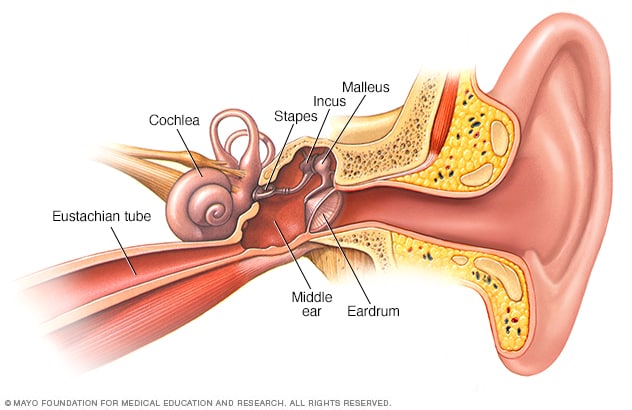
Is the eardrum located in the middle ear?
Also known as the tympanic cavity, the middle ear is an air-filled, membrane-lined space located between the ear canal and the Eustachian tube, cochlea, and auditory nerve. The eardrum separates this space from the ear canal.
Can you touch your eardrum?
The ear drum is very delicate, so you can puncture it with a Q-tip, and I've seen that many times. The other reason is that if you touch the ear drum you press on the little bones of hearing underneath — the hammer, the anvil and the stirrup.
How far into the ear is the eardrum?
The adult human ear canal extends from the pinna to the eardrum and is about 2.5 centimetres (1 in) in length and 0.7 centimetres (0.3 in) in diameter....Ear canalTA26867FMA61734Anatomical terminology11 more rows
How do I know if I have a blocked eardrum?
Signs and symptoms of earwax blockage may include:Earache.Feeling of fullness in the affected ear.Ringing or noises in the ear (tinnitus)Decreased hearing in the affected ear.Dizziness.Cough.
What happens if earwax touches eardrum?
If wax touches the ear drum, it can be painful and cause muffled hearing. There are many products on the market to remove wax using oils, solutions, syringes, ear vacuums and candles. These may seem to help in some instances, but can also cause bigger problems like damaging the ear canal or eardrum.
How do I clean my inner ear?
Just use a washcloth. You also can try putting a few drops of baby oil, hydrogen peroxide, mineral oil, or glycerin in your ear to soften the wax. Or you can use an over-the-counter wax removal kit. Besides cotton swabs or any other small or pointy objects, don't use ear candles to clean your ears.
Can your eardrum heal?
A ruptured eardrum can result in hearing loss. It can also make the middle ear vulnerable to infections. A ruptured eardrum usually heals within a few weeks without treatment. But sometimes it requires a patch or surgical repair to heal.
Can I remove earwax with water?
Your doctor can remove excess wax using a small, curved instrument called a curet or by using suction while inspecting the ear. Your doctor can also flush out the wax using a water pick or a rubber-bulb syringe filled with warm water.
What is the best ear wax removal?
Over-the-counter ear cleaning drops If you have a small amount of wax, over-the-counter ear cleaners work well. Look for drops that contain hydrogen peroxide or other kinds of peroxide. The peroxide does a good job of breaking up earwax.
Can COVID-19 affect your ears?
And, because COVID-19 causes inflammation in the nose and nasopharynx (the upper part of the throat located behind the nose), the Eustachian tube (the tube that connects the nose and middle ear) may also become inflamed during the course of the infection and lead to middle ear congestion.
Can a blocked ear be serious?
Having a blocked ear (or sometimes, even more annoyingly, blocked ears) can be a serious inconvenience, and at times, a health risk. Blocked ears can muffle and distort sounds, reducing your capacity to hear your surroundings.
Can Covid cause blocked ears?
In general, COVID-19 has not been associated with ear infections, and generally these types of infections do not share a great deal of common symptoms.
What is the eardrum?
The eardrum is divided into two general regions: the pars flaccida and the pars tensa. The relatively fragile pars flaccida lies above the lateral process of the malleus between the notch of Rivinus and the anterior and posterior malleal folds. Consisting of two layers and appearing slightly pinkish in hue, it is associated with Eustachian tube dysfunction and cholesteatomas.
What is the eardrum called?
v. t. e. In the anatomy of humans and various other tetrapods, the eardrum, also called the tympanic membrane or myringa, is a thin, cone-shaped membrane that separates the external ear from the middle ear.
What bone bridges the gap between the eardrum and the other ossicles?
The malleus bone bridges the gap between the eardrum and the other ossicles. Rupture or perforation of the eardrum can lead to conductive hearing loss. Collapse or retraction of the eardrum can cause conductive hearing loss or cholesteatoma .
What is a rupture in the middle ear?
Rupture. Unintentional perforation (rupture) has been described in blast injuries and air travel, typically in patients experiencing upper respiratory congestion that prevents equalization of pressure in the middle ear. It is also known to occur in swimming, diving (including scuba diving ), and martial arts.
Which ear is open from the front?
External and middle ear, right side, opened from the front (coronal section) Horizontal section through left ear; upper half of section. The right membrana tympani with the hammer and the chorda tympani, viewed from within, from behind, and from above. Auditory tube, laid open by a cut in its long axis.
What is the manubrium of the malleus?
The manubrium ( Latin: handle) of the malleus is firmly attached to the medial surface of the membrane as far as its center, drawing it toward the tympanic cavity. The lateral surface of the membrane is thus concave. The most depressed aspect of this concavity is termed the umbo ( Latin: shield boss ).
What is the eardrum?
What is ear drum. The external (outer) ear consists of the auricle, external auditory canal, and eardrum (Figure 1 and 2). The auricle or pinna is a flap of elastic cartilage shaped like the flared end of a trumpet and covered by skin. The rim of the auricle is the helix; the inferior portion is the lobule.
Where is the middle ear located?
The middle ear is a small, air-filled cavity in the petrous portion of the temporal bone that is lined by epithelium. It is separated from the external ear by the tympanic membrane and from the internal ear by a thin bony partition that contains two small openings: the oval window and the round window.
What happens if your eardrum is ruptured?
If your eardrum is ruptured, the skin debris can pass into your middle ear and form a cyst. A cholesteatoma provides a friendly environment for bacteria and contains proteins that can damage bones of your middle ear.
What causes a perforated eardrum?
Causes of a ruptured or perforated eardrum. Causes of a ruptured, or perforated, eardrum may include: Middle ear infection (otitis media). A middle ear infection often results in the accumulation of fluids in your middle ear. Pressure from these fluids can cause the eardrum to rupture.
What is a ruptured eardrum?
A ruptured eardrum — or tympanic membrane perforation as it’s medically known — is a hole or tear in the thin tissue that separates your ear canal from your middle ear (eardrum) 1). A ruptured eardrum can result in hearing loss. A ruptured eardrum can also make your middle ear vulnerable to infections or injury.
What is the tympanic membrane?
The tympanic membrane or ear drum is a thin, semitransparent partition between the external auditory canal and middle ear. The tympanic membrane is covered by epidermis and lined by simple cuboidal epithelium. Between the epithelial layers is connective tissue composed of collagen, elastic fibers, and fibroblasts.
How long does it take for a tympanic membrane to heal?
It may be due to pressure from a cotton swab, trauma, or a middle ear infection, and usually heals within a month. The tympanic membrane may be examined directly by an otoscope, a viewing instrument that illuminates and magnifies the external auditory canal and tympanic membrane.
What is the inner ear called?
Inner ear: The inner ear, also called the labyrinth, operates the body’s sense of balance and contains the hearing organ. A bony casing houses a complex system of membranous cells. The inner ear is called the labyrinth because of its complex shape. There are two main sections within the inner ear: the bony labyrinth and the membranous labyrinth.
Where do sound waves enter the ear?
Hair cells inside the organ of Corti detect sound and send the information through the cochlear nerve. Sound waves enter through the outer ear, move into the middle ear, and finally reach the inner ear and its intricate network of nerves, bones, canals, and cells. Last medically reviewed on January 14, 2015.
What is the most visible part of the outer ear?
The auricle or pinna is the most visible part of the outer ear and what most people are referring to when they use the word “ear.”. Middle ear: Three tiny bones — the malleus, incus, and stapes — within the middle ear transfer sound vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear. The middle ear is important because it is filled with numerous air ...
What are the functions of the ear?
The ears are organs that provide two main functions — hearing and balance — that depend on specialized receptors called hair cells.
Why is the middle ear important?
The middle ear is important because it is filled with numerous air spaces, which provide routes for infections to travel. It is also the location of the Eustachian tube, which equalizes the air pressure between the inner and outer surfaces of the tympanic membrane (eardrum).
What part of the ear is the sound?
Sound causes the eardrum and its tiny attached bones in the middle portion of the ear to vibrate, and the vibrations are conducted to the nearby cochlea. The spiral-shaped cochlea is part of the inner ear; it transforms sound into nerve impulses that travel to the brain.
What is the outer ear called?
All rights reserved. The ear has external, middle, and inner portions. The outer ear is called the pinna and is made of ridged cartilage covered by skin. Sound funnels through the pinna into the external auditory canal, a short tube that ends at the eardrum (tympanic membrane). Sound causes the eardrum and its tiny attached bones in ...
Why does my ear hurt?
Earache: Pain in the ear can have many causes. Some of these are serious, some are not serious. Otitis media(middle ear inflammation): Inflammation or infection of the middle ear (behind the eardrum). Usually, this is caused by an infection.
What is the name of the tumor that grows on the nerve traveling from the ear to the brain?
Acoustic neuroma: A noncancerous tumor that grows on the nerve traveling from the ear to the brain. Hearing loss, vertigo, and tinnitus can be symptoms. Mastoiditis: Infection of the mastoid bone, just behind the ear. Mastoiditis can result from untreated middle ear infections.
What is the first test for ear problems?
Ear Tests. Ear exam: The first test for an ear problem is often just looking at the ear. An otoscope is a device to look into the ear canal to see the drum. Auditory testing: An audiologist formally examines a person’s hearing in each ear, using sounds of varying volume and frequency.
What is the condition of the inner ear on one side?
Sudden cases are usually infections; chronic otitis is often a skin condition (dermatitis). Meniere’s disease: A condition in which the inner ear on one side malfunctions. Vertigo, tinnitus, hearing loss, and pain are common symptoms. Tinnitus: Ringing in one or both ears.
How long does it take for eardrum to heal?
The small hole usually heals within a few weeks. Acoustic neuroma: A noncancerous tumor that grows on the nerve traveling from the ear to the brain.
What is the outer ear called?
It is also sometimes referred to as the auricle or the pinna. Although the outer ear is the least important part of the ear’s hearing function, it provides the necessary structure and protection. Its dish-like shape is also essential for collecting sound waves. This sound collection is the primary purpose of all of the parts ...
What is the human ear?
Ear Anatomy. The human ear is the highly advanced result of millions of years of evolutionary progress. Everyone knows that the ear is the organ used for hearing, but not many people are aware that it’s also necessary for balance. Most people also consider the ear just one part of the human body, but it’s a complex organ composed of many smaller, ...
What is the external auditory meatus?
The external auditory meatus, or ear canal, is a narrow canal that leads from the concha to the tympanic membrane, or eardrum. Sound waves are delivered through this canal. This canal is prone to ear infections.
How to treat middle ear pressure imbalance?
This middle ear pressure imbalance can usually be alleviated by yawning or working the jaw, which exercises the mastoid bone and opens the eustachian tube. COVID 19 can occasionally enter the middle ear through the Eustachian tube. If you have been exposed to COVID 19, seek appropriate treatment or services.
What is the name of the two forks on the top of the ear called?
It is more rigid and provides more strength to the outer ear. It looks somewhat Y-shaped, and the two forks at the top of the ‘Y’ are called the superior crus and the inferior crus.
What is the concha in the ear?
The concha is the smaller cavity that funnels sound waves into the ear canal. It is bordered by the antihelix, the tragus, and the antitragus. Hearing amplification devices, such as MD HearingAids or other services, are typically nestled within this cavity.
Which part of the ear transmits sound signals to the inner ear?
It also divides the outer ear from the middle ear. It then transmits a clarified, amplified sound signal to the inner ear components. The Ossicles (malleus incus stapes) are the small, connected bones inside the middle ear that transmit sound signals from the tympanic membrane to the next area.
Why does fluid get in my middle ear?
You have a malfunction with your Eustachian tube (which helps maintain proper air pressure in your middle ear and drain fluids that may be present in there) which allowed fluid to get inside the middle ear (rare). If you have fluid in your middle ear, consult a doctor for the best way to resolve this problem.
Can you clean ear wax?
Daily cleaning is not allowed. If you feel that the earwax is hindering your hearing, go to the professional to do the removing. Or if you have in your house who knows how to remove it, allow him as he can see what he is doing. If the earwax hardened a drop of one or two of baby oil will soften it.
Can earwax damage your eardrum?
You may have created a solid, earwax ear plug. Second (and much less likely since you didn't mention pain or bleeding), you may have punctured/damaged your eardrum. Because of the latter possibility, I recommend you have it tended to by an ear professional (aka an ENT).
Can you get fluid in your ear?
Continue Reading. Yes, the eardrum is a membrane separating the middle ear from the outer ear, and is meant to be waterproof as well as airtight.
Can you poke your ear with a cotton swab?
Seriously, don’t poke it with a cotton swab (or Q-tip). Preferably don’t even use swabs inside the ear, as they can push excess wax onto the eardrum itself. I stuck a q-tip too far in my ear and woke up the next morning unable to hear out that ear.

Overview
- The eardrum has three layers: the outer layer, inner layer, and middle layer. The middle layer is made of fibers that give the eardrum elasticity and stiffness. Cartilageholds the eardrum in place. The eardrum covers the end of the external ear canal and looks like a flattened cone with its tip pointed inward toward the middle ear. It is transparen...
Structure
Clinical significance
Society and culture
In the anatomy of humans and various other tetrapods, the eardrum, also called the tympanic membrane or myringa, is a thin, cone-shaped membrane that separates the external ear from the middle ear. Its function is to transmit sound from the air to the ossicles inside the middle ear, and then to the oval window in the fluid-filled cochlea. Hence, it ultimately converts and amplifies vibration in air to vibration in cochlear fluid. The malleus bone bridges the gap between the eardr…
See also
The tympanic membrane is oriented obliquely in the anteroposterior, mediolateral, and superoinferior planes. Consequently, its superoposterior end lies lateral to its anteroinferior end.
Anatomically, it relates superiorly to the middle cranial fossa, posteriorly to the ossicles and facial nerve, inferiorly to the parotid gland, and anteriorly to the temporomandibular joint.
The eardrum is divided into two general regions: the pars flaccida and the pars tensa. The relativ…
External links
When the eardrum is illuminated during a medical examination, a cone of light radiates from the tip of the malleus to the periphery in the anteroinferior quadrant, this is what is known clinically as 5 o'clock.
Unintentional perforation (rupture) has been described in blast injuries and air travel, typically in patients experiencing upper respiratory congestion that prevents equalization of pressure in the …