Flesh-eating bacteria (necrotizing fasciitis) is a rare infection of the skin and tissues below it. It can be deadly if not treated quickly. Necrotizing fasciitis spreads quickly and aggressively in an infected person.
How do you catch flesh eating bacteria?
- Only about 205 people in the United States will get an infection from Vibrio vulnificus — also called the “flesh-eating bacteria” — this year.
- People with certain underlying conditions may be more prone to contracting the infection.
- The bacteria can also cause symptoms when ingested, such as through raw oysters.
What are the early symptoms of flesh eating bacteria?
The early symptoms are also similar to common post-surgical complaints, such as:
- Serious pain
- Inflammation
- Fever
- Nausea
What are the symptoms of flesh eating virus?
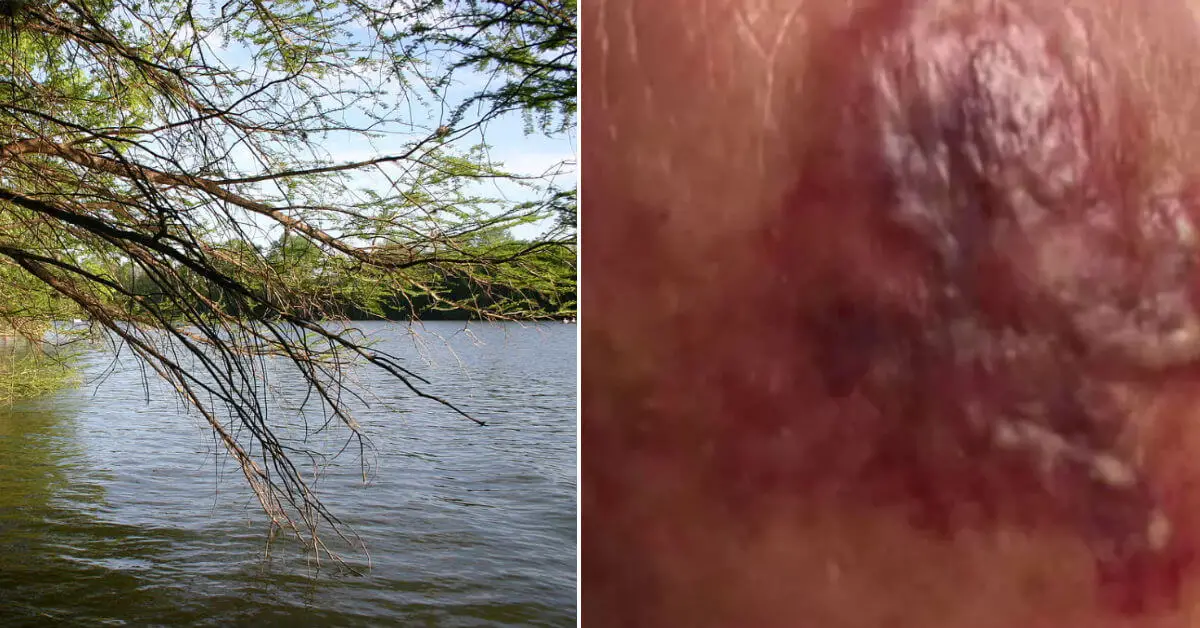
What are the early symptoms of flesh-eating disease? The early stage of necrotizing fasciitis is characterized by symptoms of redness, swelling, and pain in the affected area. Blisters may be seen in the involved area of skin. Fever, nausea, vomiting, and other flu -like symptoms are common.
What does flesh eating bacteria look like?
What does flesh eating bacteria look like? Necrotizing fasciitis (NF), commonly known as flesh-eating disease, is an infection that results in the death of parts of the body's soft tissue. It is a severe disease of sudden onset that spreads rapidly. Symptoms include red or purple skin in the affected area, severe pain, fever, and vomiting.

Where do you get flesh-eating bacteria?
Flesh-eating bacteria transmission Surgical wounds. Puncture wounds or other injury. Burns. Minor cuts.
Is there still flesh-eating bacteria?
"This is still a rare condition but can be quite serious, especially for individuals who have a compromised immune system," Rose explained in a college news release. The most common cause of flesh-eating disease ("necrotizing fasciitis") is group A strep, a common type of bacteria that also causes strep throat.
What states have the flesh-eating bacteria?
In 2019, people have reported contracting a flesh-eating disease in states like Texas, Florida, Georgia, Alabama, Mississippi, Virginia, Maryland and Delaware. Take note: All of those states are along the East and Gulf coasts.
Where is flesh-eating bacteria found Florida?
The bacteria has the potential to cause serious illness, state health officials warn. According to officials, there has only been one reported case this year in Escambia County of the flesh-eating bacteria known as "Vibrio vulnificus." There were 11 cases in 2021.
What are my chances of getting flesh-eating bacteria?
Only 700 to 1,100 cases occur every year in the United States and only one in four people die. The term flesh-eating refers to the toxins produced by a bacterial infection that can destroy your muscles, skin and fatty tissues.
Can flesh-eating bacteria be cured?
Flesh-eating strep infections or necrotizing fasciitis is considered rare. Necrotizing fasciitis is a treatable disease. Only certain rare bacterial strains are able to cause necrotizing fasciitis, but these infections progress rapidly so the sooner one seeks medical care, the better the chances of survival.
What does flesh-eating bacteria look like in the beginning?
Early symptoms of necrotizing fasciitis can include: A red, warm, or swollen area of skin that spreads quickly. Severe pain, including pain beyond the area of the skin that is red, warm, or swollen.
How quickly does flesh-eating bacteria spread?
The affected area may also spread from the infection point quickly, sometimes spreading at a rate of an inch an hour. If NF progresses to show advanced symptoms, the patient will continue to have a very high fever (over 104 degrees Fahrenheit) or may become hypothermic (low temperature) and become dehydrated.
How long does it take for flesh-eating bacteria to show?
How you get it. If ingested, usually through eating raw or undercooked oysters, the symptoms of diarrhea, cramping, fever, chills, and vomiting usually appear within 24 hours. The symptoms usually last only 3 days. If Vibrio vulnificus is exposed to open wounds, it can cause a rash that changes skin color.
Does flesh-eating bacteria live in pools?
Flesh-eating bacteria can live in lakes, oceans, swimming pools and even hot tubs.
What beaches in Florida are contaminated with bacteria?
Enterococcus bacteria can come from a variety of natural and human-made sources....As a precaution, "no swim” advisories were issued for the following beaches:Bird Key Park/ Ringling Causeway.Siesta Key Beach.Service Club Beach.Venice Fishing Pier.Brohard Beach.Casperson Beach.Manasota Key.
Can you go in the ocean with a paper cut?
If you're swimming in a pool, and it's just a small cut, such as a paper cut, don't worry—you're highly unlikely to develop anything problematic.
Does Florida have flesh-eating bacteria?
Vibrio vulnificus, commonly known in Florida as a “flesh-eating bacteria,” is a thermophilic pathogen that often thrives in warm, marine environments.
Are the beaches safe in Florida?
Home to more than 8,426 miles of coastline, Florida's beaches are all typically safe for swimming year-round, notes the Florida Department of Health.
What causes flesh-eating bacteria in the ocean?
People can contract a Vibrio infection after wading in contaminated water with an open wound or eating raw shellfish from the water. The Vibrio flesh-eating bacteria species is spreading beyond its traditional region, in part because of warming ocean temperatures caused by climate change.
Is there a flesh-eating bacteria in the ocean?
vulnificus – a flesh-eating bacteria – is commonly found in the warm waters of the Gulf of Mexico, but it can also be found along the Atlantic and Pacific coasts. Like humans, many bacteria like to spend time at the beach.
Can flesh-eating bacteria be cured?
Flesh-eating bacteria can be cured if the infection is caught in the early stages. A surgeon must remove the dead tissue and prescribe a combinatio...
What does flesh-eating disease look like when it starts?
When the infection is in the early stage, the skin may appear red, shiny or swollen. The patient will experience a lot of pain at the site of the i...
How do you catch necrotizing fasciitis?
A person with an underlying medical condition or one who has a weakened immune system may be more susceptible to infection by pathogenic bacteria t...
How long does it take for flesh-eating bacteria to show symptoms?
Symptoms generally appear within the first day if someone has flesh-eating bacteria. More severe symptoms can appear after the first 24 hours.
Where are flesh-eating bacteria found?
Flesh-eating bacteria are found in different types of environments. Some thrive in the water while others live in the soil. Bacteria can also commo...
What are the first signs of necrosis?
The first signs of necrotizing fasciitis include pain at the site of the infection. The patient may also experience symptoms similar to the flu and...
What is flesh eating bacteria?
Media reports have popularized the term flesh-eating bacteria to refer to a type of very rare but serious bacterial infection known as necrotizing fasciitis. Necrotizing fasciitis is an infection that starts in the tissues just below the skin and spreads along the flat layers of tissue (fascia) that separate different layers of soft tissue, ...
Why is flesh eating considered a disease?
The term flesh-eating has been used because the bacterial infection produces toxins that destroy tissues such as muscles, skin, and fat. Streptococcus pyogenes is a member of the group A streptococci, a group of bacteria that are commonly responsible for mild sore throat ( pharyngitis) and skin infections. Rarely, this form of strep bacterium ...
What causes flesh-eating disease?
Although necrotizing fasciitis may be caused by an infection with one or more than one bacterium, in most cases, the term flesh-eating bacteria has been applied to describe infections caused by the bacterium known as Streptococcus pyogenes. The term flesh-eating has been used because the bacterial infection produces toxins that destroy tissues such as muscles, skin, and fat. Streptococcus pyogenes is a member of the group A streptococci, a group of bacteria that are commonly responsible for mild sore throat ( pharyngitis) and skin infections. Rarely, this form of strep bacterium causes severe illnesses such as toxic shock syndrome and necrotizing fasciitis. Most infections with group A streptococci result in mild illness and may not even produce symptoms.
What bacteria cause necrotizing fasciitis?
Sometimes, other bacteria, including Klebsiella, Clostridium, E. coli, Staphylococcus aureus, or even a combination of different bacteria may produce necrotizing fasciitis. In 2012, a case was reported of a young woman who suffered a zip-lining accident on a river in West Georgia. She contracted an infection with the bacteria Aeromonas hydrophila, which produced a necrotizing infection that resulted in the loss of a leg and part of her abdomen. Vibrio vulnificus is a type of bacteria found in brackish water that has caused necrotizing fasciitis in swimmers who have been in infected water with open wounds.
How to prevent bacterial infection of skin?
Prevention of infection includes avoidance of swimming in pools or open water sources, or soaking in hot tubs, with open wounds or sores. Additionally, keeping open wounds covered with dry bandages until healed, washing hands often, and proper care of wounds and injuries, including scrapes, blisters, and cuts, can prevent necrotizing fasciitis.
How long does it take for necrotizing fasciitis to show?
Another characteristic of necrotizing fasciitis is that the symptoms develop very rapidly, usually within 24 hours after a wound in the skin has allowed the bacteria to invade the tissues beneath the skin. The pain is described as being more severe than would be expected from the appearance of the wound.
What Is Flesh-Eating Bacteria (Necrotizing Fasciitis)?
Flesh-eating bacteria ( necrotizing fasciitis) is a rare infection of the skin and tissues below it. It can be deadly if not treated quickly.
What is the term for the bacteria that infect the superficial fascia?
Necrotizing fasciitis happens when these types of bacteria infect the superficial fascia, a layer of connective tissue below the skin.
What bacteria are responsible for necrotizing fasciitis?
But, several types of bacteria, such as staphylococcus and others, have also been linked to the disease. Necrotizing fasciitis happens when these types of bacteria infect the superficial fascia, a layer of connective tissue below the skin.
How does a syphilis infection begin?
In some cases, it is unknown how the infection began. Once it takes hold, the infection rapidly destroys muscle, skin, and fat tissue.
What is the name of the bacteria that eats flesh?
The flesh-eating bacteria is a member of group A streptococcus, the same bacteria that causes strep throat. © Sebastian Kaulitzki - Dreamstime.com. Flesh-eating bacteria—also known as necrotizing fasciitis—is a quick-spreading, aggressive infection that can be fatal if not treated promptly.
How Common Is Flesh-Eating Bacteria?
Not very. “Flesh-eating bacterial infections are relatively uncommon, but not so uncommon that they are rare ,” says Dr. Amesh Adalja, Senior Scholar at Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security and spokesperson for the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA).
What is the most common cause of necrotizing fasciitis?
Flesh-eating bacteria most commonly attacks the arms, legs, and abdominal wall. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, group A streptococcus is most commonly to blame for necrotizing fasciitis, causing between 700 and 1,200 cases in the U.S. each year, although the actual number is likely higher.
How does necrotizing fasciitis spread?
It can also spread through small cuts, insect bites, and minor abrasions.
How do flesh eating bacteria spread?
The most common way to spread flesh-eating bacteria is through a break in the skin —through, for example, a bug bite, surgical wound, cut, scrape, or burn.
Where does a syphilis infection start?
The infection starts below the skin and spreads along the fascia (the flat layers of tissue that separate other tissues, including muscles, fat, and organs), destroying these tissues as it spreads through the body. Flesh-eating bacteria most commonly attacks the arms, legs, and abdominal wall. According to the Centers for Disease Control ...
What is the best treatment for a bacterial infection?
Blood transfusions. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (to preserve healthy tissues) Immunoglobulin IV therapy (to boost the body’s ability to fight infection) Surgery (to diagnose the infection, determine how far it’s spread, and remove dead or damaged tissue in hopes of stopping the bacteria’s spread)
Why does necrotizing fasciitis move so fast?
The reason necrotizing fasciitis moves so fast through the body is because the bacteria starts producing toxins immediately after entering the skin's surface. These toxins cut off blood flow to the surrounding muscle, fat and skin tissues causing them to die. As the toxins spread, they quickly eat away at the tissue and multiply. I've actually watched it move up a patient's leg while I was sitting at their bedside, that's how fast it can travel, says Dr. Linda Yancey, an Infectious Disease Specialist affiliated with Memorial Hermann.
What Causes Necrotizing Fasciitis?
There are different types of bacteria that cause necrotizing fasciitis, however, the most common is Streptococcus A, the same bacteria that causes strep throat. The strep bacteria can cause a broad range of illnesses and infections, most of which are not life-threatening. However, The Centers for Disease Control have categorized necrotizing fasciitis as an invasive group A strep disease because the infection attacks the body's connective tissue, which is not usually a target of bacterial infections.
Where is Vibrio vulnificus found?
But it’s Vibrio vulnificus, one of a dozen species of this Vibrio bacteria, that has been making headlines this summer. It’s found in the coastal waters according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Trusted Source. .
How do you get Vibrio?
Most commonly, people become infected with the bacteria by eating raw and undercooked shellfish, particularly oysters. Others encounter the bacteria through open wounds while swimming in infected waters. In rare cases, the Vibrio infection can cause necrotizing fasciitis.
How many people in the US have Vibrio vulnificus?
Only about 205 people in the United States will get an infection from Vibrio vulnificus — also called the “flesh-eating bacteria” — this year. People with certain underlying conditions may be more prone to contracting the infection. The bacteria can also cause symptoms when ingested, such as through raw oysters.
What happens if you get Vibrio Vulnificus?
If Vibrio vulnificus is exposed to open wounds, it can cause a rash that changes skin color. There’s also bruising and localized swelling, and it can be painful to the touch.
Can you eat raw oysters?
Don’t eat raw or undercooked oysters. Always wash your hands with antimicrobial soap after handling raw oysters. After cooking seafood, properly refrigerate leftovers to prevent warming. Avoid salt and brackish waters if you have an open wound including simple scrapes and open cuts.
Is it rare to get a syphilis infection?
in the United States each year. “People are concerned because this is a very dramatic infection. It affects people of all ages — you can be healthy and get the infection. Despite this, it is rare,” said Dr. William Schaffner, an infectious disease specialist at Vanderbilt University Medical Center.
Can Vibrio cause necrotizing fasciitis?
In rare cases, the Vibrio infection can cause necrotizing fasciitis. This is a soft tissue infection that progresses to the muscles and organs resulting in rapid destruction of tissues. However, if caught early, this infection can be promptly treated with antibiotics. Although you can find Vibrio vulnificus in all coastal waters ...
Why is it called a flesh eating disease?
The condition caused by these bacteria is known as ' necrotizing fasciitis .' This is more commonly called 'flesh-eating disease.' The reason it is called necrotizing fasciitis is relatively simple to explain. 'Fasciitis' comes from the word ' fascia ,' a type of fibrous connective tissue in your body. This tissue surrounds things such as the muscles, blood vessels and nerves in your body. You can basically think of the fascia as the thin skin around a sausage you may be enjoying along with your steak.
Why is necrotizing fasciitis called flesh eating disease?
Our fasciitis is necrotizing because it causes necrosis, or the death of tissues and cells.
Why is fasciitis necrotizing?
Our fasciitis is necrotizing because it causes necrosis, or the death of tissues and cells. There are many different bacteria that end up causing necrotizing fasciitis. They include: Since there are so many flesh-eating bacteria to recall, you can use the acronym 'SCABS' to help you remember everything.
What causes scabs on the body?
Therefore, the flesh-eating bacteria cause SCABS, or Staph, Clostridium, Aeromonas, Bacteriodes and Strep.
Is meat on the menu omnivore?
All sorts of things could be on the menu, from T-bone steak to rib steak. However, what's not enjoyable is when you are on the menu.
Do bacteria eat flesh?
In reality, the bacteria do not actually eat your flesh.
Who first described necrotizing soft tissue infection?
The first English description for necrotizing soft-tissue infection was by British surgeon Leonard Gillespie and British physicians Gilbert Blaine and Thomas Trotter in the 18th century. At that time, necrotizing soft-tissue infections were known variously as "phagedaenic ulcer" (ulceration that spreads and destroys surrounding tissue), "gangrenous phagedena", "gangrenous ulcer", "malignant ulcer", "putrid ulcer", "fulminating gangrene", "necrotizing erysipelas", "gangrenous erysipelas", "crepitant cellulitis", "gangrenous cellulitis", "Meleney cellulitis", "necrotizing synergistic cellulitis", "hemolytic streptococcal gangrene", "progressive bacterial synergistic gangrene", "necrotizing abscess", "galloping gangrene", or "hospital gangrene". Later, "hospital gangrene" became more commonly used. In 1871 Confederate States Army surgeon Joseph Jones reported 2,642 cases of hospital gangrene with a mortality rate of 46%. In 1883, Dr Jean-Alfred Fournier described the necrotizing infection of the perineum and scrotum, now called Fournier gangrene. The term "necrotizing fasciitis" was first coined by Wilson in 1952. Its definition has become broader, to include not only infection of fascia, but also other soft-tissue infection. Despite being disfavored by the medical community, the term "galloping gangrene" is frequently used in sensationalistic news media to refer to outbreaks of necrotizing fasciitis.
How many cases of nematosis involve more than one type of bacteria?
Between 55 and 80% of cases involve more than one type of bacteria. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is involved in up to a third of cases. Medical imaging is often helpful to confirm the diagnosis. Necrotizing fasciitis may be prevented with proper wound care and handwashing.
How to treat necrotizing fasciitis?
Necrotizing fasciitis may be prevented with proper wound care and handwashing. It is usually treated with surgery to remove the infected tissue, and intravenous antibiotics . Often, a combination of antibiotics is used, such as penicillin G, clindamycin, vancomycin, and gentamicin.
What happens when you eat shellfish?
When one of the harmful types of bacteria — Group A Streptococcus being the most common culprit — is ingested by, for instance, eating undercooked shellfish, the worst that may happen is diarrhea and vomiting. But when those bacteria cause necrotizing fasciitis, severe pain and soreness will progress ...
What is necrotizing fasciitis?
The condition known as necrotizing fasciitis, in which an infection rapidly kills the body’s soft tissue, comes when dangerous bacteria enters the bloodstream. One of the most recent cases was in September in Ocean City, Maryland, where a man was cleaning crab pots when Vibrio vulnificus bacteria got into a cut on his leg. DelmarvaNow reported that the man, Michael Funk, fell ill within hours. “Days later, ulcerated and full of lesions, it was ‘like something out of a horror movie,’ his wife, Marcia, told the newspaper. The flesh-eating bacteria was in his bloodstream.” Funk died four days after getting the cut.
Is it safe to eat raw shellfish?
Prevention is the most effective defense against flesh-eating bacteria, however. Live Science notes that not eating raw or undercooked shellfish is one way to avoid a foodborne bacterial illness, and properly caring for wounds could also stop bacteria from entering your system.
Is fever a real disease?
But the illness is real when someone is infected with flesh-eating bacteria.
Is flesh eating bacteria deadly?
Flesh-eating bacteria is deadly if it enters your bloodstream. Image courtesy of Pixabay, public domain. Infections of flesh-eating bacteria are rare, and are more likely to occur in people who have weakened immune systems, like those who have liver disease. But in these rare cases, the bacteria infects tissue around muscles, nerves, ...
Where does the feces eating bacteria come from?
It comes from the rivers down to the south of us—the Brazoria and the Colorado rivers.”. Flesh-eating bacteria infections can occur when the microorganisms enter the body, typically through an open wound or break in the skin. People who are immunocompromised, have chronic liver disease, a weakened immune system or are pregnant should exercise ...
What river dumps into Louisiana?
“If you look at the currents, the Mississippi River dumps into Louisiana and then into Mississippi, Alabama and then into the panhandle of Florida,” Billingsley said.
Is flesh eating bacteria a misnomer?
This is nothing new or unusual, experts say. “Flesh-eating bacteria is a misnomer and actually there are several bacteria under that umbrella. You can have a flesh-eating bacteria like Group A Streptococcus, MRSA and Vibrio vulnificus,” said Laila Woc-Colburn, M.D., associate professor of infectious diseases and director ...
Can bacteria live on the Gulf Coast?
As temperatures along the Gulf Coast rise with summer waterside visits, so can cases of flesh-eating bacteria.
Can you get Vibrio vulnificus from eating oysters?
The bacteria can be contracted by swimming in coastal waters and by eating shellfish or raw oysters. Severe cases of Vibrio vulnificus can lead to necrotizing fasciitis, which can result in amputations or death. The CDC also tracks necrotizing fasciitis caused by Group A Strep.