
What is the cochlear™ nucleus system?
Small and discrete solutions using our latest technology designed to help you to hear better. There are two main components of the Cochlear™ Nucleus® system: an internal implant and an external sound processor.
What is the cochlear complex in anatomy?
Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy. [edit on Wikidata] The cochlear nuclear (CN) complex comprises two cranial nerve nuclei in the human brainstem, the ventral cochlear nucleus (VCN) and the dorsal cochlear nucleus (DCN). The ventral cochlear nucleus is unlayered whereas the dorsal cochlear nucleus is layered.
Where is the ventral cochlear nucleus located?
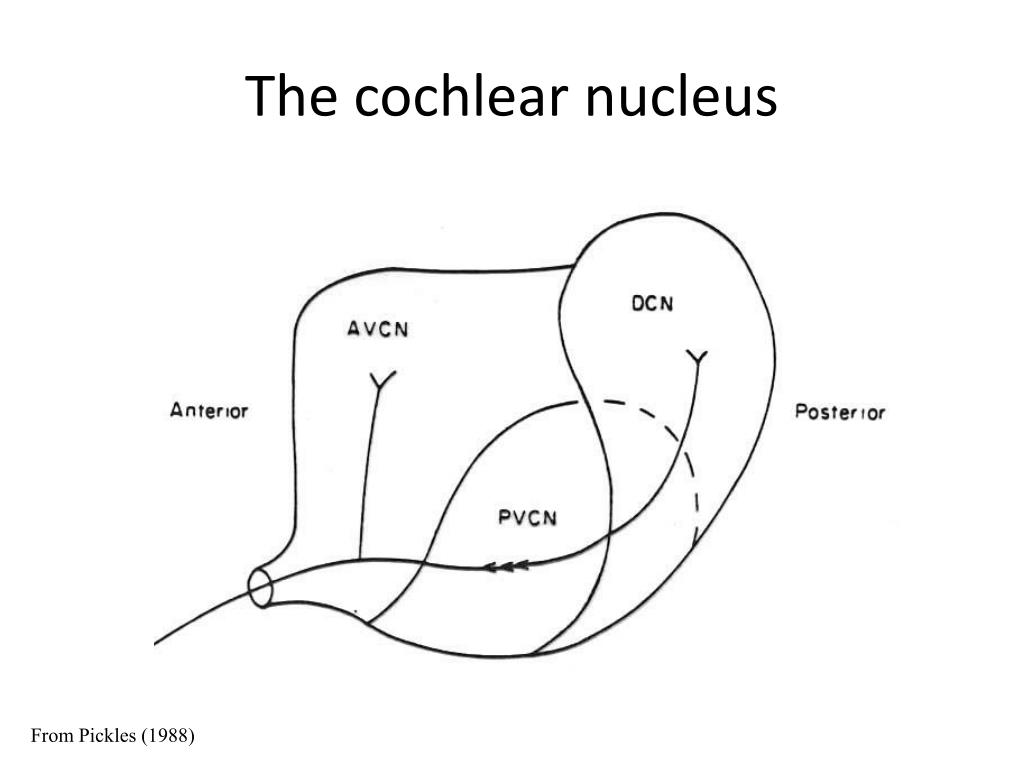
The ventral cochlear nucleus (VCN) on the ventral aspect of the brain stem, ventrolateral to the inferior peduncle. The dorsal cochlear nucleus (DCN), also known as the tuberculum acusticum or acoustic tubercle, curves over the VCN and wraps around the cerebellar peduncle.
How many cochlear nuclei are there in the human body?
In humans, as in all other mammals studied, two major cochlear nuclei are recognized: a dorsal cochlear nucleus (DCN) and a ventral cochlear nucleus (VCN). The latter is often subdivided into anterior and posterior divisions.

Where is the cochlear nucleus located in the ear?
Structure. The cochlear nuclei (CN) are located at the dorso-lateral side of the brainstem, spanning the junction of the pons and medulla.
What is the cochlear nucleus?
The cochlear nucleus (CN) is the first central auditory structure to receive input from the cochlea via the auditory nerve. The spiral ganglion cells leaving the cochlea bifurcate to form the dorsal (DCN) and ventral cochlear nucleus (VCN).
Is the cochlear nucleus in the cochlea?
The cochlear nucleus (CN) is the first central auditory structure to receive input from the cochlea via the auditory nerve. The spiral ganglion cells leaving the cochlea bifurcate to form the dorsal (DCN) and ventral cochlear nucleus (VCN).
Where are the dorsal and ventral cochlear nuclei?
rostral medullaThe dorsal and ventral cochlear nuclei themselves are located laterally in the rostral medulla at the pontine–medullary junction near the vestibulocochlear nerve.
How much does a cochlear nucleus 7 cost?
$1,800-$3,000Nucleus® 7 and Kanso® 2 Sound Processors The average cost of a cochlear implant sound processor upgrade is $1,800-$3,000, depending on your health plan.
What happens if the cochlea is damaged?
It is the main organ of hearing and is part of your inner ear. Cochlear Damage means that all or part of your inner ear has been hurt. Damage to the cochlea typically causes permanent hearing loss. This is called sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL).
What part of the brain is for hearing?
temporal lobeSignals from the right ear travel to the auditory cortex located in the temporal lobe on the left side of the brain. Signals from the left ear travel to the right auditory cortex. The auditory cortices sort, process, interpret and file information about the sound.
Is the cochlea part of the brain?
The cochlea is a portion of the inner ear that looks like a snail shell (cochlea is Greek for snail). The cochlea receives sound in the form of vibrations, which cause the stereocilia to move. The stereocilia then convert these vibrations into nerve impulses which are taken up to the brain to be interpreted.
What does the word cochlear mean?
(kŏk′lē-ə, kō′klē-ə) pl. coch·le·ae (-lē-ē′, -lē-ī′) also coch·le·as. A spiral-shaped cavity of the inner ear that resembles a snail shell and contains nerve endings essential for hearing.
What does the superior olivary nucleus do?
The superior olivary complex (SOC) is a group of auditory nuclei in the brainstem of amphibians, reptiles, and mammals. One major function of the SOC is to encode the cues that contribute to sound lateralization on the basis of convergent binaural ascending inputs arising from both ventral cochlear nuclei.
What do the hair cells in the cochlea do?
This action is passed onto the cochlea, a fluid-filled snail-like structure that contains the organ of Corti, the organ for hearing. It consists of tiny hair cells that line the cochlea. These cells translate vibrations into electrical impulses that are carried to the brain by sensory nerves.
What's the function of cochlea?
Excerpt. The cochlea is a hollow, spiral-shaped bone found in the inner ear that plays a key role in the sense of hearing and participates in the process of auditory transduction. Sound waves are transduced into electrical impulses that the brain can interpret as individual frequencies of sound.
What is the meaning of cochlear?
-ˌī, ˈkä-klē- : a hollow tube in the inner ear of higher vertebrates that is usually coiled like a snail shell and contains the sensory organ of hearing see ear illustration.
What does the dorsal cochlear nucleus do?
The dorsal cochlear nucleus (DCN) integrates auditory and multisensory signals at the earliest levels of auditory processing. Proposed roles for this region include sound localization in the vertical plane, head orientation to sounds of interest, and suppression of sensitivity to expected sounds.
What does the ventral cochlear nucleus do?
The ventral cochlear nucleus (VCN) has two main types of cell, which are specialized for encoding intensity (stellate cells) and timing (bushy cells), thus providing information about sound location, while the dorsal cochlear nucleus (DCN) encodes pitch information and analyses the quality of sound.
Where is the cochlear nucleus located?
The cochlear nuclei (CN) are located at the dorso-lateral side of the brainstem, spanning the junction of the pons and medulla . The ventral cochlear nucleus (VCN) on the ventral aspect of the brain stem, ventrolateral to the inferior peduncle.
What is the dorsal cochlear nucleus?
The dorsal cochlear nucleus (DCN), also known as the tuberculum acusticum or acoustic tubercle, curves over the VCN and wraps around the cerebellar peduncle. The VCN is further divided by the nerve root into the posteroventral cochlear nucleus (PVCN) and the anteroventral cochlear nucleus (AVCN).
What is the cochlear nuclear complex?
Function. The cochlear nuclear complex is the first integrative, or processing, stage in the auditory system. Information is brought to the nuclei from the ipsilateral cochlea via the cochlear nerve. Several tasks are performed in the cochlear nuclei.
What are the fiber bundles of the cochlear nucleus?
There are three major fiber bundles, axons of cochlear nuclear neurons, that carry information from the cochlear nuclei to targets that are mainly on the opposite side of the brain. Through the medulla, one projection goes to the contralateral superior olivary complex (SOC) via the trapezoid body, whilst the other half shoots to the ipsilateral SOC. This pathway is called the ventral acoustic stria (VAS or, more commonly, the trapezoid body). Another pathway, called the dorsal acoustic stria (DAS, also known as the stria of von Monakow), rises above the medulla into the pons where it hits the nuclei of the lateral lemniscus along with its kin, the intermediate acoustic stria (IAS, also known as the stria of Held). The IAS decussates across the medulla, before joining the ascending fibers in the contralateral lateral lemniscus. The lateral lemniscus contains cells of the nuclei of the lateral lemniscus, and in turn projects to the inferior colliculus. The inferior colliculus receives direct, monosynaptic projections from the superior olivary complex, the contralateral dorsal acoustic stria, some classes of stellate neurons of the VCN, as well as from the different nuclei of the lateral lemniscus.
What are the two types of principal cells?
Two types of principal cells convey information out of the dorsal cochlear nucleus (DCN) to the contralateral inferior colliculus. The principal cells receive two systems of inputs. Acoustic input comes to the deep layer through several paths.
What type of cells are found in the ventral nucleus?
Three types of principal cells convey information out of the ventral cochlear nucleus: Bushy cells, stellate cells, and octopus cells. Bushy cells are found mainly in the anterior ventral cochlear nucleus (AVCN).
Which cell is responsible for the timing of firing of the auditory nerve?
The cells of the ventral cochlear nucleus extract information that is carried by the auditory nerve in the timing of firing and in the pattern of activation of the population of auditory nerve fibers.
What is a cochlear implant?
A cochlear implant is an established, effective and long term solution for people with moderate to profound hearing loss. Back to Products and candidacy. Professionals. Products and candidacy.
Which sound processor sits behind the ear?
Whether a patient prefers a device that sits off-the-ear such as the Nucleus® Kanso® 2 Sound Processor, or one that sits behind-the-ear, like the Nucleus® 7 Sound Processor, they will find a Cochlear™ processor to suit them.
Can you stream audio directly to a Nucleus sound processor?
The Mini Microphone 2+ also has a line-in direct audio input that allows recipients to stream wirelessly from portable technology, such as a laptop, with a 3.5 mm audio port to a Nucleus Sound Processor.
Is the Nucleus Kanso 2 waterproof?
Built to withstand dust, dirt, sand and water, both the Nucleus Kanso 2 and Nucleus 7 sound processors are designed for adventures. With an Aqua+ accessory, the sound processors are waterproof. #
Where is the anterior cochlear nucleus located?
The posterior cochlear nucleus ( dorsal cochlear nucleus) and the anterior cochlear nucleus ( ventral cochlear nucleus) are located lateral and posterior to the restiform body and are partially on the surface of the brainstem at the pontomedullary junction ( Fig. 21.9A ). The posterior cochlear nucleus drapes over the restiform body just inferior to the pontomedullary junction. At this level, the posterior part of the anterior cochlear nucleus is small in proportion to the posterior cochlear nucleus ( Fig. 21.9A, B ). The anterior cochlear nucleus extends rostral to the posterior cochlear nucleus ( Fig. 21.9C ), where it may be covered by the flocculus and by caudal fascicles of the middle cerebellar peduncle.
What are the two distinct nuclei of the cochlear nucleus?
The cochlear nuclei in all mammals, including human ( Moore and Osen, 1979a ), comprises two distinct nuclei, the layered DCN and the unlayered VCN that is the focus of this chapter ( Fig. 1 ).
How many different types of cells are there in the cochlear nucleus?
Although the cochlear nucleus is made up of at least 14 different cell types based on Golgi material (e.g., Lorente De No, 1933; Brawer et al., 1974 ), the most useful cell classifications are those of Osen (1969a), Warr (1982), and Morest et al., (1990) which are based on Nissl preparations.
What is the CN in the auditory system?
The CN is the first central nervous system station in the auditory system that integrates multisensory information. Specific sensory projection neurons to the CN originate in the trigeminal ganglion and the spinal trigeminal nucleus (Sp5), dorsal root ganglion and dorsal column nuclei (DCoN), saccule, and vestibular nucleus ( Wu et al., 2015 ). Most of the projections from nonauditory sensory ganglia and brainstem nuclei terminate in the CN granular cell domain (GCD; Fig. 3.7 ). The trigeminal ganglia directly innervate neurons in the cochlea, middle ear, shell area of the VCN including the GCD and the fusiform cell layer of the DCN. Their synapses contain small, spherical vesicles, indicating excitatory transmission ( Shore, 2005 ). The interpolar and caudal Sp5 subnuclei project to many of the same CN regions as the trigeminal ganglion. These nuclei primarily relay pressure and proprioceptive information from the jaw, face, and scalp ( Wu et al., 2015 ). The DCN processes externally generate auditory stimuli partly by comparing them with the sounds produced by an animal’s own movements ( Roberts and Portfors, 2008 ). A cerebellar-like circuitry, consisting of a principal output cell, the fusiform cell, and several inhibitory interneurons, assist in the suppression of self-generated sounds.
What are the inhibitory cells in the cochlear nucleus?
Local inhibitory cells in the cochlear nucleus are either glycinergic (e.g., D-multipolar, vertical and cartwheel) or GABAergic (stellate and Golgi) ( Young and Oertel, 1998 ).
Why are cochlear nuclei similar in birds?
The principal reason for arguing that the similarities in the cochlear nuclei of birds and mammals may be due to similar selective pressures , and not homology, is that the ancestors of birds and mammals separately developed true tympanic ears ( Clack, 1997 ). A second reason is that close comparisons of bird and mammal cochlear nuclei reveal many differences. A third is that the observed similarity in the morphology and physiology of cochlear neurons is a plausible outcome of parallel evolution, because neurons in both birds and mammals experience similar constraints in detecting sound. Thus, although a common population of brainstem auditory neurons existed in the tetrapod ancestor, distinct evolutionary forces may have acted on these two groups allowing for the emergence of different ears and in turn, dissimilar organization in the brainstem.
Where do cochlear nerve fibers end?
All cochlear nerve fibers end in the cochlear nuclei on the ipsilateral side ( Fig. 21.10 ). As these fibers enter the brainstem at the cerebellopontine angle, they divide into ascending and descending bundles. Fibers in the ascending bundle synapse in the anterior part of the anterior cochlear nucleus, whereas fibers in the descending bundle synapse in the posterior part of the anterior cochlear nucleus and in the posterior cochlear nucleus.
Where is the Nucleus 7?
About the Nucleus 7. Cochlear Ltd. is a global company headquartered in Australia, and one of the pioneers in the field of cochlear implants. Cochlear was the first company to be approved in the United States for their multi-channel cochlear implant in 1984. Today they provide a range of implantable solutions including osseointegrated ...
How long do cochlear implants last?
The internal implant is rarely replaced and is expected to last for multiple decades —often for the life of the recipient.
How much does the Nucleus 6 processor increase battery life?
Improved battery life – Up to 50% increase compared to the Nucleus 6 processor. Direct streaming – Allows for direct streaming from compatible Apple and Android devices eliminating the need for a separate remote or other device to enable the connection.
What is the Nucleus app?
The Nucleus Smart App is a smartphone app available for compatible Apple and Android devices.
Is Kanso 2 compatible with Nucleus 22?
Implant compatibility – The Kanso 2 is not compatible with the older Nucleus 22 implant, however, it is compatible with all other Nucleus implants. Rechargeability – Kanso 2 is rechargeable but does not allow for standard batteries which may be an issue if the power in your home is interrupted.
Can you talk to someone who has a cochlear implant?
The companies can also likely refer you to a recipient in your area so that you can talk to someone who is wearing a cochlear implant. Also discuss with your audiologists and surgeons about their preferences asking for reasons behind those preferences. Regardless of your choice, the improvements that cochlear implants can provide for the appropriate candidate are worth pursuing.
Is the Nucleus 7 compatible with the Nucleus 22 implant?
Nucleus 7 (CP 1000) Key Features. Compatibility – The N7 is now compatible with all generations of implants including the Nucleus 22 implant. Smaller Size – 25% smaller and 24% lighter than the previous generation of BTE processor, the Nucleus 6 (CP 900 series). Rechargeable or standard batteries – Two sizes of rechargeable batteries ...
Where is Cochlear manufactured?
Cochlear manufactures principally in Sweden and Australia, including at a purpose-built facility at Macquarie University in Sydney. The company's products are supplied to over 100 countries internationally, with 43% sales revenue ($403 million) derived from the Americas, 40% ($377.6 million) from Europe, the Middle East and Africa and 17% ($161.3 million) from the Asia-Pacific region as of 2015. Cochlear spent $128 million on research and development in FY15.
What is a cochlear implant?
Cochlear ( ASX : COH) is a medical device company that designs, manufactures and supplies the Nucleus cochlear implant, the Hybrid electro-acoustic implant and the Baha bone conduction implant. Based in Sydney, Cochlear was formed in 1981 with finance from the Australian government to commercialise ...
What is the nucleus?
Nucleus is a system combining an electrical simulation device that is surgically implanted behind a patient's ear, a processor that captures sounds, and an electrode array that relays the sounds to the brain. It is a direct descendant of the original cochlear implants, also known as Nucleus, developed by Dr Graeme Clark in Melbourne during ...
Overview
The cochlear nuclear (CN) complex comprises two cranial nerve nuclei in the human brainstem, the ventral cochlear nucleus (VCN) and the dorsal cochlear nucleus (DCN). The ventral cochlear nucleus is unlayered whereas the dorsal cochlear nucleus is layered. Auditory nerve fibers, fibers that travel through the auditory nerve (also known as the cochlear nerve or eighth cranial nerve) carry …
Structure
The cochlear nuclei (CN) are located at the dorso-lateral side of the brainstem, spanning the junction of the pons and medulla.
• The ventral cochlear nucleus (VCN) on the ventral aspect of the brain stem, ventrolateral to the inferior peduncle.
• The dorsal cochlear nucleus (DCN), also known as the tuberculum acusticum or acoustic tubercle, curves over the VCN and wraps around the cerebellar peduncle.
Function
The cochlear nuclear complex is the first integrative, or processing, stage in the auditory system. Information is brought to the nuclei from the ipsilateral cochlea via the cochlear nerve. Several tasks are performed in the cochlear nuclei. By distributing acoustic input to multiple types of principal cells, the auditory pathway is subdivided into parallel ascending pathways, which can simultaneously extract different types of information. The cells of the ventral cochlear nucleus e…
See also
• Auditory system
• Cochlear nerve
• Unipolar brush cell
Additional images
• Dissection of brain-stem. Lateral view.
• The cranial nerve nuclei schematically represented; dorsal view. Motor nuclei in red; sensory in blue.
• Primary terminal nuclei of the afferent (sensory) cranial nerves schematically represented; lateral view.
External links
• University of Buffalo at the Library of Congress Web Archives (archived 2001-11-27)
• Illustration and text: Bs97/TEXT/P12/intro.htm at the University of Wisconsin-Madison Medical school
• Medical research council