
Full Answer
Does RNA contain sugar deoxyribose?
RNA is a single-stranded nucleic acid. RNA has a ribose sugar instead of a deoxyribose sugar like DNA. RNA nucleotides have a uracil base instead of thymine. What are the 3 types of RNA?
What is the biological function of deoxyribose?
In the formation of DNA, deoxyribose is an important pentose sugar and helps with cell replication. Explore the definition of deoxyribose, its structure in DNA, and the importance of this type of sugar.
What is the chemical formula for Deoxyribose?
Deoxyribose, or more precisely 2-deoxyribose, is a monosaccharide with idealized formula H− (C=O)− (CH 2 )− (CHOH) 3 −H. Its name indicates that it is a deoxy sugar, meaning that it is derived from the sugar ribose by loss of an oxygen atom. Deoxyribose is most notable for its presence in DNA.
What is the structure of deoxyribose?
What is Deoxyribose?
- Ribose and Deoxyribose
- Difference between Deoxyribose and Ribose. What is Deoxyribose? Deoxyribose is an aldopentose sugar with an attached aldehyde group. ...
- Deoxyribose Structure. Deoxyribose may exist as a five- or six-membered ring or as a linear molecule on its own. ...
- Importance of Deoxyribose. Deoxyribose forms the very backbone of DNA. ...
1. Why Deoxyribose for DNA and Ribose for RNA?
Deoxyribose is an aldopentose sugar with an attached aldehyde group. This aids in the differentiation of ribonucleic and deoxyribonucleic acid by e...
2. Explain the difference between the Structure of Ribose and Deoxyribose?
Ribose and Deoxyribose are two types of simple sugars or monosaccharides found in living organisms. They are extremely important biologically becau...
3. What is the major function of deoxyribose?
The major function of deoxyribose is upon the DNA in the human body. The description for which is given on Deoxyribose. Deoxyribose is the five-car...
4. How do students know about the kinds of questions that might come from deoxyribose?
Students will know about the types of questions that might come from the chapter if they read Deoxyribose on Vedantu’s online tutoring platforms. T...
5. Have biology teachers created Deoxyribose on Vedantu?
Yes, Biology teachers who are quite good at the subject have contributed to this page. Vedantu never compromises on its study material and so, empl...
6. What is the deoxyribose sugar structure?
The structure can be understood if Vedantu is referred to. Deoxyribose. The monosaccharide deoxyribose, or more specifically 2-deoxyribose, has an...
7. Is ribose the same as deoxyribose?
No, both have major differences. The differences between both get clearer as one reads from Deoxyribose on Vedantu.The difference between deoxyribo...
What is the sugar in DNA?
As mentioned, deoxyribose is the sugar in the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA. DNA is a polymer made up of a series of nucleotides. One nucleotide consists of a purine or pyrimidine nucleobase, one deoxyribose, and one phosphate group. In other words, a deoxyribose nucleotide contains a deoxyribose sugar and is the building block of DNA. Individual genes are comprised of different sequences of nucleotides. Those sequences contain the biological instructions to create living organisms. Additionally, nucleotides carry energy throughout cells.
What is Deoxyribose?
What is deoxyribose? The Deoxyribose definition is a pentose (5-carbon sugar) biological molecule. Deoxyribose sugar, along with phosphate, makes up the sugar-phosphate backbone in deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). DNA is the genetic code present in living organisms. Under certain conditions, deoxyribose can be extracted from DNA through hydrolysis, a reaction that breaks down molecules in the presence of water.
What is the difference between DNA and RNA?
DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid and is made up of a sugar-phosphate backbone that contains deoxyribose as sugar. RNA stands for ribonucleic acid, and it is made of a sugar-phosphate backbone that contains the sugar ribose. Both DNA and RNA are made of nucleotides. Nucleotides carry energy throughout cells and consist of a purine or pyrimidine base, one sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and one phosphate group.
What is the difference between ribose and deoxyribose?
Like the term saccharide, the word ending -ose also means "sugar". Since ribose must lose one oxygen to become deoxyribose , the latter is considered a modified sugar. Deoxyribose is the sugar component in DNA, while ribose is the sugar component in ribonucleic acid (RNA).
What happens when ribose loses oxygen?
When ribose loses an oxygen atom, deoxyribose becomes less susceptible to hydrolysis. In other words, deoxyribose plays a critical role in helping DNA remain intact. Considering that DNA is present in every living organism and contains the genetic code to be passed generationally, it is imperative that it remains structurally and functionally sound with very few modifications over time.
What is the sugar in the sugar-phosphate backbone of deoxyribonucleic acid?
Deoxyribose is the sugar in the sugar-phosphate backbone of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). DNA contains the genetic code for all living organisms.
What is a simple sugar with 5 carbons called?
Simple sugars with five carbons are called pentose monosaccharides. Mono means "one" and saccharide means "sugar." Deoxy denotes that a molecule has lost an oxygen atom. In this case, the sugar ribose lost one oxygen at its second carbon, hence the name 2-deoxyribose.
What is deoxyribose sugar?
Deoxyribose is an aldopentose sugar with an attached aldehyde group . This aids in the differentiation of ribonucleic and deoxyribonucleic acid by enzymes found in the living body.
How does deoxyribose affect DNA?
Although this may seem to be a minor improvement, it has a significant impact on DNA's resistance to hydrolysis. With the extra oxygen, RNA can interact with water molecules more effectively. The phosphodiester bonds that connect ribose molecules can be hydrolyzed as a result of this. The phosphodiester bonds that connect deoxyribose molecules naturally interact with waterless and break down less through hydrolysis. This allows DNA molecules to be passed down through generations with only small modifications.
What is Ribose?
Ribose is a pentose sugar with an openly attached aldehyde group at the end of the chain. Ribonucleoside is made up of ribose sugar and a nitrogenous base. A ribonucleotide is formed when this ribonucleoside is bound to a phosphate group.
Why are ribose and deoxyribose important?
They are extremely important biologically because they aid in the formation of the organism's blueprint, which is then passed down over generations. Any shift in the blueprint in one generation of a species manifests itself in the next generation as physical or evolutionary changes. However, there are some slight but important variations between ribose and deoxyribose.
What are monosaccharides?
Monosaccharides, or basic sugars, are ribose and deoxyribose. They are aldopentoses that are phosphorylated to form deoxyribonucleotide and ribonucleotide, respectively. They play a crucial role in the creation of an organism's blueprint, which is passed down over generations.
What is the chemical formula for deoxyribose?
Deoxyribose is a part of DNA and is often referred to as 2-deoxyribose. A sugar is any molecule that ends in the letter 'ose.' C5H10O4 is the chemical formula for deoxyribose. The letters reflect the names of elements from the periodic table, and the numbers (presented in subscript) tell us how much of each of these elements make up a specific covalent bond. Deoxyribose is made up of 5 carbon atoms, 10 hydrogen atoms, and 4 oxygen atoms, according to the deoxyribose formula. Atoms are the essential chemical elements of life and can be found everywhere.
What is the backbone of DNA?
Deoxyribose can act as the backbone of DNA by substituting a phosphate group and a nucleic acid base on this ring, as shown in the diagram below.
What is the role of deoxyribose derivatives in DNA?
As a component of DNA, 2-deoxyribose derivatives have an important role in biology. The DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) molecule, which is the main repository of genetic information in life, consists of a long chain of deoxyribose-containing units called nucleotides, linked via phosphate groups.
Why is deoxyribose not 2′ hydroxyl?
The absence of the 2′ hydroxyl group in deoxyribose is apparently responsible for the increased mechanical flexibility of DNA compared to RNA, which allows it to assume the double-helix conformation, and also (in the eukaryotes) to be compactly coiled within the small cell nucleus.
What is the base of DNA?
In the standard nucleic acid nomenclature, a DNA nucleotide consists of a deoxyribose molecule with an organic base (usually adenine, thymine, guanine or cytosine) attached to the 1′ ribose carbon.
What is the formula for deoxyribose?
Chemical compound. Deoxyribose, or more precisely 2-deoxyribose, is a monosaccharide with idealized formula H− (C=O)− (CH 2 )− (CHOH) 3 −H. Its name indicates that it is a deoxy sugar, meaning that it is derived from the sugar ribose by loss of an oxygen atom. Deoxyribose is most notable for its presence in DNA.
Is deoxyribose a precursor to ribose?
Since the pentose sugars arabinose and ribose only differ by the stereochemistry at C2′, 2-deoxyribose and 2-deoxyarabinose are equivalent, although the latter term is rarely used because ribose, not arabinose, is the precursor to deoxyribose.
Is RNA a single stranded protein?
The backbone of RNA and DNA are structurally similar, but RNA is single stranded, and made from ribose as opposed to deoxyribose. Other biologically important derivatives of deoxyribose include mono-, di-, and triphosphates, as well as 3′-5′ cyclic monophosphates.
What are the bases of sugar?
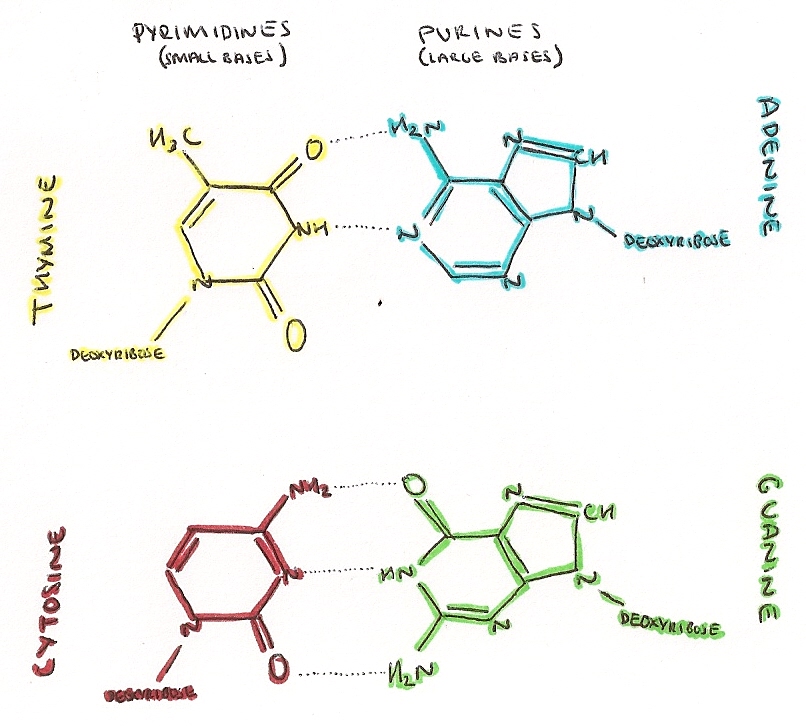
Attached to each sugar is one of four bases--adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T). The two strands are held together by bonds between the bases; adenine bonds with thymine, and cytosine bonds with guanine.
What is the name of the structure of DNA?
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the central information storage system of most animals and plants, and even some viruses. The name comes from its structure, which is a sugar and phosphate backbone which have bases sticking out from it--so-called bases.
How many bases are in DNA?
The bases go by the names of adenine, cytosine, thymine, and guanine, otherwise known as A, C, T, and G. DNA is a remarkably simple structure. It's a polymer of four bases--A, C, T, and G--but it allows enormous complexity to be encoded by the pattern of those bases, one after another. DNA is organized structurally into chromosomes ...
What is DNA made of?
The DNA molecule consists of two strands that wind around one another to form a shape known as a double helix. Each strand has a backbone made of alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate groups. Attached to each sugar is one of four bases--adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T). The two strands are held together by bonds between the bases; adenine bonds with thymine, and cytosine bonds with guanine. The sequence of the bases along the backbones serves as instructions for assembling protein and RNA molecules.
What is the sugar in DNA called?
The simple sugar in DNA, called deoxyribose, gives DNA what?
Which molecules do not contain carbon and hydrogen?
Molecules that do not contain carbon and hydrogen. Water and table salt.
What is genetic instruction?
Genetic instructions. Information about a living thing passed down from parents to offspring.
Is RNA single stranded?
RNA is single stranded, has uracil instead of thymine, and is just ribose, not deoxyribose.
