What are 4 examples of eukaryotic cells?
What are 10 examples of eukaryotic cells?
- Animal cells. (Humans, Dog, cat)
- plant cells.
- fungi. (Yeast, Rhizopus, mushrooms)
- algae. (Golden Algae, Brown algae)
- Protozoa. (Amoeba, Rhizopoda)
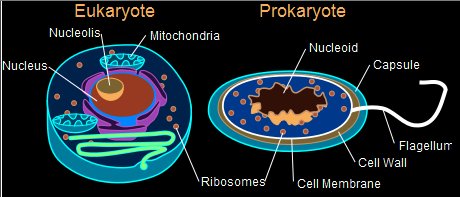
- Eukaryotic Cell: • Eukaryotic cells are the cells, which contains nucleus in them.
What is an example of an eukaryotic cell?
What are 10 examples of eukaryotic cells?
- Animals such as cats and dogs have eukaryotic cells.
- Plants such as apple trees have eukaryotic cells.
- Fungi such as mushrooms have eukaryotic cells.
- Protists such as amoeba and paramecium have eukaryotic cells.
- Insects have eukaryotic cells.
- Humans are composed entirely of eukaryotic cells.
What are the features of an eukaryotic cell?
What are the 3 main features of a eukaryotic cell?
- a membrane-bound nucleus.
- numerous membrane-bound organelles (including the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts, and mitochondria)
- several rod-shaped chromosomes.
What do all eukaryotic cells have in common?
Eukaryotic cells are very diverse in shape, form and function. Some internal and external features, however, are common to all. These include a plasma (cell) membrane, a nucleus, mitochondria, internal membrane bound organelles and a cytoskeleton.

Where is the genetic material in a prokaryotic cell?
the nucleoidMost prokaryotes carry a small amount of genetic material in the form of a single molecule, or chromosome, of circular DNA. The DNA in prokaryotes is contained in a central area of the cell called the nucleoid, which is not surrounded by a nuclear membrane.
Where is genetic material found in the prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell?
The nucleus is where eukaryotes store their genetic information. In prokaryotes, DNA is bundled together in the nucleoid region, but it is not stored within a membrane-bound nucleus.
In what organelle is the genetic material found inside?
Nucleus. Known as the cell's “command center,” the nucleus is a large organelle that stores the cell's DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). The nucleus controls all of the cell's activities, such as growth and metabolism, using the DNA's genetic information.
What are found in eukaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells also contain organelles, including mitochondria (cellular energy exchangers), a Golgi apparatus (secretory device), an endoplasmic reticulum (a canal-like system of membranes within the cell), and lysosomes (digestive apparatus within many cell types).
Is genetic material prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
There are several differences between the two, but the biggest distinction between them is that eukaryotic cells have a distinct nucleus containing the cell's genetic material, while prokaryotic cells don't have a nucleus and have free-floating genetic material instead.
Is DNA found in prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells?
Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have structures in common. All cells have a plasma membrane, ribosomes, cytoplasm, and DNA....Prokaryotic Cells.Prokaryotic CellsEukaryotic CellsDNASingle circular piece of DNAMultiple chromosomesMembrane-Bound OrganellesNoYes2 more rows•May 24, 2021
Where is genetic material stored?
cell nucleusMost DNA is located in the cell nucleus (where it is called nuclear DNA), but a small amount of DNA can also be found in the mitochondria (where it is called mitochondrial DNA or mtDNA).
Where in a prokaryotic cell would you find the genetic material quizlet?
In prokaryotes, where can you find the genetic material? Near the center of the cell (in an area called the nucleoid).
Are eukaryotic cells unicellular or multicellular?
Eukaryotic cells may be unicellular or multicellular. Paramecium, Euglena, Trypanosoma, Dinoflagellates are unicellular eukaryotes. Plants and anim...
What is the most important characteristic of eukaryotic cells that distinguishes it from prokaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells have a membrane-bound nucleus. On the contrary, prokaryotic cells lack a true nucleus, i.e., they have no nuclear membrane. Unlike...
Are viruses eukaryotes?
Viruses are neither eukaryotes nor prokaryotes. Since viruses are a link between living and non-living they are not considered in either category.
What are the salient features of a eukaryotic cell?
A eukaryotic cell has the following important features: A eukaryotic cell has a nuclear membrane. It has mitochondria, Golgi bodies, cell wall. It...
How does a eukaryotic cell divide?
A eukaryotic cell divides by the process of mitosis. It undergoes the following stages during cell division: Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase...
When did the first eukaryotic cell evolve?
The first eukaryotic cells evolved about 2 billion years ago. This is explained by the endosymbiotic theory that explains the origin of eukaryotic...
What is the evidence for endosymbiotic theory?
The first evidence in support of the endosymbiotic theory is that mitochondria and chloroplast have their own DNA and this DNA is similar to the ba...
Where are eukaryotic cells found?
Eukaryotic cells are exclusively found in plants, animals, fungi, protozoa, and other complex organisms. The examples of eukaryotic cells are mentioned below:
What is an eukaryotic cell?
What is a Eukaryotic Cell? Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus enclosed within the nuclear membrane and form large and complex organisms. Protozoa, fungi, plants, and animals all have eukaryotic cells. They are classified under the kingdom Eukaryota.
Which reticulum lacks ribosomes?
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum that lacks ribosomes and is therefore smooth.
What is the process of dividing cells called?
The cells divide by a process called mitosis. The eukaryotic cells contain a cytoskeletal structure. The nucleus contains a single, linear DNA, which carries all the genetic information.
Which structure is found only in plant cells?
These are double-membraned structures and are found only in plant cells. These are of three types: Chloroplast that contains chlorophyll and is involved in photosynthesis. Chromoplast that contains a pigment called carotene that provides the plants yellow, red, or orange colours.
What is the membrane that separates cells from the outside environment?
Plasma Membrane. The plasma membrane separates the cell from the outside environment. It comprises specific embedded proteins, which help in the exchange of substances in and out of the cell.
Why are cells called powerhouses?
These are also known as “powerhouse of cells” because they produce energy.
What is Genetic Material of Eukaryotes?
Fungi, protists, plants, and animals are eukaryotes. Their genetic material is located inside the membrane-bound nucleus. Hence, eukaryotic DNA is not found freely in the cytoplasm, unlike prokaryotic DNA.
What is the material of eukaryotic genes?
The eukaryotic genetic material is linear and wrapped around proteins called histones. It contains many sequences which are non-coding. Moreover, eukaryotic genes do not transcribe together. They transcribe separately and make their own mRNA molecules. One promoter regulates the transcription of one gene in eukaryotes.
What are the Similarities Between Genetic Material of Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes?
The genetic material of prokaryotes and eukaryotes are made up of DNA molecules.
What is the difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
Another important difference between is that the prokaryotes have a small genome and contain plasmids. They also have a large coiled double-stranded circular chromosome whereas, eukaryotes have a larger genome and do not possess plasmids. Prokaryotes and eukaryotes are two types of organisms. Bacteria and Archaea are prokaryotes.
Which cell has a large coiled double stranded circular chromosome?
In contrast, DNA which resides inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell is known as the genetic material of a eukaryote. Further, prokaryotes have a small genome and contain plasmids. They also have a large coiled double-stranded circular chromosome. Eukaryotes, however, have a larger genome and do not possess plasmids.
Is Archaea a prokaryote?
Bacteria and Archaea are prokaryotes. Prokaryotes have a simple cellular organization. They do not have a nucleus and true organelles. On the other hand, eukaryotes have a complex cellular organization with a membrane-bound nucleus and true organelles. Fungi, protists, plants, and animals are eukaryotes.
Do prokaryotes have a nucleus?
Prokaryotes are the organisms that do not have a nucleus. They are single-celled. Hence they have a simple cell organization. Furthermore, they don’t have true cell organelles. The genetic material of prokaryotes floats in the cytoplasm. Bacteria have a large circular chromosome which is highly coiled.
Where do chromosomes align in a cell?
The chromosomes align along the metaphase plate of the cell.
How many daughter nuclei are there in a cell?
Two distinct daughter nuclei form in the cell.
How many chromatids are in a cell at the beginning of mitosis?
A cell contains 40 chromatids at the beginning of mitosis. How many chromosomes will it contain at the completion of cytokinesis?
Where are sister chromatids pulled apart?
The sister chromatids are pulled apart toward opposite sides of the cell.
How many units of DNA are in a fruit fly?
A cell biologist examined the DNA content of a cell from a fruit fly larva during the G1 phase and determined that it had 150 units of DNA. After measuring the DNA content of the same type of cell after the G2 phase, it was discovered that the cell had 300 units of DNA. How is this possible?
What is the internal membrane of an eukaryotic cell called?
A eukaryotic cell has a nucleus an internal membrane-bound compartments called organelles
Which sacs enclose molecules and keep them separate from the cytoplasm?
Membranous sacs that ENCLOSES the molecules and keep them SEPARATE from the cytoplasm
What are diffuse threads in animal cells?
In an animal cell, diffuse threads containing DNA and protein
What is the sac in an animal cell?
In an animal cell, small membrane-bound sac that stores and transports substances
What are short cylinders of microtubules that help organize a mitotic spindle for?
In an animal cell, short cylinders of MICROTUBULES that help organize a mitotic spindle for chromosome movement during animal cell division
What is the function of phospholipid bilayers in animal cells?
In an animal cell, a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins, functions to regulate the entrance and exit of molecules from the cell.