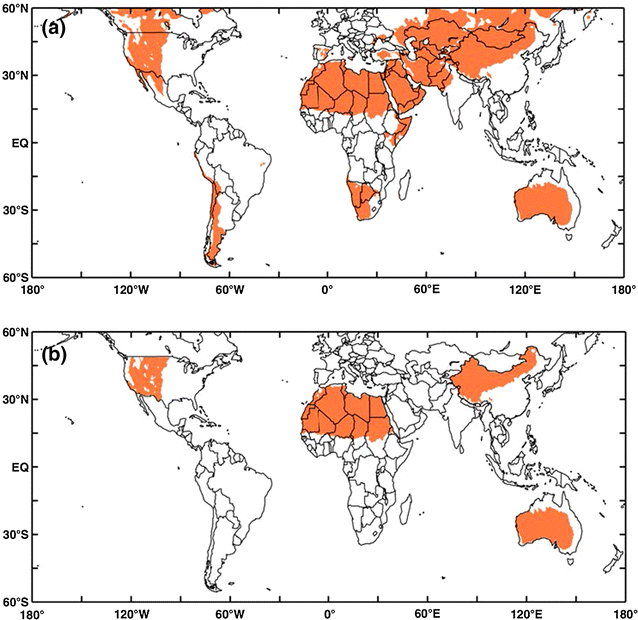
Hot semi-arid climates are most commonly found around the fringes of subtropical deserts. Hot semi-arid climates are most commonly found in Africa, Australia and South Asia. In Australia, a large portion of the Outback surrounding the central desert regions lies within the hot semi-arid climate region.
What does a semiarid climate look like?
Semi-arid climate receives very minimal rainfall that can support large vegetations or forests. The regions experiencing semi-arid climate are characterized by small plants like shrubs and grasses. Some of these plants have thorny branches or waxy cuticles which help them reduce water loss. Click to see full answer.
What is the difference between arid and semiarid climate zones?
Hyper-arid zones have an index of less than 0.03 and cover 4.2% of land on the planet, arid zones have an index range of 0.03 -0.20 and cover 14.6% while semi-arid zones have an index range of 0.20-0.50 and cover 12.2%. An arid climate is known for being hot and dry.
How does an arid or semiarid climate occur?
Precipitation (or the lack of) is the main factor that defines Arid climate. To have an Arid climate, an area must receive less than 10 inches of rain per year. Cold currents carry dry air, so these lands are blasted with dry air most of the year, which causes the low precipitation.
Which animals live in an arid climate?
Top 15 Animals Found in Arid Zone. Article Shared by. ADVERTISEMENTS: The animals are: 1. Gazelle 2. Blackbuck 3. Neelgai or Blue Bull 4. Indian Wild Ass 5. Wolf 6. Desert Fox 7. Desert Cat 8. Hare 9. Jackal 10. Great Indian Bustrad 11. Houbara Bustard 12. Common Indian Sandgrouse 13.

What states have a semi-arid climate?
Northern Arizona and New Mexico, central and northern Nevada and most of Utah (outside higher mountain areas) have a temperate semi-desert to desert climate, but with colder and snowier winters than in Phoenix and similar areas, and less-hot summers (as at Salt Lake City, Utah).
What is an example of semi-arid?
The definition of semiarid is a climate or place that is partially arid, or semi-dry and has less than 20 inches of rain each year. An example of semiarid climates is the hot, semiarid climate of the Outback in Australia.
What is the climate like in the semi-arid?
The climate of semi-arid areas are highly variable with droughts, as well as irregular episodes of above-average rainfall making water scarcity and salinity particularly insidious issues in these climates. They tend to occur near arid deserts or inland at higher elevations.
What are semi desert areas?
Semiarid regions are a subtype of dry land with an aridity index (i.e., ratio of total annual precipitation to potential evapotranspiration) between 0.20 and 0.50 (Lal, 2004).
What countries are in arid?
Countries with an arid climateSaudi Arabia.South Africa.Peru.Kazakhstan.
Where are semi-arid deserts located?
Semi-arid deserts are found in North America, Greenland, Europe, and Asia. Coastal deserts are a bit more humid than other types of deserts. Although heavy fogs blow in from the coast, rainfall is still rare. The Atacama Desert of Chile in South America is an example of a coastal desert.
Is California semi-arid?
In general, Northern California is more moist with a Mediterranean climate according to the Koppen Climate Classification system. Southern California is drier with areas of semi-arid or desert climate.
What seasons are in semi-arid climate?
Semiarid deserts have two main seasons, summer and winter. The semiarid desert has an average temperature of 23° C during the summer, though it can reach 38° C during the day and 10° C at night. During the winter, temperatures can reach as low as -3° C. Average rainfall is very low, at 2-4 cm a year (The Desert Biome).
What does semi-arid mean?
Definition of semiarid : characterized by light rainfall especially : having from about 10 to 20 inches (25 to 51 centimeters) of annual precipitation.
Is South Africa a semi-arid country?
South Africa is famous for its sunshine – an average of 2,500 hours of sun every year. It's a dry country, classified as semi-arid. The average annual rainfall for the whole of South Africa is about 464 mm. The world average is about 860mm.
What is the difference between desert and semi desert?
The main difference between a true desert and a semi-desert is that a semi-desert receives at least twice as much rain per year as a true desert. The main exception to this is the Gobi desert, which is the largest desert region in Asia.
What is semi-arid region in India?
Two zones of semi-arid climate are recognized in India, one in the north contiguous with the desert of Thar, extending into Rajasthan, the Punjab and North Gujarat and the other in parts of the Deccan and Madras State in the south.
What causes semi-arid climate?
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate.
How much rain does a semi-arid climate get?
10 to 20 inchesSemi-arid regions receive 10 to 20 inches (25 to 50 centimeters) of rain per year.
What are the characteristics of an arid climate?
The defining characteristic of an arid climate is a lack of moisture. The soil is dry, the air is dry, and yearly precipitation is very low. A variety of factors combine to steer storms and moisture away from arid regions. In some arid climates, evaporation rates exceed precipitation, leading to a net moisture loss.
What is the difference between a desert and a semi-desert?
The main difference between a true desert and a semi-desert is that a semi-desert receives at least twice as much rain per year as a true desert. The main exception to this is the Gobi desert, which is the largest desert region in Asia.
What is semi-arid climate?
Definition of semiarid : characterized by light rainfall especially: having from about 10 to 20 inches (25 to 51 centimeters) of annual precipitation.
What is an example of a semi-arid climate?
The definition of semiarid is a climate or place that is partially arid, or semi-dry and has less than 20 inches of rain each year. An example of s...
What are the characteristics of a semi-arid climate?
Semi-arid climate receives very minimal rainfall that can support large vegetations or forests. The regions experiencing semi-arid climate are char...
Where are semi-arid climates?
Semi-arid areas associated with the arid deserts generally occur north and/or south of the deserts (in Africa, Asia and Australia) or inland and at...
What is an example of a semi-arid desert?
Semi-arid deserts are found in North America, Greenland, Europe, and Asia. Coastal deserts are a bit more humid than other types of deserts. Althou...
What is the climate of Gran Chaco?
The Gran Chaco region in South America experiences a hot semi-arid climate. The semi-arid climate, also known as steppe, is the next driest climate after the desert climate. It receives slightly more rainfall than the desert climate. Steppe climate receives precipitation of between 10 and 20 inches annually, and is often considered ...
What are the two types of semi-arid climates?
The semi-arid climate is further divided into two categories: hot and cold semi-arid climate. The two types of semi-arid climates can be delineated from each other by use of isotherms. An isotherm is a line connecting two places with the same temperature. Hot semi-arid climates characterize the tropics and sub-tropics located in ...
How to determine if a steppe is semi-arid?
To determine whether a region is characterized by a semi-arid climate, the threshold should be first determined by multiplying average temperature throughout the year by 20 then adding 140 ...
What are the characteristics of a semi-arid climate?
The regions experiencing semi-arid climate are characterized by small plants like shrubs and grasses.
What are the animals that live in semi-arid areas?
Usually, only animals that are adapted to grassland ecosystem are found in the semi-arid areas, meaning only animals such as bison, antelopes, and zebras among other ungulates can be found in the region. Large predators such as lion, jackals, and wolves may also be found in the semi-arid areas depending on the continent in question and also whether the region is temperate or subtropical.
Where are hot semi-desert areas located?
Hot semi-desert climate is known for hot summer and cool winter, with relatively low precipitation. Hot semi-arid areas are mainly in Africa, South Asia, and Australia. They also characterize some parts of Europe, particularly Spain, portions of North America (Mexico and Southwestern US), and parts of South America.
Where is semi-arid climate common?
This type of semi-arid climate is common is some areas in Asia and parts of North America but can also characterize some parts of Africa (north and South Africa) as well as Europe and parts of South America.
What are the characteristics of semiarid regions?
In such regions, regolith thickness, vegetation cover, slope degree, slope length and crack pattern may considerably vary in space and time as a consequence of variable badland material behaviour . Such variable behaviour influences the development of different processes, such as coupling and decoupling of rills ( Faulkner et al., 2008 ), pipes, gullies, slopes and mass movements. Desir and Marín (2013) in the semiarid badland landscape of Bardenas Reales in the Navarra Province (Northern Spain) observed a strict relation between climatic factors and erodibility of the materials, as well as the presence of a biocrust, typical of such semiarid regions. They also observed the important role of annual rainfall distribution on materials behaviour: rainfall maxima inhibits infiltration and favours soil loss, whereas during periods of cyclonic rains infiltration through cracks is favoured so that in presence of high slope gradient shear strength is overcome giving rise to flows and slides.
Why are semiarid soils considered hot spots?
Despite these sensitivities, semiarid soils are considered “hot spots” due to their importance for crop production and human food security. Highlighting their potential as C sinks as well as their importance to the global C cycle and role as climate regulators, semiarid ecosystems have been shown to contribute most to interannual variability of the land CO 2 sink with 57% (0.04 Pg C year − 1 ), while the global is 0.07 Pg C year − 1 ( Ahlstrom et al., 2015 ). Unfortunately, due to poor management, semiarid soils are currently a source of GHGs. Increased drought risk and interannual variation in rainfall associated with climate change pose particular risks to water and temperature sensitive semiarid ecosystems ( Kottek et al., 2006; Sommer et al., 2011 ).
What are the threats to semiarid soils?
Major threats to soils in semiarid regions include erosion, salinity, and degradation due to human activities (FAO, 2016).
What is the mean annual precipitation in semiarid regions?
Semiarid regions are characterized by a mean annual precipitation between 200 and 700mm (Gallart et al., 2002), often with stormy character, and clustered in alternating seasons.
How does drought affect the ecosystem?
And it is during a drought that ecosystem degradation in the form of denudation and soil erosion occur at an accelerated pace, as people try to survive in a parched habitat by cutting the trees for fuel and browse, and by animals overgrazing the wilted grass. The topsoil, laid bare and pulverized by tillage or the trampling of livestock, is then exposed to a greatly increased risk of wind erosion. When the coveted rains recur, they tend to scour the erodible soil. Whenever human pressure on the land ceases or is diminished, even a severely eroded soil may recover gradually. However, on the time-scale of years to a few decades, especially if overgrazing and overcultivation continue, soil erosion may become, in effect, irreversible.
What are the effects of glacial periods on the atmosphere?
During glacial periods, these sparsely vegetated regions were a source of mineral aerosols for the atmosphere. Higher eolian dust transport during glacial periods is supported by sediment data (Kohfeld et al., 2005 ). Mineral aerosols diffuse light and reduce the amount of solar radiation that reaches the surface. Radiative transfer models estimate that increased atmospheric dust concentrations during the LGM led to about 2–3 W m −2 reduction in radiative forcing in the tropics, which roughly corresponds to the radiative effect of lower glacial CO 2 levels in the region ( Claquin et al., 2003 ). As a result, sparser vegetation cover amplified LGM cooling through the dust feedback.
Why is groundwater depleting in India?
Semiarid and arid regions of India, which are agriculturally prosperous, are experiencing groundwater depletion due to its intensive use. Eastern India on the contrary shows poor agricultural growth in spite of having abundant groundwater. In spite of shallow water table, there is economic scarcity of groundwater as poor small and marginal farmers are not able to afford irrigation wells. Many researchers have argued for groundwater intensive to trigger agricultural growth in the region through subsidizing power connections, flat-rate mode of pricing electricity, and energized solar pumps offered at highly subsidized rates.
What are alluvial fans made of?
Alluvial fans are fan-shaped piles of sediment that form where a rapidly flowing mountain stream enters a relatively flat valley. As water slows down, it deposits sediment (alluvium). As the stream migrates back and forth in the open valley, the sediment gradually builds a fan.#N#Bajadas are are aprons of rocky debris that form when alluvial fans coalesce to form a ramp that spreads out toward the valley floor. A bajada or piedmont slope partially buryies the range front in its own sediment.#N#Stream terraces are long bench-like surface bordering a stream or wash. A terrace is a level or near-level area of land above a water course and separated from it by a steeper slope. A stream terrace is made by the stream at some time in the past when the river flowed at a higher level. A terrace may be made of stream deposits such as gravel or sand, or it could be an erosional cut by the stream on bedrock.#N#Playas are shallow, short-lived lakes that form where water drains into basins with no outlet to the sea and quickly evaporates. Playas are common features in arid (desert) regions and are among the flattest landforms in the world.#N#Basins are depression in the Earth’s surface that collect sediment. Rock particles that wash down from mountain sides collect in adjacent basins, in some places burying the bedrock under thousands of feet of rock debris.
What are the shallow lakes that drain into the sea?
Playas are shallow, short-lived lakes that form where water drains into basins with no outlet to the sea and quickly evaporates. Playas are common features in arid (desert) regions and are among the flattest landforms in the world. Basins are depression in the Earth’s surface that collect sediment.
What are the erosional processes in arid and semi-arid regions?
Erosional processes in arid and semi-arid regions include: mass wasting (surface creep, landslides, mud and debris flows, and rock topples and falls), water-driven or fluvial processes, and. wind-driven or aeolian processes (dust, loess, sand dunes). Surprisingly, water is an important agent of erosion in arid lands.
What are the two types of mountains with steep slopes?
Mesas and Buttes. Mesas are broad flat topped mountains with at least one steep side. Buttes are smaller flat topped mountains or hills with steep slopes on all sides. Spires (also towers, needles, and balanced rock) are slender isolated columns of rock, that form as the erosional remnant of a butte.
How much rain does an arid region get?
Arid regions by definition receive little precipitation—less than 10 inches (25 centimeters) of rain per year. Semi-arid regions receive 10 to 20 inches (25 to 50 centimeters) of rain per year. Although the rocks and tectonic features underlying arid regions may not differ from other areas, the landscape is distinctive.
What is a bajada?
Bajadas are are aprons of rocky debris that form when alluvial fans coalesce to form a ramp that spreads out toward the valley floor. A bajada or piedmont slope partially buryies the range front in its own sediment. Stream terraces are long bench-like surface bordering a stream or wash.
What is a stream terrace?
Stream terraces are long bench-like surface bordering a stream or wash. A terrace is a level or near-level area of land above a water course and separated from it by a steeper slope. A stream terrace is made by the stream at some time in the past when the river flowed at a higher level.
How much of Los Angeles' rain fell to the sea?
In the 1920s, approximately 5% of precipitation in the Los Angeles region lowed to the sea. Today, extensive impervious cover and massive stormwater conveyance systems deliver 50% of the rain falling in the region to the sea, even as more than 80% of the city’s water demand is met by costly imports from distant locations.
Where is the green roof?
The green roof installed atop the EPA Region 8 Oice in Denver, Colorado, for instance, retains more than 80% of the rainfall it receives. When designed appropriately, green roofs may ofer a water-eicient approach to urban stormwater management in arid and semi arid regions.
How does rain affect landscapes?
When rain falls on natural landscapes, much of it either soaks into the ground or is returned to the atmosphere by plants or evaporation. Rain that is not absorbed into the soil lows into nearby washes, arroyos, creeks, or streams. By armoring landscapes with parking lots, roads, and rooftops, we dramatically change this water balance. Much less precipitation is absorbed into the soil, and much more lows across the land, gathering oils, pesticides, animal waste, and trash along the way. Gray stormwater infrastructure relies on storm sewers to drain this water and its pollutants to the nearest body of water— increasing looding, pollutant loads, and erosion, and degrading water quality and habitat.
What is green infrastructure?
Green infrastructure refers to a set of practices that mimic natural processes to retain and use stormwater. By promoting iniltration, evapotranspiration, and harvesting throughout the landscape, green infrastructure preserves and restores the natural water balance. Though many green infrastructure practices were irst developed and applied in temperate regions, green infrastructure is perhaps
Why do we need to excavate soil?
Excavation may be required to increase soil storage and accommodate plant roots, and soil amendments may be required to increase soil water retention and maintain healthy plants . In arid and semi-arid regions, rain garden design must be conscious of the limited water supply.
What is a riparian bufer?
Riparian bufers are one example of a watershed-scale approach to green infrastructure. Riparian bufers restrict development in the land adjacent to washes, arroyos, creeks, or streams to reduce erosion and preserve channel form and function. When applied throughout a watershed, riparian bufers can provide multiple environmental and social beneits. By preserving an interconnected network of habit, riparian bufers can increase wildlife diversity in urban areas. Many communities designate recreational trails within riparian bufers. These trails can provide access to nature as well as opportunities for physical activity.
How does porous pavement work?
Porous pavement reduces runof volumes and contaminant loads by allowing more precipitation to iniltrate into the soil. Porous pavement systems generally consist of a permeable surface (often porous asphalt, porous concrete, or interlocking concrete pavers) and several layers of bedding.
What is the weather like in the summer?
In the Atlantic Ocean, the Bermuda High creates a south-southwest flow of tropical air masses over the southeastern, south-central and central United States – resulting in warm to hot temperatures, high humidity and frequent intense (but usually brief) showers and/or thunderstorms as the heat builds in the afternoon. In the Northern Hemisphere summer, high pressure in the Pacific Ocean builds toward the California coast, resulting in a northwesterly airflow, creating the cool, dry, and stable weather conditions prevalent along the West Coast in summer.
How many people die from lightening?
Approximately 43 people die by lightening strike each year in the United States, and 90 percent of those struck will survive. Americans have a one in 15,300 chance of being struck by lightening in their lifetime.
What are the main drivers of weather?
The primary drivers of weather in the contiguous United States are the seasonal change in the solar angle, the migration north–south of the subtropical highs, and the seasonal change in the position of the polar jet stream.
How many climate zones are there in Hawaii?
Hawaii has 11 different climate zones, influenced by altitude and topographical effect on wind and rainfall. These include tropical at sea level, arid, semi-arid, temperate, and alpine at the highest elevations. Snow sometimes occurs in high mountain areas.
What is the climate of Alaska?
The state of Alaska, on the northwestern corner of the North American continent, is largely dominated by a subarctic climate, but with a subpolar oceanic climate in the southeast (Alaska Panhandle), southwestern peninsula and Aleutian Islands, and a polar climate in the north.
Why is the climate of the United States different?
The climate of the United States varies due to changes in latitude, and a range of geographic features, including mountains and deserts. Generally, on the mainland, the climate of the U.S. becomes warmer the further south one travels, and drier the further west, until one reaches the West Coast.
Where does the clipper storm come from?
Across the northern states in winter usually from Montana eastward, "Alberta clipper" storms track east and bring light to moderate snowfalls from Montana and the Dakotas across the upper Midwest and Great Lakes states to New England, and often, windy and severe Arctic outbreaks behind them.
How far can tule fog be seen?
Accidents caused by the tule fog are the leading cause of weather-related deaths in California; visibility is usually less than an eighth of a mile (about 600 feet or 183–200 m), but can be less than 10 feet (3 m).
What is the climate of the Sierra Nevada?
The high mountains, including the Sierra Nevada, the Cascade Range, and the Klamath Mountains, have a mountain climate with snow in winter and mild to moderate heat in summer.
What is the weather pattern of May and June?
May Gray / June Gloom: A characteristic weather pattern of late spring (May and June) in which a combination of inland heat, off-shore cool water, and prevailing wind patterns bring foggy and overcast weather to coastal regions. From Point Conception northwards the gloom continues until early autumn.
What is the name of the storm that brings torrential rain to California?
As the Santa Ana winds are channeled through the mountain passes they can approach hurricane force. The combination of speed, heat, and dryness turns the chaparral into explosive fuel for wildfires. Pineapple Express: A complex combination of events, bringing high levels of torrential precipitation to California.
What are the winds in Santa Ana?
Santa Ana winds: Santa Anas are hot, high winds that blow from the eastern mountains and deserts towards coastal southern California, usually in the spring and fall. They are the result of air pressure buildup between the Sierra Nevada and the Rocky Mountains. This air mass spills out, is pulled by gravity, and circulates clockwise around the high pressure area, bringing winds from the east and northeast; as the air descends in elevation, it heats up and the humidity plummets to less than 15 percent. It is often said that the air is heated and dried as it passes through the nearby deserts, but according to meteorologists this is a popular misconception (it is actually due to adiabatic compression as the air flows from the higher elevations down to sea level); during Santa Ana conditions, it is typically hotter along the coast than in the deserts. As the Santa Ana winds are channeled through the mountain passes they can approach hurricane force. The combination of speed, heat, and dryness turns the chaparral into explosive fuel for wildfires.
What was the highest temperature in California?
The highest temperature ever recorded in California was 134 °F ( 57 °C) in Death Valley on July 10, 1913. This is also the highest temperature ever recorded on Earth. The lowest was −45 °F (−43 °C) in Boca on January 20, 1937.
What is the climate in the Southwest?
The extreme southwest, around San Diego, has a subtropical semi-arid or steppe climate (Koppen BSh) as winters are drier there.
