Tehachapi Mountains
The Tehachapi Mountains are a mountain range in the Transverse Ranges system of California in the Western United States. The range extends for approximately 40 miles in southern Kern County and northwestern Los Angeles County.
What is the Garlock Fault in California?
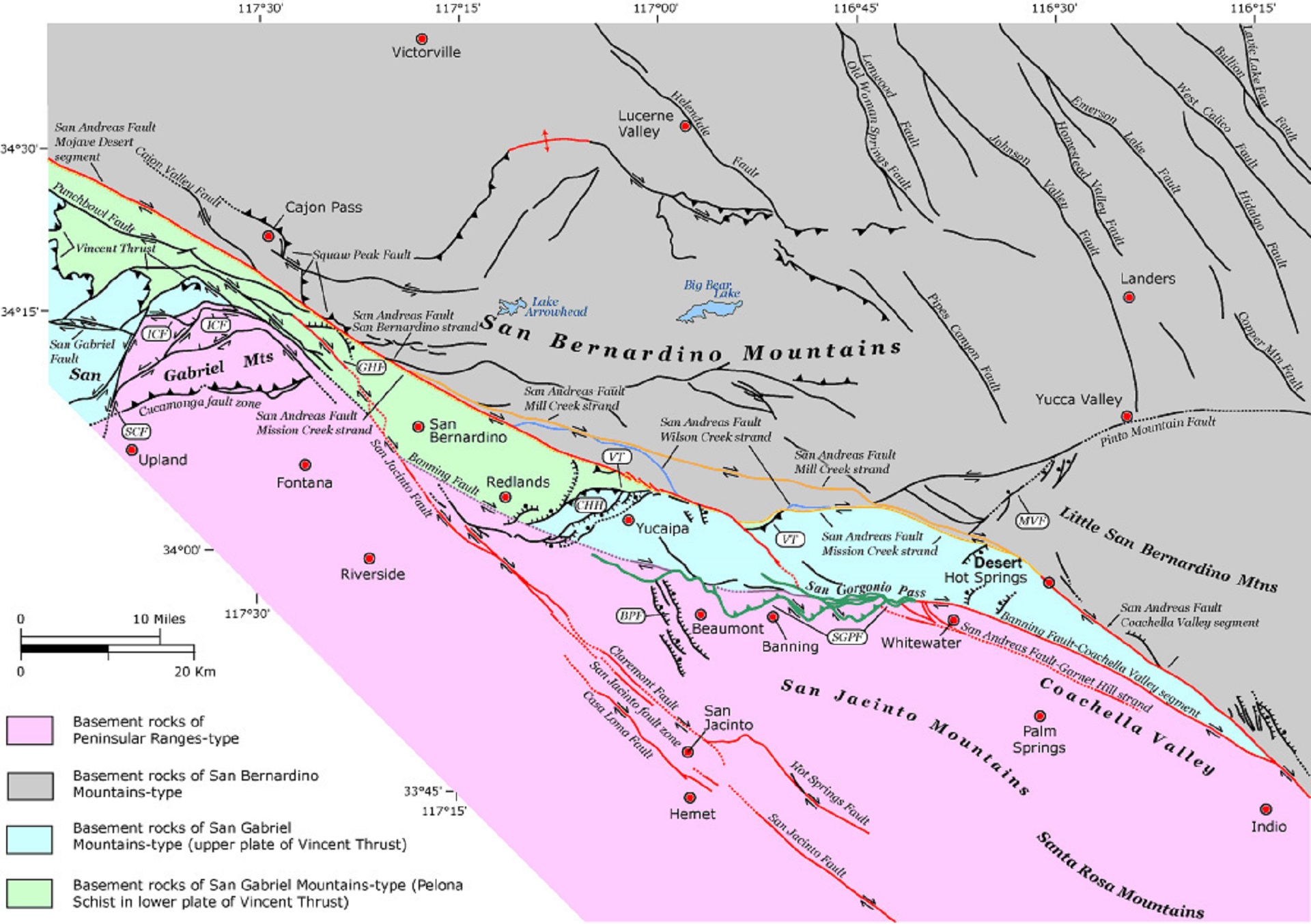
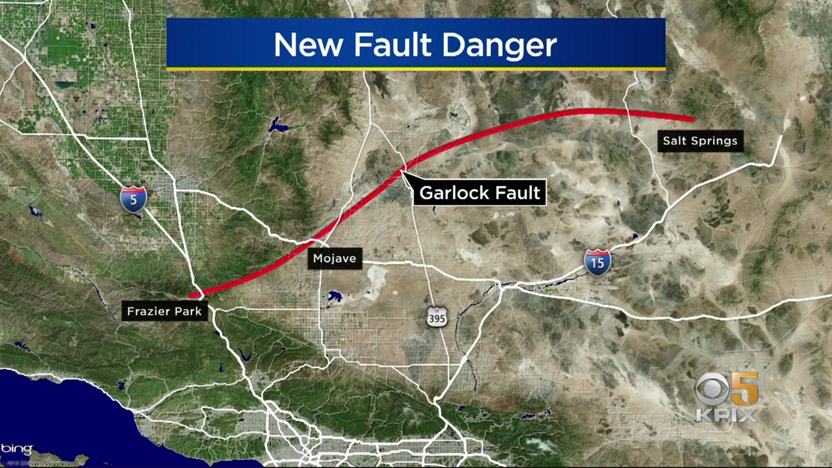
The Garlock Fault is a left-lateral strike-slip fault running northeast–southwest along the north margins of the Mojave Desert of Southern California, for much of its length along the southern base of the Tehachapi Mountains.
Where is the Garlock?
Nov 24, 2019 · The Garlock Fault is a left-lateral, strike-slip fault that runs along the northernmost margins of southern California’s Mojave Desert. Most of this fault’s length stretches alongside the Tehachapi Mountains. Photo Credit: La Mag Having a left-lateral slip makes the Garlock Fault different from almost all of the other faults.
What would happen if the Garlock Fault ruptured?
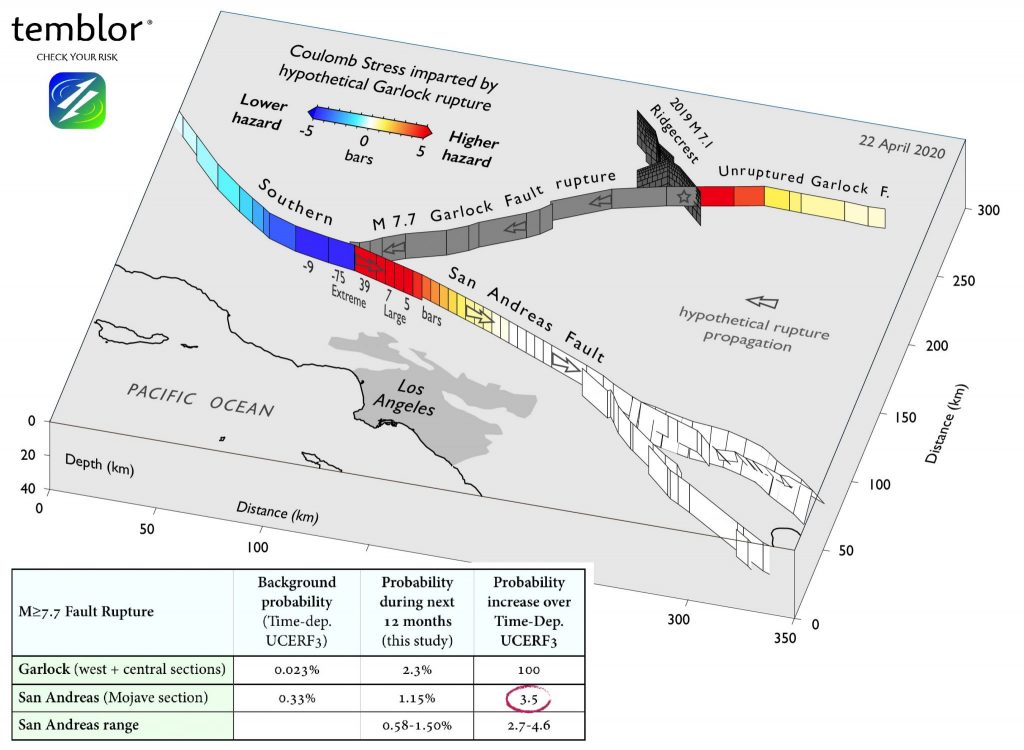
The Garlock fault line isn’t known to many in a state hyper-focused on the more famous San Andreas fault, but it could turn out to be the more deadly result. The Garlock fault stretches 160 miles across the northernmost part of the Mojave desert. In modern record-keeping, the fault has been completely dormant.
Is the Central Valley on a fault line?
The Garlock Fault is the defining fault between the Mojave Desert and Basin and Range geomorphic provinces. The fault also defines the boundary between the northwestern most Mojave and the southern portion of the Sierra Nevada geomorphic province. The intersection of the San Andreas (the blue line) and Garlock (orange line) faults in southern California reflects …
Is the Garlock fault active?
While the Garlock Fault has been considered largely dormant for the last 500 years, it appears to have awakened after July's events.Oct 18, 2019
What type of fault is Garlock?
left-lateral strike-slip faultThe Garlock fault, which runs along the northern edge of the Mojave Desert, is a left-lateral strike-slip fault. Big normal faults are found all over the Great Basin. Big reverse faults are found near subduction zones, such as in Alaska.
What is the most active fault line in California?
The San Andreas faultThe San Andreas fault is the primary feature of the system and the longest fault in California, slicing through Los Angeles County along the north side of the San Gabriel Mountains. It can cause powerful earthquakes—as big as magnitude 8.
Where is the safest place to live in California from earthquakes?
Sacramento Is the Safest Place to Live in California from Earthquakes.Dec 6, 2021
Is the Garlock Fault a plate boundary?
The intersection of the San Andreas (the blue line) and Garlock (orange line) faults in southern California reflects two different tectonic forces: the northwest-southeast sliding along the boundaries of the Pacific and North American plates, and the roughly east-west crustal extension within the North American plate.
How deep is the Garlock Fault?
A M=3.5 shock at a depth of 5 km struck on the active Garlock fault. The mainshock has a focal mechanism consistent with the left-lateral motion of this 250-km (150-mi) long and major fault that bounds the Mojave desert to the south and the Tehachapi mountains to the north.Jan 13, 2016
What part of California does not have earthquakes?
Los Angeles Times also reported that Sacramento is the best city to avoid quakes in all of California's territory. This city has a great advantage because no active fault lines can be found nearby.Sep 4, 2020
Which city in California has the most earthquakes?
San Francisco has the highest risk of an earthquake as it is located directly on the San Andreas fault, one of the most volatile in the world. Because of its location relative to major fault lines, the Greater Bay Area experiences many earthquakes year-round.
What part of California has the most earthquakes?
Which part of California has the most earthquakes? The greater San Francisco Bay Area has a high likelihood of future damaging earthquakes as it straddles the San Andreas fault system—the major geologic boundary between the North American and Pacific tectonic plates.Nov 29, 2021
What city in California has the least amount of earthquakes?
SacramentoIn fact, Sacramento — based on historical records and fault maps — is unquestionably the safest earthquake refuge among all of California's major metropolitan areas.Jul 15, 2019
What town is known as the earthquake capital of the world?
ParkfieldKnown as the "Earthquake Capital of the World" for its location along California's San Andreas fault line, Parkfield is the most closely scientifically observed earthquake zone in the world. Historically, a 6.0-plus-magnitude earthquake has occurred every 22 years.
How overdue is the San Andreas Fault?
Parts of the San Andreas fault have not ruptured in over 200 years, meaning it's overdue for a high-magnitude earthquake commonly referred to as "The Big One." Here's what experts say could happen in seconds, hours, and days after the Big One hits the West Coast.Sep 21, 2021
Where is the Garlock fault?
The Garlock Fault is a left-lateral strike-slip fault running northeast–southwest along the north margins of the Mojave Desert of Southern California, for much of its length along the southern base of the Tehachapi Mountains .
How fast does the Garlock Fault move?
The Garlock Fault moves at a rate of between 2 and 11 mm a year, with an average slip of around 7 millimeters. While most of the fault is locked, certain segments have been shown to move by aseismic creep, which is motion without resulting earthquakes.
How long is the Mojave Block?
Stretching for 250 kilometers (160 mi), it is the second-longest fault in California, and one of the most prominent geological features in the southern part of the state. It marks the northern boundary of the area known as the Mojave Block, as well as the southern ends of the Sierra Nevada and the valleys of the westernmost Basin and Range province.
When was the last time the Garlock was ruptured?
The last significant ruptures on the Garlock were thought to be in the years 1050 AD and 1500 AD. Research has pinned the interval between significant ruptures on the Garlock as being anywhere between 200 and 3,000 years, depending on the segment of the fault.
Is the Garlock Fault left or right?
Unlike most of the other faults in California, slip on the Garlock Fault is left-lateral; that is, the land on the other side of the fault moves to the left from the perspective of someone facing the fault. Thus, the terrain north of the fault is moving westward and that on the south is moving eastward.
What would happen if the Garlock went?
Theoretically, if the Garlock went, it could change stresses on the San Andreas over near the coast. That said, the San Andreas is such a high-risk fault anyway. The probability of a big earthquake happening where the Garlock connects to it all the way down to, like, Palm Springs is pretty high.
Is the Garlock fault line moving?
The bulging of the Garlock fault line in California can be seen from space and it's moving in ways never seen before, raising the question for Californians if it raises the risk of "The Big One."
Where is the San Andreas fault?
The main trace of the San Andreas fault runs through much of the State of California, including the Santa Cruz Mountains and up the San Francisco Peninsula, before heading offshore at Daly City and returning onshore again at Bolinas and continuing up the Marin and Sonoma County coasts.
Which faults are responsible for the 1994 Northridge earthquake?
There are over a hundred smaller active faults in the region that can cause damaging earthquakes like the Northridge earthquake in 1994, such as the Raymond fault, the Santa Monica fault, the Hollywood fault, the Newport-Inglewood fault, and the San Jacinto and Elisnore faults.
What fault is the biggest earthquake threat in San Diego?
The Rose Canyon fault runs along the coast and beneath downtown San Diego. Geologists say this is the biggest earthquake threat to San Diego, capable of earthquakes of magnitude 6.9. The Elsinore and San Jacinto faults cut through East County and can also generate moderately-sized but potentially damaging earthquakes.
How far away from faults do most Californians live?
Most Californians live within 30 miles of an active fault. 15,700. Known faults in California (and scientists continue to discover new ones) Select your county from the dropdown menu above to learn more about California earthquake risk and faults near you. *The probability is based on a 30-year period, beginning in 2014.
What is the chance of a magnitude 6.0 earthquake in San Francisco?
They also say there’s a 98 percent chance of one or more magnitude-6.0 or greater quakes occurring in the San Francisco area during that same timeframe. Soils in lowland areas away from major faults may be subject to liquefaction. Houses on liquefied soil may settle or even move laterally on gentle slopes.
Which fault system causes earthquakes?
The Calaveras and Hayward faults extend up the east side of the San Francisco Bay. These and several other major faults in the region are part of the San Andreas fault system and can cause damaging earthquakes, like the 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake.
What is the Cascadia subduction zone?
The Cascadia Subduction Zone stretches underneath the Humboldt-Del Norte county region, extending from Cape Mendocino all the way up through the Pacific Northwest. This zone is capable of generating an earthquake of a magnitude 9 or larger, occurring—on average—once every 500 years.