
What is a cranial fossa?
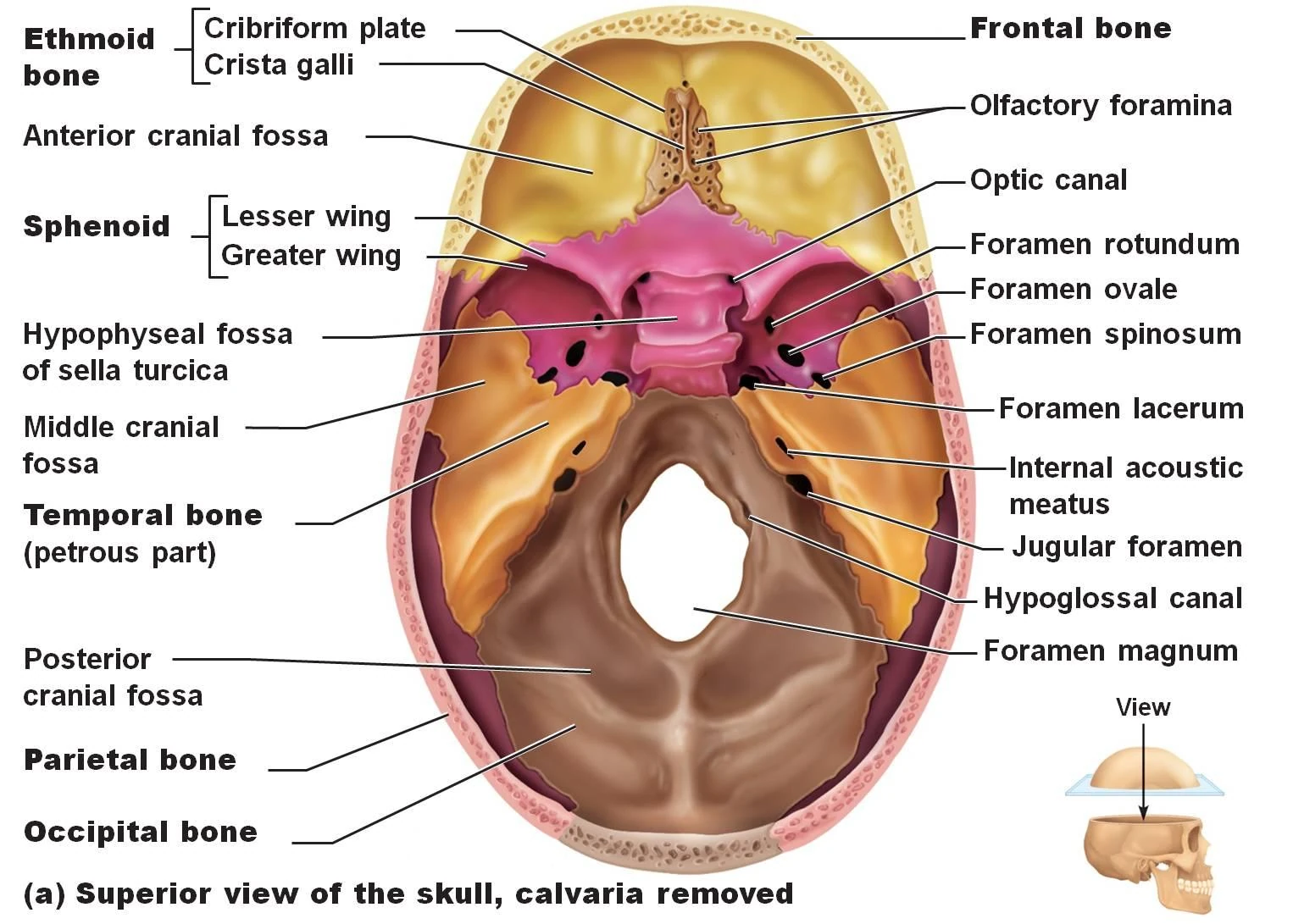
A cranial fossa is formed by the floor of the cranial cavity. There are three distinct cranial fossae: Anterior cranial fossa (fossa cranii anterior), housing the projecting frontal lobes of the brain. Middle cranial fossa (fossa cranii media), separated from the posterior fossa by the clivus and the petrous crest.
What is the floor of the cranial cavity?
The floor of the cranial cavity is divided into three distinct depressions. They are known as the anterior cranial fossa, middle cranial fossa and posterior cranial fossa. Each fossa accommodates a different part of the brain.
What is the difference between anterior and posterior cranial fossa?
Anterior cranial fossa ( fossa cranii anterior ), housing the projecting frontal lobes of the brain Posterior cranial fossa ( fossa cranii posterior ), between the foramen magnum and tentorium cerebelli, containing the brainstem and cerebellum
What bone forms the depressed lateral part of the middle cranial fossa?
The depressed lateral parts of the middle cranial fossa are formed by the greater wings of the sphenoid bone, and the squamous and petrous parts of the temporal bones. They support the temporal lobes of the brain.
Where is the cranial fossa found?
A cranial fossa is formed by the floor of the cranial cavity.
What is cranial fossa?
Medical Definition of cranial fossaa : the posterior one that is the largest and deepest of the three and lodges the cerebellum, pons, and medulla oblongata. ... b : the middle one that lodges the temporal lobes laterally and the hypothalamus medially. ... c : the anterior one that lodges the frontal lobes.
Where is the fossa in anatomy?
Fossa - A shallow depression in the bone surface. Here it may receive another articulating bone or act to support brain structures. Examples include trochlear fossa, posterior, middle, and anterior cranial fossa.
Why is cranial fossa important?
In addition to its contents, the middle cranial fossa acts as a potential space for infection and hemorrhage. The complex anatomy of this region makes it a difficult area for surgeons to traverse, but also provides access to various areas of the brain for a variety of procedures.
How do you remember cranial fossa?
A mnemonic phrase that I've used to help remind us of the anatomical locations and names of the paired foramina in the cranial floor is this: Old Rotund Owls Spin Lazily Across Jugs.
What part of the brain is in the middle cranial fossa?
temporal lobesThe middle cranial fossa is a butterfly-shaped depression of the skull base, which is narrow in the middle and wider laterally. It houses the temporal lobes of the cerebrum.
What part of the brain is in the posterior cranial fossa?
The posterior cranial fossa contains the lowest part of the midbrain and the pons, cerebellum and medulla oblongata. The region of the cranial cavity immediately above the tentorium cerebelli contains the occipital lobes of the cerebral hemispheres of the brain.
What nerves are in middle cranial fossa?
Cranial NervesSummary.Olfactory Nerve (CN I)Optic Nerve (CN II)Oculomotor Nerve (CN III)Trochlear Nerve (CN IV)Trigeminal Nerve (CN V)Abducens Nerve (CN VI)Facial Nerve (CN VII)More items...
What does fossa mean in medical terms?
Fossa = a depression or hollow, (literal translation = ditch, trench, Latin) Iliac fossa = the depression in the inner surface of the ileum. Fossa ovalis = depression on wall of the right atrium that separates the right atrium from the left.
What does the middle cranial fossa control?
It houses the temporal lobes of the brain and the pituitary gland. A middle fossa craniotomy is one means to surgically remove acoustic neuromas (vestibular schwannoma) growing within the internal auditory canal of the temporal bone.
How many types of fossa are there?
Across Madagascar, people distinguish two kinds of fossa—a large fosa mainty ("black fossa") and the smaller fosa mena ("reddish fossa")—and a white form has been reported in the southwest.
What is cranial nerve and its function?
The cranial nerves are a set of 12 paired nerves in the back of your brain. Cranial nerves send electrical signals between your brain, face, neck and torso. Your cranial nerves help you taste, smell, hear and feel sensations. They also help you make facial expressions, blink your eyes and move your tongue.
Where is the cranial fossa formed?
A cranial fossa is formed by the floor of the cranial cavity .
What are the boundaries of the cranial fossa?
Green: Posterior cranial fossa. Boundaries. 1: Sphenoidal limbus (anterior margin of the chiasmatic groove) 2: Posterior borders of the lesser wings of the sphenoid. 3: Dorsum sellae of the sphenoid bone. 4: Superior borders of the petrous part of the temporal bone. 5: Groove for transverse sinus of the occipital bone. Identifiers.
What is a middle fossa craniotomy?
A middle fossa craniotomy is one means to surgically remove acoustic neuromas ( vestibular schwannoma) growing within the internal auditory canal of the temporal bone. Middle cranial fossa surgical anatomy as demonstrated in a right cadaver temporal bone by Dr Jack M Kartush - view from above.
What are the lateral parts of the middle fossa?
Lateral parts. The lateral parts of the middle fossa are of considerable depth, and support the temporal lobes of the brain . They are marked by depressions for the brain convolutions and traversed by furrows for the anterior and posterior branches of the middle meningeal vessels .
How is the chiasmatic groove separated from the posterior fossa?
It is separated from the posterior fossa by the clivus and the petrous crest . It is bounded in front by the posterior margins of the lesser wings of the sphenoid bone, the anterior clinoid processes, and the ridge forming the anterior margin of the chiasmatic groove; behind, by the superior angles of the petrous portions ...
What is the lateral to the foramen ovale?
Lateral to the foramen ovale is the foramen spinosum, for the passage of the middle meningeal vessels, and a recurrent branch from the mandibular nerve.
What is the sella turcica?
The sella turcica is bounded posteriorly by a quadrilateral plate of bone, the dorsum sellae, the upper angles of which are surmounted by the posterior clinoid processes: these afford attachment to the tentorium cerebelli, and below each is a notch for the abducent nerve .
Where does the clinoid process end?
It begins behind at the foramen lacerum, and ends on the medial side of the anterior clinoid process, where it is sometimes converted into a foramen (carotico-clinoid) by the union of the anterior with the middle clinoid process; posteriorly, it is bounded laterally by the lingula .
Which vessel is medial to the foramen ovale?
Medial to the foramen ovale is the foramen Vesalii, which varies in size in different individuals, and is often absent; when present, it opens below at the lateral side of the scaphoid fossa , and transmits a small vein.
What is the fossa?
The fossa accommodates the anteroinferior portions of the frontal lobes of the brain. In this article, we shall look at the borders, contents and clinical correlations of the anterior cranial fossa. The anterior cranial fossa consists of three bones: the frontal bone, ethmoid bone and sphenoid bone.
Which part of the anterior cranial fossa is most likely to fracture?
The cribriform plate of the ethmoid is the thinnest part of the anterior cranial fossa, and therefore most likely to fracture. There are two major consequences of cribriform plate fracture: Anosmia - the olfactory nerve fibres run through the cribriform plate, and can be 'sheared', resulting in loss of sense of smell.
What bone is the anterior border of the prechiasmatic sulcus?
Posteriorly and medially it is bounded by the limbus of the sphenoid bone. The limbus is a bony ridge that forms the anterior border of the prechiasmatic sulcus (a groove running between the right and left optic canals).
What are the three depressions in the cranial cavity?
The floor of the cranial cavity is divided into three distinct depressions. They are known as the anterior cranial fossa, middle cranial fossa and posterior cranial fossa. Each fossa accommodates a different part of the brain.
What is the floor of the cranial cavity called?
The Anterior Cranial Fossa. The floor of the cranial cavity is divided into three distinct depressions. They are known as the anterior cranial fossa, middle cranial fossa and posterior c ranial fossa. Each fossa accommodates a different part of the brain.
What is the frontal bone?
There are several bony landmarks present in the anterior cranial fossa. The frontal bone is marked in the midline by a body ridge , known as the frontal crest. It projects upwards, and acts as a site of attachment for the falx cerebri (a sheet of dura mater that divides the two cerebral hemispheres).
Which bone contains the main foramina?
The ethmoid bone in particular contains the main foramina (openings that transmit vessels and nerves) of the anterior cranial fossa. The cribriform plate is a sheet of bone seen either side of the crista galli which contains numerous small foramina – these transmit olfactory nerve fibres (CN I) into the nasal cavity.
What is the middle cranial fossa?
Middle cranial fossa. The middle cranial fossa is butterfly shaped and is located posteroinferior to the anterior fossa (Figure 3) . Both the greater wings of the sphenoid and temporal bone create the lateral sections of the fossa. The middle cranial fossa contains 6 foramina:
Where is the anterior fossa located?
The anterior fossa is formed from the frontal bone anteriorly, the ethmoid bone in the midline and the body and the lesser wings of the sphenoid bone posteriorly (Figure 2) . Two skull foramina located in the anterior fossa:
Which fossa is the deepest?
Posterior Cranial Fossa. The posterior fossa is the largest and deepest of the 3 fossae. The occipital bone is the main contributor to the fossa and the temporal bone forms the antero-lateral boundaries (Figure 4). There are 4 foramina found in the posterior cranial fossa: Internal acoustic meatus. Jugular foramen.
What are the 3 depressions in the neurocranium?
Figure 1 displays the 3 depressions/fossae. The fossae increase in depth from anterior to posterior and are termed the: Anterior cranial fossa. Middle cranial fossa.
What are the bones of the posterior cranial fossa?
The posterior cranial fossa is comprised of three bones: the occipital bone and the two temporal bones. Anteriorly and medially it is bounded by the dorsum sellae of the sphenoid bone. This is a large superior projection of bone that arises from the body of the sphenoid.
Which fossa is the most posterior?
The posterior cranial fossa is the most posterior and deep of the three cranial fossae. It accommodates the brainstem and cerebellum.
What are the three depressions in the cranial cavity?
The floor of the cranial cavity is divided into three distinct depressions. They are known as the anterior cranial fossa, middle cranial fossa and posterior cranial fossa. Each fossa accommodates a different part of the brain.
What is the floor of the cranial cavity?
The floor of the cranial cavity is divided into three distinct depressions. They are known as the anterior cranial fossa , middle cranial fossa and posterior cranial fossa. Each fossa accommodates a different part of the brain. The posterior cranial fossa is the most posterior and deep of the three cranial fossae.
Where are the bony landmarks and foramina located?
There are several bony landmarks and foramina present in the posterior cranial fossa (a foramen is simply a hole that allows the passage of a structure – usually a blood vessel or nerve).
Where is the foramina located?
Foramina. There are several bony landmarks and foramina present in the posterior cranial fossa (a foramen is simply a hole that allows the passage of a structure - usually a blood vessel or nerve). Temporal Bone.
Which part of the brain houses the cerebellum?
The posterior cranial fossa houses the brainstem and cerebellum.
Contents of middle cranial fossa
The middle cranial fossa accommodates the following anatomical structures:
Openings of middle cranial fossa
There are many openings in the middle cranial fossa connecting it to other parts of the skull:
What is the middle cranial fossa?
The middle cranial fossa is a butterfly-shaped depression of the skull base, which is narrow in the middle and wider laterally. It houses the temporal lobes of the cerebrum.
Which structure is present in the posterior clinoid?
Structures present in the lateral part from anterior to posterior are: superior orbital fissure. foramen rotundum.
Which part of the brain is deeper than the medial part?
In the medial part, the following structures are present from anterior to posterior: The lateral part is considerably deeper than the medial part to allow for the temporal lobes. Structures present in the lateral part from anterior to posterior are:
Overview
A cranial fossa is formed by the floor of the cranial cavity.
There are three distinct cranial fossae:
• Anterior cranial fossa (fossa cranii anterior), housing the projecting frontal lobes of the brain
• Middle cranial fossa (fossa cranii media), separated from the posterior fossa by the clivus and the petrous crest housing the temporal lobe
Middle part
Lateral parts
See also
The middle cranial fossa, deeper than the anterior cranial fossa, is narrow medially and widens laterally to the sides of the skull. It is separated from the posterior fossa by the clivus and the petrous crest.
It is bounded in front by the posterior margins of the lesser wings of the sphenoid bone, the anterior clinoid processes, and the ridge forming the anterior margin …
Additional images
The middle part of the fossa presents, in front, the chiasmatic groove and tuberculum sellae; the chiasmatic groove ends on either side at the optic foramen, which transmits the optic nerve and ophthalmic artery to the orbital cavity.
Behind the optic foramen the anterior clinoid process is directed backward and medialward and gives attachment to the tentorium cerebelli.
External links
The lateral parts of the middle fossa are of considerable depth, and support the temporal lobes of the brain.
They are marked by depressions for the brain convolutions and traversed by furrows for the anterior and posterior branches of the middle meningeal vessels.
These furrows begin near the foramen spinosum, and the anterior runs forward and upward to th…