
Where is areolar tissue located and it function?
The areolar tissue is located beneath the layer of the dermis. Areolar tissue is also present underneath the epithelial tissue of all the body systems that have external openings. This tissue is widely located within the body and helps in protection and cushioning primarily.
Where is areolar located?
The areolar tissue located in the skin binds the outer layers of the skin to the muscles beneath. Areolar tissue is also found in or around mucous membranes, and around blood vessels, nerves, and the organs of the body.
Where can a connective tissue be found?
They are mostly found within the walls of large blood vessels, elastic cartilages, yellow ligaments, lungs and skin. Variations in the cell and protein fiber combinations and arrangements result in the different types of connective tissue. Connective tissue proper is found throughout the entire body.
What are the three types of fibers in loose connective tissue?
the three basic types of fibers that are found in connective tissue are collagen fibers, elastic fibers, and reticular fibers.What three basic types of fibers are found in connective tissuewww.answers.com/Q/What_three_basic_types_of_fibers_are_found_in_connective_tissue
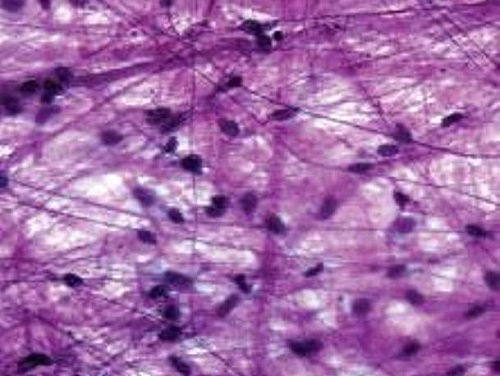
What is Areolar loose connective tissue?
Loose connective tissue, sometimes called areolar tissue, is a cellular connective tissue with thin and relatively sparse collagen fibers. Its ground substance occupies more volume than the fibers do.
Where is areolar tissue found example?
The areolar tissue is a loose connective tissue that can be seen between the skin and muscles; in the bone marrow as well as around the blood vessels and nerves.
Where is Areolar connective tissue found quizlet?
Location- The areolar tissue located in the skin binds the outer layers of the skin to the muscles beneath. Areolar tissue is also found in or around mucous membranes, and around blood vessels, nerves, and the organs of the body.
Which three are locations of areolar connective tissue quizlet?
Location: Wherever areolar connective tissue is located: subcutaneous layer deep to skin, around heart and kidneys, yellow bone marrow, padding around joints and behind eyeball in eye socket.
What are examples of loose connective tissue?
Examples of loose connective tissue include the tendons, ligaments, fat, cartilage, and blood. Loose connective tissue is any tissue in the body that helps to attach one organ or tissue to another.
Where is connective tissue located in the body?
Dense connective tissue is what makes up tendons and ligaments and consist of a higher density of collagen fibers. Examples of specialized connective tissues are adipose tissue, cartilage, bone, blood, and lymph.
What is Areolar connective tissue quizlet?
Areolar (loose) Connective Tissue. Connective Tissue that contains all three types of fibers, usually arranged in a disorderly fashion (found in the subcutaneous layers of the skin). It holds organs in place and attaches epithelial tissue to other underlying tissues. It also surrounds the blood vessels and nerves.
Where is loose CT found in the body quizlet?
Loose connective tissue found beneath the dermis layer and under the epithelial tissue of all the body systems that have external openings.
What is found in areolar tissue?
Areolar tissue is found in many locations in the body. It consists of a meshwork of collagen, elastic tissue, and reticular fibres - with many connective tissue cells in between the meshwork of fibres. The fibres that form the mesh structure of areolar tissue include: Collagen fibres, elastic fibres, reticular fibres.
What is an example of adipose tissue?
Adipose tissue is commonly known as body fat. It is found all over the body. It can be found under the skin (subcutaneous fat), packed around internal organs (visceral fat), between muscles, within bone marrow and in breast tissue.
Where is fibroblast found?
The fibroblast is a specific type of connective tissue cell that's in our skin and in our tendons.
Which is an example of connective tissue proper?
Examples of specialized connective tissues are adipose tissue, cartilage, bone, blood, and lymph.
Where in the body is loose connective tissue found?
Loose connective tissue is found all throughout the body. It is located under the epidermis and dermis layers of the skin.
What are the 3 types of loose connective tissue?
The three types of loose connective tissue include adipose, areolar and basement membrane. There are two types of adipose; brown and white, and the...
Which loose connective tissue is the most common?
The most common of all of the loose connective tissues is the areolar loose connective tissue. It is found throughout the body under the dermis lay...
What are examples of loose connective tissues?
Examples of loose connective tissue include the tendons, ligaments, fat, cartilage, and blood. Loose connective tissue is any tissue in the body th...
What is the function of loose and dense connective tissue?
Loose connective tissue serves as an anchor for organs and other tissues in the body to each other. Dense connective tissue acts as a barrier or co...
Is loose connective tissue fat?
No. Fat is a type of loose connective tissue. There are two types of fat or adipose tissue in the body. They are brown fat and white fat.
Where is the areolar tissue located?
The areolar tissue is found beneath the dermis layer and is also underneath the epithelial tissue of all the body systems that have external openings. It is also a component of the lamina propria of the digestive and respiratory tracts, the mucous membranes of reproductive and urinary system, the stroma of glands, and the hypodermis of the skin.
What is connective tissue?
Connective (supporting) tissue is a voluminous, strong, yet elastic type of tissue with significant roles in the human body. It provides mechanical strength, together with physical and metabolic support to all the other types of tissues. You can think of it as a mesh-like matrix that physically connects other tissues between them. This extracellular matrix (ECM) is responsible for the physical properties of connective tissue and it is a major constituent of this tissue type. The ECM is a mixture of protein fibers and ground substance. The protein fibers, these being collagen and elastin, are responsible for providing connective tissue with tensile strength and elasticity, respectively. The ground substance is a wet gel that permits the exchange of nutrients and wastes between cells and the blood. It is composed of glycoproteins and complex carbohydrates.
What is the classification of connective tissue?
Connective tissue is classified according to the composition and organization of the ECM and cellular components, as follows: Classification of the connective tissue. Embryonic connective tissue. Mesenchyme. Muscous connective tissue.
What are elastic fibers?
Elastic fibers - fibers responsible for the flexibility of the tissue. Location. Dermis, lamina propria of the digestive and respiratory tracts, mucous membranes of reproductive and urinary tracts, glandular stroma, mesentery. Clinical relations.
How do macrophages protect the LCT?
Macrophages are phagocytes and they protect the LCT by ingesting potential pathogens and cell debris. Subsequently, they can activate the adaptive immune system by releasing cytokines and presenting antigens, if required.
What is the importance of connective tissue?
Situated virtually at every site, both internally and externally, it is crucial for providing strength, elasticity and metabolic support for all other tissues.
What is the role of ground substance in tissue?
It plays a significant role in the diffusion of gases, nutrients and metabolic wastes between the cells and the vessels that perfuse the tissue. Out of the types of fibers, the reticular ones predominate, but they are thin and loosely arranged.
Where is the areolar connective tissue located?
It is sturdier than adipose tissue but still flexible. Areolar connective tissue is predominantly found in the layer under the dermis of the skin. The fibers in areolar connective tissue are loosely organized and allow fluid to flow through it. The cells in the epithelial tissue get their nutrients from the fluid that flows through the areolar connective tissue. The fibers can also be more densely packed in some areas of the body, such as the mucus membranes. The areolar connective tissue is a mesh of collagenous and elastic fibers.
What is Loose Connective Tissue?
Loose connective tissue is the tissue that contains and attaches to organs. It is called loose connective tissue because its extracellular matrix is organized into loose strands and cells that are interwoven together and look like a loose weave. Loose connective tissue is different from other connective tissue. The extracellular matrix of loose connective tissue is arranged more loosely, hence the name, whereas dense connective tissue has an extracellular matrix that is densely packed together.
What is the most abundant fiber in loose connective tissue?
Loose connective tissue is the tissue that connects organs to other tissues in the body. Collagenous fibers are the most abundant fiber in loose connective tissue. Elastic fibers are the fibers that contain elastin. Reticular fibers are interwoven fibers of collagen. The two types of adipose tissue, or fat tissue, are brown adipose tissue, present during fetal and infant stages of life, and white adipose tissue, the tissue that acts as an insulator and brings energy to the body. Areolar tissue is the most abundant of the connective tissue in the body. The basement membrane is the thin, dense membrane that separates the body into compartments. The two types of cells that make up the loose connective tissue are fixed cells, also called resident cells that reside in the connective tissue at all times, and wandering cells, also called transient cells which are cells that move in and out of the loose connective tissue.
What are the cells that make up the extracellular matrix?
The fixed cells of the loose connective tissue are fibroblasts, macrophages, adipocytes or fat cells, and mast cells. The fibroblasts are the most abundant of the fixed cells. They secrete the cells that make up the extracellular matrix. The adipocytes are cells that contain fat. The macrophages are immune system cells that engulf foreign substances, cell debris, and microbes in the body. Finally, the mast cells are responsible for releasing molecules that cause immune cells to come to a site of injury. They also release molecules that cause blood vessels to enlarge more.
Why are elastic fibers called elastic fibers?
Elastic fibers get their name because they contain the protein elastin. Elastin allows the elastic fibers to stretch to many times their size and return to their original size afterward. The fibroblasts produce it in the extracellular matrix as well as smooth muscle and epithelial cells. Thus, elastic fibers can be found in every part of the body that stretches, such as the skin and ligaments of the vertebral column. Elastic fibers are interwoven with collagen fibers to give them some strength to prevent stretching to the point of tearing.
Why is loose connective tissue called loose?
Loose connective tissue is called loose because it contains fewer fibers than what is seen in dense connective tissue. The fibers are organized in a manner where they are loosely scattered throughout the tissue. Loose connective tissue is the most abundant of the connective tissues in the body. It is widespread and, as such, is found throughout the body. Loose connective tissue has fibers so widely placed that it allows the tissue to be flexible.
What are wandering cells?
Wandering cells are also called transient cells. As the name suggests, these are cells that move around. However, they are not always found in the loose connective tissue. Instead, they come into the loose connective tissue when there is an injury or some other breach in the tissue. These cells include the immune cells such as the plasma cells, monocytes, and granulocytes. The plasma cells produce antibodies when there is an antigen or pathogen in the body. One type of granulocyte is involved in inflammation in the body to help get rid of invading organisms.
What is Areolar Connective Tissue?
Areolar connective tissue is a type of dense, irregular connective tissue found in the human body. It consists mainly of a network of fibers and cells which are held together by a gel-like matrix.
What happens if there’s a problem with areolar connective tissue?
If there is a problem with areolar connective tissue, it can lead to lactation problems and, in some cases, breast cancer.
What causes areolar connective tissue to be stretched?
There are several diseases and conditions that cause problems with areolar connective tissue. The most common is Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS), which is a group of hereditary disorders that affect connective tissues. This can cause overly flexible joints (which can potentially dislocate joints easily), tendons and ligaments to stretch too much, skin to be extraordinarily stretchy but fragile, and blood vessels easily form blood clots.
Which tissue is dense and rigid?
The areolar tissue is also dense with collagen fibers, which makes it strong and rigid.
Where is the areolar tissue located?
The areolar tissue is located beneath the layer of the dermis. Areolar tissue is also present underneath the epithelial tissue of all the body systems that have external openings. This tissue is widely located within the body and helps in protection and cushioning primarily.
What is areolar tissue?
Structurally, areolar tissue has a viscous, gelatinous consistency, which may fluctuate in different parts of the body due to changes in temperature or pH . Alongside this, areolar tissue allows gliding between various muscles and organs. And areolar tissue also permits the diffusion of substances like Oxygen or nutrients from small vessels to the cells. Henceforth, also aiding the diffusion of metabolites back to the vessels.
What is the group of tissues that maintain the structure of the body and its organs?
Connective tissue is the group of tissues in the body that maintain the structure of the body and its organs. They also provide cohesion and internal support. The connective tissues include different types of fibrous tissue that vary only in their density and the number of cells present within them, as well as the more specialized and identifiable types.
What is the tissue that fills the spaces between organs?
Areolar tissue fills the spaces between various organs. Thereby holding them in place while providing them with protection and cushioning.
What is the initial site where antigens and other bacteria or pathogens, and other agents that have breache?
Areolar tissue is the initial site where antigens and other bacteria or pathogens, and other agents that have breached an epithelial surface can be killed. It also forms a mesh-like tissue with a fluid matrix that supports the epithelial tissues, such as the skin and other covering membranes.
What is the epithelial tissue?
Epithelial tissue is the group of cells that cover the outer surfaces of the body. Most of the epithelial tissue is located towards the outer surface of the body. Their origin is ectodermal, and they usually protect the body from external agents or irritation. They also help us sense various things through our surroundings.
What are collagen fibers made of?
Collagenous fibers consist of collagen. They consist of bundles of fibrils that are coils of collagen molecules.
