Where is Perga located?
Today, it is a large site of ancient ruins 15 kilometres (9.3 mi) east of Antalya on the coastal plain. An acropolis located there dates back to the Bronze Age. Perga was an ancient and important city of Pamphylia, between the rivers Catarrhactes and Cestrus (Turkish Aksu Çayı).
What is the significance of Perga in the Bible?
Perga, Greek Perge, modern Murtina or Murtana, ancient city of Pamphylia, now in Antalya il (province), Turkey. It was a centre of native culture and was a seat of the worship of “Queen” Artemis, a purely Anatolian nature goddess. In Perga St. Paul, the Apostle, and St. Barnabas began their first mission in Anatolia (Acts of the Apostles 13:13).
Where is Pamphylia in the Bible?
Easton's Bible Dictionary The capital of Pamphylia, on the coast of Asia Minor. Paul and his companions landed at this place from Cyprus on their first missionary journey (Acts 13:13, 14), and here Mark forsook the party and returned to Jerusalem.
Why did Paul go to Perga?
Acts indicates that Paul deliberately traveled to cities with Jewish populations. Perga was a major city, and the presence of a Jewish community there made it an ideal base for Paul’s first missionary journey through Anatolia.

Where is the Biblical Perga?
AnatoliaPerga or Perge (Greek: Πέργη Perge, Turkish: Perge) was an ancient Greek city in Anatolia, once the capital of Pamphylia Secunda, now in Antalya Province on the southwestern Mediterranean coast of Turkey.
Does Perga exist?
The major part of the magnificent ancient city of Perga still remains underground. Archaeological excavations take a long time and take place under the framework of a specific plan. A large portion of the city is still under the ground but excavation works continue in an organized manner.
Where is attalia located today?
Antalya, TurkeyAttalia (modern Antalya, Turkey) was a city and bishopric of Pamphylia. Although inscriptions and remains indicate some prosperity in late antiquity, Attaleia became most important in the 9th-11th century as a naval and military center.
What is the meaning of Perga?
The name Perga is primarily a female name of Greek origin that means Earthy. In the Bible, Perga is a place name - a city in Pamphylia where Paul visited to get support for the new church.
How do you pronounce perga?
0:130:46How to Pronounce Perga? (CORRECTLY) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipPlaces as well.MorePlaces as well.
How old is Perge?
Perge is one of the most popular historical sites along the Antalya region. Being an ancient Greek city, Perge is famous for its Roman ruins dating back to 1300 BC and its big amphitheater with a capacity of 15,000 people.
Is Antalya and Anatolia same?
Antalya is on the shores of the Mediterranean Sea and situated in the gulf bearing the same name, in the south of the Anatolia peninsula....Technical Information of original imageAcq. Date:30 June 1984 and 06 July 20155 more rows
Why is Antalya famous?
Antalya is a wonderful city in the Republic of Turkey That hosts millions of visitors annually. The city is famous for its charming nature and glamorous atmosphere. Moreover, The city has many beautiful destinations that make the city one of the most visited destinations around the world.
Where is Antioch in the Bible?
Antioch on the Orontes (/ˈænti. ɒk/; Ancient Greek: Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου, Antiókheia hē epì Oróntou; also Syrian Antioch) was a Hellenistic city on the eastern side of the Orontes River. Its ruins lie near the current city of Antakya, Turkey, to which the ancient city lends its name.
Where is Perga located?
An important city of the ancient province of Pamphylia, situated on the river Cestris, 12 miles Northeast of Attalia. According to Acts 13:13, Paul, Barnabas and John Mark visited the place on their first missionary journey, and 2 years later, according to Acts 14:24, 25, they may have preached there. Though the water of the river Cestris has now been diverted to the fields for irrigating purposes, in ancient times the stream was navigable, and small boats from the sea might reach the city. It is uncertain how ancient Perga is; its walls, still standing, seem to come from the Seleucidan period or from the 3rd century B.C. It remained in the possession of the Seleucid kings until 189 B.C., when Roman influence became strong in Asia Minor. A long series of coins, beginning in the 2nd century B.C., continued until 286 A.D., and upon them Perga is mentioned as a metropolis. Though the city was never a stronghold of Christianity, it was the bishopric of Western Pamphylia, and several of the early Christians were martyred there. During the 8th century under Byzantine rule the city declined; in 1084 Attalia became the metropolis, and Perga rapidly fell to decay. While Attalia was the chief Greek and Christian city of Pamphylia, Perga was the seat of the local Asiatic goddess, who corresponded to Artemis or Diana of the Ephesians, and was locally known as Leto, or the queen of Perga. She is frequently represented on the coins as a huntress, with a bow in her hand, and with sphinxes or stags at her side.
What is the name of the goddess that lived in Perga?
While Attalia was the chief Greek and Christian city of Pamphylia, Perga was the seat of the local Asiatic goddess, who corresponded to Artemis or Diana of the Ephesians, and was locally known as Leto, or the queen of Perga.
What are the ruins of Perga called?
The Ruins: The ruins of Perga are now called Murtana. The walls, which are flanked with towers, show the city to have been quadrangular in shape. Very broad streets, running through the town, and intersecting each other, divided the city into quarters.
When was Perga a metropolis?from bibleatlas.org
A long series of coins, beginning in the 2nd century B.C., continued until 286 A.D., and upon them Perga is mentioned as a metropolis. Though the city was never a stronghold of Christianity, it was the bishopric of Western Pamphylia, and several of the early Christians were martyred there.
What is the history of Perga?from en.wikipedia.org
Ruins of Perga. Perga was an ancient and important city of Pamphylia, between the rivers Catarrhactes and Cestrus (Turkish Aksu Çayı). A treaty between the Hittite Great King Tudhaliya IV and his vassal, the king of Tarhuntassa, defined the latter's western border at the city "Parha" and the "Kastaraya River".
What Can I Do in Perge?from antalyatouristinformation.com
Among the important remains, you will find bath complexes, four fountains, colonnaded streets, an agora, two basilicas, hellenistic towers, palaestras, a theater, a stadium, and a temple dedicated to Goddess Athena. The fortification walls are still visible.
What does the coin of Perge represent?from en.wikipedia.org
The coins of Perge represent both the goddess and her temple. In 46 A.D., according to the Acts of the Apostles, St. Paul journeyed to Perga, from there continued on to Antiocheia in Pisidia, then returned to Perga where he preached the word of God (Acts 14:25). Then he left the city and went to Attaleia.
What empire did Perge rule?from en.wikipedia.org
Alexander's rule was followed by the Diadochi empire of the Seleucids, then the Romans. Perge gained renown for the worship of Artemis, whose temple stood on a hill outside the town, and in whose honour annual festivals were celebrated. The coins of Perge represent both the goddess and her temple.
What is the closest Roman ruin to Antalya?from turkeytravelplanner.com
Perge is the closest significant Roman ruin to Antalya, and well worth a visit!
How old is the Iphigenia statue?from en.wikipedia.org
In 2017, discovered a mosaic depicting the sacrifice of Iphigenia. A 1,700-year-old full-body statue of a dressed female with her broken head from the Hellenistic period were revealed by archaeologists headed by Sedef Cokay Kepçe in July in 2020.
What is Perga in Greek?from en.wikipedia.org
Associated with. Apollonius. The agora. The stadium. Perga or Perge ( Greek: Πέργη Perge, Turkish: Perge) was an ancient Greek city in Anatolia, once the capital of Pamphylia Secunda, now in Antalya Province on the southwestern Mediterranean coast of Turkey.
When was Perga a metropolis?from bibleatlas.org
A long series of coins, beginning in the 2nd century B.C., continued until 286 A.D., and upon them Perga is mentioned as a metropolis. Though the city was never a stronghold of Christianity, it was the bishopric of Western Pamphylia, and several of the early Christians were martyred there.
What does the coin of Perge represent?from en.wikipedia.org
The coins of Perge represent both the goddess and her temple. In 46 A.D., according to the Acts of the Apostles, St. Paul journeyed to Perga, from there continued on to Antiocheia in Pisidia, then returned to Perga where he preached the word of God (Acts 14:25). Then he left the city and went to Attaleia.
What is the history of Perga?from en.wikipedia.org
Ruins of Perga. Perga was an ancient and important city of Pamphylia, between the rivers Catarrhactes and Cestrus (Turkish Aksu Çayı). A treaty between the Hittite Great King Tudhaliya IV and his vassal, the king of Tarhuntassa, defined the latter's western border at the city "Parha" and the "Kastaraya River".
What empire did Perge rule?from en.wikipedia.org
Alexander's rule was followed by the Diadochi empire of the Seleucids, then the Romans. Perge gained renown for the worship of Artemis, whose temple stood on a hill outside the town, and in whose honour annual festivals were celebrated. The coins of Perge represent both the goddess and her temple.
What is the Perge?from en.wikipedia.org
The Perge has been dubbed as “Turkey’s second Zeugma ” for the alluring appearance of the mosaics that have been unearthed so far. In 2003, archaeologists discovered well-preserved Greek mosaics showcasing Oceanus and Medusa. In 2017, discovered a mosaic depicting the sacrifice of Iphigenia.
How old is the Iphigenia statue?from en.wikipedia.org
In 2017, discovered a mosaic depicting the sacrifice of Iphigenia. A 1,700-year-old full-body statue of a dressed female with her broken head from the Hellenistic period were revealed by archaeologists headed by Sedef Cokay Kepçe in July in 2020.
What is the history of Perga?
Little that is certain is known of the early history of Perga. The name itself is prob. pre-Gr. It seems likely that Gr.-speaking colonists occupied the Pamphylian coastal plain in an early Aegean diaspora associated perhaps with the continued pressure and irruption of the Dorian tribes into the area, and the ensuing collapse of the Mycenaean civilization. If Rhys Carpenter’s theories of climatic change, and the shifting of population in consequence to maritime environments exposed to the wet W winds, are found acceptable, a spread of colonization along the Pamphylian coast is equally probable. At any rate, there is some evidence of Arcadian speech in the region to lend support to the contention that Perga was a foundation of very early Gr. origin.
Who were the founders of Perga?
Legends and dedications mention Calchas, the diviner of the Greeks before Troy, and Mopsus, diviner of the Argonauts, as foundation heroes. Both figures, coming from the area of mingled myth and history associated with the breakdown of the Mycenaean culture, give color to a theory of early settlement from a disrupted Aegean. Like the founders of Ephesus, the founders of Perga took over a Bronze Age goddess under the name of Artemis, and Perga became notable for her cult. Artemis of Perga, like Artemis of Ephesus, was no doubt worshiped in the form of some primitive image, perhaps a meteoric stone.
Why did John Mark leave Perga?
The reason for John Mark’s withdrawal from the party at Perga is no doubt to be found somewhere in this set of circumstances, whether it was dispute over the priority of the Perga synagogue, resort to a Rom. colon y, or confrontation with physical peril. Little that is certain is known of the early history of Perga.
Did Perga become independent?
With the breaking of the Seleucid power at this time by the Romans, Perga appears to have become independent, and subsequent coinage tells a story that runs from this time until three centuries into the Christian era. Little, however, is known of the history of the city, beyond the fragmented evidence of coinage and inscr. The notorious Verres, destroyed in court by a set of famous forensic orations of Cicero, appears to have practiced some of his familiar depredations there, and sundry emperors of the first two centuries are honored in surviving inscrs.
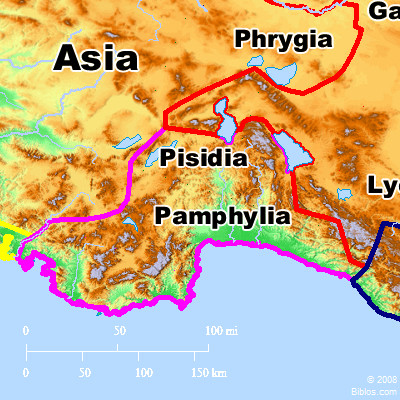
Where is Pamphylia located?
PAMPHYL'IA, a Roman province in Asia Minor, bounded e. by Cilicia, n. by Pisidia, w. by Lycia, and s. by the Mediterranean. Perga appears to have been the capital and Attalia its chief seaport.
Who introduced Christianity to Pamphylia?
Christianity was first introduced to Pamphylia by Paul and Barnabas (Acts 13:13; Acts 14:24), but because their stay in the country was brief, or because of the difficulty of communication with the neighboring countries, or because of the Asiatic character of the population, it was slow in being established.
What was the high land called that was once called "Pisidia"?
Beyond the steps is the high land which was once called "Pisidia," but which the Romans, in 70 A.D., made a part of Pamphylia. 2. Importance: Pamphylia, unless in pre-historic times, was never an independent kingdom; it was subject successively to Lydia, Persia, Macedonia, Pergamos and Rome.
Where is Perga located?
An important city of the ancient province of Pamphylia, situated on the river Cestris, 12 miles Northeast of Attalia. According to Acts 13:13, Paul, Barnabas and John Mark visited the place on their first missionary journey, and 2 years later, according to Acts 14:24, 25, they may have preached there. Though the water of the river Cestris has now been diverted to the fields for irrigating purposes, in ancient times the stream was navigable, and small boats from the sea might reach the city. It is uncertain how ancient Perga is; its walls, still standing, seem to come from the Seleucidan period or from the 3rd century B.C. It remained in the possession of the Seleucid kings until 189 B.C., when Roman influence became strong in Asia Minor. A long series of coins, beginning in the 2nd century B.C., continued until 286 A.D., and upon them Perga is mentioned as a metropolis. Though the city was never a stronghold of Christianity, it was the bishopric of Western Pamphylia, and several of the early Christians were martyred there. During the 8th century under Byzantine rule the city declined; in 1084 Attalia became the metropolis, and Perga rapidly fell to decay. While Attalia was the chief Greek and Christian city of Pamphylia, Perga was the seat of the local Asiatic goddess, who corresponded to Artemis or Diana of the Ephesians, and was locally known as Leto, or the queen of Perga. She is frequently represented on the coins as a huntress, with a bow in her hand, and with sphinxes or stags at her side.
What are the ruins of Perga?
The ruins of Perga are now called Murtana. The walls, which are flanked with towers, show the city to have been quadrangular in shape. Very broad streets, running through the town, and intersecting each other, divided the city into quarters. The sides of the streets were covered with porticos, and along their centers were water channels in which a stream was always flowing. They were covered at short intervals by bridges. Upon the higher ground was the acropolis, where the earliest city was built, but in later times the city extended to the South of the hill, where one may see the greater part of the ruins. On the acropolis is the platform of a large structure with fragments of several granite columns, probably representing the temple of the goddess Leto; others regard it as the ruin of an early church. At the base of the acropolis are the ruins of an immense theater which seated 13,000 people, the agora, the baths and the stadium. Without the walls many tombs are to be seen. E. J. Banks
What city is 4011. Perga?
4011. Perge -- Perga, a city of Pamphylia
What city is 825?
825. Attaleia -- Attalia, a city of Pamphylia
What is the city of Pamphylia?
A city of Pamphylia, Acts 13:13; 14:25. This is not a maritime city, but is situated on the river Cestrus, at some distance from its mouth, which has long been obstructed by a bar. It was one of the most considerable cities in Pamphylia; and when that province was divided into two parts, this city became the metropolis of one part, and side of the other. On a neighboring mountain was a splendid temple of Diana, which gave celebrity to the city.
Where did the Perga people go when they spoke the word?
When they had spoken the word in Perga, they went down to Attalia.
When did Perga coins start?
PERGA. ... A long series of coins, beginning in the 2nd century BC, continued until
What is the Roman province of Pamphylia?
Anatolia / Asia Minor in the Greco-Roman period. The classical regions, including Pamphylia, and their main settlements. Pamphylia ( Ancient Greek: Παμφυλία, Pamphylía, modern pronunciation Pamfylía / pæmˈfɪliə /) was a region in the south of Asia Minor, between Lycia and Cilicia, extending from ...
Where did the name Pamphylia come from?
The name Pamphylia comes from the Greek Παμφυλία, itself from Ancient Greek: πάμφυλος ( pamphylos ), literally "of mingled tribes or races", a compound of πᾶν ( pan ), neuter of πᾶς ( pas) "all" + φυλή ( phylē ), "race, tribe". Herodotus derived its etymology from a Dorian tribe, the Pamphyloi (Πάμφυλοι), who were said to have colonized the region.
What language was spoken in the Pamphylia region?
West of Parha were the "Lukka Lands". The Pamphylian language was likely a late Luwic dialect, related to Carian, Lycian, Lydian and/or Milyan . When the region returns to history its population is "Pamphylian", that is Greek-speaking. On Cyrus's defeat of Croesus, Pamphylia passed to the Persian Empire.
What happened to Pamphylia after Alexander the Great defeated Darius III?
Upon Alexander the Great 's defeat of Darius III, Pamphylia passed back to Greek rule, now Macedonians. After the defeat of Antiochus III in 190 BC they were included among the provinces annexed by the Romans to the dominions of Eumenes of Pergamum; but somewhat later they joined with the Pisidians and Cilicians in piratical ravages, and Side became the chief centre and slave mart of these freebooters. Pamphylia was for a short time included in the dominions of Amyntas, king of Galatia, but after his death lapsed into a district of a Roman province.
What is the significance of the Greek contribution to the origin of the Pamphylians?
The significance of the Greek contribution to the origin of the Pamphylians can be attested alike by tradition and archaeology and Pamphylia can be considered a Greek country from the early Iron Age until the early Middle Ages.
What is the name of the river that flows through the city of Parha?
A treaty between the Hittite Great King Tudḫaliya IV and his vassal, the king of Tarḫuntašša, defined the latter's western border at the city "Parha" and the "Kastaraya River". The river is assumed to be the classical Kestros (Turkish Aksu Çayı); Parha, the future Perge. West of Parha were the "Lukka Lands".
Was the Pamphylians the same as the Pisidians?
There can be little doubt that the Pamphylians and Pisidians were the same people, though the former had received colonies from Greece and other lands, and from this cause, combined with the greater fertility of their territory, had become more civilized than their neighbours in the interior.
When was Perga a metropolis?from bibleatlas.org
A long series of coins, beginning in the 2nd century B.C., continued until 286 A.D., and upon them Perga is mentioned as a metropolis. Though the city was never a stronghold of Christianity, it was the bishopric of Western Pamphylia, and several of the early Christians were martyred there.
What is the history of Perga?from en.wikipedia.org
Ruins of Perga. Perga was an ancient and important city of Pamphylia, between the rivers Catarrhactes and Cestrus (Turkish Aksu Çayı). A treaty between the Hittite Great King Tudhaliya IV and his vassal, the king of Tarhuntassa, defined the latter's western border at the city "Parha" and the "Kastaraya River".
What does the coin of Perge represent?from en.wikipedia.org
The coins of Perge represent both the goddess and her temple. In 46 A.D., according to the Acts of the Apostles, St. Paul journeyed to Perga, from there continued on to Antiocheia in Pisidia, then returned to Perga where he preached the word of God (Acts 14:25). Then he left the city and went to Attaleia.
What empire did Perge rule?from en.wikipedia.org
Alexander's rule was followed by the Diadochi empire of the Seleucids, then the Romans. Perge gained renown for the worship of Artemis, whose temple stood on a hill outside the town, and in whose honour annual festivals were celebrated. The coins of Perge represent both the goddess and her temple.
What is the Perge?from en.wikipedia.org
The Perge has been dubbed as “Turkey’s second Zeugma ” for the alluring appearance of the mosaics that have been unearthed so far. In 2003, archaeologists discovered well-preserved Greek mosaics showcasing Oceanus and Medusa. In 2017, discovered a mosaic depicting the sacrifice of Iphigenia.
How old is the Iphigenia statue?from en.wikipedia.org
In 2017, discovered a mosaic depicting the sacrifice of Iphigenia. A 1,700-year-old full-body statue of a dressed female with her broken head from the Hellenistic period were revealed by archaeologists headed by Sedef Cokay Kepçe in July in 2020.
Was Perga a secular city?from en.wikipedia.org
As the Cestrus silted up over the late Roman era, Perga declined as a secular city. In the first half of the 4th century, during the reign of Constantine the Great (324-337), Perga became an important centre of Christianity, which soon became the official religion of the Roman Empire. The city retained its status as a Christian centre in the 5th and 6th centuries.
Where did Paul travel from Perga?
Mark R. Fairchild suggests that Paul traveled from Perga up the Kestros River Valley to Pisidian Antioch, the route indicated in green. Subscribers: Read “Why Perga? Paul’s Perilous Passage through Pisidia” by Mark R. Fairchild as it appears in the November/December 2013 issue of BAR.
Where did Paul and Barnabas go to Perga?
The rock-cut road to Perga. All photos courtesy of Mark R. Fairchild. After sailing from Cyprus to the Turkish coast, Paul and Barnabas visit the city of Perga before traveling to Pisidian Antioch and other cities on the Anatolian interior. When they head back to the coast, the travelers follow the same route.
Did St P go to Sagalassos?
If this is the case, he did not go to Sagalassos, which is far off the N-S route. Milyas is misplaced (if he means Milli, it is SW from Pednelissos), Cremna, Adada, Parlais and the important road junction at Gönen are unplaced and Eğirdir lake was in fact 2 lakes – Hoyran and Eğirdir – until recently.
Is Milyas misplaced?
Milyas is misplaced (if he means Milli, it is SW from Pednelissos), Cremna, Adada, Parlais and the important road junction at Gönen are unplaced and Eğirdir lake was in fact 2 lakes – Hoyran and Eğirdir – until recently. ] Paul’s First Missionary Journey through Perga and Pisidian Antioch […]
