
Explore
Pneumococcal Disease. Streptococcus pneumoniae, or pneumococcus, is a type of bacterium that causes pneumococcal [noo-muh-KOK-uhl] disease. Pneumococcal infections can range from ear and sinus infections to pneumonia and bloodstream infections. Children younger than 2 years old and adults 65 years or older are among those most at risk for disease.
What is pneumococcus pneumoniae?
Pneumococcus bacteria are spread through coughing, sneezing, and close contact with an infected person. Symptoms of pneumococcal disease depend on the part of the body that is infected.
How do you get pneumococcus?
Pneumococcal disease is caused by bacteria called Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus). People with pneumococcal disease can spread the bacteria to others when they cough or sneeze.
What is the pathophysiology of pneumococcal disease?
What Is Bacterial Pneumonia? Bacterial pneumonia is an infection of your lungs caused by certain bacteria. The most common one is Streptococcus (pneumococcus), but other bacteria can cause it too.
What is bacterial pneumonia?
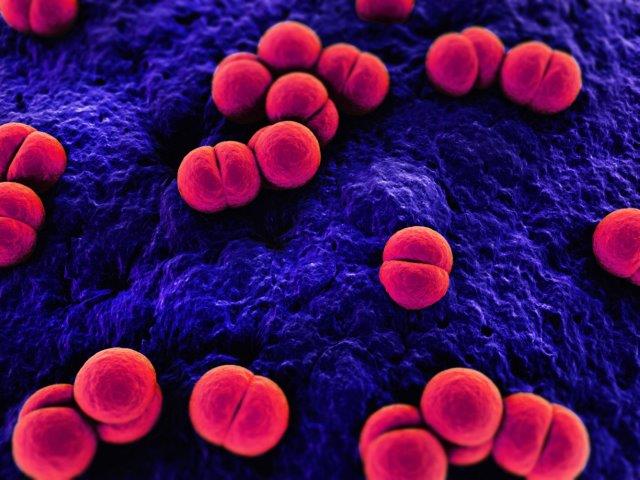
Where is pneumococcal found?
What is invasive Streptococcal pneumoniae infection (Pneumococcal disease)? Streptococcus pneumoniae is a bacterium commonly found in the nose and throat. The bacterium can sometimes cause severe illness in children, the elderly and other people with weakened immune systems.
Where did pneumococcal come from?
Streptococcus pneumoniae causes acute bacterial infections. The bacterium, also called pneumococcus, was first isolated by Louis Pasteur in 1881 from the saliva of a patient with rabies.
Where is Streptococcus pneumoniae found in the environment?
Streptococcus pneumoniae is found predominantly in the mucus layer overlying the epithelial surface of the upper respiratory tract.
Where is Streptococcus pneumoniae most likely to be found in the world?
Definition. Streptococcus pneumoniae is a bacteria that is commonly found in the nose and throat.
How do you catch pneumococcal?
People spread pneumococcal bacteria to others through direct contact with respiratory secretions, like saliva or mucus. Many people, especially children, have the bacteria in their nose or throat at one time or another without being ill.
How is pneumococcal spread?
How is pneumococcal disease spread? It spreads from person-to-person by coming into contact with fluids like the saliva or mucus of someone who is sick. Many people, especially children, can have this bacteria in their nose or throat without being ill and can still transmit the disease to others.
How does Streptococcus bacteria enter the body?
These bacteria are spread by direct contact with discharges from the nose and throat of infected people or by contact with infected wounds or sores on the skin. The risk of spreading the infection is highest when a person is ill, such as when people have "strep throat" or an infected wound.
Where is pneumococcal disease most prevalent?
Pneumococcal disease is deadly The rates are highest among Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander children, especially in central Australia. Pneumococcal disease is also an important cause of pneumonia in adults 65 years of age or over. Older people are especially at risk of death from this disease.
Is Streptococcus pneumoniae part of normal flora?
Streptococcus pneumoniae is part of the normal bacterial flora of the narsopharynx, but is also associated with several invasive and non-invasive diseases.
How common is pneumococcal bacteria?
Pneumococcal pneumonia hospitalizes about 150,000 people in the US each year—killing about 5-7 percent, or 1 in 20 of those infected. The death rate is even higher among adults age 65 years and older and people with certain medical conditions or other risk factors.
What is the difference between pneumonia and pneumococcal pneumonia?
Pneumonia can be classified into bacterial, viral, fungal or aspiration as the cause. Pneumococcal pneumonia specifically refers to a pneumonia caused by the Strep pneumo bacteria,” Dr. Jenkins says.
How does Streptococcus pneumoniae grow?
Streptococcus pneumoniae is a fastidious bacterium, growing best in 5% carbon dioxide. Nearly 20% of fresh clinical isolates require fully anaerobic conditions. In all cases, growth requires a source of catalase (e.g. blood) to neutralize the large amount of hydrogen peroxide produced by the bacteria.
What is pneumococcal pneumonia caused by?
What is pneumococcal disease? Pneumococcal disease is caused by bacteria called Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus). People with pneumococcal disease can spread the bacteria to others when they cough or sneeze. Symptoms of pneumococcal infection depend on the part of the body affected.
What bacteria causes pneumococcal disease?
Disease information Pneumococcal disease is an infection caused by a type of bacteria called Streptococcus pneumoniae.
What is the main cause of pneumonia?
Common Causes of Pneumonia Viruses, bacteria, and fungi can all cause pneumonia. In the United States, common causes of viral pneumonia are influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and SARS-CoV-2 (the virus that causes COVID-19). A common cause of bacterial pneumonia is Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus).
What is the difference between pneumonia and pneumococcal pneumonia?
Pneumonia can be classified into bacterial, viral, fungal or aspiration as the cause. Pneumococcal pneumonia specifically refers to a pneumonia caused by the Strep pneumo bacteria,” Dr. Jenkins says.
Where do pneumococci occur?
Many serological types have been differentiated. Pneumococci normally occur in the upper respiratory tract. Pneumococci have proved useful in elucidating microbial genetics. The phenomenon of transformation —an alteration of one cell by another—was first observed in these organisms in 1928.
What is the name of the bacterium that causes pneumonia?
Pneumococcus, ( Streptococcus pneumoniae ), spheroidal bacterium in the family Streptococcaceae that causes human diseases such as pneumonia, sinusitis, otitis media, and meningitis.
What is pneumococcal disease?
Pneumococcal disease is caused by bacteria called Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus). People with pneumococcal disease can spread the bacteria to others when they cough or sneeze.
What are the symptoms of pneumococcal infection?
Symptoms can include fever, cough, shortness of breath, chest pain, stiff neck, confusion, increased sensitivity to light, joint pain, chills, ear pain, sleeplessness, and irritability.
What can travelers do to prevent pneumococcal disease?
Getting vaccinated is the best way to protect against pneumococcal disease. Pneumococcal vaccines are routinely recommended in the United States.
When were pneumococci first described?
More than 80 serotypes of pneumococci had been described by 1940.
When was S. pneumoniae first isolated?
S. pneumoniae first isolated by Pasteur in 1881. Confused with other types of pneumonia until discovery of Gram stain in 1884. More than 80 serotypes described by 1940. First pneumococcal vaccine licensed in U.S. in 1977; first conjugate pneumococcal vaccine in 2000. Streptococcus pneumoniae causes acute bacterial infections.
What is pneumoniae?
S. pneumoniae bacteria are lancet-shaped, gram-positive, facultative anaerobic organisms. They are typically observed in pairs (diplococci) but may also occur singularly or in short chains. Most pneumococci are encapsulated, and their surfaces are composed of complex polysaccharides. Capsular polysaccharides are one determinant of the pathogenicity of the organism. They are also antigenic and form the basis for classifying pneumococci by serotypes. One hundred serotypes were documented as of 2020, based on their reaction with type-specific antisera. Type-specific antibody to capsular polysaccharide is protective against disease caused by that serotype. These antibodies and complement interact to opsonize pneumococci, which facilitates phagocytosis and clearance of the organism. Antibodies to some pneumococcal capsular polysaccharides may cross-react with related types as well as with other bacteria, providing protection against additional serotypes.
What is the name of the bacteria that causes bacterial infections?
Streptococcus pneumoniae causes acute bacterial infections. The bacterium, also called pneumococcus, was first isolated by Louis Pasteur in 1881 from the saliva of a patient with rabies. The association between pneumococcus and lobar pneumonia was first described in 1883, but pneumococcal pneumonia was confused with other types of pneumonia until the development of the Gram stain in 1884. Between 1915 and 1945, the chemical structure and antigenicity of the pneumococcal capsular polysaccharide, its association with virulence, and the role of bacterial polysaccharides in human disease were described. More than 80 serotypes of pneumococci had been described by 1940.
What age group is most likely to have pneumococcal infection?
Bacteremia without a known site of infection is the most common invasive clinical presentation of pneumococcal infection among children age 2 years or younger, accounting for approximately 40% of invasive disease in this age group.
What is the definitive diagnosis of S. pneumoniae?
A definitive diagnosis of infection with S. pneumoniae generally relies on isolation of the organism from blood or other normally sterile body sites ( e.g., CSF, middle ear fluid, joint fluid, and peritoneal fluid). Tests are also available to detect capsular polysaccharide antigen in body fluids.
How many hospitalizations from pneumonia occur annually?
Over 150,000 hospitalizations from pneumococcal pneumonia are estimated to occur annually in the United States and it has been demonstrated to complicate influenza infection. Pneumococci is the most common bacterial cause of childhood pneumonia, especially in children younger than age 5 years.
Where does pneumonia spread?
S. pneumoniae can spread from the nose and throat to the upper and lower respiratory tract.
When diagnosing pneumococcal diseases, a doctor will ask about the symptoms and carry out a?
When diagnosing pneumococcal diseases, a doctor will ask about the symptoms and carry out a physical examination.
What causes a cough and a sneezing cough?
If the eardrum becomes perforated, pus may drain into the ear canal. Bronchitis: Acute bronchitis is an inflammation of the airways, resulting in a cough with the production of mucus. It usually lasts up to 3 weeks and often affects children below the age of 5 years.
What happens if a doctor tests for bacteria?
If tests show what bacteria are causing the problem, the doctor may then change the antibiotics to target the specific microbe.
Why do people who are exposed to bacteria have no symptoms?
Most people who become exposed to the bacteria have no symptoms because their immune system stops the germs from moving to another part of the body.
Can pneumonia spread through sneezing?
Coughing and sneezing in public places can spread the infection. S. pneumoniae bacteria are common in the throats and noses of children. Bacteria can spread through droplets in the air, for example, when a person with the infection coughs or sneezes. The bacteria do not spread through contaminated food or water.
Can bacterial infection cause death?
Bacteremia: A bacterial infection of the blood causes this condition and can be fatal. It often progresses rapidly to sepsis. Symptoms include fever, chills, and reduced alertness. Sepsis: This is a potentially life-threatening infection response by the body.
When was the pneumococcus first isolated?
History. In 1881, the organism, known later in 1886 as the pneumococcus for its role as a cause of pneumonia, was first isolated simultaneously and independently by the U.S. Army physician George Sternberg and the French chemist Louis Pasteur. The organism was termed Diplococcus pneumoniae from 1920 because of its characteristic appearance in ...
What is the role of Streptococcus pneumoniae?
Streptococcus pneumoniae played a central role in demonstrating that genetic material consist s of DNA. In 1928, Frederick Griffith demonstrated transformation of life turning harmless pneumococcus into a lethal form by co-inoculating the live pneumococci into a mouse along with heat-killed virulent pneumococci.
What is the main cause of pneumonia?
Streptococcus pneumoniae is the main cause of community acquired pneumonia and meningitis in children and the elderly, and of sepsis in those infected with HIV. The organism also causes many types of pneumococcal infections other than pneumonia. These invasive pneumococcal diseases include bronchitis, rhinitis, acute sinusitis, otitis media, conjunctivitis, meningitis, sepsis, osteomyelitis, septic arthritis, endocarditis, peritonitis, pericarditis, cellulitis, and brain abscess.
Why was Streptococcus pneumoniae renamed?
It was renamed Streptococcus pneumoniae in 1974 because it was very similar to streptococci. Streptococcus pneumoniae played a central role in demonstrating that genetic material consists of DNA.
How many genes are in the genome of S. pneumoniae?
pneumoniae is a closed, circular DNA structure that contains between 2.0 and 2.1 million base pairs depending on the strain. It has a core set of 1553 genes, plus 154 genes in its virulome, which contribute to virulence and 176 genes that maintain a noninvasive phenotype.
What is the effect of S pneumoniae on the host?
The ability of S. pneumoniae to repair the oxidative DNA damages in its genome, caused by this host defense, likely contributes to this pathogen's virulence.
What are the symptoms of pneumonia?
pneumoniae diseases which include symptoms such as fever and chills, cough, rapid breathing, difficulty breathing, and chest pain. For the elderly, they may include confusion, low alertness, and the former listed symptoms to a lesser degree.
What is the bacterial flora that causes pneumococcal infection?
Pneumococcal infection. A pneumococcal infection is an infection caused by the bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae, which is also called the pneumococcus. S. pneumoniae is a common member of the bacterial flora colonizing the nose and throat of 5–10% of healthy adults and 20–40% of healthy children. However, it is also a cause ...
Where is pneumonia found?
S. pneumoniae is normally found in the nose and throat of 5–10% of healthy adults and 20–40% of healthy children. It can be found in higher amounts in certain environments, especially those where people are spending a great deal of time in close proximity to each other (day-care centers, military barracks). It attaches to nasopharyngeal cells through interaction of bacterial surface adhesins. This normal colonization can become infectious if the organisms are carried into areas such as the Eustachian tube or nasal sinuses where it can cause otitis media and sinusitis, respectively. Pneumonia occurs if the organisms are inhaled into the lungs and not cleared (again, viral infection, or smoking -induced ciliary paralysis might be contributing factors). The organism's polysaccharide capsule makes it resistant to phagocytosis and if there is no pre-existing anticapsular antibody alveolar macrophages cannot adequately kill the pneumococci. The organism spreads to the blood stream (where it can cause bacteremia) and is carried to the meninges, joint spaces, bones, and peritoneal cavity, and may result in meningitis, brain abscess, septic arthritis, or osteomyelitis .
What are the risk factors for pneumonia?
Other risk factors include smoking, injection drug use, Hepatitis C, and COPD.
Is a pneumococci gram positive?
Pneumococci are typically gram-positive cocci seen in pairs or chains. When cultured on blood agar plates with added optochin antibiotic disk they show alpha-hemolytic colonies and a clear zone of inhibition around the disk indicating sensitivity to the antibiotic. Pneumococci are also bile soluble.
Can you detect pneumococcal antigen in body fluids?
Pneumococcal antigen (cell wall C polysaccharide) may be detected in various body fluids. Older detection kits, based on latex agglutination, added little value above Gram staining and were occasionally false-positive. Better results are achieved with rapid immunochromatography, which has a sensitivity (identifies the cause) of 70–80% and >90% specificity (when positive identifies the actual cause) in pneumococcal infections. The test was initially validated on urine samples but has been applied successfully to other body fluids. Chest X-rays can also be conducted to confirm inflammation though are not specific to the causative agent.
Where does bacteremia spread?
The organism spreads to the blood stream (where it can cause bacteremia) and is carried to the meninges, joint spaces, bones, and peritoneal cavity, and may result in meningitis, brain abscess, septic arthritis, or osteomyelitis.
Does S. pneumoniae have virulence factors?
pneumoniae expresses different virulence factors on its cell surface and inside the organism. These virulence factors contribute to some of the clinical manifestations during infection with S. pneumoniae .
How to get rid of bacterial pneumonia?
Use a humidifier or take a warm bath (more gunk-loosening). Don’t smoke. Stay home until your fever goes down and you aren’t coughing anything out. Most people who are treated for bacterial pneumonia start feeling better in a few days, but it can take a few weeks before you feel 100% better.
What are the different types of pneumonia?
Types of Pneumonia. Walking Pneumonia. Viral Pneumonia. Bacterial Pneumonia. Chemical Pneumonia. Bacterial pneumonia is an infection of your lungs caused by certain bacteria. The most common one is Streptococcus (pneumococcus), but other bacteria can cause it too. If you’re young and basically healthy, these bacteria can live in your throat without ...
How to tell if you have pneumonia?
Your doctor might be able to tell if you have bacterial pneumonia just by examining you and asking questions about your symptoms and general health. They’ll probably listen to your lungs with a stethoscope. That will allow them to hear sounds that show there’s fluid in your lungs. But if they are not sure, you might have to get a chest X-ray.
How to get rid of pneumonia in children?
Besides getting shots, you can lower your risk of getting bacterial pneumonia by doing these things: Wash your hands regularly, especially after you go to the bathroom and before you eat. Eat right, with plenty of fruits and vegetables. Exercise.
What to do if you have pneumonia?
If the pneumonia is stubborn or severe, you might have to go to the hospital. If you go to the hospital you might get: Oxygen treatment. IV fluids and medications. Treatments to help loosen up the gunk.
How long does it take to feel better after pneumonia?
Most people who are treated for bacterial pneumonia start feeling better in a few days, but it can take a few weeks before you feel 100% better. Make sure you keep your follow-up appointments so your doctor can check your lungs.
Can drinking alcohol cause pneumonia?
Drink too much alcohol. Have viral pneumonia. People who have a weakened immune system also have an increased risk for bacterial pneumonia. These include those who recently had an organ transplant.
What is the cause of pneumonia?
Pneumococcal disease is caused by common bacteria ( Streptococcus pneumoniae) that can attack different parts of the body. When these bacteria invade the lungs, they can cause pneumonia; when they invade the bloodstream, they can cause sepsis; and when they invade the covering of the brain, they can cause meningitis. These invasive infections are serious, often require treatment in the hospital, and can lead to death. The bacteria can also cause milder common conditions like middle-ear infection (otitis media) and sinusitis.
How many people die from pneumonia each year?
About 1.3 million persons visit emergency departments in the US each year with pneumonia, which is often caused by pneumococcal infections, and nearly 50,000 people will die from pneumonia.
What is the treatment for a bacterial infection?
Treatment may start with a broad-spectrum antibiotic, which works against a wide range of bacteria. After testing, once the sensitivity of the bacteria is known, a more targeted antibiotic may be selected. Reviewed September 2020. Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Pathogenicity of Pneumococcus
Pneumococcus is the most common cause of bloodstream infections, pneumonia, meningitis, and middle ear infections ( Otitis media) in young children. Severe infections can occur in the elderly and those already in poor health or immunosuppressed. The risk of infection is increased following splenectomy. In tropical and developing countries, S.
Laboratory Diagnosis of Pneumococcus
Specimens: Depending on the site of infection, specimens may include sputum, exudate, blood for culture, and cerebrospinal fluid.
Treatment
Useful antibacterial drugs are ampicillin, amoxicillin, erythromycin, cotrimoxazole, doxycycline, ofloxacin, vancomycin, chloramphenicol (nitrofurantoin in case of urine ), teicoplanin, linezolid. Penicillin-resistant strains are becoming an increasing problem.
Further Readings
Bailey & Scott’s Diagnostic Microbiology. Editors: Bettey A. Forbes, Daniel F. Sahm & Alice S. Weissfeld, 12th ed 2007, Publisher Elsevier.

Streptococcus pneumoniae
Pathogenesis
Clinical Features
Epidemiology
Secular Trends in The United States
- Pneumococci are common inhabitants of the respiratory tract and may be isolated from the nasopharynx of 5% to 90% of healthy persons. Rates of asymptomatic carriage vary with age, environment, and the presence of upper respiratory infections. Among school-age children, 20% to 60% may be colonized. Only 5% to 10% of adults without children are colon...
Pneumococcal Vaccines
- The major clinical syndromes of invasive pneumococcal disease are pneumonia, bacteremia, and meningitis.
Vaccination Schedule and Use
- Occurrence
Pneumococcal disease occurs throughout the world. - Reservoir
S. pneumoniaeis a human pathogen. The reservoir for pneumococci is the nasopharynx of asymptomatic humans. There is no animal or insect vector.