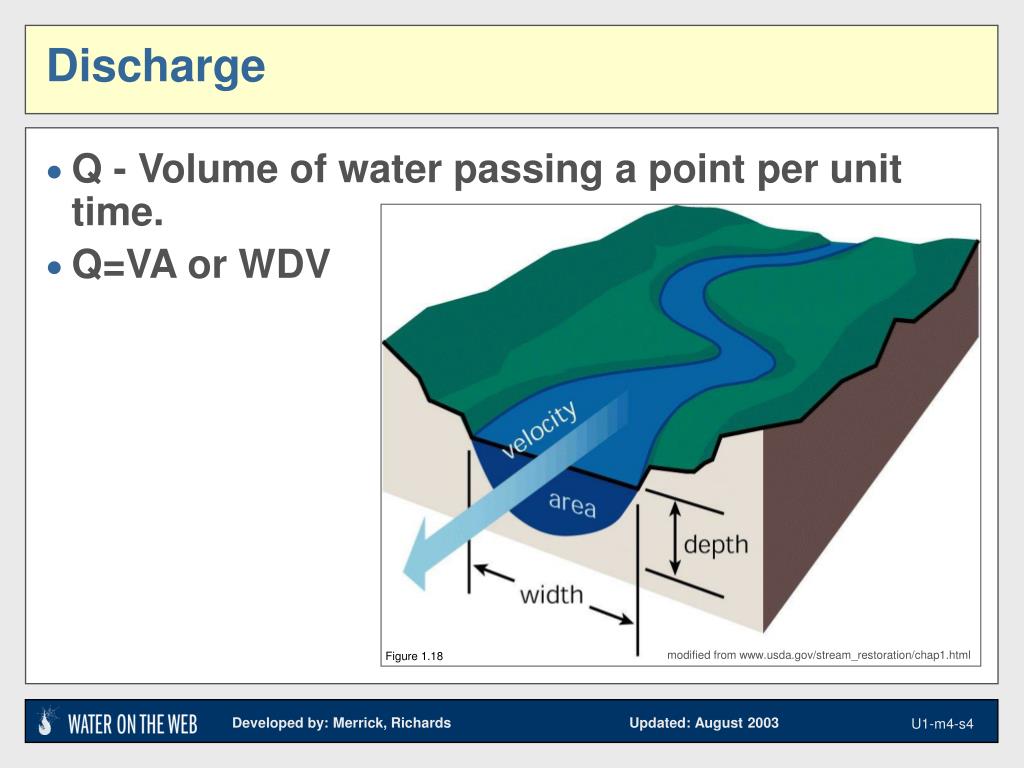
What is stream discharge?
Streamflow, or discharge, is the volume of water moving down a stream or river per unit of time, commonly expressed in cubic feet per second or gallons per day. Because stream discharge cannot be measured directly, it must be computed from variables that can be measured directly, such as stream depth, stream width, and streamflow velocity.
How does the width of a river affect its discharge?
The width and depth of the river also affects it; a larger river at the same speed will have higher discharge. You can calculate stream discharge using this equation: the discharge equals the velocity in meters per second multiplied by the width of the stream in meters multiplied by the depth of the stream in meters.
What are the factors that affect stream discharge?
There are several factors that affect stream discharge. The velocity of the water affects it; faster water means more passes per second so more discharge. The width and depth of the river also affects it; a larger river at the same speed will have higher discharge.
Can a streamgage measure discharge?
Although stage is valuable information for some purposes, most users of streamgage data are interested in streamflow or discharge—the amount of water flowing in the stream or river, commonly expressed in cubic feet per second or gallons per day. However, it is not practical for a streamgage to continuously measure discharge.

Where does a stream typically have its greatest discharge?
The deepest part of channel occurs where the stream velocity is the highest. Both width and depth increase downstream because discharge increases downstream. As discharge increases the cross sectional shape will change, with the stream becoming deeper and wider.
Is discharge greater upstream or downstream?
1. Upstream has generally higher value than downstream due to water lost in different processes, but not always less as sometimes water could be added in downstream as well. If there is a bridge and no water is lost then upstream of the bridge and downstream has almost equal discharge values.
What causes high stream discharge?
As the amount of water in a stream increases, the stream must adjust its velocity and cross sectional area in order to form a balance. Discharge increases as more water is added through rainfall, tributary streams, or from groundwater seeping into the stream.
What is the discharge of a stream?
Discharge is the volume of water moving down a stream or river per unit of time, commonly expressed in cubic feet per second or gallons per day.
Why does discharge increase downstream?
Discharge increases downstream because of additional water from tributaries. Velocity increases due to the additional water from tributaries and less water is in contact with the bed and banks so there is less friction. Find out more about the long profile of a river.
Why does discharge in a stream usually increase downstream quizlet?
Why does the velocity of a stream generally increase downstream even though the gradient decreases? Velocity generally increases downstream because channels are generally smoother downstream and because stream volume tends to increase as more tributaries enter downstream.
Which part of the river has the greatest discharge?
List of rivers by dischargeNoContinentRiver1South AmericaAmazon2AfricaCongo (Zaire)3AsiaGanges-Brahmaputra/Meghna4South AmericaOrinoco46 more rows
Where does water flow fastest in a stream?
middleThe speed at which a stream flows is called the stream velocity. A fast river moves at a rate of about 5 miles per hour. The water moves most rapidly in the middle of the channel, where the water is deepest and friction is minimal.
Where is the stream most likely flowing the fastest?
Water flow in a stream is primarily related to the stream's gradient, but it is also controlled by the geometry of the stream channel. As shown in Figure 13.14, water flow velocity is decreased by friction along the stream bed, so it is slowest at the bottom and edges and fastest near the surface and in the middle.
What is stream discharge quizlet?
stream discharge. the volume of water passing a given point over a set time.
Where does the river get discharged?
The river's discharge at that location depends on the rainfall on the catchment or drainage area and the inflow or outflow of groundwater to or from the area, stream modifications such as dams and irrigation diversions, as well as evaporation and evapotranspiration from the area's land and plant surfaces.
Which factors determine the discharge of a stream?
There are several factors that affect stream discharge. The velocity of the water affects it; faster water means more passes per second so more discharge. The width and depth of the river also affects it; a larger river at the same speed will have higher discharge.
Does discharge increase or decrease downstream?
Both width and depth increase downstream because discharge increases downstream. As discharge increases the cross sectional shape will change, with the stream becoming deeper and wider.
Why does the discharge of a river decrease downstream?
Because river slope generally decreases in a downstream direction, it is generally supposed that velocity of flow also decreases downstream. Analysis of some of the large number of velocity measurements made at stream-gaging stations demonstrates that mean velocity generally tends to increase downstream.
How does river discharge change along the course of a river?
The discharge of a river increases along its course as tributaries join it adding more water. Velocity also increases along the course of a river.
How does discharge typically change in a stream seasonally?
It is affected by weather, increasing during rainstorms and decreasing during dry periods. It also changes during different seasons of the year, decreasing during the summer months when evaporation rates are high and shoreline vegetation is actively growing and removing water from the ground.
What is a stream discharge rating curve?
A stage-discharge rating curve depicts the relation between stream stage and stream discharge at a location along a stream, generally at a streamgage. Rating curves are developed from numerous physical stream discharge measurements collected over a period of time and over a range of stages (from low flow to flood stage). Each point on the stage-discharge graph represents one discharge measurement. The stage-discharge relation depends on the shape, size, slope and roughness of the stream channel at each gage and is different for every streamgage. The rating curve for almost every streamgage will vary over time due to changes in the stream channel resulting from sedimentation, scour, ice, debris, growth of aquatic vegetation, etc. To keep rating curves accurate and up-to-date, USGS hydrographers visit each streamgage about once every 6 weeks to make a discharge measurement. They also measure high flows whenever they happen. USGS computers are used to apply the stream-discharge rating curve for a given streamgage to the continuous water level (stage) data for the gage to estimate continuous streamflow (discharge) for the site.
How to measure discharge in a river?
For some rivers, the typical stage-discharge relation does not apply, because stage is not uniquely related to discharge due to tides, low slope, or density currents. The advent of hydroacoustic or ultrasonic velocity meters has made it possible to continuously monitor discharge at these types of streams using the index velocity method. In this method, a hydroacoustic or ultrasonic velocity meter is placed in the river to continuously monitor the water velocity for a section of the river; this is called the index velocity. Periodic discharge measurements are paired with the index velocity to develop a relation between the index velocity and the mean velocity. This index velocity versus mean velocity relation is used along with a continuous record of the stage and a stage versus cross-sectional area relation to determine the continuous record of discharge at the site.
How to measure streamflow velocity?
Two of the more common methods are the mechanical current-meter method and the Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler (ADCP) method. In the mechanical current-meter method, the stream channel cross section is divided into vertical subsections and a current meter is used to estimate the velocity in each subsection. As water flows past the current meter, a wheel of metal cups revolves around a vertical axis and transmits an electronic signal on each revolution, allowing the revolutions to be counted and timed. The rate at which the cups revolve is translated into water velocity. Subsection velocities are multiplied by corresponding subsection areas; these values are summed to compute total discharge for the cross section. In contrast, ADCPs are hydroacoustic instruments that use the principles of the Doppler Effect to measure water velocity by sending a sound pulse into the water and measuring the change in the frequency of the sound pulse reflected back to the ADCP by sediment or other particulates being transported in the water. The change in frequency, or Doppler Shift, that is measured by the ADCP is translated into water velocity. The ADCP provides a detailed profile of water velocity and direction for the majority of a cross section, rather than limiting measurements to point locations within subsections of the stream channel. This improves discharge measurement accuracy.
What is a rapid deployment gage?
Rapid-deployment gages (RDGs) are gages that are temporarily fixed on structures above streams and rivers (such as bridges) during emergencies to provide water level information when a streamgage does not exist or is damaged. Super gages are a small subset of streamgages that collect both streamflow and continuous water-quality data.
What is a streamgage?
A streamgage is a structure installed beside a stream or river that contains equipment that measures and records the water level (called gage height or stage) of the stream. Streamflow (also called discharge) is computed from measured water levels using a site-specific relation (called a stage-discharge rating curve) developed from onsite water level and streamflow measurements made by USGS hydrographers. The water level and streamflow data are quality assured and made available online.
What is streamflow measurement?
Although streamflow is computed from measurements of other variables, the term “streamflow measurement” or “discharge measurement” is generally applied to the final result of the calculations. Diagram of channel cross section with subsections.
How often do stream gauges measure stage?
A streamgage usually measures stage every 15 minutes. When intense rainfall and runoff cause a stream or river to rise quickly, however, the time intervals can be as short as every 5 minutes. The data are typically transmitted to USGS computers on a preset schedule by way of satellite—usually every 1 to 4 hours.