
Where is the distal femoral metaphysis located?
It is classically, located in the medullary cavity of long bone epiphyses, and apophyses, and it is rarely, found in the cortex of the long bone metaphysis.
What is the metaphysis of the femur?
The metaphysis is the neck portion of a long bone between the epiphysis and the diaphysis. It contains the growth plate, the part of the bone that grows during childhood, and as it grows it ossifies near the diaphysis and the epiphyses.
How long does a distal femur take to heal?
Depending on health and injury pattern this bone can take 3-4 months to heal without surgery. Physical therapy for knee range of motion is started around 6 weeks once bone has healed enough to prevent displacement with motion.
How is a distal femur fracture treated?
Most distal femur fractures are treated with surgery. The broken bone will take a minimum of 2 months to heal. Some can take more than 6 months to heal. Surgery may take place anywhere from 1-5 days after your injury.
Where is the metaphysis located?
The metaphyses (singular: metaphysis) are the wide portions of long bones and the regions of the bone where growth occurs. Growth occurs at the section of the metaphysis that is adjacent to the growth plate (physis). The metaphysis is located between the diaphysis and epiphysis.
Where is the metaphysis of a bone?
The metaphysis is the region where the epiphysis joins the diaphysis; in a growing bone this corresponds to the calcified layer of the epiphyseal plate together with the interdigitating bone (see Figure 4.19). The interface between the hypertrophic and calcified layers is sometimes referred to as the tidemark.
Is walking good for a broken femur?
Is walking after a femur fracture impossible? No. Walking after a femur fracture is a goal that is typically achieved within the first few weeks after surgery. You will need a walker or crutches to walk at the beginning of your rehabilitation until you build enough strength.
Can a femur heal without surgery?
Most people with a fractured femur need some sort of surgery, usually ORIF. Without the surgery, your broken femur may not heal properly. ORIF can place your bones back into their proper configuration. This significantly increases the chance that your bone will heal properly.
Can I walk normal after femur fracture?
If the femur fracture does not require surgery, it is often treated with a cast or removable brace, and patients are typically advised not to put any weight on the leg for about 8 weeks. A physical therapist will help the patient to walk safely using crutches or a walker, or other assistive device.
How bad is a distal femur fracture?
As the distal femur fracture usually involves the weight bearing joint it may cause long term problems such as loss of knee motion or instability and long term arthritis.
How long does it take for a broken femur to stop hurting?
What to Expect at Home. Recovery most often takes 4 to 6 months. The length of your recovery will depend on how severe your fracture is, whether you have skin wounds, and how severe they are. Recovery also depends on whether your nerves and blood vessels were injured, and what treatment you had.
Is distal femur fracture common?
Distal femur fractures include fractures of the supracondylar and intercondylar region and are relatively common injuries. The goals of treatment follow AO principles of anatomic reduction of the articular surface, restoration of limb alignment, length, and rotation.
What is the function of the metaphysis?
function in bone structure This region (metaphysis) functions to transfer loads from weight-bearing joint surfaces to the diaphysis. Finally, at the end of a long bone is a region known as an epiphysis, which exhibits a cancellous internal structure and comprises the bony substructure of the joint surface.
What does metaphysis mean?
metaphysis (plural metaphyses) (anatomy) The part of a long bone that grows during development. change of form; transformation.
What is a metaphysis fracture?
Metaphyseal fractures are also known as corner fractures, bucket handle fractures or metaphyseal lesions. It refers to an injury to the metaphysis which is the growing plate at each end of a long bone (such as tibia, femur, etc).
Why is metaphysis important?
Why is Metaphysics important? Metaphysics is the foundation of philosophy. Without an explanation or an interpretation of the world around us, we would be helpless to deal with reality. We could not feed ourselves, or act to preserve our lives.
What causes a distal femur fracture?
Distal femur fractures are mainly caused by high- and low energy types of injuries.
Where is the fracture of the femur?
A Fracture that occurs at the distal end of the femur bone, which includes the femoral condyles and the metaphysis.
What classification system is used for distal femur fractures?
The most common classification system used for distal femur fractures is the AO/OTA system.
What causes shortening of the distal articular segment?
Shortening of the fracture with varus and extension of the distal articular segment is the typical deformity.3 Shortening is caused by the quadriceps and hamstrings. The varus and extension deformities are due to the unopposed pull of the hip adductors and gastrocnemius muscles respectively.
What is the typical clinical picture during the inspection of the knee?
Clinical/Physical examination: the typical clinical picture during the inspection of the knee is swelling in the knee region and clear dislocation.
What is low energy fracture?
Low energy fractures: mostly occurs in elderly people , secondary to osteoporosis (predominantly in women over 65years). These fractures most commonly occurs with twisting motions or falls.
What is a distal femur fracture?
Distal femur fractures include fractures of the supracondylar and intercondylar region of the distal femur and are relatively common injuries. To avoid the high morbidity and mortality correlating with this fracture, it requires prompt diagnosis and treatment. This article reviews the evaluation and treatment of distal femur fractures ...
What percentage of femur fractures are distal?
Distal femur fractures account for less than 1% of all fractures and about 3 to 6% of all femoral fractures. [1][4] The incidence of distal femur fractures has been reported to be 37 per 100000 people in the United States.[5] These fractures occur in a bimodal distribution: young males, particularly after high-energy motor trauma and elderly females. One study reported that 80% of patients 35 years of age or older with a distal femur fracture secondary to moderate trauma had evidence of generalized osteopenia.[6] Periprosthetic fractures about the distal femur have also become more common. The incidence of distal femur fractures around a primary total knee arthroplasty has been reported to be from 0.3% to 5.5%, and upwards to 30% after revision knee arthroplasty. [7]
What is the best way to manage a distal femur fracture?
Distal femur fractures are best managed by an interprofessional team that includes the emergency department physician, orthopedic surgeon, internist, orthopedic nurses, and physical therapist. The majority of distal femur fractures require surgical intervention; thus, consultation of the orthopedic surgeon is essential. Vascular surgery requires a consult if there is any suspicion for vascular compromise to the limb. The management of the elderly patient requires advanced training and education in the handling of patients with co-morbidities and a significant change in their life trajectory. After surgery, patients need nursing care with prophylaxis against pressure sores and deep vein thrombosis. Nursing can also serve as a bridge between rehabilitative care and the treating clinician, as physical therapy is a vital part of rehabilitation. A social worker should be involved to ensure that the patient's home environment is safe and that the patient has support services. The recovery is often slow, and many patients need pain control; hence, a pharmacist may be helpful to educate the patient on modes of pain management. Open communication between the team members is vital to improving patient outcomes. These interprofessional team dynamics can improve patient outcomes. [Level 5]
What is the classification of distal femur fractures?
Classification of distal femur fractures may be descriptive, including extra-articular, intra-articular unicondylar, intra-condylar bicondylar, and pattern of fracture, including the degree of comminution.
What is a floating knee fracture?
Fractures of the distal femur with associated tibia plateau injury, referred to as a floating knee, often require CT imaging and aggressive treatment. Distal femur fractures that result from a gunshot injury, high-energy trauma, or open injury present with a high risk for vascular injury.
What type of fracture is antegrade nailing?
Antegrade nailing is a good option for extraarticular OTA 33 type A fractures and some type C1 and C2 fractures. [27] The advantages of antegrade nailing include the ability to treat ipsilateral femoral shaft fractures with associated supracondylar femoral fractures with one device. Relative contraindications to antegrade nailing include OTA 33 type B3 and C3 fractures. [28]
What is intramedullary nail fixation?
Intramedullary nail fixation has the benefit of providing a stable construct with minimal soft tissue and periosteum disruption. Antegrade and retrograde options are available depending on fracture characteristics. Pearls to successful intramedullary nailing include obtaining an optimal starting point to pass the reamer and maintaining reduction throughout the procedure. Blocking screws may be placed in the proximal or distal fragment to guide the trajectory of the nail and obtain satisfactory reduction.
What is a distal femur fracture?
Distal femur fractures vary. The bone can break straight across (transverse fracture) or into many pieces (comminuted fracture). Sometimes these fractures extend into the knee joint and separate the surface of the bone into a few (or many) parts. These types of fractures are called intra-articular. Because they damage the cartilage surface of the bone, intra-articular fractures can be more difficult to treat.
Why is distal femur surgery good?
Because of newer techniques and special materials, the results of surgical treatment are good, even in older patients who have poor bone quality. Timing of surgery. Most distal femur fractures are not operated on right away — unless the skin around the fracture has been broken (open fracture).
Why does my knee wear down?
Because the knee is the largest weightbearing joint in the body, any defect can damage the protective articular cartilage and, over time, result in arthritis. In some cases, the joint surface may wear down to bare bone. Arthritis caused by fracture or injury is called post-traumatic arthritis.
What part of the knee supports the bottom part of the knee?
The distal femur makes up the top part of your knee joint. The upper part of the shinbone (tibia) supports the bottom part of your knee joint. The ends of the femur are covered in a smooth, slippery substance called articular cartilage. This cartilage protects and cushions the bone when you bend and straighten your knee.
What is a fractured thigh bone?
A fracture is a broken bone. Fractures of the thighbone that occur just above the knee joint are called distal femur fractures. The distal femur is where the bone flares out like an upside-down funnel.
How long does it take to recover from a distal femur fracture?
Depending on several factors — such as your age, general health, and the type of fracture you have — it may take a year or more of rehabilita tion before you are able to return to all everyday activities.
What muscles are used to bend and straighten the knee?
The normal anatomy of the knee. Strong muscles in the front of your thigh (quadriceps) and back of your thigh (hamstrings) support your knee joint and allow you to bend and straighten your knee.
What is the most common distal femoral condyle fracture?
A common distal femoral condyle fracture is the Hoffa fracture (see Case 4).
What is the ICd 11 code for distal femoral fracture?
Distal femoral fractures - ICD-11 NC72.6Z involve the femoral condyles and the metaphyseal region and are often the result of high energy trauma such as motor vehicle accidents or a fall from a height. In the elderly, they may occur as a domestic accident 1-3.
How rare are femoral fractures?
They are quite rare and represent 3-6 % of all femoral fractures and less than 0.5% of all fractures 1-3. Young patients, especially males are affected, and in the elderly, women are more often affected.
What does a fracture show?
Fractures will usually show a radiolucency or cortical breach. Depending on how they are displaced there may be features of overlay and/or impaction.
Can a CT be used to diagnose a distal femoral fracture?
Plain radiographs remain the mainstay of diagnosis and characterization of distal femoral fractures. However, CT is often helpful, since most distal femoral fractures are intra-articular 1. MRI can be helpful if concomitant meniscal or ligamentous injury is suspected 3.
What is a distal femur fracture?
Distal femur fractures are traumatic injuries involving the region extending from the distal metaphyseal-diaphyseal junction to the articular surface of the femoral condyles.
Which condyle is more distal than lateral?
medial condyle extends more distal than lateral. distal femur becomes trapezoidal in cross-section towards the knee. lateral cortex of femur slopes ~10 degrees, medial cortex slopes ~25 degrees in the axial plane. posterior halves of both condyles are posterior to the posterior cortex of femoral shaft. Muscles.
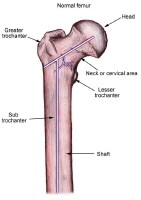
Definition/Description
Clinically Relevant Anatomy
- The femur, also known as the thigh bone, is the longest bone in the body. Distally, the lateral and medial condyles articulate with the Tibial plateau of the Tibia forming the tibiofemoral joint, and the patellar surface of the femur articulates with the patella, forming the patellofemoral joint. Together these two joints form the kneejoint, which is the largest weight-bearing joint in the bod…
Mechanism of Injury / Pathological Process
- Distal femur fractures are mainly caused by high- and low energy types of injuries. 1. High energy fractures: usually occur in young adults (predominantly 30year old males) and result in intra-articular fractures. Mechanism of injury commonly includes motor vehicle accidents, high-velocity missile injuries and/ or a direct blow mechanism. 2. Low energy fractures: mostly occur in elderl…
Clinical Presentation
- Most common symptoms of distal femur fracture include: 1. Pain with weight-bearing 2. Swelling and bruising 3. Tenderness to touch 4. Deformity. (Shortening of the fracture with varus and extension of the distal articular segment is the typical deformity.3 Shortening is caused by the quadriceps and hamstrings. The varus and extension deformities are due to the unopposed pull …
Diagnostic Procedures
- Clinical/Physical examination: the typical clinical picture during the inspection of the knee is swelling in the knee region and clear dislocation. Radiographic examination:AP and lateral views of the femur. CT-scans:Highly recommended with high energy trauma and if an intra-articular fracture is suspected. (55% of distal femur fractures are intra-articular.) The most common clas…
Management / Interventions
- Surgical management for distal femur fractures is since the 1970s regarded superior to non-surgical management.
Physical Therapy Management
- The main aim of Physiotherapy post distal femur fracture is to get the patient back to his/ her baseline function and to prevent complications. Whilst the patient is admitted to hospital, the Physiotherapist will teach the patient how to mobilise using the correct walking aid, with the correct weight-bearingstatus as discussed with the doctor. Thorough education regarding the c…
Complications