Full Answer
What is the brain of a snake like?
The bone-encased snake brain and sensory organs are contained in the snake’s head. Snakes have almost all the senses we do, with several interesting modifications in the hearing, sight and smell organs. However, the really interesting question is what’s behind that brain, and how intelligent are they?
What are the sensory organs in a snake?
The bone-encased snake brain and sensory organs are contained in the snake’s head. Snakes have almost all the senses we do, with several interesting modifications in the hearing, sight and smell organs.
What do monkeys see when they see snakes?
When monkeys see photos of snakes, neurons in a specific part of the brain light up. The neurons respond to photos of the reptiles more than to monkey faces. Eeek, Snake! Your Brain Has A Special Corner Just For Them Eeek, Snake! Your Brain Has A Special Corner Just For Them
What is the function of the pit organ in a snake?
The neural pathways from the pit organs connect to the same brain structure as pathways from the snake’s eyes, the optic tectum. Behavioral studies by Bakken and Krochmal in 2007 indicate that the pit organ must be able to respond to temperature changes as minute as 0.001 degree C or less!
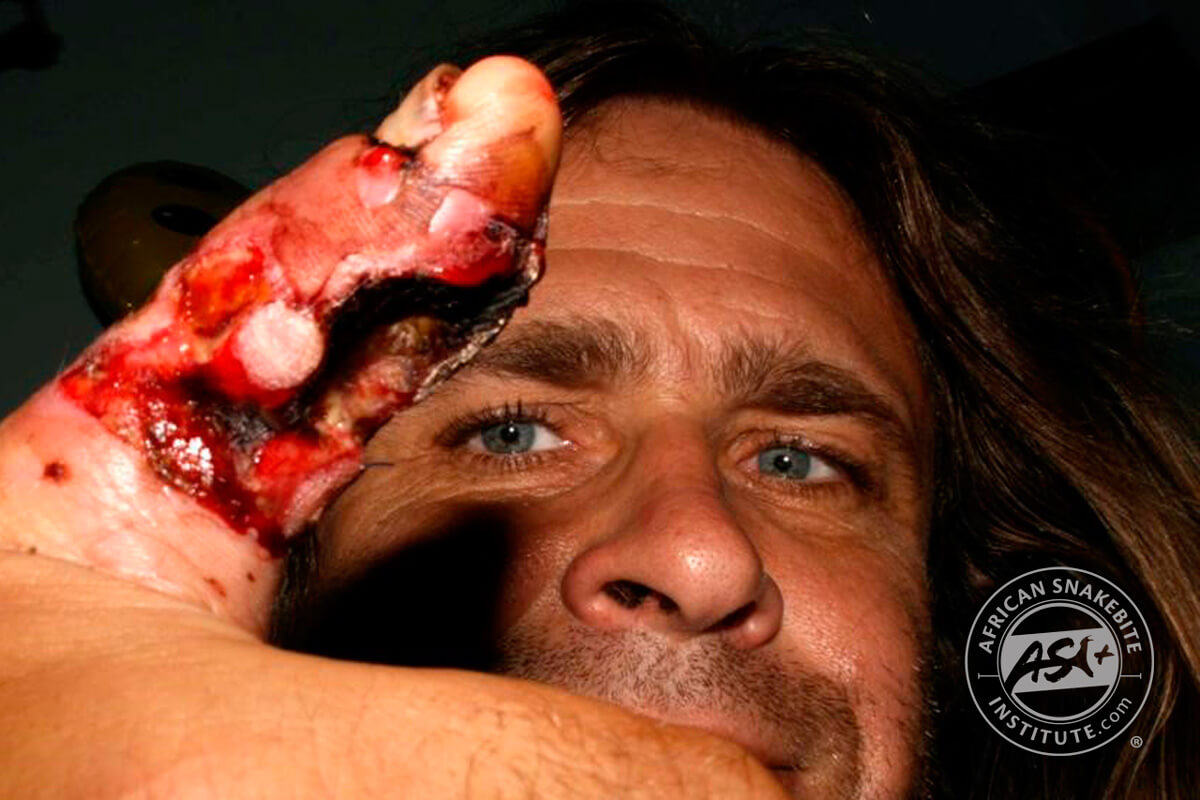
Where is a snakes brain located?
A snake's head contains the eyes, nostrils, mouth (and structures within), brain, and a special sensory structure called the vomeronasal or Jacobson's organ.
Is snake have a brain?
Snakes appear to be characterized by relatively small brains, and crocodilians appear to possess the largest brains among living reptiles, with the exception of birds.
Do snakes have 2 brains?
“Both heads tongue flick and react to movement, but not always in the same way. Two-headed snakes are unlikely to survive in the wild as the two brains make different decisions that inhibit the ability to feed or escape from predators. The snake is currently being cared for and monitored by FWC staff.”
How many brain cells do snakes have?
10,629,000Whole nervous systemNameNeurons in the brain & whole nervous systemCorn snake10,629,000Acanthosaura capra10,724,000Gallotia galloti10,903,000Eutropis multifasciata10,944,000216 more rows
Can snakes think?
Snakes have mental activity and mental events. They do not think abstractly. Their mental activity is based primarily on the immediate situation and feelings and instincts. You can tell what a snake is focused on.
Does a snake have a heart?
Like all other reptiles, snakes have hearts that makes their blood circulate. Blood circulation is vital to snakes because it brings around the nutrients and oxygen that the cells of the snake need to survive! A snake's heart is located about one fourth body length down from its head.
What animal does not have a brain?
Almost all animals have a brain, but there are a few exceptions. There is one organism that has no brain or nervous tissue of any kind: the sponge. Sponges are simple animals, surviving on the sea floor by taking nutrients into their porous bodies.
Do snakes have feelings?
Generally, reptiles do demonstrate basic emotions. According to Dr. Sharman Hoppes, clinical assistant professor at the Texas A&M College of Veterinary Medicine & Biomedical Sciences, the main two are fear and aggression, but they may also demonstrate pleasure when stroked or when offered food.
What is a 3 headed snake called?
The first appearance of a three-headed Cerberus occurs on a mid-sixth-century BC Laconian cup (see below). Horace's many snake-headed Cerberus followed a long tradition of Cerberus being part snake.
What animal has 32 brains?
LeechLeech has 32 brains. A leech's internal structure is segregated into 32 separate segments, and each of these segments has its own brain. Leech is an annelid.
Do snakes have memory?
Herpetologist David Holtzman, who has spent years studying spatial learning and memory in snakes, has found that the reptiles possess a remarkable aptitude for learning.
What animal has the closest brain to a human?
BIOLOGISTS have long thought that the chimpanzee was the animal closest in intelligence to the human, but recent work assigns that honour to the dolphin.
What animal does not have a brain?
Almost all animals have a brain, but there are a few exceptions. There is one organism that has no brain or nervous tissue of any kind: the sponge. Sponges are simple animals, surviving on the sea floor by taking nutrients into their porous bodies.
Are snakes intelligent?
Although humans are some of the most intelligent creatures, snakes are oddly intelligent too. They have highly impressive abilities to learn and apply what they have learned to their lives. Although the exact level of intelligence of snakes is hotly debated, no one denies the fact that they are capable creatures.
Do snakes have feelings?
Generally, reptiles do demonstrate basic emotions. According to Dr. Sharman Hoppes, clinical assistant professor at the Texas A&M College of Veterinary Medicine & Biomedical Sciences, the main two are fear and aggression, but they may also demonstrate pleasure when stroked or when offered food.
Do snakes feel pain?
Because of their slow metabolisms, snakes remain conscious and able to feel pain and fear long after they are decapitated.
How do snakes hear?
The sounds wave that travel through the air come into contact with the snake, this then transfers through the muscle until reaching the inner ear bone under the skull of the snake, this then is moved to the brain for processing what it is.
What organ does a snake use to understand smell?
Connected to the brain is the Jacobson’s organ, this organ is where a snake forked tongue will retract back into the mouth of the snake, then press into this organ. Now this is how a snake understands and recognises smells as the smell in the Jacobson organ goes straight to the brain to understand.
How does a snake process smell?
Second is how a snake will process smells, unlike most animals which use their nose which directs takes in air and is processed by the brain. A snake’s brain processes the smells slightly differently. There is just an added step which is the tongue of a snake will go out flicker up and down repeatedly gather air particles, it them retreats into the mouth and press into the slots at the top of the mouth known as the Jacobson’s organ.
Why can't snakes care less?
A snake’s brain will not show emotion or get attached to another snake or owner, even if they have been caring for the snake for 15 years, the snake couldn’t care less. This is not because snakes are not particularly nice animals, it is their brain does not have the ability to process emotion.
Can you teach a snake tricks?
You will not be able to teach a snake tricks like a dog is able to learn, their brain does not understand the communication, snakes are solitary reptiles, so there is no need for them to be social with any other creature.
Is a snake smarter than a dog?
We will use a dog as the comparison, a snake is nowhere near as smart as a dog. They are great hunting predators and their ability to have such a high population in the world without legs or arms showcases just how much of a hunter they are.
Do snakes remember the day they were fed?
They use their brains for tactical hunting and captive snakes will remember the day which they are fed if it is on a schedule.
What happens when a snake is held in front of a warm object?
The researchers found that when a warm or cold object was held in front of the snake’s face, the firing rate of nerve impulses either suddenly increased or decreased depending on whether the object was slightly warmer or colder than room temperature.
What branch of the trigeminal nerve connects the pit organs to the brain?
The scientists surgically exposed the superficial branch of the superior maxillary division of the trigeminal nerve that connects the pit organs to the brain.
What is the chemical that causes snakes to degenerate?
In 2002 Terashima and Ogawa reported that capsaicin, the fiery ingredient in hot peppers, caused the nerve terminals in the infrared receptors of snakes to degenerate. This is a clue that the molecular mechanism of detecting warmth somehow shares affinity with how we sense the burn of hot sauce.
What did Noble and Schmidt discover about blindfolded snakes?
In 1937 Noble and Schmidt put blindfolds on rattlesnakes and found that the blindfolded snakes could magically strike at moving objects very accurately, such as a dead rat or a cloth-wrapped light bulb. Moreover, the snakes had the ability to distinguish between identical warm and cold objects.
How many Hz does a rattlesnake rattle?
The western diamondback rattlesnake can rattle its tail at frequencies of 90 Hz and do this continuously for hours. This is about the frequency of sound handled by the subwoofer in your fancy home theater system.
Do vipers have visual senses?
It is difficult to imagine a sensory ability that we humans do not have, but these pit organs likely give the viper a visual sense. The neural pathways from the pit organs connect to the same brain structure as pathways from the snake’s eyes, the optic tectum.
Do snakes have nostrils?
Snakes do have nostrils, but snakes “smell” with their tongues (that’s another story). They flick their tongue in the direction of a warm blooded prey item just before striking--something I observed, but my trigger finger was too slow to catch it on camera.
Where did the term "reptilian brain" come from?
The term, 'reptilian brain' (or 'reptilian complex') is derived from a longstanding belief within the field of neuroanatomy that the forebrains of reptiles, and other small animals, were dominated by these structures. Paul MacLean suggested, within the Triune brain model, that the basal ganglia and a number ...
Which brain structure is responsible for aggression, dominance, territoriality, and ritual displays?
Paul MacLean suggested, within the Triune brain model, that the basal ganglia and a number of the surrounding structures within the base of the forebrain are responsible for 'species-typical' behaviors, which are present in aggression, dominance, territoriality, and ritual displays.
What is the role of the primal brain?
One of the major functions of the primal brain is to help us distinguish between threatening and non-threatening stimuli. At its most basic form, this function is represented in our ability to distinguish between familiar objects, things, people, scenarios, etc. and unfamiliar objects, etc. immediately. Designing according to the primal brain can encompass all of the basic drives we have, but one of the most effective ways of targeting the primal brain is to make new things seem familiar.
What are the three major brain structures?
First of all, the basal ganglia (found at the center of the human brain) was 'acquired', followed by the limbic system (which consists of various component brain structures, such as the amygdala and hippocampus), ...
Which brain structure is responsible for self-preserving behavior patterns?
The Reptilian or Primal Brain. In MacLean's triune brain model, the basal ganglia are referred to as the reptilian or primal brain, as this structure is in control of our innate and automatic self-preserving behavior patterns, which ensure our survival and that of our species.
Why are the three brains called separate brains?
These three structures are often referred to as separate 'brains', due to the, now redundant, belief that they operate independently (while in fact they are simultaneously active in all circumstances). Those who subscribed to the triune brain model believed that the three major brain structures developed sequentially.
How does the brainstem help us?
At the most basic level, the brainstem helps us identify familiar and unfamiliar things. Familiar things are usually seen as safe and preferable, while unfamiliar things are treated with suspicion until we have assessed them and the context in which they appear.
How many neurons are sensitive to snake pictures?
Forty percent of the 91 neurons were highly responsive to snake pictures, with face-sensitive neurons coming in second. Image Quan Van Le et al., via PNAS. 2
What is the monkey and the snake?
National Geographic: “ The Monkey and the Snake: How the Primate Brain Reacts to Serpents ” . The Snake Detection Theory has been one of more controversial ideas about how the brains of primates and eventually people evolved. The theory recently got a neurobiological boost from the discovery that macaque monkeys that have never even seen ...
What is the primary way primates evaluate their environments?
Vision is the primary way primates evaluate their environments, relying more heavily on sight than on any other sense. The position and structure of primate eyes as well as “complex and energetically costly neural components” 11 devoted to vision “demands an adaptive explanation,” 12 Isbell, Nishijo, and colleagues write. The team hypothesized that “primate-specific regions of the pulvinar evolved in part to assist primates in detecting and thus avoiding snakes.” 13 They declare the high proportion of snake-sensitive neurons in the pulvinar as “evidence in support of the snake detection theory.” 14
How many neurons are monitored in the pulvinar?
The monkeys were shown images of angry and calm monkey faces, monkey hands, simple geometric shapes, and snakes. The neurobiologists monitored 91 neurons in the pulvinar— a subcortical portion of primate brains thought ...
Why is it important to see snakes?
“It's important to be able to see them before they see us so we can stop in time to do that acrobatic jumping away.”.
How fast do snakes respond to stimuli?
Reaction time of the “snake-best” neurons also outstripped all others, firing 15 to 25 milliseconds faster than neurons responsive to other stimuli.
How long ago did the Macaques' brains flood?
Much of the fossil record, rather, is the record of the order in which organisms were catastrophically buried as the global Flood of Noah’s day, less than 4,500 years ago , overwhelmed various habitats. Thus the authors have learned something interesting about the brains of macaques.
What part of the brain does a monkey have?
The answer involves monkeys, the evolution of primate vision and a part of the brain called the pulvinar, which Isbell explains in Monday's Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Do monkeys fear snakes?
The new study appears to explain Mineka's own research showing that even monkeys raised in labs where there are no snakes can quickly learn to fear the repti les. But it's still unclear whether the brain response of the monkeys in this study showed they were truly afraid of snakes or just had an innate ability to recognize the potentially venomous reptiles.
Do lemurs have better vision than primates?
Primates in parts of the world with lots of poisonous snakes evolved better vision than primates elsewhere, Isbell found out. It's no accident that lemurs in Madagascar have the worst vision in the primate world, she says. There are no venomous snakes.
