Where is meristem tissue found in plants?
Promeristem
- The earliest and youngest meristematic tissue.
- It originates from the embryo.
- The primary meristem arises from the promeristem.
- It is found in the root and the shoot tips.
Where is the meristem located?
meristem, region of cells capable of division and growth in plants. Meristems are classified by their location in the plant as apical (located at root and shoot tips), lateral (in the vascular and cork cambia), and intercalary (at internodes, or stem regions between the places at which leaves attach, and leaf bases, especially of certain monocotyledons—e.g., grasses).
Are undifferentiated cells found in meristematic tissue?
The meristem is a type of tissue found in plants. It consists of undifferentiated cells ( meristematic cells) capable of cell division. Cells in the meristem can develop into all the other tissues and organs that occur in plants. These cells continue to divide until a time when they get differentiated and then lose the ability to divide.
Where is xylem tissue located?
Xylem is located in roots, stems and leaves of the plant and it transports water and minerals from plant roots to aerial parts. With phloem it forms vascular bundles. Dead cells in Xylem contribute to wooden parts of the plant. Furthermore, what is the xylem of a plant? Xylem is one of the two types of transport tissue in vascular plants, phloem being the other.

Where are meristematic tissue found?
The meristematic tissue is usually found in the apices of the root systems and the shoots and is in a continuous state of division.
What is the location and function of meristematic tissue?
Meristematic tissues are responsible for plant growth. They are present at the tips of roots,stem and branches. The cells present in these tissues constantly divide to produce new cells. The cells actively divide to produce new cells.
Where is meristematic tissue located Class 9?
It is located in the stems and roots on the lateral side.
What is meristematic tissue in plants?
Meristematic tissues, or simply meristems, are tissues in which the cells remain forever young and divide actively throughout the life of the plant. When a meristematic cell divides in two, the new cell that remains in the meristem is called an initial, the other the derivative.
What is meristematic tissue class 9 short answer?
Meristematic tissues are the tissues in which the cells divide continuously and help in increasing the length and girth of the plant.
What is meristematic tissue class 9 short?
Meristematic tissues are the cells or groups of cells that have the ability to divide. These cells divide continuously and thus helps in increasing the length and thickness of the plant.
1. Define Meristematic Tissue?
A plant tissue that has the power to divide itself actively throughout its life is called a Meristematic Tissue.
2. Who discovered Meristematic Tissue?
The term meristem was coined by Carl Wilhelm von Nägeli.
3. What are the characteristics of Meristematic Tissue?
The characteristics of meristematic tissue are the following - The cells of these tissues are known as Meristems It has the quality of self-renewal...
4. What are the two types of Meristematic Tissue?
The meristematic tissue is of two types - On the basis of their position On the basis of their function
5. What is an Intercalary Meristem?
An intercalary meristem is located within the leaves and internodes at the intercalary position. These help to increase the length of the internode...
6. Explain the characteristics of Meristematic Tissue?
Meristematic tissue has the following characteristics:Meristems are the cells that make up these tissues.It has the ability to self-renew because w...
7. List of the uses of Meristematic Tissue?
Meristematic tissues have the following characteristics:They're alive, and they're made up of an undifferentiated swarm of rapidly dividing cells.T...
8. What is the Meristematic tissue function?
Functions of Meristematic Tissue:They are the plant's actively dividing and rapidly dividing tissues, resulting in endless expansion.The plant's pr...
9. Explain the formation of Meristematic tissue on the basis of Function?
ProtodermThe epidermis is the outermost layer of plant tissue.It safeguards the plants against mechanical shocks.ProcambiumIt is the most inner tis...
What is Meristematic Tissue?
Carl Wilhelm von Nägeli coined the term “meristem.” Meristematic tissue contains undifferentiated cells, which are the building blocks of the specialized plant structures.
Where is the lateral meristem located?
Lateral Meristem. It is located in the stems and roots on the lateral side. It increases the thickness of the plant. Vascular cambium and cork cambium are the two lateral meristems. These divide preclinically or radially and give rise to secondary permanent tissues.
Which meristem contains procambium?
Apical meristem is divided into-promeristem zone, which contains actively dividing cells, and the meristematic zone, which contains protoderm, procambium and ground meristem.
Which tissue has the quality of self-renewal?
The meristematic tissue has the quality of self-renewal. Every time the cell divides, one cell remains identical to the parent cell, and the others form specialized structures. They have very small and few vacuoles. The meristematic tissue is living and thin-walled. The protoplasm of the cells is very dense.
What is the zone of the cell that divides to form specialized structures?
The cells have no intercellular space. The zone where these cells exist is known as meristem. The cells of the meristematic tissue divide actively to form specialized structures such as buds of leaves and flowers, tips of roots and shoots, etc. These cells help to increase the length and girth of the plant. Let us have a detailed look ...
Where is the syringe located?
It is present below the promeristem and forms the permanent tissue.
What is the apical meristem?
Apical Meristem. These are present at the tips of the roots and shoots and helps in the increase of the height of the plants. Various cell divisions facilitate the growth of the cells in the roots and shoots and help in cellular enlargement.
What is Meristematic Tissue?
Meristematic tissues have undifferentiated cells which form the building blocks of the specialized plant structures. Meristematic tissues have living cells with varied shapes. They possess a large nucleus devoid of the vacuole. The cells have no intercellular space. The place where these cells exist is called Meristem. The cells of the meristematic tissue have the capability to divide itself actively to make specialized structures like buds of leaves and flowers, tips of roots and shoots, etc. These cells help to increase the length and bulkiness of the plant.
What are the characteristics of meristematic tissue?
It has the quality of self-renewal as every time the cell divides, one cell remains just like the parent cell and the others form specialized structures. They have very small and few vacuoles. The meristematic tissues are living and thin-walled. The protoplasm of the cells is very dense.
What tissue divides itself to make specialized structures?
The cells of the meristematic tissue have the capability to divide itself actively to make specialized structures like buds of leaves and flowers, tips of roots and shoots, etc. These cells help to increase the length and bulkiness of the plant.
Where is the intercalary meristem located?
Intercalary Meristem. It is located within the leaves and internodes at the intercalary position. These help to increase the length of the internode. It is in a neighbourhood with the grass, monocots, and pines. It is a part of apical meristem and adds to the peak of the plant.
Which tissue heals the injuries of an injured plant?
The meristematic tissues heal the injuries of an injured plant.
What is the place where cells exist called?
They possess a large nucleus devoid of the vacuole. The cells have no intercellular space. The place where these cells exist is called Meristem.
What is the apical meristem?
Apical Meristem. These are present at the tips of the roots and shoots and help in the increase in height of the plants. Various cell divisions facilitate the growth of the cells in the roots and shoots. and help in cellular enlargement.
What is Meristem?
Meristems in plants are the center of active mitotic cell division where plant growth occurs. Mitotic cell division happens when a parent cell divides into two identical daughter cells. Meristematic tissues are groups of densely packed cells with thin cell walls.
Meristematic Function
Meristem comes from the Greek word meristos, which means divisible. The main function of meristematic tissue is to begin the process of new cell growth. Plant meristematic tissue is also responsible for the formation of post-embryonic organs (organogenesis). Meristematic cells are often compared to stem cells in animals.
Meristematic Tissue
The role and function of meristematic tissue are dependent on its location on the plant.
What is meristematic tissue?
Meristematic tissue is that which occurs at the growing points on a plant. It is where growth by cell division occurs. The cells of meristematic tissue are undifferentiated into specialized cell types (xylem, phloem, floral tissues, etc.). Their job is to make new cells that will become the structural and functional tissues of the plant.
Where are meristematic cells found?
This tissue is found in most plants containing undifferentiated cells (meristematic cells), found in zones of the plant where growth can take place . Meristematic cells are growing cells and all plant organs have them in specific areas.
Where is the vascular cambium located?
Lateral meristems I. e vascular cambium is present in between xylem and phloem of dicot plants and it allows growth in thickness of stem. Cork cambium is present in the cortical region of stem and it also adds to the thickness of stem and root in dicots.
Where is the intercalary meristem located?
Intercalary meristem is basically located near the node in stem and roots. As it is growing part of plants, cell of this part has prominent nuclei, thin cellulose walls and dense cytoplasm but lacks vacuole. Characteristics of cells in growing parts remain same but slowly changes as they grow and mature with time and prominent difference is noticed with components of other tissues.
Where is the meristem found?
A meristem is the tissue found in most plants that contain multiple undifferentiated cells, which can be found in the zones of the plant where growth takes place.
Which type of tissue has specific function and the growth is ceased?
Permanent tissues have specific function and the growth is ceased whereas the meristamatic tissues grow rapidly and perform cell division.
Where are plant tissue found?
In case of plants, these tissue are found in different regions like on the tip of the shoot and root.
What is the role of meristematic tissue in plants?
This type of meristematic tissue is responsible for the growth of the stem, leaves, and floral organs. Unlike most other tissues in a plant’s life cycle, meristematic cells, once formed, remain in the same position the rest of their lives unless they are actively dividing.
What are Induced Meristematic Tissues?
Induced meristematic tissues are plant organs that have meristematic cells. These tissues are formed through artificial treatment. The new tissues formed by this treatment are not genetically identical to the original tissue. Examples of Induced meristematic procedures are:
What is the vascular cambium?
The vascular cambium is a cylinder of undifferentiated cells. These cells produce xylem to the inside and phloem to the outside. This meristematic tissue forms during the summer months in many species, and its development is regulated by auxins, which stimulate cell division.
How are lateral meristems created?
Lateral meristems are created by specialized cells that divide rapidly to form new cells. The cells in secondary meristems are undifferentiated and can form many kinds of plant tissue.
What is the primary meristem?
Primary meristems are the first set of meristems that develop. During this process, cells divide rapidly and without any differentiation until organ primordia have been formed. The primary meristem is responsible for the growth of cells in the tips, roots, and leaves’ surface. The cells will then differentiate into other types of plant tissue.
How is tissue recombination used to create transgenic plants?
Tissue recombination is used to create transgenic plants. The genetic makeup of the plant cells is modified by inserting a piece of DNA with new traits into the cell.
What are the three main types of meristems?
Primary meristems are the first meristem to develop. There are three major types: axillary, intercalary, and apical. These are responsible for growth throughout a plant’s life.
What are meristematic cells?
Meristematic cells are typically small and nearly spherical. They have a dense cytoplasm and relatively few small vacuoles (watery saclike enclosures). Some of these cells, known as initials, maintain the meristem as a continuing source of new cells and may undergo mitosis (cell division) many times before differentiating into the specific cells required for that region of the plant body. The cells that emanate from the apical meristem are arranged in lineages of partially differentiated tissues known as primary meristems. There are three primary meristems: the protoderm, which will become the epidermis; the ground meristem, which will form the ground tissues comprising parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma cells; and the procambium, which will become the vascular tissues ( xylem and phloem ).
Which meristem forms the ground tissues?
There are three primary meristems: the protoderm, which will become the epidermis; the ground meristem, which will form the ground tissues comprising parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma cells; and the procambium, which will become the vascular tissues ( xylem and phloem ). root and shoot apical meristems.
What is the function of apical meristems?
Apical meristems give rise to the primary plant body and are responsible for the extension of the roots and shoots. Lateral meristems are known as secondary meristems because they are responsible for secondary growth, or increase in stem girth and thickness. Meristems form anew from other cells in injured tissues and are responsible ...
Where is the apical meristem?
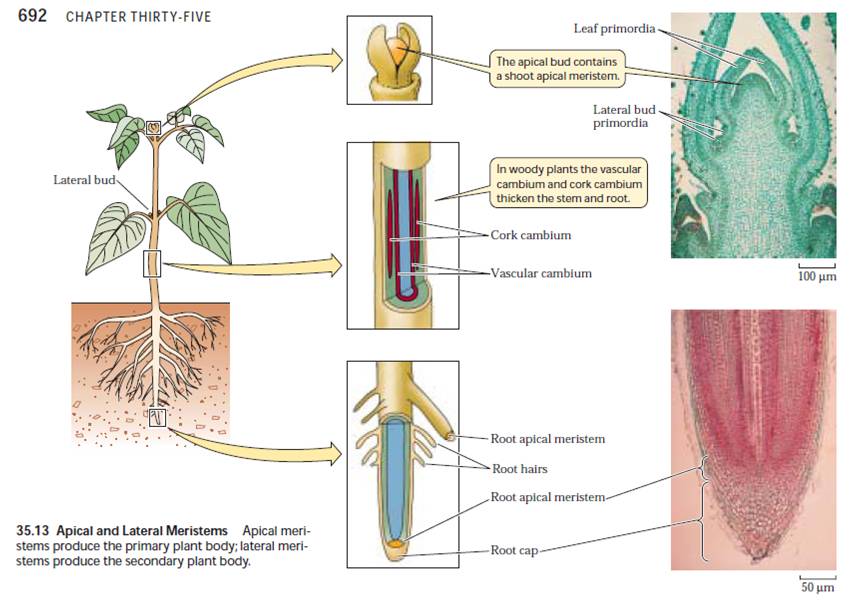
The shoot apical meristem of Hypericum uralum (left) appears at the topmost aspect of the stem. Immediately behind the apical meristem are three regions of primary meristematic tissues. The root apical meristem (right) appears immediately behind the protective root cap.
How do vascular plants grow?
Characteristically, vascular plants grow and develop through the activity of organ-forming regions, the growing points. The mechanical support and additional conductive pathways needed by increased bulk are provided by the enlargement of the older parts of the shoot and root axes. New cells are…