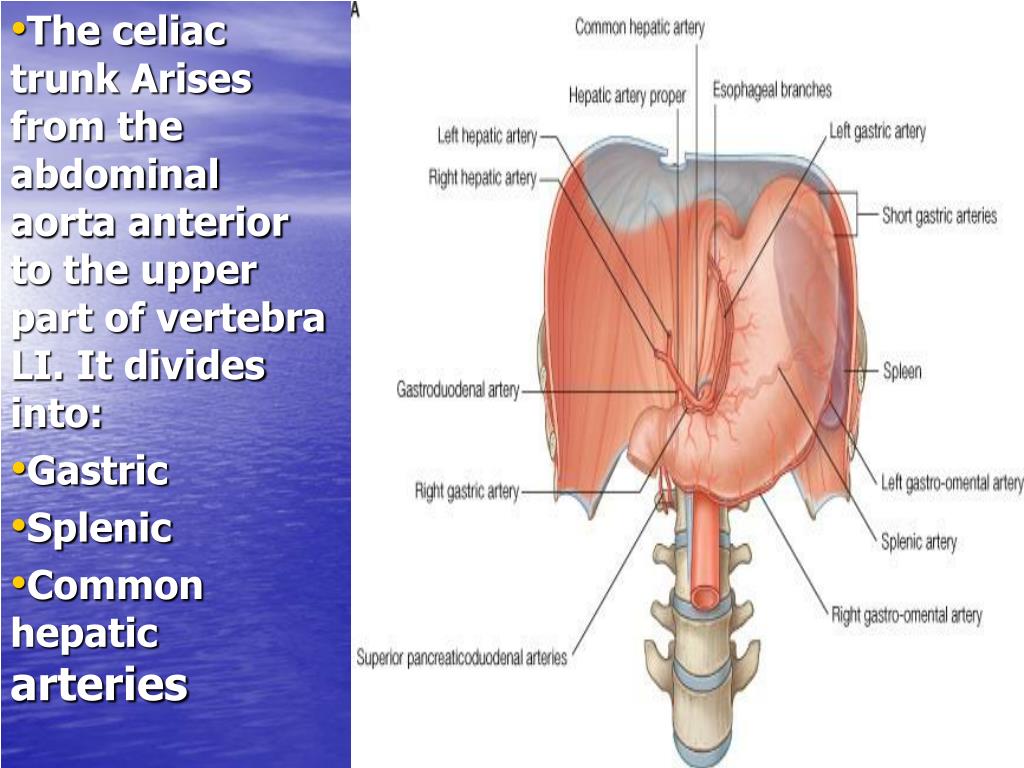
How many branches does the celiac artery have?
How to locate a celiac trunk?
What is the name of the artery that supplies the foregut of the gastrointestinal tract?
Which artery supplies the inferior part of the oesophagus?
Which artery connects the stomach to the liver?
Which artery supplies the midgut?
Where does the foregut go?
See 4 more
About this website

Is the celiac artery on the left or right?
The celiac artery arises anteriorly from the abdominal aorta just below the diaphragm at the T12 level, behind the median arcuate ligament, just as the aorta enters the abdomen in between the right and left crura.
What organs are affected by the celiac trunk?
The celiac trunk supplies blood to several major organs of the digestive system, including the lower part of the esophagus, liver, pancreas, gallbladder, and spleen through its three major branches.
What happens when the celiac artery is blocked?
Patients with celiac artery compression syndrome may complain of abdominal pain in the epigastric area, anorexia, and/or diarrhea. Typically, the onset of the pain is after food intake (post-prandial pain). The pain may be associated with nausea and emesis.
What are the symptoms of a celiac artery aneurysm?
The major presentation of celiac artery aneurysm is gastrointestinal symptoms, including abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, appetite loss, or symptoms of mesenteric ischemia. Rupture is a devastating presentation, with reported mortality rates ranging from 25 to 70%.
How serious is celiac artery stenosis?
A: It could be the cause of persistent abdominal pain that has not been treated successfully. This condition is generally not life threatening, but it is debilitating.
What is celiac artery compression syndrome?
Celiac artery compression syndrome is defined as chronic, recurrent abdominal pain related to compression of the celiac artery by the median arcuate ligament. It is also referred to as celiac axis syndrome, median arcuate ligament syndrome, and Dunbar syndrome.
Can the celiac artery be stented?
Celiac arterial stenting, as shown in our two patients, could be easily and safely employed in patients with PDA aneurysm associated with a stenotic celiac arterial root to release the stenosis of the celiac arterial root and to prevent further possible bleeding.
How is celiac artery blockage treated?
Patients with celiac artery stenosis/occlusion are treated by interventional radiology (IR) via dilation of the pancreaticoduodenal arcade. In patients with dilation of the pancreaticoduodenal arcade on SMA angiograms, IR through this artery may be successful.
What causes narrowing of the celiac artery?
Celiac trunk stenosis is a relatively common finding; the most common causes of this obstruction are median arcuate ligament syndrome, pancreatitis, local invasion of various malignancies originating from the pancreatic body, atherosclerosis or it can be idiopathic.
How serious is a celiac artery aneurysm?
CELIAC ARTERIAL aneurysms represent the fourth most common visceral arterial aneurysm. Although rare, they carry a definite risk for rupture and/or other complications. The reported risk for rupture varies in the literature, but appears to range from 10% to 20%.
How common is celiac artery aneurysm?
Aneurysms of the celiac artery are rare vascular lesions that represent only 3.6% to 4% of splanchnic artery aneurysms. The estimated incidence of celiac artery aneurysms ranges from 0.005% to 0.01%. Since the anomaly was first described in 1745,1 178 additional cases have been reported.
How important is the celiac artery?
The celiac artery supplies oxygenated blood to the liver, stomach, abdominal esophagus, spleen, and the superior half of both the duodenum and the pancreas. These structures correspond to the embryonic foregut.
What does the celiac trunk connect to?
The coeliac trunk (or celiac trunk) supplies the foregut, superior mesenteric artery supplies the midgut and the inferior mesenteric artery supplies the hindgut. The coeliac artery arises from the abdominal aorta as soon as it passes through the diaphragm at the level of the twelfth thoracic vertebrae.
What major organs does the superior mesenteric artery supply?
The superior mesenteric artery provides blood to the pancreas and parts of the small intestine and large intestine. As a peripheral artery in the body's circulatory system, it has several branches that send blood to various parts of the GI tract.
What are the 3 branches of the celiac trunk?
Classification of the celiac trunk becomes easy if one considers the trunk to be composed of three main stems: the splenic, the hepatic and the left gastric artery, other vessels being less important collaterals.
What organs does the SMA supply?
The superior mesenteric artery supplies the midgut from the ampullary region of the second part of the duodenum to the splenic flexure of the large intestine. The inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery arises from the SMA and, along with the superior pancreaticoduodenal artery, supplies the head of the pancreas.
Branches of the Celiac Trunk Flashcards | Quizlet
1. Left Gastric Artery 2. Splenic Artery 3. Common Hepatic Artery a. Proper Hepatic Branches into: R. Gastric, R. Heptaic, L. Hepatic, & Cystic Artery
Celiac Trunk Anatomy, Diagram & Function | Body Maps - Healthline
The first major branch of the abdominal aorta, the celiac trunk is responsible for supplying oxygen-rich blood to the stomach, spleen, liver, esophagus, and also parts of the pancreas and duodenum.
The branches of the celiac trunk - PubMed
156 abdominal preparations were explored by arteriography, corrosion and dissection. Classification of the celiac trunk becomes easy if one considers the trunk to be composed of three main stems: the splenic, the hepatic and the left gastric artery, other vessels being less important collaterals. Us …
What is the celiac trunk?
Medically reviewed by the Healthline Medical Network — Written by the Healthline Editorial Team on January 20, 2018. The first major branch of the abdominal aorta, the celiac trunk is responsible for supplying oxygen-rich blood to the stomach, spleen, liver, esophagus, and also parts of the pancreas and duodenum.
What are the three main divisions of the celiac trunk?
There are three main divisions of the celiac trunk: the left gastric artery, the common hepatic artery, and the splenic artery. The left gastric artery runs along the smaller curve of the stomach and connects to the lower esophagus, while the common hepatic artery supplies blood to the liver, duodenum, pancreas, and part of the stomach.
Which artery is the largest in the abdominal cavity?
Along with the superior and inferior mesenteric arteries, it is one of three frontal branches of the abdominal aorta, the largest artery in the abdominal cavity. Although the celiac trunk is only one of three arteries that branches off the abdominal aorta, it is essential to many major organs.
Where is the celiac trunk located?
The celiac trunk runs forward across the lower border of the caudate lobe of the liver and the upper border of the pancreas. It lies behind the lesser omentum, which is the double layer of peritoneum that runs from the liver to the lesser curvature of the stomach and the origin of the duodenum, and the ascending layer of the posterior parietal peritoneum (posterior section of the layer of the peritoneum that lines the internal surface of the abdominopelvic wall/wall of the abdominal and pelvic cavity). The right celiac ganglion (one of the two masses of nerve tissue that supply the stomach, liver, spleen, gallbladder, kidney, small intestine, and the ascending colon and transverse colon of the large intestine) and the caudate lobe of the liver are on its right side, and the left celiac ganglion lies on its left.
What is the celiac artery?
The celiac artery, which is also referred to as the celiac trunk, is a major branch of the abdominal aorta. At the top of the hip bones, the abdominal aorta branches into the common iliac arteries that supply oxygenated blood to the legs. The celiac trunk is one of the three main branches of the abdominal aorta.
What are the two branches of the abdominal aorta?
The other two branches of abdominal aorta include the superior mesenteric artery and the inferior mesenteric artery. The former arises at the first vertebra of the lumbar spine, whereas the latter arises at the third vertebra. The superior mesenteric artery supplies oxygenated blood to the lower section of the duodenum, ascending colon, and transverse colon, and its branches include inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery (supplies to the head of pancreas and some parts of duodenum), intestinal arteries that branch to ileum and jejunum, ileocolic artery (supplies blood to the terminal section of the ileum, cecum, and the appendix), right colic artery (supplies blood to the ascending colon), and middle colic artery (supplies blood to the transverse colon). The branches of inferior mesenteric artery include left colic artery (supplies blood to the descending colon), sigmoid branches, and superior rectal artery (supplies blood to the rectum). Around the jejunum and ileum, loops of arteries are present that provide oxygenated blood to the large intestine at regular intervals.
What is the largest artery in the human body?
Aorta, which comprises the ascending aorta, aortic arch (part of the aorta that bends and turns downward), and the descending aorta, is the largest artery of the human body. It originates from the left ventricle of the heart. It performs the vital function of carrying blood from the left ventricle of the heart to the coronary arteries.
Where is the dorsal pancreatic artery?
The dorsal pancreatic artery lies behind the junction of the splenic vein and superior mesenteric vein. It passes under the neck of pancreas and supplies blood to the head and body of pancreas. It has two branches to the right, which supply blood to the head of the pancreas.
Which artery is the narrowest?
Left Gastric Artery. While the left gastric artery, which is the narrowest branch of the celiac trunk branches upward, the common hepatic artery and the splenic arteries lie to the right and left. It must be noted that the branches of the celiac trunk are named after the region of distribution or supply.
Where does the celiac artery originate?
The celiac artery originates from the abdominal aorta located just below the diaphragm and branches into the left gastric artery, common hepatic artery, and the splenic artery. Bodytomy provides a labeled celiac artery diagram to help you understand the location, anatomy, and function of this artery. The celiac artery originates from the abdominal ...
What is the coeliac artery?
(Coeliac artery visible at center.) The coeliac ( / ˈsiːli.æk /) artery, also known as the coeliac trunk, or truncus coeliacus, is the first major branch of the abdominal aorta. It is about 1.25 cm in length.
How many divisions are there in the celiac artery?
There are three main divisions of the celiac artery, and each in turn has its own named branches:
What is the clinical significance of an aneurysm in the celiac artery?
Clinical significance. Aneurysms in the celiac artery account for around 4% of visceral artery aneurysms. This may cause abdominal pain. The celiac artery is vulnerable to compression from the crus of the diaphragm during ventilation where it originates from the abdominal aorta.
How long is the aorta branch?
It is about 1.25 cm in length. Branching from the aorta at thoracic vertebra 12 (T12) in humans, it is one of three anterior/ midline branches of the abdominal aorta (the others are the superior and inferior mesenteric arteries ).
Which veins drain the midgut?
In contrast to the drainage of midgut and hindgut structures by the superior mesenteric vein and inferior mesenteric vein respectively, venous return from the coeliac artery is through either the splenic vein emptying into the hepatic portal vein or via smaller tributaries of the portal venous system.
Which arteries give rise to inferior phrenic arteries?
The celiac artery may also give rise to the inferior phrenic arteries.
Where does blood go when it comes back from the digestive system?
Most blood returning from the digestive organs (including from the area of distribution of the celiac artery) is diverted to the liver via the portal venous system for further processing and detoxification in the liver before returning to the systemic circulation via the hepatic veins .
What is the branching of the celiac artery into the left gastric artery?
Classic branching of the celiac artery into the left gastric artery, splenic artery , and the common hepatic artery is seen in approximately 70%. Variations are present in approximately 30%. In general, any of the three celiac branches may arise independently from the aorta or SMA, or the celiac artery may give rise to other branches. A celiacomesenteric trunk occurs when both the SMA and the celiac trunk originate as a single trunk from the aorta.
What arteries are located in the quadrifurcating trunk?
quadrifurcating or pentafurcating trunk with the gastroduodenal artery, right and left hepatic arteries and dorsal pancreatic artery potentially originating from the trunk: 10% 4.
What is the name of the artery that supplies the foregut?
Celiac artery. The celiac artery, also known as the celiac axis or celiac trunk, is a major splanchnic artery in the abdominal cavity supplying the foregut. It arises from the abdominal aorta and commonly gives rise to three branches: left gastric artery, splenic artery, and common hepatic artery .
Which artery can give rise to other branches?
In general, any of the three celiac branches may arise independently from the aorta or SMA, or the celiac artery may give rise to other branches. A celiacomesenteric trunk occurs when both the SMA and the celiac trunk originate as a single trunk from the aorta.
Which artery is the first branch of the splenic artery?
The left gastric artery is usually the first branch, after which the celiac artery bifurcates into the splenic artery (coursing to the left) and the common hepatic artery (coursing to the right).
Which artery has the second and third order branches?
There is also a plethora of variations in the branching of the second and third-order branches of the celiac artery, particularly hepatic arterial anatomy which is discussed with the common hepatic artery.
Where does the aorta originate?
Arises anteriorly from abdominal aorta just below diaphragm at the T12 level, behind the median arcuate ligament, just as the aorta enters the abdomen in between right and left crura.
What is celiac artery compression syndrome?
Celiac artery stenosis--also known as celiac artery compression syndrome--is an unusual abnormality that results in a severe decrease in the amount of blood that reaches the stomach and abdominal region.
How to tell if celiac artery stenosis is a murmur?
An abdominal bruit is a murmur--an abnormal sound in the flow of blood--that can be detected by listening with a stethoscope over the part of the abdomen where the abdominal aorta lies.
What is the name of the artery that provides bloodflow to the stomach, liver, pancreas and small?
Definition. Celiac artery stenosis is a condition in which the celiac artery--a major artery in the abdomen that provides bloodflow to the stomach, liver, pancreas and small intestine--is compressed by the abnormal development of the median arcuate ligament.
Why do twins have celiac artery stenosis?
The exact cause of celiac artery stenosis remains unknown; however, medical researchers have determined that abnormal placement of the ligament that is responsible for the condition is present at birth. Other research that indicates twins have a higher incidence of having the defect than non-twins, suggests that the problem begins with abnormal development of the embryo or fetus in the uterus.
Can celiac artery stenosis be treated?
Seen most often in young, underweight women, celiac artery stenosis sufferers display a number of distinct symptoms. The condition is not completely understood and treatment options are controversial.
How many branches does the celiac artery have?
Althought the celiac artery only has 3 branches, your memory can still fail you sometimes. Thankfully kenhub is here to help! Just memorise the mnemonic ' L eft H and S ide' and it will help you remember the branches:
How to locate a celiac trunk?
Celiac trunk inside a cadaver: The easiest way to locate and isolate the celiac trunk (it is only 2 cm long) during a cadaveric dissection is to follow the common hepatic artery towards the left side of the abdomen. The celiac trunk arises from the anterior surface of the abdominal aorta at the level of the 12th thoracic vertebra.
What is the name of the artery that supplies the foregut of the gastrointestinal tract?
Celiac trunk. The coeliac trunk (or celiac trunk) is a major artery that supplies the foregut of the gastrointestinal tract. It arises from the abdominal aorta at the level of the twelfth thoracic vertebrae. It gives off three major branches called left gastric, common hepatic and splenic arteries. The gastrointestinal tract extends ...
Which artery supplies the inferior part of the oesophagus?
Here it anastomoses with right gastric artery. Some branches of the left gastric artery also supply the inferior part of the oesophagus.
Which artery connects the stomach to the liver?
Left gastric artery. This is the smallest and the first branch that arises from the coeliac trunk and passes into the lesser omentum (which connects the lesser curvature of the stomach to the liver) along the lesser curvature of the stomach to supply its superior portion. Here it anastomoses with right gastric artery.
Which artery supplies the midgut?
The coeliac trunk (or celiac trunk) supplies the foregut, superior mesenteric arter y supplies the midgut and the inferior mesenteric artery supplies the hindgut. The coeliac artery arises from the abdominal aorta as soon as it passes through the diaphragm at the level of the twelfth thoracic vertebrae.
Where does the foregut go?
The foregut extends from the mouth to the major duodenal papilla (where the ampulla of Vater empties into the duodenum ). The midgut extends from this point to two thirds of the way along the transverse colon. The hindgut runs from this point to the superior rectum.
