioavailability of 100%. 10 Tmax, or the time to reach the maximum concentration of digoxin was measured to be 1.0 h in one clinical study of healthy patients taking 0.25 mg of digoxin with a placebo. 19 Cmax, or maximum concentration, was 1.32 ± 0.18 ng/ml−1 in the same study, and AUC (area under the curve) was 12.5 ± 2.38 ng/ml−1. 19 If digoxin is ingested after a meal, absorption is slowed but this does not change the total amount of absorbed drug. If digoxin is taken with meals that are in fiber, absorption may be decreased. 24
Where is digoxin distributed?
25 A large portion of digoxin is distributed in the skeletal muscle followed by the heart and kidneys. 6 It is important to note that the elderly population, generally having a decreased muscle mass, may show a lower volume of digoxin distribution. 25
How does digoxin affect the heart?
Digoxin exerts hemodynamic, electrophysiologic, and neurohormonal effects on the cardiovascular system. 7 It reversibly inhibits the Na-K ATPase enzyme, leading to various beneficial effects. The Na-K ATPase enzyme functions to maintain the intracellular environment by regulating the entry and exit of sodium, potassium, and calcium (indirectly). Na-K ATPase is also known as the sodium pump 25. The inhibition of the sodium pump by digoxin increases intracellular sodium and increases the calcium level in the myocardial cells, causing an increased contractile force of the heart. 25, 11 This improves the left ventricular ejection fraction (EF), an important measure of cardiac function. 7, 22
What is Digoxin used for?
Digoxin is a cardiac glycoside used in the treatment of mild to moderate heart failure and for ventricular response rate control in chronic atrial fibrillation.
Why is digoxin not removed from the body?
Digoxin is not effectively removed from the body by dialysis, exchange transfusion, or during cardiopulmonary bypass because most of the drug is bound to extravascular tissues. 25
Which transporter is used to transport digoxin?
The results of one in vitro study suggest that this drug is transported by the bile salt export pump.
Where did the drug foxglove come from?
This drug originates from the foxglove plant, also known as the Digitalis plant 21, studied by William Withering, an English physician and botanist in the 1780s. 8, 9 Prior to this, a Welsh family, historically referred to as the Physicians of Myddvai, formulated drugs from this plant.
What are the effects of digoxin on the body?
Patients who receive the combination almost always will have a significant elevation in their digoxin plasma concentrations and can suffer digoxininduced toxicity, including arrhythmias, anorexia, altered color vision, and mental changes.
Which drugs increase digoxin concentrations?
Since that time, several other drugs?including cyclosporine, erythromycin, clarithromycin, propafenone, itraconazole, amiodarone, verapamil, and diltiazem?were noted to increase digoxin plasma concentrations. Although some investigators noted a reduction in digoxin renal and total body clearance, the underlying mechanism for these interactions remained undefined.
How do antibiotics increase digoxin?
Some investigators suggested that antibiotics might increase digoxin absorption by inactivating gastrointestinal bacteria thought to metabolize digoxin in the gut. 2 This mechanism, however, would appear to be incapable of raising digoxin concentrations 2- to 3-fold, because digoxin is well absorbed with a bioavailability of about 75%. Assuming that the intestinal bacteria were responsible for this reduction of digoxin absorption, the greatest increase in bioavailability one could expect would be about 25%. At that point, the bioavailability of digoxin would be 100%, and no further increase in concentration could occur by this mechanism. Another mechanism for the interaction was needed to explain the large changes in digoxin concentrations that had been reported.
Where do drugs go when taken orally?
When a drug is taken orally, drug molecules have to pass through the enterocyte to enter the blood. As the molecules diffuse through the enterocyte, P-gp can pick up the molecules and carry them back to the luminal side of the cell, where they are dumped back into the lumen of the intestine.
Does quinidine increase P-gp?
If the activity of P-gp is inhibited, more drug will be absorbed through the enterocytes, and plasma concentrations will increase. In addition, drug that is normally eliminated by P-gp in the bile or urine will accumulate in the body. Thus, when quinidine is coadministered with digoxin, quinidine inhibition of P-gp results in an increase in digoxin ...
What does P-GP do to the body?
This action prevents drug molecules from reaching the systemic circulation, effectively limiting bioavailability. Because P-gp is found throughout the intestinal tract, it affects the absorption of all susceptible oral drugs, including sustained-release formulations.
Does quinidine inhibit digoxin?
3 In 1996, it was demonstrated that the effect of quinidine on plasma digoxin concentrations was the result of quinidine-induced inhibition of P-gp in the intestine, as well as at sites of digoxin elimination such as the kidney. 4
Uses For Digoxin
Digoxin is used to treat heart failure, usually along with other medications. It is also used to treat certain types of irregular heartbeat (such as chronic atrial fibrillation).
May Treat: Chronic heart failure · Ventricular rate control in atrial fibrillation
Brand Names: Lanoxicaps · Lanoxin · Digox · Digitek · Lanoxin Pediatric and more
Drug Class: Digitalis Glycosides
Availability: Prescription Required
Pregnancy: Consult a doctor before using
May Treat: Chronic heart failure · Ventricular rate control in atrial fibrillation
Brand Names: Lanoxicaps · Lanoxin · Digox · Digitek · Lanoxin Pediatric and more
Drug Class: Digitalis Glycosides
Availability: Prescription Required
Pregnancy: Consult a doctor before using
Lactation: Does not adversely affect lactation
Driving: May cause drowsiness or dizziness. Use caution
Digoxin Dosage and Administration
Cautions For Digoxin
Interactions For Digoxin
Stability
Actions
Advice to Patients
Preparations