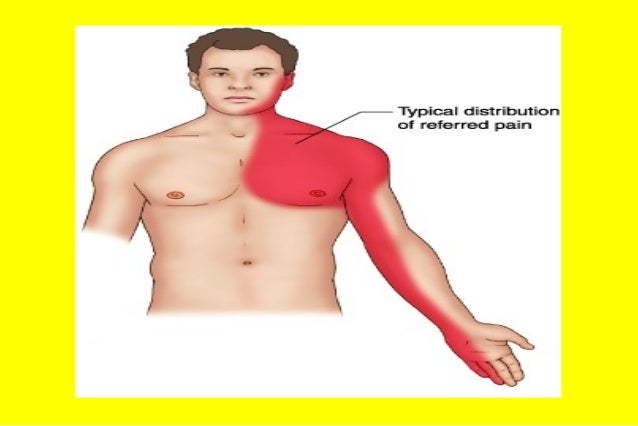
Where is Precordial chest pain located?
The precordial chest pain. A precordial chest pain is a pain that is felt around the left side of the chest especially near the area of the nipple. The first occurrence of precordial chest pain was recorded in 1955. Although it may appear similar to the pain caused by a heart attack, this condition is harmless and non-threatening.
What causes substernal pain?
There are also some medical conditions which can cause Substernal Chest Pain like:
- Pneumonia.
- Pneumothorax.
- Hemothorax.
- Anemia.
- Pericarditis.
- Pulmonary hypertension.
- Mitral Valve Prolapse.
- Uncontrolled High Blood Pressure.
- Hereditary hypercholesterolemia.
Can I treat chest pain at home?
Using a humidifier at home can also help in coping up with chest pain. Keeping a humidifier at home is healthy for breathing and well as throat issues. This can mainly help the chest pain caused by pneumonia. It is easily available in the market and online as well. 2. Steam inhalation Basically, bouts of dry cough can provoke muscular pain.
What can cause pain in center of chest?
- Hyperventilation, often from a panic attack
- Indigestion and peptic ulcers
- Muscle strain or tightness
- Inflammation of the soft tissue between the ribs (costochondritis)
- Injury to the chest or upper abdomen
- Arthritis of the spine
- Drug use, including amphetamines and cocaine

What does substernal pain feel like?
Classic angina presents with substernal chest pain that's described as “squeezing” or “pressure-like.” It often radiates to the arms or jaw and is made worse by exertion or emotion and made better by rest or nitroglycerin. It may be associated with diaphoresis, nausea, weakness or shortness of breath.
What does chest pain Substernal mean?
Substernal pain is discomfort occurring behind or below the sternum. It often results from gastrointestinal conditions. Some of the most common causes of sternum and substernal pain are: costochondritis. sternum fracture.
Where is gastric chest pain located?
You may feel it on the right side or the left side or in the middle. Sometimes the pain radiates to your neck, left arm or back. You may notice that it occurs after eating, or that it is accompanied by heartburn, a burning sensation in the chest. It can last for a few minutes or a few hours.
How do you know if chest pain is from esophagus?
Signs and symptoms of esophageal spasms include: Squeezing pain in your chest. The pain is often intense, and you might mistake it for heart pain (angina). Difficulty swallowing solids and liquids, sometimes related to swallowing specific substances, such as red wine or extremely hot or cold liquids.
Where is Substernal area?
It is a type of pain felt behind the sternum bone; a flat bone located in the middle of the chest. This bone may also be referred to as the breastbone. Due to the relative location of substernal pain, it is often confused with a variety of different medical conditions, which can induce unnecessary anxiety in sufferers.
How do you treat substernal chest pain?
Typical treatment includes nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). If necessary, your doctor might suggest steroids. Antibiotics could be prescribed if the pericarditis is caused by infection. If the pericarditis is chronic, colchicine (Colcrys) could be prescribed.
How can you tell the difference between gastric pain and heart pain?
“If you belch or pass gas and the pain goes away, you could just be experiencing stomach pain or heartburn,” said Joseph Lash, M.D., cardiologist with Norton Heart and Vascular Institute. “If the pain persists and you have shortness of breath or nausea, it could be a heart-related issue.”
How can you tell the difference between cardiac and non cardiac chest pain?
Classically, cardiac chest pain is in the left chest. However, it may occur in the center or right chest. Non-cardiac chest pain may have many of the above symptoms. However, non-cardiac chest pain may change with respiration, cough, or position.
How do you know if chest pain is muscular?
Symptoms of muscle strain in chestpain, which may be sharp and intense pull or chronic pain.swelling.muscle contractions.trouble moving the injured area.pain while breathing.bruising.
What does GERD chest pain feel like?
It's a painful burning sensation in the middle of your chest caused by irritation to the lining of the esophagus caused by stomach acid. This burning can come on anytime but is often worse after eating. For many people heartburn worsens when they recline or lie in bed, which makes it hard to get a good night's sleep.
What does an inflamed esophagus feel like?
Symptoms of esophagitis include: Difficult and/or painful swallowing. Heartburn. Acid regurgitation (bringing food back up to the mouth from the stomach)
What is the most common symptom of esophageal disease?
The most common symptom of esophageal disease is heartburn, which is defined as a sensation of substernal burning. Chest pain without typical heartburn may occur in a variety of esophageal disorders, including gastroesophageal reflux and motor disorders such as in achalasia.
Is substernal chest pain serious?
Brief substernal pain resulting from myocardial ischemia, commonly provoked by physical activity or emotional stress, is a common and significant symptom of coronary heart disease. Patients with angina, especially unstable or severe angina, are at increased risk for arrhythmias, MI, and sudden death.
What is the meaning of Substernal?
Medical Definition of substernal : situated or perceived behind or below the sternum substernal pain.
What is the difference between Substernal and Retrosternal?
Background. A substernal goiter, also known as a retrosternal goiter, is an enlarged thyroid gland that grows inferiorly and passes through the thoracic inlet into the thoracic cavity. A substernal goiter is generally defined as a thyroid mass that has 50% or more of its volume located below the thoracic inlet.
What causes pain in sternum?
You can have pain in this area because of infection, inflammation, injury, or the breakdown of cartilage affecting the sternum itself. Problems with nearby organs like the heart, lungs, and esophagus can also cause pain in this area. This includes a heart attack, pleurisy (a lung inflammation), and acid reflux.
What does substernal chest pain feel like?
Substernal chest pain can be symptomized by:#N#• Presence of a sour taste in the mouth or a sensation of regurgitation where that the swallowed food reenters the mouth#N#• Individual having problems with swallowing#N#• Presence of chest tenderness with deep palpation#N#• Individual having symptoms of heartburn with a burning sensation behind the breastbone.#N#• Pressure, fullness or tightness in your chest#N#• Crushing or searing pain that radiates to your back, neck, jaw, shoulders and arms particularly your left arm#N#• Pain that lasts more than a few minutes, gets worse with activity, goes away and comes back or varies in intensity#N#• Cold sweats#N#• Dizziness or weakness#N#• Nausea or vomiting#N#• Pain that gets better or worse when you change your body position#N#• Pain that intensifies when you breathe deeply or cough
What causes substernal chest pain?
There are various factors which lead to Substernal Chest Pain, some of which can be extremely serious to include Pulmonary Embolism, Aortic Stenosis, Stable Angina Pectoris, Acute Coronary Syndrome, Myocardial Infarction, Atrial Fibrillation and the like.
How many people have substernal chest pain?
It is estimated that about 25% of people in the United States experience Substernal chest pain for one reason or another. Substernal chest pain usually can be diagnosed by history and physical examination if other etiologies have been excluded.
Why does my chest hurt?
Some chest pain is described as crushing or burning. Chest pain can be caused by acute pericarditis, perhaps following a viral illness. In this condition, chest pain radiates to the back, neck, or shoulders and often worsens when the patient inhales.
Is substernal pain a heart condition?
Substernal Chest Pain can be quite painful. If an individual experiences pain just below the sternal bone, then it is termed as Substernal Chest Pain. Typical chest pains are related to heart complications, and substernal pain falls under this category.
What is chest cavity deformity?
Chest cavity deformities or compensatory breathing patterns (eg, a barrel chest deformity and use of accessory muscle of respiration are indicative of emphysema)
Where is the stress image of the left ventricular myocardium?
The stress images (top row) show perfusion defect located at the distal inferior wall and apex that normalizes at rest . This reversible perfusion defect is consistent with stress-induced ischemia in this region.
What does short axis MR cine in systole show?
Short-axis MR cine in systole shows area of hypokinesis in the anterior and anteroseptal walls associated with increased myocardial signal (edema) indicat ing AMI. Note the pericardial effusion .
Why does my gastric mucosa hurt?
An inflammation of the superficial gastric mucosa may be the result of the intake of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, alcohol or excessive meals. There is usually epigastric pain of short duration.
Is pulmonary embolism pain pleuritic?
Although precordial pain related to the sudden onset of pulmonary hypertension can develop in cases of acute pulmonary embolism, embolism-associated pain is much more likely to be pleuritic in character, whether or not there is pulmonary infarction. 38
Does pulmonary hypertension cause neck pain?
Persons with pulmonary hypertension may experience crushing or constricting substernal pain that at times radiates to the neck or arms, thus resembling the pain of myocardial ischemia.34 Pain from pulmonary hypertension has been reported in patients with conditions that are acute (e.g., multiple or massive pulmonary emboli) and chronic (e.g., Eisenmenger syndrome, pulmonary vasculitis, or mitral stenosis). In addition, approximately half of the patients with primary pulmonary hypertension may have precordial chest pain. 35
Why does my sternum hurt?
Sternum pain is usually caused by problems with the muscles and bones near the sternum and not the sternum itself. Pain felt just behind or below the sternum is called substernal pain and is sometimes caused by gastrointestinal problems. Some of the most common causes of sternum and substernal pain are: costochondritis. collarbone injuries.
What causes pain in the upper chest and shoulder?
Collarbone injuries. Collarbone injuries may lead to long-lasting pain or limited movement in the shoulder and upper chest. While the collarbone itself is not part of the sternum, it is connected to the sternum by cartilage. Injuries to the collarbone may cause pain in the sternum area.
What is the sternum?
The sternum is sometimes known as the breastbone. This flat bone sits at the front of the chest and connects to the ribs with cartilage.
What is the cause of burning in the chest?
Acid reflux or GERD. Acid reflux happens when stomach acid wears away the lining of the windpipe (esophagus). This happens primarily in people with gastroesophageal reflux disease ( GERD ). Acid reflux may cause substernal pain and discomfort in the chest and is generally accompanied by a burning feeling.
Why does my collarbone hurt?
Injuries to the collarbone may cause pain in the sternum area. Collarbone injuries are often the result of trauma, such as a car accident or sports injury, although infections or arthritis can also cause them. Symptoms of a collarbone injury include: severe pain when raising the arm.
What joint connects the top of the sternum to the collarbone?
The sternoclavicular joint connects the top of the sternum to the collarbone. Injuries to this joint generally cause pain and discomfort at the top of the sternum in the upper chest area.
What causes sternum fractures?
Sternum fractures usually occur as a direct result of trauma, such as a car accident or sports injury. People who believe they may have a sternum fracture should seek immediate medical attention, as the heart and lungs may also be injured. Symptoms of a sternum fracture include: pain during inhaling or coughing.
Why does my chest hurt?
Chest pain can stem from dozens of conditions besides heart attack, from pancreatitis to pneumonia or panic attack. Millions of Americans with chest pain are seen in hospital emergency departments every year. Only 20% of them are diagnosed with a heart attack or an episode of unstable angina, a warning sign that a heart attack may happen soon.
Is a stabbing pain a heart attack?
A few seconds of recurrent stabbing pain is less likely to be a heart attack ( see box), while pain centered in the chest that spreads out to the left arm or jaw is more likely to be one.
Where are substernal goiters located?
Symptoms of substernal/retrosternal goiters. The thyroid sits on top of the trachea (windpipe) and esophagus (swallowing tube). Due to the size and location of substernal goiters, they likely will produce some compressive symptoms. However, approximately 15-50% of patients have no symptoms whatsoever.
What is a substernal thyroid goiter?
Thyroid goiters are usually composed of multiple thyroid nodules. They can be cystic or sold or a mixture of both. A thyroid goiter is a thyroid that has grown to a large size. Substernal means “below the sternum” and therefore into the chest. Substernal and retosternal “behind the sternum” are often used without differences really considered between either. A substernal/retrosternal goiter is therefore a large thyroid that has grown so big that it has grown out of the neck and into the area of the chest. Substernal goiters can cause compressive symptoms and can harbor a thyroid cancer. These goiters can push and displace the breathing tube, swallowing tube and important blood vessels in the neck and chest. They also have the potential of hiding thyroid cancers as well. This page discusses symptoms, diagnosis, and surgery for substernal thyroid goiters.Written by Rashmi Roy, MD, FACS Find out more about our surgeons here. Link What patients say about their surgeons is also important. See our patient reviews and 5 star ratings on Healthgrades as well as our many reviews on Google as well. Our patients are our focus. Last updated September 1, 2020.
What causes substernal goiters?
The most common cause of substernal goiters are long standing multinodular goiters that have grown over many, many years into the chest cavity. The incidence of substernal goiters among patients with thyroid goiters is reported to range from approximately 5-15%. (Y.
What is the name of the thyroid gland that has grown out of the neck and into the area of the chest?
Substernal and retosternal “behind the sternum” are often used without differences really considered between either. A substernal/retrosternal goiter is therefore a large thyroid that has grown so big that it has grown out of the neck and into the area of the chest.
How to diagnose substernal goiter?
The diagnosis of a substernal goiter is made with a comprehensive ultrasound examination of the entire thyroid gland and neck lymph nodes. Ultrasound exposes you to no radiation whatsoever. It uses sound waves to look beneath the skin at the important structures of your neck. Needle biopsy is only indicated if there is a mass within the thyroid goiter which is suspicious for malignancy or abnormal lymph nodes in your neck are identified.
Can substernal goiters cause thyroid cancer?
Substernal goiters can cause compressive symptoms and can harbor a thyroid cancer. These goiters can push and displace the breathing tube, swallowing tube and important blood vessels in the neck and chest. They also have the potential of hiding thyroid cancers as well.
