Where is the radius located in the body?
The radius is the thicker and shorter of the two long bones in the forearm. It is located on the lateral side of the forearm parallel to the ulna (in anatomical position with arms hanging at the sides of the body, palms facing forward) between the thumb and the elbow. The radius and ulna pivot around one another to allow rotation of the wrist.
Is the humerus proximal or distal to the radius?
The proximal end of the humerus articulates with the glenoid cavity of the scapula at the glenohumeral joint. At the distal end, the humerus articulates with the head of the radius and the trochlear notch of the ulna, forming the elbow joint. Like other long bones, the humerus has three main parts - a proximal end, a shaft, and a distal end.
Where is the radius and ulna located?
Ulna and radius of the lower arm. The ulna is located on the medial side of the forearm, and the radius is on the lateral side. These bones are attached to each other by an interosseous membrane.On the ulna several landmarks (bone markings) are noticeable. The olecranon processthat fits into the fossa on the humerus is our elbow.
Where in your body is the radius and ulna?
The radius and ulna are the bones of the forearm. The forearm is the region of the upper limb that extends from the elbow to the wrist. The radius bone ( os radius) supports the lateral (thumb) side of the forearm and the ulna bone ( os ulna) supports the medial (little finger) side.

Where is the dorsal distal radius?
The dorsal distal radius is approached through a straight, longitudinal incision in line with the third metacarpal and centered just ulnar to the Lister tubercle, between the third and fourth dorsal compartments (Fig. 78-5 ).
What is the purpose of distal radius fracture?
The purpose of treatment for distal radius fractures is to restore articular congruity and normal anatomic alignment of the distal radius, and to prevent articular malalignment and the development of arthritis of the wrist .
What are the most common complications of distal radius fracture?
Malunion is the most common complication that occurs after distal radius fractures. 9 Important radiographic measurements that may affect functional outcomes in the wrist are radial inclination (normal average: 23°), radial length (normal average: 12 mm), palmar tilt (normal average: 11°) and congruity of articular surfaces ( Fig. 13.1 ). Loss of radial inclination causes radial deviation of the wrist, whereas radial shortening leads to incongruity of the DRUJ and positive ulnar variance. Excessive dorsal tilt results in carpal malalignment, leading to carpal instability and arthritis. Although corrective osteotomy of the distal radius may be required for severe malunions, 10 salvage procedures such as the Darrach (resection of the ulnar head) 11 or Sauvé–Kapandji procedures (fusion of the DRUJ) 12 are required to improve overall wrist function if symptomatic DRUJ arthritis exists. This chapter describes the following two important surgical procedures for the distal radius and DRUJ: volar plating of distal radius fractures, and the Darrach procedure.
How are radial and lunate fossa separated?
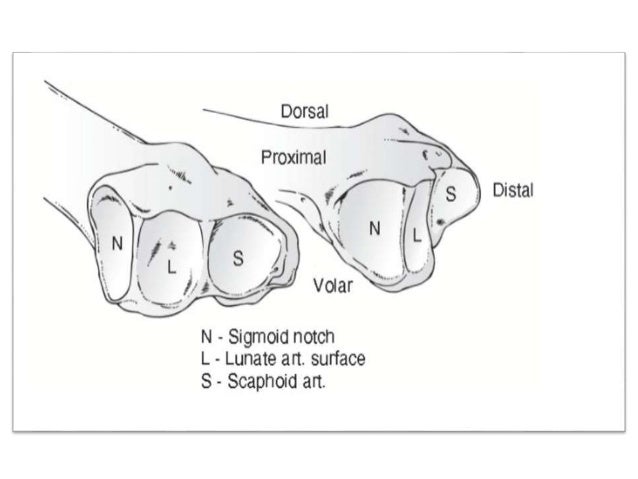
Radial and lunate fossae are separated by ridge
Which surface is concave in both mediolateral and anteroposterior directions?
Distal radius has three articular surfaces, which are concave in both mediolateral and anteroposterior directions: sigmoid notch, scaphoid fossa, and lunate fossa. From: Comparative Kinesiology of the Human Body, 2020. Download as PDF. About this page.
Why is the EPL tendon left above the retinaculum?
The EPL tendon is left above the retinaculum at closure to minimize the risk for tendon injury by ischemia or direct contact with an implant.
Why is distal radius used for bone grafting?
The distal radius lends itself to bone grafting as a result of the metaphyseal defects often caused by impacting fractures to this area. The recent development of multiple bone graft substitutes has increased the options available. Fixed-angle plates have decreased the need for structural support provided by bone grafting.
How to tell if you have a distal radius fracture?
When you have a distal radius fracture, you will almost always have a history of a fall or some other kind of trauma. You will usually have pain and swelling in the forearm or wrist. You may have a deformity in the shape of the wrist if the fracture is bad enough. The presence of bruising (black and blue discoloration) is common. See your doctor if you have enough pain in your arm to stop you from using it normally. You may want to go directly to an orthopaedist (bone doctor), who can usually take an X-ray right in the office and tell you what is going on. If your doctor's office is closed, the injury is not very painful and the wrist is not deformed, you can usually wait until the next day. Go to the emergency room if the injury is very painful, the wrist is deformed, you have numbness, or your fingers are not pink. You may want to protect the wrist with a splint and apply ice to the wrist and elevate it until you get to the doctor's office.
Why is distal radius fracture more difficult to treat?
Many distal radius fractures in people over 60 are due to osteoporosis (decreased density of the bones) if the fall was relatively minor (a fall from a standing position).
How to fix a fractured arm?
One choice is to leave the bone the way it is, if the bone is in a pretty good position. Your doctor may apply a plaster cast until the bone heals. Or if the position (alignment) of your bone is not good and likely to limit the future use of your arm, your orthopaedic surgeon may suggest correcting the deformity (the medical term for correcting the deformed bone is reduction). If the bone is straightened out (reduced) without cutting into the skin (incision), this is called a closed reduction. After the bone is properly aligned, a splint or cast may be placed on your arm. A splint is usually used for the first few days, to allow for a small amount of normal swelling. A cast is usually added a few days to a week or so later, after the swelling goes down, and changed two or three weeks later as the swelling goes down more and the cast gets loose. X-rays are taken, depending on the nature of the facture, either at weekly intervals for three weeks and then at six weeks (if the fracture was reduced or felt to be unstable), or less often if the fracture was not reduced and thought to be stable. The cast is removed about six weeks after the fracture happened. At that point, physical therapy is often started to help improve motion and function of the injured wrist.
What is the term for a broken wrist?
When someone falls on their outstretched hand, they sometimes get a "broken wrist.". The bone that is usually broken is called the radius. The end of the bone nearest the wrist is called the distal end. The medical term for "broken bone" is fracture. Therefore, the medical term for the most common type of "broken wrist" is a distal radius fracture ...
What is the name of the bone in the forearm that is broken?
Sometimes, the other forearm bone (the ulna) is also broken. When this happens, it is called a distal ulna fracture. This fracture was first described by an Irish surgeon and anatomist, Abraham Colles, in 1814; hence the name, "Colles' " fracture. A broken wrist usually causes pain and swelling, and frequently causes a deformity, ...
How many wrist fractures are there?
Finally, osteoporosis is a factor in as many as 250,000 wrist fractures. It has been suggested that people who suffer a wrist fracture may need to be screened for osteoporosis, especially if they have other risk factors. Ask your doctor if you need to be screened or treated for osteoporosis.
What is it called when a bone breaks into two pieces?
If the bone is broken into more than two pieces, it is called a comminuted fracture.
What is the distal radius?
Distal Radius Fractures (Broken Wrist) The radius is the larger of the two bones of the forearm. The end toward the wrist is called the distal end. A fracture of the distal radius occurs when the area of the radius near the wrist breaks. Distal radius fractures are very common. In fact, the radius is the most commonly broken bone in the arm.
How far from the end of the bone does a distal radius fracture occur?
A distal radius fracture almost always occurs about 1 inch from the end of the bone. The break can occur in many different ways, however.
What causes a distal radius fracture?
Cause. The most common cause of a distal radius fracture is a fall onto an outstretched arm. Osteoporosis (a disorder in which bones become very fragile and more likely to break) can make a relatively minor fall result in a broken wrist. Many distal radius fractures in people older than 60 years of age are caused by a fall from a standing position.
Why is distal radius fracture recovery so different?
Because the kinds of distal radius fractures are so varied and the treatment options are so broad, recovery is different for each individual. Talk to your doctor for specific information about your recovery program and return to daily activities.
What is the other bone of the forearm called?
Sometimes, the other bone of the forearm (the ulna) is also broken. This is called a distal ulna fracture.
How long does it take for a cast to be removed from a fractured wrist?
The cast is removed about 6 weeks after the fracture happened. At that point, physical therapy is often started to help improve the motion and function of the injured wrist.
Do people return to activities after distal radius fracture?
Rehabilitation and Return to Activity. Most people do return to all their former activities after a distal radius fracture. The nature of the injury, the kind of treatment received, and the body's response to the treatment all have an impact, so the answer is different for each individual.
Types of Distal Radius Fractures
The most common location for a distal radius fracture is about one inch from the wrist. The break can take place at different angles and unequal amounts of dislocation. The three prominent types of distal radius fractures are:
What Are the Causes of a Distal Radius Fracture?
The most commonly observed cause of a distal radius fracture is some form of trauma or injury to the wrist. This may be caused by a fall, a vehicular accident, or a sports injury.
What Are the Symptoms of a Distal Radius Fracture?
The most obvious distal radius fracture symptoms are immediate pain and tenderness at the wrist. You may also see significant swelling and bruising. In some cases, the wrist may be deformed or bent/twisted in an odd position.
What Is the Treatment for a Distal Radius Fracture?
There are non-surgical and surgical treatments for distal radius fractures, depending on the severity of the break, potential nerve injury, joint involvement, and the person’s age and activity levels:
What Is Recovery and Rehabilitation?
Fractures can hurt for a few days or weeks, depending on the extent of the injury. Over-the-counter pain relief medications are usually effective at managing the pain. Ibuprofen and acetaminophen may be prescribed to relieve inflammation at the wrist. Elevating the wrist up above the heart and applying ice packs can also help soothe the pain.
What is a distal radius fracture?
A distal radius fracture, also known as wrist fracture, is a break of the part of the radius bone which is close to the wrist. Symptoms include pain, bruising, and rapid-onset swelling. The wrist may be broken for life.
How old is the average person with a distal radius fracture?
In adults, the average age of occurrence is between 57 and 66 years. Men who sustain distal radius fractures are usually younger, generally in their 40s (vs. 60s in females). Low energy injury (usually fall from standing height) is the usual cause of distal end radius fracture (66 to 77% of cases).
What would happen if the wrist was ulnar deviated?
Radial styloid fracture would occur if the wrist is ulnar deviated and vice versa. If the wrist is bent back less, then proximal forearm fracture would occur, but if the bending back is more, then the carpal bones fracture would occur. With increased bending back, more force is required to produce a fracture.
How long does it take to cast a radius?
Treatment is with casting for six weeks or surgery. Surgery is generally indicated if the joint surface is broken and does not line up, the radius is overly short, or the joint surface of the radius is tilted more than 10% backwards.
Who first described distal end radius fracture?
In 1814, Abraham Colles described the characteristics of distal end radius fracture. In 1841, Guilaume Dupuytren acknowledged the contributions by Petit and Pouteau, agreeing that the distal end radius fracture is indeed a fracture, not a dislocation.
Can a distal radius fracture cause nerve injury?
Nerve injury, especially of the median nerve and presenting as carpal tunnel syndrome, is commonly reported following distal radius fractures. Tendon injury can occur in people treated both nonoperatively and operatively, most commonly to the extensor pollicis longus tendon. This can be due to the tendon coming in contact with protruding bone or with hardware placed following surgical procedures.
What is a distal radius fracture?
A distal radius fracture (DRF) is a very frequent pathology, involving 15% of women after age of 50 years, in relation with decrease of bone mineral density (85% low BMD, 51% osteoporosis). Development and innovation of not only the anatomy’s comprehension, but also of the implants and approaches have considerably improved the function of these patients.
What are the three articular surfaces of the distal radius?
The three concave articular surfaces are the scaphoid fossa, the lunate fossa, and the sigmoid notch. The anterior surface is concaved, palmary directed and covered by the pronator quadratus ( Fig. 2 A).
What is the pronator quadratus line?
The pronator quadratus line marks the highest part of the epiphysis and helps the surgeon visualize the patient-specific radius curvature. If an implant goes beyond this line when viewed on lateral radiographs, there is a potential for impingement with the thumb and finger flexor tendons.
What is the anterior surface of the styloid?
The anterior surface is concaved, palmary directed and covered by the pronator quadratus ( Fig. 2 A). The surface is rough for the attachment of the palmar radiocarpal ligaments extending radially form the radial styloid ulnarly to the TFCC. The lateral surface extends along the lateral margin to form the styloid process ( Fig. 2 B). The styloid process is conical and projects 10–12 mm distal to the articular surface for the proximal scaphoid and lunate. The radial styloid area may have a flat groove for the tendon of the first dorsal compartment (abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis tendons).
Why is advanced knowledge of anatomy and individual variations deemed mandatory for the anatomic reduction of distal radius fractures?
Advanced knowledge of basic anatomy and individual variations are deemed mandatory for the anatomic reduction of distal radius fractures (mainly in case of comminution) as well as to obtain fracture fixation while “staying out of trouble,” hence avoiding iatrogenic tendinous/ligamentous injuries when anatomic principles are violated.
Where is the dorsal tubercle located?
The prominent dorsal tubercle (Lister’s tubercle) lies from 5 to 10 mm from the distal joint surface. On the medial aspect of the dorsal tubercle is a smooth groove for passage of the extensor pollicis longus tendon.
Which area of the styloid has a flat groove?
The radial styloid area may have a flat groove for the tendon of the first dorsal compartment (abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis tendons). The dorsal surface of the distal radius is irregular, convex, and acts as a fulcrum for extensor tendon function ( Fig. 2 C). The prominent dorsal tubercle (Lister’s tubercle) ...
What is the head proximal radius?
Proximal radius (head, neck and tuberosity) The head can be found proximally and is known as the caput radii, which articulates with the capitulum of the humerus as part of the compound joint of the elbow and is concave to look at.
Which muscle attaches to the lateral aspect of the radius?
Supinator muscle (radial head) attaches to the lateral aspect of the radius, covering a large area of it. Pronator teres muscle also adheres to the radial shaft (below the supinator's attachment) and inserts on the pronator tuberosity, which is a well-demarcated, rough area.
What are the bones of the forearm?
Radius and ulna. The radius and the ulna constitute as the bones of the forearm. The antebrachial region, as it is clinically known, spans the length of the region which extends roughly from elbow to wrist. The radius is the lateral of the two bones, which makes the ulna the medial bone of the forearm. These bones are specially designed in order ...
Where does the abductor pollicis longus originate?
Abductor pollicis longus which originates just below the posterior margin of the attachment of the supinator muscle.
What muscle attaches to the radial shaft?
Pronator teres muscle also adheres to the radial shaft (below the supinator's attachment) and inserts on the pronator tuberosity, which is a well-demarcated, rough area.
How does the radius communicate with the head of the ulna?
The radius also communicates with the head of the ulna by articulating with the ulna’s radial notch via its own circumference. The neck is the area of the bone that narrows in between the head and the radial or bicipital tuberosity.
What are some interesting facts about the radius and ulna?
Key facts about the radius and ulna. Proximal end of the radius. Head (upper surface for the joint with the capitulum of the humerus; the circumference for the joint with the radial notch of the ulna), neck (gives support to the radial head), radial tuberosity. Shaft of the radius.
