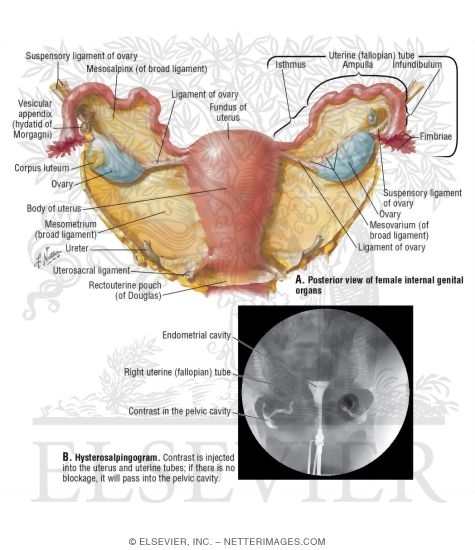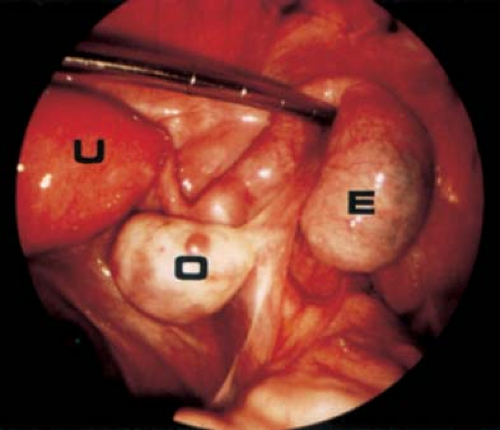
What structures are considered the uterine adnexa?
The most common causes include:
- Ovarian cysts. These fluid-filled cysts form on your ovaries. ...
- Noncancerous ovarian tumors. When abnormal cells grow and multiply in the ovaries, they become solid masses, with occasional cystic components. ...
- Ovarian cancer. ...
- Ectopic pregnancy. ...
- Broad ligament leiomyoma. ...
- Hydrosalpinx. ...
- Tubo ovarian abscess. ...
Where is the right adnexal region located?
Where is the right adnexal region located? Adnexa: Region adjacent to the uterus that includes the ovary, fallopian tube, and associated structures. Where is Adnexa located? The adnexa of the uterus is the space in your body occupied by the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes. An adnexal mass is defined as a lump in the tissue located near the ...
Where is the endocervical gland located?
Treatment of endocervical cysts
- Radiosurgical method. ...
- The radio wave method. ...
- Laser removal. ...
- Cryotherapy. ...
- If the endocervix cyst is diagnosed with a chronic complication in the form of adnexitis (inflammation of the uterine appendages: the fallopian tubes, ovaries, ligaments) or an inflammatory tumor neoplasm, ...
Where would an adnexal mass be located?
Types of Adnexal Tumors
- Benign ovarian. These masses are not cancerous and usually don't cause symptoms. ...
- Malignant ovarian. These tumors are cancerous. ...
- Benign nonovarian. Ectopic pregnancy. ...
- Malignant nonovarian. These are cancerous masses that form outside of the ovaries. ...
- Nongynecologic. ...
What part of the body is the adnexa?
The term “adnexa” refers to the ovaries, fallopian tubes and ligaments that secure the female reproductive organs.
Where is adnexa in uterus?
The adnexa is the region adjoining the uterus that contains the ovary and fallopian tube, as well as associated vessels, ligaments, and connective tissue. Pathology in this area may also be related to the uterus, bowel, or retroperitoneum, or metastatic disease from another site.
Where is the adnexal mass located?
Adnexal tumors are growths near the uterus. They're also known as adnexal masses. They usually form in the ovaries, which make eggs and hormones, or the fallopian tubes, which connect your uterus and ovaries. The tumors can form in the connective tissue around this part of your body.
What causes an adnexal cyst?
What Causes Adnexal Cysts? Fluid-filled cysts on the ovaries are usually caused by hormonal stimulation or bleeding at the time of ovulation (hemorrhagic ovarian cysts).
Is the cervix part of the adnexa?
The ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix and vagina (vaginal canal) make up the female reproductive system. Adnexal tumors are growths of cells that form on the organs and connective tissues around the uterus. Adnexal tumors most often aren't cancerous, but they can be cancerous.
What is another name for adnexa?
uterine appendagesThe adnexa, or more formally the adnexa uteri, and also known as the uterine appendages, is a collective term for the: ovaries. fallopian tubes. broad ligaments.
Is adnexal cyst the same as ovarian cyst?
Ovarian cysts, also known as ovarian masses or adnexal masses, are frequently found incidentally in asymptomatic women. Ovarian cysts can be physiologic (having to do with ovulation) or neoplastic and can be benign, borderline (low malignant potential), or malignant.
How do you examine the adnexa?
Adnexal masses are usually diagnosed by a pelvic exam, ultrasound, or both. Often, in cases when the woman isn't showing any symptoms, the growth is detected during routine exams. Once diagnosed, your doctor will decide if your case is an emergency.
What are the symptoms of adnexal mass?
Common symptoms associated with adnexal masses include irregular vaginal bleeding, bloating, increased abdominal girth, dyspareunia, urinary symptoms, pelvic pain, and abdominal pain.
When should an adnexal cyst be removed?
Large or persistent ovarian cysts, or cysts that are causing symptoms, usually need to be surgically removed. Surgery is also normally recommended if there are concerns that the cyst could be cancerous or could become cancerous. There are 2 types of surgery used to remove ovarian cysts: a laparoscopy.
Is Adnexa and ovary the same?
Adnexa is a Latin word meaning attachment or appendages. It refers to the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and ligaments that hold the reproductive organs in place. These are all located in your lower abdomen near your pelvic bone.
Do adnexal cysts cause pain?
Symptoms of an ovarian cyst An ovarian cyst usually only causes symptoms if it splits (ruptures), is very large or blocks the blood supply to the ovaries. In these cases, you may have: pelvic pain – this can range from a dull, heavy sensation to a sudden, severe and sharp pain. pain during sex.
What's the meaning of adnexa?
Medical Definition of adnexa : conjoined, subordinate, or associated anatomic parts the uterine adnexa include the ovaries and fallopian tubes.
What does adnexa mean on ultrasound?
INTRODUCTION. Adnexa refer to the anatomical area adjacent to the uterus, and contains the fallopian tube, ovary, and associated vessels, ligaments, and connective tissue.
What is an adnexal?
Listen to pronunciation. (ad-NEK-sul…) A lump in tissue near the uterus, usually in the ovary or fallopian tube. Adnexal masses include ovarian cysts, ectopic (tubal) pregnancies, and benign (not cancer) or malignant (cancer) tumors.
What is the meaning of left adnexa?
Adnexa: In gynecology, the appendages of the uterus, namely the ovaries, the Fallopian tubes, and the ligaments that hold the uterus in place.
What is the adnexa?
The adnexa is the region adjoining the uterus that contains the ovary and fallopian tube, as well as associated vessels, ligaments, and connective tissue. Pathology in this area may also be related to the uterus, bowel, or retroperitoneum, or metastatic disease from another site.
What is the term for benign growths arising from the uterine smooth muscle that are most likely to cause symptoms
Leiomyoma (fibroid): Benign growths arising from the uterine smooth muscle that are most likely to cause symptoms among women in their late 30s and 40s. Müllerian ducts: Normally regress in the male fetus and form the fallopian tubes, uterus, and upper vagina in the female fetus.
Can a cystectomy be done on a black ischemic adnexa?
Ovarian cystectomy during detorsion of the black-bluish ischemic adnexa should also be avoided because handling of the edematous, friable, and ischemic adnexa may cause additional damage to the ovary, and a high proportion of the ovarian masses are functional cysts, which should not be removed.
Is ocular adnexal lymphoma a lymphoma?
The ocular adnexa may be secondarily involved by lymphomas that arise in other sites. An estimated 5% of patients with non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma develop ocular adnexal involvement during the course of the disease. Patients with secondary ocular adnexal lymphoma usually are adults and, on average, are slightly younger or about the same age as patients with primary ocular adnexal lymphoma.1,3,6 A variety of types of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma can be found in this setting. The most common is follicular lymphoma, followed by marginal zone lymphoma. 3,4 Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, mantle cell lymphoma and, rarely, splenic marginal zone lymphoma, 3 hairy cell leukemia, 7 and T-cell or extranodal NK/T-cell lymphomas also may secondarily involve the ocular adnexa. 3,7,24 In the rare cases in which NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type, affects the ocular adnexa, the primary site may be sinonasal. 26 In rare cases, Hodgkin’s lymphoma can relapse in the ocular adnexa. 3
Is adnexal disease common in adolescents?
Surgical disorders of the adnexa are common, particularly in the adolescent period. Ultrasonography has increased the level of understanding regarding the development and natural history of ovarian cysts. New less-invasive surgical techniques allow more conservative management of adnexal disease in children.
What is the adnexa?
The adnexa, or more formally the adnexa uteri, and also known as the uterine appendages, is a collective term for the: ovaries. fallopian tubes. broad ligaments. Some texts also include the associated blood vessels, nerves and other supporting tissues in the definition.
What is the adjectival form of adnexa?
The adjectival form for adnexa is adnexal. The term adnexitis is sometimes used for an inflammation of the adnexa uteri and the term adnexectomy as a synonym for a bisalpingo-oophorectomy.
Is "adnexus" a plural word?
It is an unusual word (for English-speakers) as it has an identical spelling and pronunciation whether used in a singular or plural sense. Therefore the terms 'adnexus/adnexum' for a single adnexa or 'adnexae' for more than one adnexa are erroneous, and should not be used.
What are adnexal tumors?
Adnexal tumors occur in the: 1 Ovaries 2 Fallopian tubes 3 Connective tissue around the ovaries or fallopian tubes
What is the term for connective tissue around the ovaries?
Fallopian tubes. Connective tissue around the ovaries or fallopian tubes. Diagnosis of adnexal tumors involves a careful physical exam, imaging tests and, sometimes, surgery. Treatment for adnexal tumors depends on the specific location and types of cells involved.
adnexa
appendages; accessory organs, as of the eye ( adnex´a oc´uli) or uterus ( adnex´a u´teri ). adj., adj adnex´al.
adnexa
Accessory or adjoining anatomical parts, as ovaries and fallopian tubes in relation to the uterus.
adnexa
Ancillary structures to main structure. Among health professionals, adnexa usually refers to the fallopian tubes, broad and round uterine ligaments and the ovaries, considered together.
adnexa
Adjoining parts of the body. The adnexa of the eyes are the lacrimal glands, the eyelids, and the lacrimal drainage system. The uterine adnexa are the FALLOPIAN TUBES and the OVARIES. The term is derived from the Latin annexere , to tie on.
What is the ocular adnexa?
In this lesson, we'll go over the definition of ocular adnexa, some of examples, as well as their functions. This will include the orbit, extraocular muscles, lacrimal system, and optic nerves.
What is the bone that holds the eye called?
The Orbit, Extraocular Muscles, & Eyelids. The bony cavity that contains your eyeball is called the orbit. Basically, it's the socket that holds the eye. When you see a human skull at a museum or in a Halloween decoration, it's the hole where the eye would have gone.
Overview
An adnexal (ad-nek-suhl) mass is a growth that develops around the uterus, usually in your ovaries, fallopian tubes and neighboring connective tissues. Some adnexal tumors are fluid-filled, while others are solid. They can appear at any age, and most of them go away on their own within a few months.
Diagnosis and Tests
Adnexal tumors are most often detected during routine examinations. They may also be discovered during pelvic examinations or ultrasounds. Once you receive a diagnosis, your healthcare provider can run additional lab and imaging tests to determine what caused the adnexal mass.
Management and Treatment
Not always. In many cases, adnexal masses aren’t harmful and will eventually resolve on their own. However, if they cause uncomfortable symptoms, then surgical removal may be recommended. If intense pain or fevers are experienced, you should contact your health care provider immediately to assess for ovarian torsion, which is a surgical emergency.
Prevention
There is currently no way to prevent adnexal tumors. However, with early detection, you can reduce your risk for associated complications. If you’re diagnosed with an adnexal tumor, it’s important to see your healthcare provider for frequent follow-ups. Medications can sometimes be offered to decrease the risk of recurrent ovarian cysts.
Living With
If you’ve been diagnosed with an adnexal tumor, you should see your healthcare provider for frequent follow-ups. During these visits, they will check to see if the tumor has grown. Additionally, you should call your provider any time you develop painful or uncomfortable symptoms.
Where is the adnexal mass located?
An adnexal mass is defined as a lump in the tissue located near the uterus or pelvic area (called the adnexa of uterus). Adnexal tenderness occurs when there is pain or general tenderness around the area where an adnexal mass is located. Adnexal tenderness usually occurs in the ovary or fallopian tubes. Examples of adnexal masses include:
Why does my adnexal area hurt?
Adnexal tenderness that persists over a long period of time could be due to a cyst or other condition within your adnexal region.
What are some examples of adnexal masses?
Examples of adnexal masses include: ovarian cysts. ectopic pregnancies. benign tumors. malignant or cancerous tumors. Symptoms of adnexal tenderness are similar to those of uterine tenderness or cervical motion pain.
What to do if you have adnexal tenderness?
If you’ve been experiencing tenderness for a long period and don’t think it’s related to your menstrual cycle, you should bring the issue up to your doctor or gynecologist.
How often do you have adnexal mass?
How are adnexal masses diagnosed? You may have an adnexal mass if you experience any of the following symptoms that do not follow your normal menstrual symptoms or are present more than 12 times per month: abdominal pain. pelvic pain. bloating. lack of appetite.
Can you have a laparotomy for an adnexal torsion?
This is a rare occurrence, but it’s regarded as an emergency condition. Most often, you’ll need a laparoscopy or laparotomy to help address the adnexal torsion. During the surgery, or depending on the damage during torsion, you may lose viability in that ovary.
Types of Adnexal Tumors
Adnexal masses are classified based on where they're located and if they're cancerous or not. There are many types of adnexal masses, including:
How Are Adnexal Tumors Diagnosed?
Your doctor will listen to your symptoms and your medical history. They will perform a pelvic exam. Many adnexal masses aren't apparent with a pelvic exam, so you may need to have blood tests or an ultrasound. An ultrasound uses sound waves to create a picture of the inside of your body that displays on a monitor.
How Are Adnexal Tumors Treated?
The treatment for an adnexal tumor will depend on several factors, including what's causing it and where it's located. Generally, there are three options for treating adnexal masses: